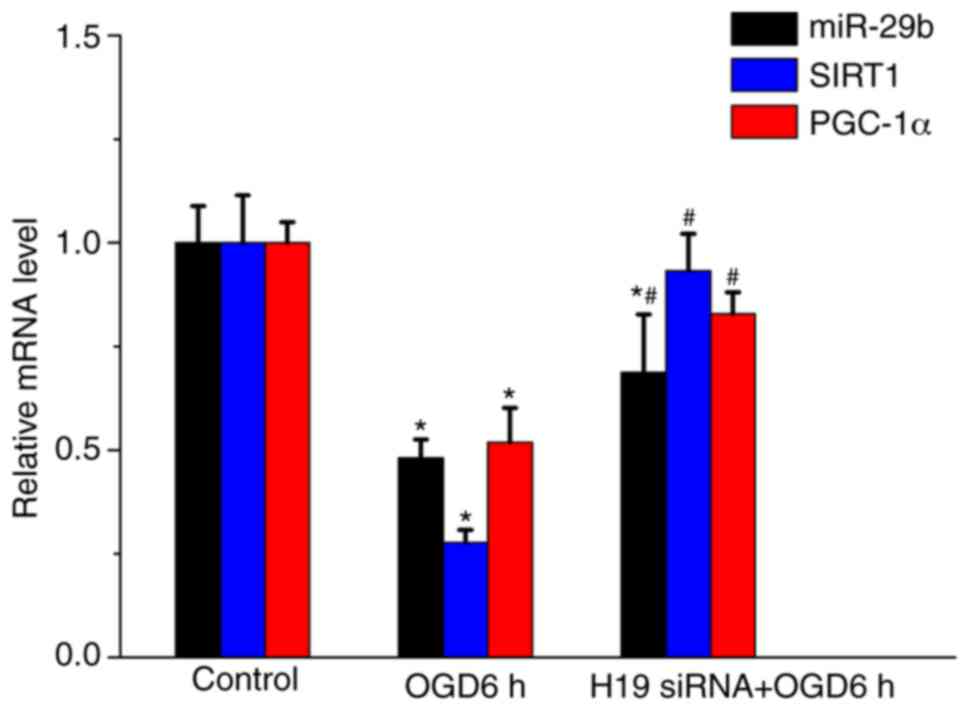
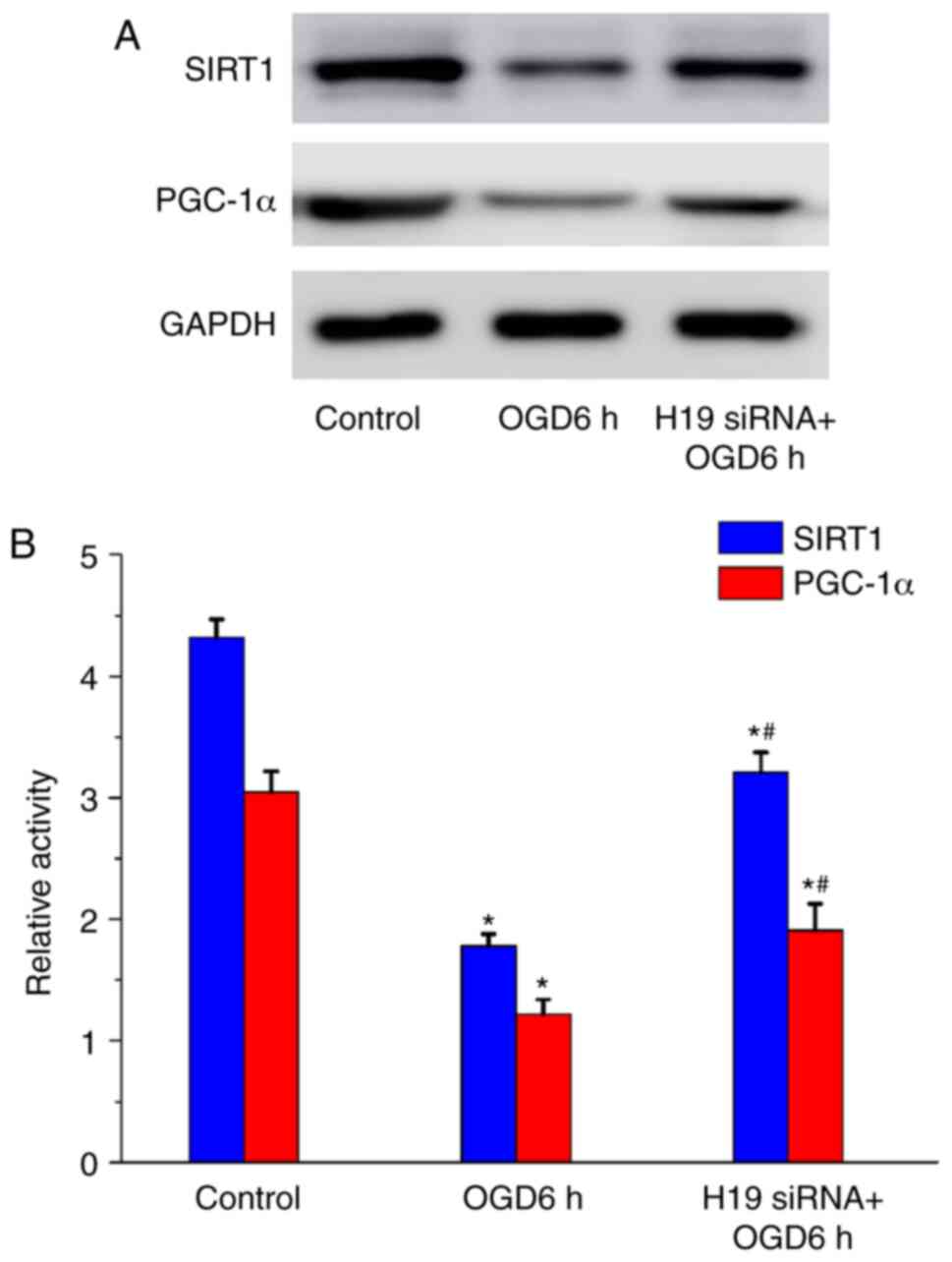
|
1
|
Writing Group Members, ; Mozaffarian D,
Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de
Ferranti S, Despres JP, Fullerton HJ, et al: Heart disease and
stroke statistics-2016 update: A report from the American heart
association. Circulation. 133:e38–e360. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mo Y, Sun YY and Liu KY: Autophagy and
inflammation in ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 15:1388–1396.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yao RW, Wang Y and Chen LL: Cellular
functions of long noncoding RNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 21:542–551. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shi X, Sun M, Liu H, Yao Y and Song Y:
Long non-coding RNAs: A new frontier in the study of human
diseases. Cancer Lett. 339:159–166. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang Y, Yujiao W, Fang W, Linhui Y, Ziqi
G, Zhichen W, Zirui W and Shengwang W: The roles of miRNA, lncRNA
and circRNA in the development of osteoporosis. Biol Res.
53:402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang Y: The novel regulatory role of
lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis in cardiovascular diseases. J Cell Mol Med.
22:5768–5775. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu L and Xu PC: Downregulated LncRNA-ANCR
promotes osteoblast differentiation by targeting EZH2 and
regulating Runx2 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
432:612–617. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Y, Xu Z, Jiang J, Xu C, Kang J, Xiao
L, Wu M, Xiong J, Guo X and Liu H: Endogenous miRNA sponge
lincRNA-RoR regulates Oct4, Nanog, and Sox2 in human embryonic stem
cell self-renewal. Dev Cell. 25:69–80. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang J, Zhao H, Fan Z, Li G, Ma Q, Tao Z,
Wang R, Feng J and Luo Y: Long noncoding RNA H19 promotes
neuroinflammation in ischemic stroke by driving histone deacetylase
1-dependent M1 microglial polarization. Stroke. 48:2211–2221. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bao MH, Szeto V, Yang BB, Zhu SZ, Sun HS
and Feng ZP: Long non-coding RNAs in ischemic stroke. Cell Death
Dis. 9:2812018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang X, Tang X, Liu K, Hamblin MH and Yin
KJ: Long noncoding RNA malat1 regulates cerebrovascular pathologies
in ischemic stroke. J Neurosci. 37:1797–1806. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yan H, Yuan J, Gao L, Rao J and Hu J: Long
noncoding RNA MEG3 activation of p53 mediates ischemic neuronal
death in stroke. Neuroscience. 337:191–199. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bartolomei MS, Zemel S and Tilghman SM:
Parental imprinting of the mouse H19 gene. Nature. 351:153–155.
1991. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gabory A, Jammes H and Dandolo L: The H19
locus: Role of an imprinted non-coding RNA in growth and
development. Bioessays. 32:473–480. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dey BK, Pfeifer K and Dutta A: The H19
long noncoding RNA gives rise to microRNAs miR-675-3p and
miR-675-5p to promote skeletal muscle differentiation and
regeneration. Genes Dev. 28:491–501. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Voellenkle C, Garcia-Manteiga JM, Pedrotti
S, Perfetti A, De Toma I, Da Silva D, Maimone B, Greco S, Fasanaro
P, Creo P, et al: Implication of long noncoding RNAs in the
endothelial cell response to hypoxia revealed by RNA-sequencing.
Sci Rep. 6:241412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Matouk IJ, Raveh E, Abu-lail R, Mezan S,
Gilon M, Gershtain E, Birman T, Gallula J, Schneider T, Barkali M,
et al: Oncofetal H19 RNA promotes tumor metastasis. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1843:1414–1426. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang WT, Ye H, Wei PP, Han BW, He B, Chen
ZH and Chen YQ: LncRNAs H19 and HULC, activated by oxidative
stress, promote cell migration and invasion in cholangiocarcinoma
through a ceRNA manner. J Hematol Oncol. 9:1172016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Matouk IJ, Mezan S, Mizrahi A, Ohana P,
Abu-Lail R, Fellig Y, Degroot N, Galun E and Hochberg A: The
oncofetal H19 RNA connection: Hypoxia, p53 and cancer. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1803:443–451. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang J, Cao B, Han D, Sun M and Feng J:
Long non-coding RNA H19 induces cerebral ischemia reperfusion
injury via activation of autophagy. Aging Dis. 8:71–84. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ding D, Li C, Zhao T, Li D, Yang L and
Zhang B: LncRNA H19/miR-29b-3p/PGRN axis promoted
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer cells by
acting on wnt signaling. Mol Cells. 41:423–435. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang X, Zou M, Li J, Wang B, Zhang Q, Liu
F and Lu G: LncRNA H19 targets miR-22 to modulate
H2O2-induced deregulation in nucleus pulposus
cell senescence, proliferation, and ECM synthesis through Wnt
signaling. J Cell Biochem. 119:4990–5002. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lu YF, Liu Y, Fu WM, Xu J, Wang B, Sun YX,
Wu TY, Xu LL, Chan KM, Zhang JF and Li G: Long noncoding RNA H19
accelerates tenogenic differentiation and promotes tendon healing
through targeting miR-29b-3p and activating TGF-β1 signaling. FASEB
J. 31:954–964. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang X, Cheng L, Xu L, Zhang Y, Yang Y,
Fu Q, Mi W and Li H: The LncRNA, H19 mediates the protective effect
of hypoxia postconditioning against hypoxia-reoxygenation injury to
senescent cardiomyocytes by targeting microRNA-29b-3p. Shock.
52:249–256. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Boutant M and Canto C: SIRT1 metabolic
actions: Integrating recent advances from mouse models. Mol Metab.
3:5–18. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kitada M, Ogura Y, Monno I and Koya D:
Sirtuins and type 2 diabetes: Role in inflammation, oxidative
stress, and mitochondrial function. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
10:1872019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fang WJ, Wang CJ, He Y, Zhou YL, Peng XD
and Liu SK: Resveratrol alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats
by improving mitochondrial function through PGC-1α deacetylation.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 39:59–73. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu H, Wu X, Luo J, Wang X, Guo H, Feng D,
Zhao L, Bai H, Song M, Liu X, et al: Pterostilbene attenuates
astrocytic inflammation and neuronal oxidative injury after
ischemia-reperfusion by inhibiting NF-ΚB phosphorylation. Front
Immunol. 10:24082019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang Q, Huang Q, Hu Z and Tang X:
Potential neuroprotective treatment of stroke: Targeting
excitotoxicity, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Front Neurosci.
13:10362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fang D and Zhu J: Molecular switches for
regulating the differentiation of inflammatory and IL-10-producing
anti-inflammatory T-helper cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 77:289–303.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Grysiewicz RA, Thomas K and Pandey DK:
Epidemiology of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke: Incidence,
prevalence, mortality, and risk factors. Neurol Clin. 26871–895.
(vii)2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Anrather J and Iadecola C: Inflammation
and stroke: An overview. Neurotherapeutics. 13:661–670. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Matouk IJ, DeGroot N, Mezan S, Ayesh S,
Abu-lail R, Hochberg A and Galun E: The H19 non-coding RNA is
essential for human tumor growth. PLoS One. 2:e8452007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang J, Cao B, Zhao H, Gao Y, Luo Y, Chen
Y and Feng J: Long noncoding RNA H19 prevents neurogenesis in
ischemic stroke through p53/Notch1 pathway. Brain Res Bull.
150:111–117. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hong Y, He H, Sui W, Zhang J, Zhang S and
Yang D: (Corrigendum) Long noncoding RNA H19 promotes cell
proliferation and invasion by acting as a ceRNA of miR138 and
releasing EZH2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol.
53:9152018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li M, Chen H, Zhao Y, Gao S and Cheng C:
H19 Functions as a ceRNA in promoting metastasis through decreasing
miR-200s activity in osteosarcoma. DNA Cell Biol. 35:235–240. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li L and Stary CM: Targeting glial
mitochondrial function for protection from cerebral ischemia:
Relevance, mechanisms, and the role of microRNAs. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2016:60323062016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ouyang YB, Xu L, Yue S, Liu S and Giffard
RG: Neuroprotection by astrocytes in brain ischemia: Importance of
microRNAs. Neurosci Lett. 565:53–58. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hattori Y, Okamoto Y, Nagatsuka K,
Takahashi R, Kalaria RN, Kinoshita M and Ihara M: SIRT1 attenuates
severe ischemic damage by preserving cerebral blood flow.
Neuroreport. 26:113–117. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fusco R, Scuto M, Cordaro M, D'Amico R,
Gugliandolo E, Siracusa R, Peritore AF, Crupi R, Impellizzeri D,
Cuzzocrea S and Di Paola R: N-Palmitoylethanolamide-oxazoline
protects against middle cerebral artery occlusion injury in
diabetic rats by regulating the SIRT1 pathway. Int J Mol Sci.
20:48452019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Duan J, Cui J, Zheng H, Xi M, Guo C, Weng
Y, Yin Y, Wei G, Cao J, Wang Y, et al: Aralia taibaiensis protects
against I/R-induced brain cell injury through the Akt/SIRT1/FOXO3a
pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019:76097652019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Canto C and Auwerx J: Caloric restriction,
SIRT1 and longevity. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 20:325–331. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rodgers JT, Lerin C, Gerhart-Hines Z and
Puigserver P: Metabolic adaptations through the PGC-1 alpha and
SIRT1 pathways. FEBS Lett. 582:46–53. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen SD, Yang DI, Lin TK, Shaw FZ, Liou CW
and Chuang YC: Roles of oxidative stress, apoptosis, PGC-1α and
mitochondrial biogenesis in cerebral ischemia. Int J Mol Sci.
12:7199–7215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yan X, Yu A, Zheng H, Wang S, He Y and
Wang L: Calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucoside attenuates OGD/R-induced damage
by preventing oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis via the
SIRT1/FOXO1/PGC-1α pathway in HT22 cells. Neural Plast.
2019:87980692019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|