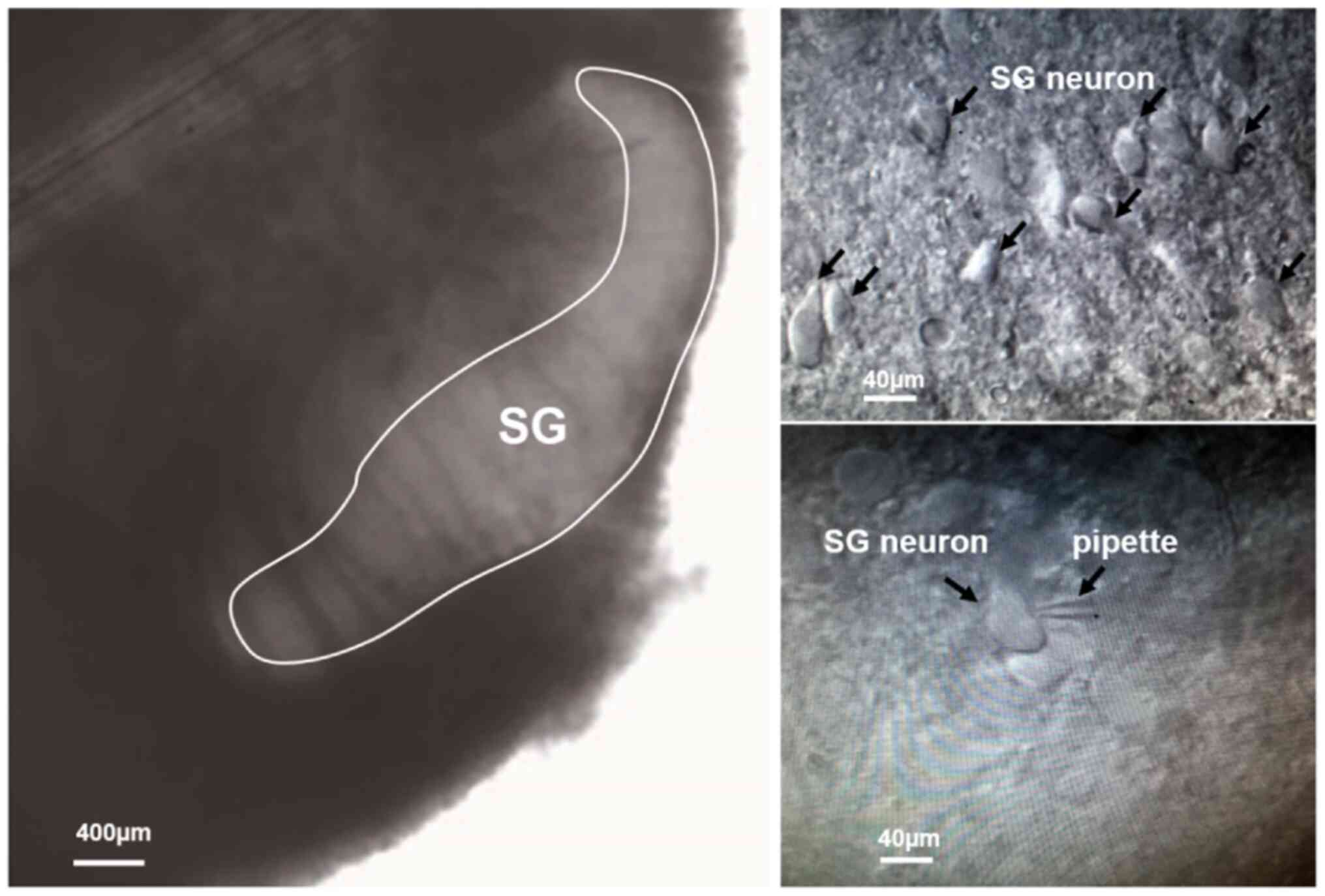
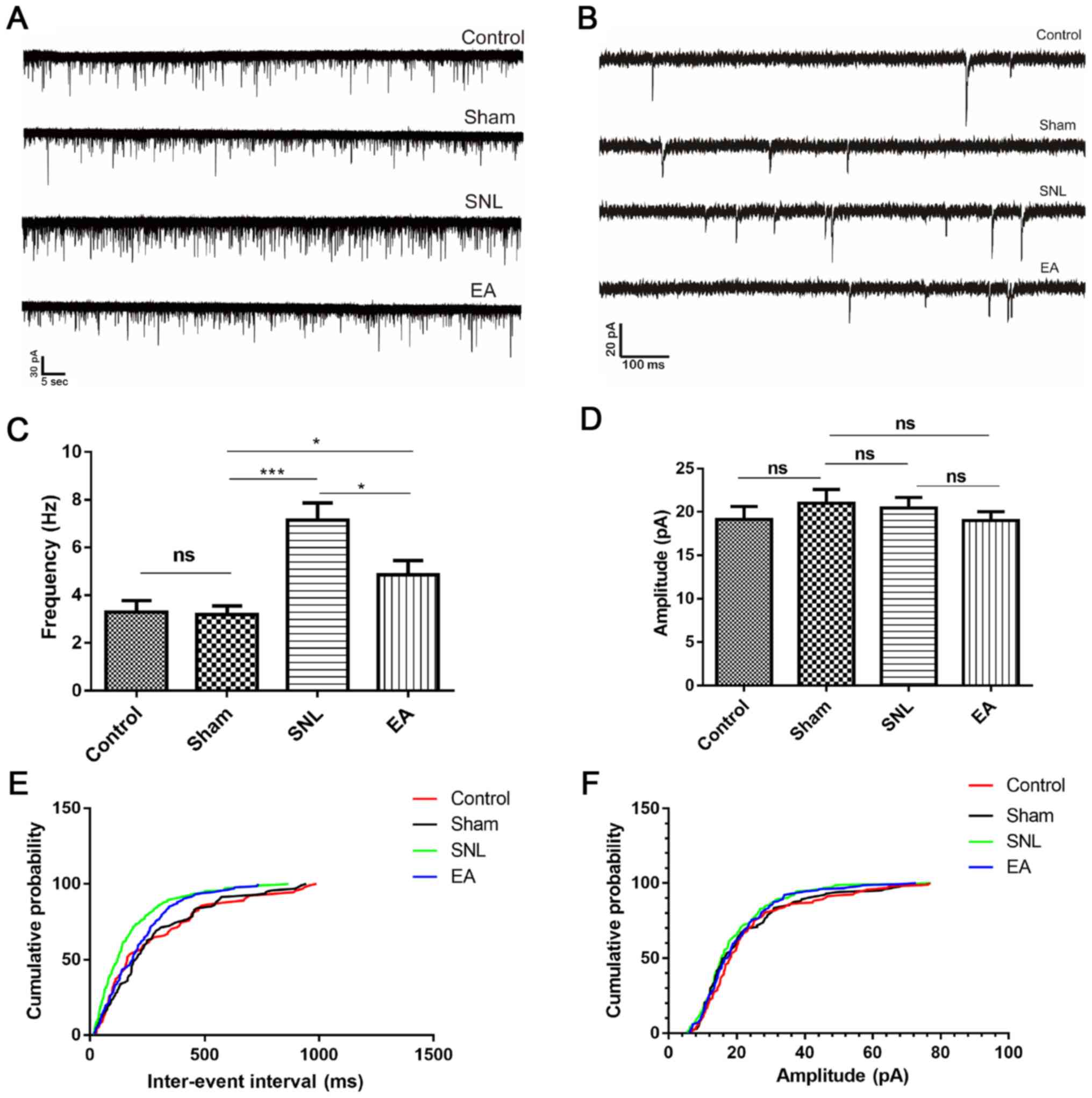
|
1
|
Wang JY, Chen R, Chen SP, Gao YH, Zhang
JL, Feng XM, Yan Y, Liu JL, Gaischek I, Litscher D, et al:
Electroacupuncture reduces the effects of acute noxious stimulation
on the electrical activity of pain-related neurons in the
hippocampus of control and neuropathic pain rats. Neural Plast.
2016:65210262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang Y, Zhao Y, Ma X, Li J, Hou J and Lv
X: Beneficial Effects of Electroacupuncture on Neuropathic Pain
Evoked by Spinal Cord Injury and Involvement of PI3K mTOR
Mechanisms. Biol Res Nurs. 21:5–13. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen XM, Xu J, Song JG, Zheng BJ and Wang
XR: Electroacupuncture inhibits excessive interferon-γ evoked
up-regulation of P2X4 receptor in spinal microglia in a CCI rat
model for neuropathic pain. Br J Anaesth. 114:150–157. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao ZQ: Neural mechanism underlying
acupuncture analgesia. Prog Neurobiol. 85:355–375. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Park JH, Kim SK, Kim HN, Sun B, Koo S,
Choi SM, Bae H and Min BI: Spinal cholinergic mechanism of the
relieving effects of electroacupuncture on cold and warm allodynia
in a rat model of neuropathic pain. J Physiol Sci. 59:291–298.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim SK, Park JH, Bae SJ, Kim JH, Hwang BG,
Min BI, Park DS and Na HS: Effects of electroacupuncture on cold
allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain: Mediation by spinal
adrenergic and serotonergic receptors. Exp Neurol. 195:430–436.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Padi SS and Kulkarni SK: Minocycline
prevents the development of neuropathic pain, but not acute pain:
Possible anti-inflammatory and antioxidant mechanisms. Eur J
Pharmacol. 601:79–87. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tsuda M, Tozaki-Saitoh H and Inoue K:
Purinergic system, microglia and neuropathic pain. Curr Opin
Pharmacol. 12:74–79. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Beggs S, Trang T and Salter MW:
P2X4R+ microglia drive neuropathic pain. Nat Neurosci.
15:1068–1073. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun S, Cao H, Han M, Li TT, Zhao ZQ and
Zhang YQ: Evidence for suppression of electroacupuncture on spinal
glial activation and behavioral hypersensitivity in a rat model of
monoarthritis. Brain Res Bull. 75:83–93. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tsuda M, Shigemoto-Mogami Y, Koizumi S,
Mizokoshi A, Kohsaka S, Salter MW and Inoue K: P2X4 receptors
induced in spinal microglia gate tactile allodynia after nerve
injury. Nature. 424:778–783. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tsuda M and Inoue K: Neuron microglia
interaction by purinergic signaling in neuropathic pain following
neurodegeneration. Neuropharmacology. 2015.
|
|
13
|
Tu WZ, Cheng RD, Cheng B, Lu J, Cao F, Lin
HY, Jiang YX, Wang JZ, Chen H and Jiang SH: Analgesic effect of
electroacupuncture on chronic neuropathic pain mediated by P2X3
receptors in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neurochem Int.
60:379–386. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu J, Chen XM, Zheng BJ and Wang XR:
Electroacupuncture relieves nerve injury-induced pain
hypersensitivity via the inhibition of spinal P2X7
receptor-positive microglia. Anesth Analg. 122:882–892. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Grace PM, Rolan PE and Hutchinson MR:
Peripheral immune contributions to the maintenance of central glial
activation underlying neuropathic pain. Brain Behav Immun.
25:1322–1332. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tsuda M, Masuda T, Kitano J, Shimoyama H,
Tozaki-Saitoh H and Inoue K: IFN-γ receptor signaling mediates
spinal microglia activation driving neuropathic pain. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 106:8032–8037. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Phelps CE, Navratilova E, Dickenson AH,
Porreca F and Bannister K: Kappa opioid signaling in the right
central amygdala causes hind paw specific loss of diffuse noxious
inhibitory controls in experimental neuropathic pain. Pain.
160:1614–1621. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Navratilova E, Ji G, Phelps C, Qu C, Hein
M, Yakhnitsa V, Neugebauer V and Porreca F: Kappa opioid signaling
in the central nucleus of the amygdala promotes disinhibition and
aversiveness of chronic neuropathic pain. Pain. 160:824–832. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sosanya NM, Kumar R, Clifford JL, Chavez
R, Dimitrov G, Srinivasan S, Gautam A, Trevino AV, Williams M,
Hammamieh R, et al: Identifying Plasma Derived Extracellular
Vesicle (EV) Contained Biomarkers in the Development of Chronic
Neuropathic Pain. J Pain. Jun 19–2019.(Epub ahead of print).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gofman L, Fernandes NC and Potula R:
Relative Role of Akt, ERK and CREB in Alcohol-Induced Microglia
P2X4R Receptor Expression. Alcohol Alcohol. 51:647–654. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou K, Wu J, Chen J, Zhou Y, Chen X, Wu
Q, Xu Y, Tu W, Lou X, Yang G, et al: Schaftoside ameliorates oxygen
glucose deprivation-induced inflammation associated with the
TLR4/Myd88/Drp1-related mitochondrial fission in BV2 microglia
cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 139:15–22. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou K, Chen J, Wu J, Wu Q, Jia C, Xu YXZ,
Chen L, Tu W, Yang G, Kong J, et al: Atractylenolide III
ameliorates cerebral ischemic injury and neuroinflammation
associated with inhibiting JAK2/STAT3/Drp1-dependent mitochondrial
fission in microglia. Phytomedicine. 59:1529222019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rivera-Arconada I, Roza C and Lopez-Garcia
JA: Characterization of hyperpolarization-activated currents in
deep dorsal horn neurons of neonate mouse spinal cord in vitro.
Neuropharmacology. 70:148–155. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yasaka T, Tiong SY, Hughes DI, Riddell JS
and Todd AJ: Populations of inhibitory and excitatory interneurons
in lamina II of the adult rat spinal dorsal horn revealed by a
combined electrophysiological and anatomical approach. Pain.
151:475–488. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sankar SB, Pybus AF, Liew A, Sanders B,
Shah KJ, Wood LB and Buckley EM: Low cerebral blood flow is a
non-invasive biomarker of neuroinflammation after repetitive mild
traumatic brain injury. Neurobiol Dis. 124:544–554. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Todd AJ: Neuronal circuitry for pain
processing in the dorsal horn. Nat Rev Neurosci. 11:823–836. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kohno T, Wang H, Amaya F, Brenner GJ,
Cheng JK, Ji RR and Woolf CJ: Bradykinin enhances AMPA and NMDA
receptor activity in spinal cord dorsal horn neurons by activating
multiple kinases to produce pain hypersensitivity. J Neurosci.
28:4533–4540. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang K, Kumamoto E, Furue H and Yoshimura
M: Capsaicin facilitates excitatory but not inhibitory synaptic
transmission in substantia gelatinosa of the rat spinal cord.
Neurosci Lett. 255:135–138. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kawasaki Y, Zhang L, Cheng JK and Ji RR:
Cytokine mechanisms of central sensitization: Distinct and
overlapping role of interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, and tumor
necrosis factor-α in regulating synaptic and neuronal activity in
the superficial spinal cord. J Neurosci. 28:5189–5194. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Berman BM, Langevin HM, Witt CM and Dubner
R: Acupuncture for chronic low back pain. N Engl J Med.
363:454–461. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lau WK, Lau YM, Zhang HQ, Wong SC and Bian
ZX: Electroacupuncture versus celecoxib for neuropathic pain in rat
SNL model. Neuroscience. 170:655–661. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen SP, Kan Y, Zhang JL, Wang JY, Gao YH,
Qiao LN, Feng XM, Yan YX and Liu JL: Involvement of hippocampal
acetylcholinergic receptors in electroacupuncture analgesia in
neuropathic pain rats. Behav Brain Funct. 12:132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vieira JS, Toreti JA, de Carvalho RC, de
Araújo JE, Silva ML and Silva JRT: Analgesic Effects Elicited by
Neuroactive Mediators Injected into the ST 36 Acupuncture Point on
Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain in Mice. J Acupunct Meridian
Stud. 11:280–289. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liang Y, Du JY, Qiu YJ, Fang JF, Liu J and
Fang JQ: Electroacupuncture attenuates spinal nerve
ligation-induced microglial activation mediated by p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase. Chin J Integr Med. 22:704–713.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jiang H, Yu X, Ren X and Tu Y:
Electroacupuncture alters pain related behaviors and expression of
spinal prostaglandin E2 in a rat model of neuropathic pain. J
Tradit Chin Med. 36:85–91. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gao Y, Xu C, Liang S, Zhang A, Mu S, Wang
Y and Wan F: Effect of tetramethylpyrazine on primary afferent
transmission mediated by P2X3 receptor in neuropathic pain states.
Brain Res Bull. 77:27–32. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Inoue K and Tsuda M: Microglia and
neuropathic pain. Glia. 57:1469–1479. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
He WJ, Cui J, Du L, Zhao YD, Burnstock G,
Zhou HD and Ruan HZ: Spinal P2X(7) receptor mediates microglia
activation-induced neuropathic pain in the sciatic nerve injury rat
model. Behav Brain Res. 226:163–170. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kobayashi K, Takahashi E, Miyagawa Y,
Yamanaka H and Noguchi K: Induction of the P2X7 receptor in spinal
microglia in a neuropathic pain model. Neurosci Lett. 504:57–61.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Masuda T, Iwamoto S, Yoshinaga R,
Tozaki-Saitoh H, Nishiyama A, Mak TW, Tamura T, Tsuda M and Inoue
K: Transcription factor IRF5 drives P2X4R+-reactive
microglia gating neuropathic pain. Nat Commun. 5:37712014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Biber K, Tsuda M, Tozaki-Saitoh H,
Tsukamoto K, Toyomitsu E, Masuda T, Boddeke H and Inoue K: Neuronal
CCL21 up-regulates microglia P2X4 expression and initiates
neuropathic pain development. EMBO J. 30:1864–1873. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ulmann L, Hirbec H and Rassendren F: P2X4
receptors mediate PGE2 release by tissue-resident macrophages and
initiate inflammatory pain. EMBO J. 29:2290–2300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Williams WA, Linley JE, Jones CA, Shibata
Y, Snijder A, Button J, Hatcher JP, Huang L, Taddese B, Thornton P,
et al: Jones Antibodies binding the head domain of P2X4 inhibit
channel function and reverse neuropathic pain. Pain. 160:1989–2003.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gao F, Xiang HC, Li HP, Jia M, Pan XL, Pan
HL and Li M: Electroacupuncture inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome
activation through CB2 receptors in inflammatory pain. Brain Behav
Immun. 67:91–100. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhan J, Qin W, Zhang Y, Jiang J, Ma H, Li
Q and Luo Y: Upregulation of neuronal zinc finger protein A20
expression is required for electroacupuncture to attenuate the
cerebral inflammatory injury mediated by the nuclear factor-kB
signaling pathway in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats. J
Neuroinflammation. 13:2582016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang R, Lao L, Ren K and Berman BM:
Mechanisms of acupuncture-electroacupuncture on persistent pain.
Anesthesiology. 120:482–503. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang Y, Zhang RX, Zhang M, Shen XY, Li A,
Xin J, Ren K, Berman BM, Tan M and Lao L: Electroacupuncture
inhibition of hyperalgesia in an inflammatory pain rat model:
Involvement of distinct spinal serotonin and norepinephrine
receptor subtypes. Br J Anaesth. 109:245–252. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Harrison C: Inflammatory disorders:
Steroids modulate microglia-mediated inflammation. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 10:492–493. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhuang ZY, Gerner P, Woolf CJ and Ji RR:
ERK is sequentially activated in neurons, microglia, and astrocytes
by spinal nerve ligation and contributes to mechanical allodynia in
this neuropathic pain model. Pain. 114:149–159. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Liu X, Liu H, Xu S, Tang Z, Xia W, Cheng
Z, Li W and Jin Y: Spinal translocator protein alleviates chronic
neuropathic pain behavior and modulates spinal astrocyte-neuronal
function in rats with L5 spinal nerve ligation model. Pain.
157:103–116. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Burke NN, Kerr DM, Moriarty O, Finn DP and
Roche M: Minocycline modulates neuropathic pain behaviour and
cortical M1-M2 microglial gene expression in a rat model of
depression. Brain Behav Immun. 42:147–156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|