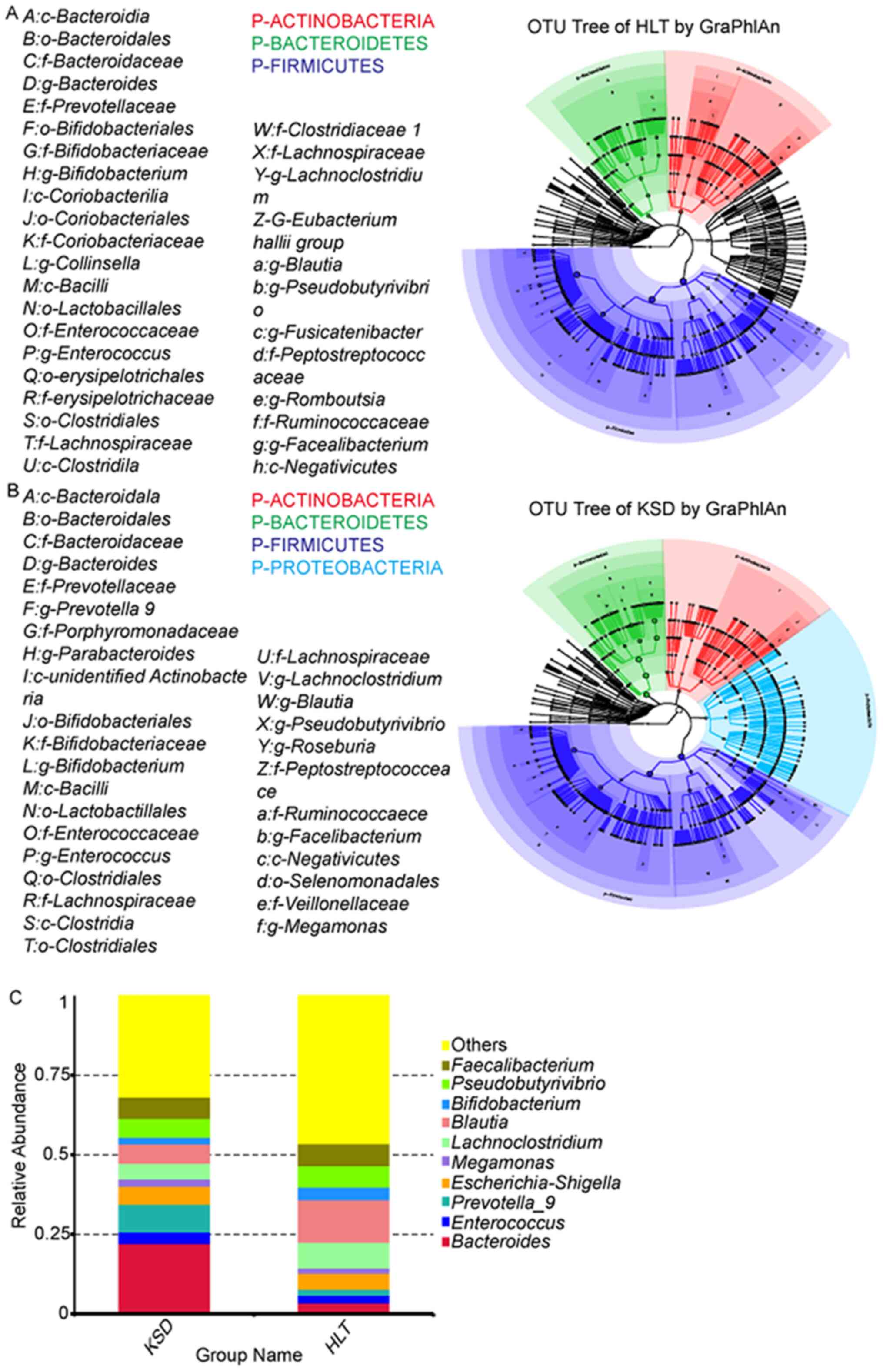
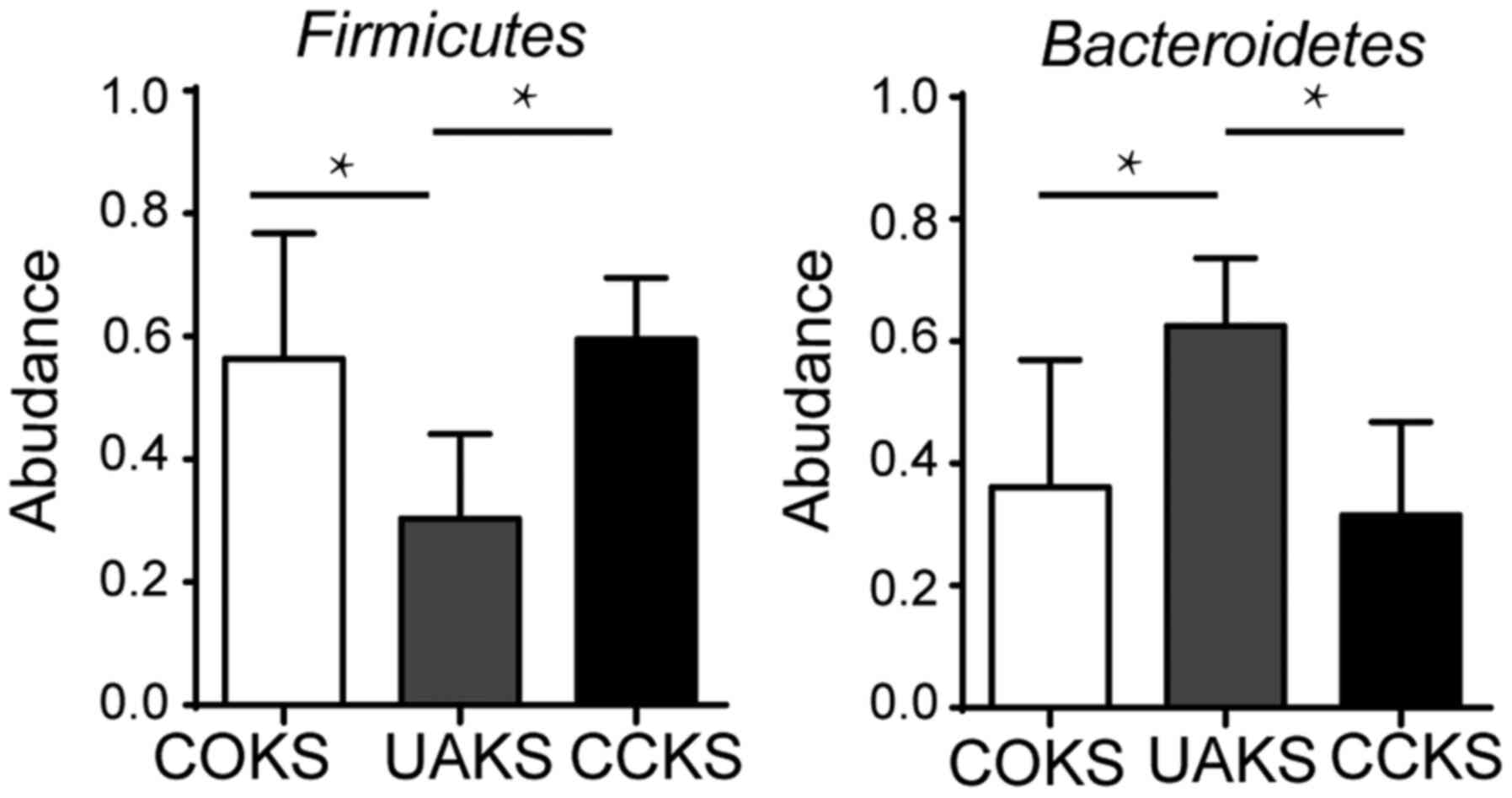
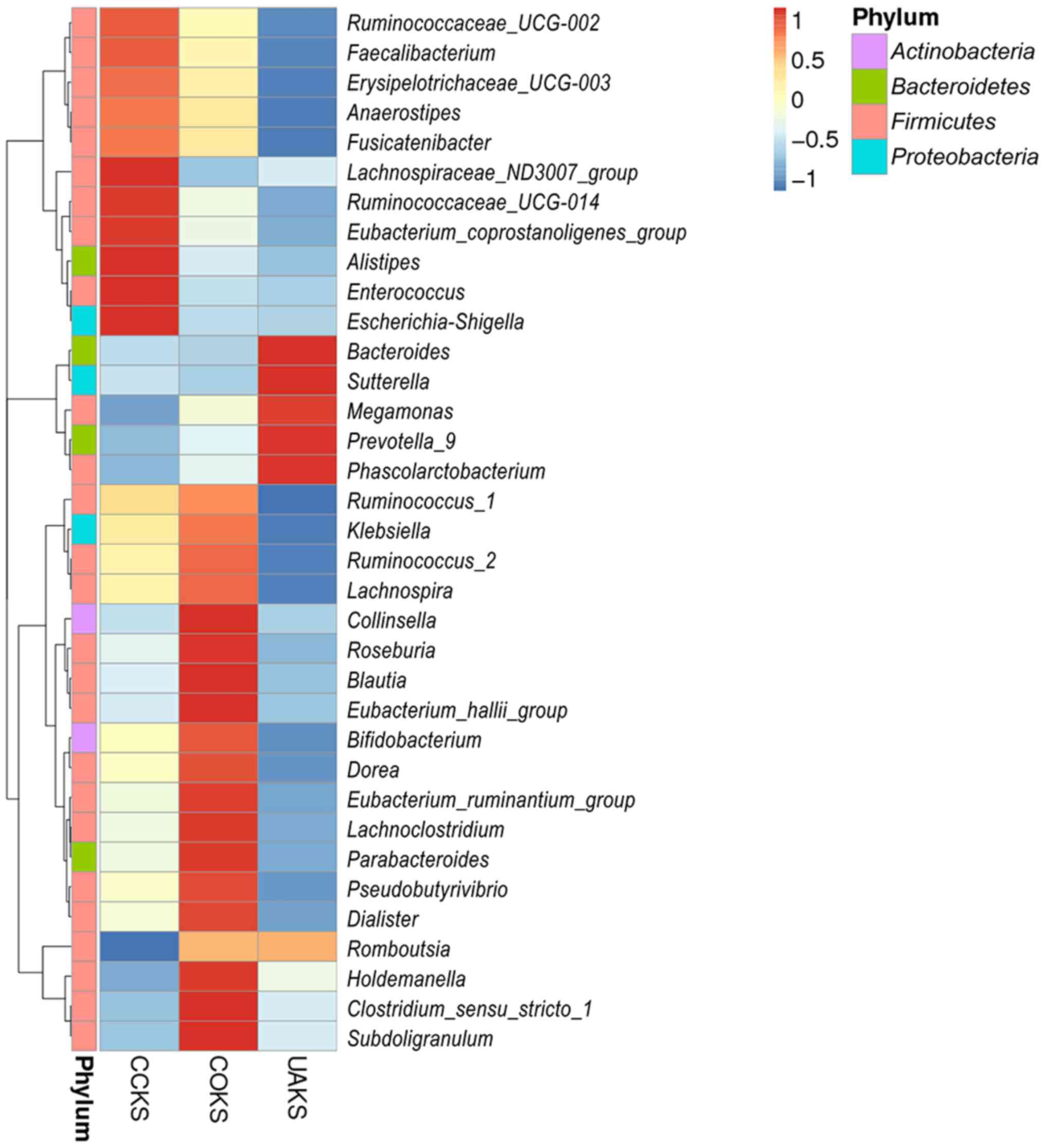
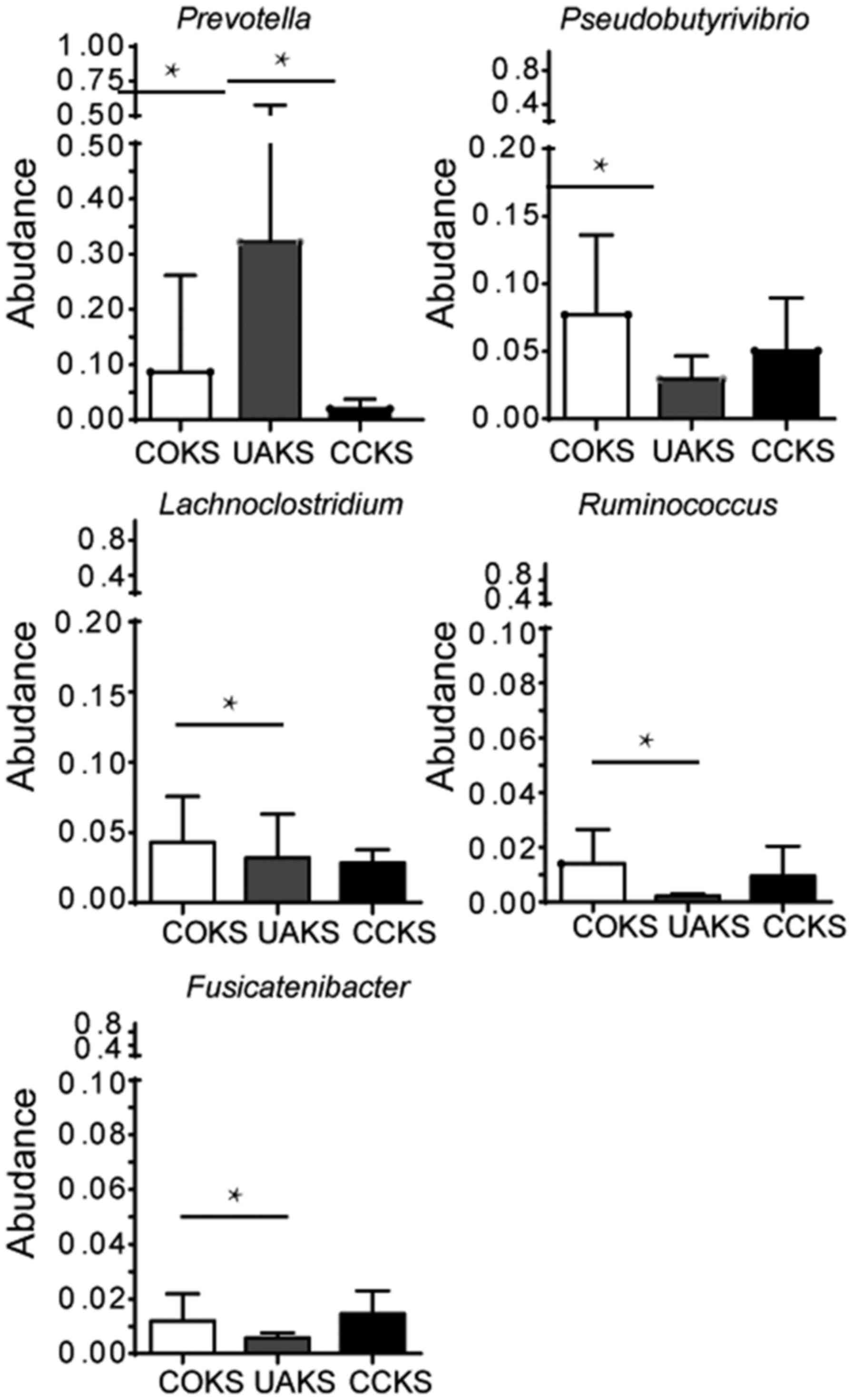
|
1
|
Scales CD Jr, Smith AC, Hanley JM and
Saigal CS; Urologic Diseases in America Project, : Prevalence of
kidney stones in the United States. Eur Urol. 62:160–165. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stern JM, Moazami S, Qiu Y, Kurland I,
Chen Z, Agalliu I, Burk R and Davies KP: Evidence for a distinct
gut microbiome in kidney stone formers compared to non-stone
formers. Urolithiasis. 44:399–407. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Daudon M, Dore JC, Jungers P and Lacour B:
Changes in stone composition according to age and gender of
patients: A multivariate epidemiological approach. Urol Res.
32:241–247. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Taylor EN, Stampfer MJ and Curhan GC:
Dietary factors and the risk of incident kidney stones in men: New
insights after 14 years of follow-up. J Am Soc Nephrol.
15:3225–3232. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tracy CR, Best S, Bagrodia A, Poindexter
JR, Adams-Huet B, Sakhaee K, Maalouf N, Pak CY and Pearle MS:
Animal protein and the risk of kidney stones: A comparative
metabolic study of animal protein sources. J Urol. 192:137–141.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Borghi L, Schianchi T, Meschi T, Guerra A,
Allegri F, Maggiore U and Novarini A: Comparison of two diets for
the prevention of recurrent stones in idiopathic hypercalciuria. N
Engl J Med. 346:77–84. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brunkwall L and Orho-Melander M: The gut
microbiome as a target for prevention and treatment of
hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes: From current human evidence to
future possibilities. Diabetologia. 60:943–951. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Karlsson FH, Tremaroli V, Nookaew I,
Bergstrom G, Behre CJ, Fagerberg B, Nielsen J and Backhed F: Gut
metagenome in European women with normal, impaired and diabetic
glucose control. Nature. 498:99–103. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qin J, Li Y, Cai Z, Li S, Zhu J, Zhang F,
Liang S, Zhang W, Guan Y, Shen D, et al: A metagenome-wide
association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature.
490:55–60. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dumas ME, Barton RH, Toye A, Cloarec O,
Blancher C, Rothwell A, Fearnside J, Tatoud R, Blanc V, Lindon JC,
et al: Metabolic profiling reveals a contribution of gut microbiota
to fatty liver phenotype in insulin-resistant mice. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 103:12511–12516. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pedersen HK, Gudmundsdottir V, Nielsen HB,
Hyotylainen T, Nielsen T, Jensen BA, Forslund K, Hildebrand F,
Prifti E, Falony G, et al: Human gut microbes impact host serum
metabolome and insulin sensitivity. Nature. 535:376–381. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Le Chatelier E, Nielsen T, Qin J, Prifti
E, Hildebrand F, Falony G, Almeida M, Arumugam M, Batto JM, Kennedy
S, et al: Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with
metabolic markers. Nature. 500:541–546. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ussar S, Griffin NW, Bezy O, Fujisaka S,
Vienberg S, Softic S, Deng L, Bry L, Gordon JI and Kahn CR:
Interactions between gut microbiota, host genetics and diet
modulate the predisposition to obesity and metabolic syndrome. Cell
Metab. 22:516–530. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tang WH, Wang Z, Shrestha K, Borowski AG,
Wu Y, Troughton RW, Klein AL and Hazen SL: Intestinal
microbiota-dependent phosphatidylcholine metabolites, diastolic
dysfunction, and adverse clinical outcomes in chronic systolic
heart failure. J Card Fail. 21:91–96. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Z, Klipfell E, Bennett BJ, Koeth R,
Levison BS, Dugar B, Feldstein AE, Britt EB, Fu X, Chung YM, et al:
Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular
disease. Nature. 472:57–63. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu W, Gregory JC, Org E, Buffa JA, Gupta
N, Wang Z, Li L, Fu X, Wu Y, Mehrabian M, et al: Gut microbial
metabolite TMAO enhances platelet hyperreactivity and thrombosis
risk. Cell. 165:111–124. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Suryavanshi MV, Bhute SS, Jadhav SD,
Bhatia MS, Gune RP and Shouche YS: Hyperoxaluria leads to dysbiosis
and drives selective enrichment of oxalate metabolizing bacterial
species in recurrent kidney stone endures. Sci Rep. 6:347122016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mandel NS, Mandel IC and Kolbach-Mandel
AM: Accurate stone analysis: The impact on disease diagnosis and
treatment. Urolithiasis. 45:3–9. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Y and Qian PY: Conservative fragments
in bacterial 16S rRNA genes and primer design for 16S ribosomal DNA
amplicons in metagenomic studies. PLoS One. 4:e74012009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Smith BC, McAndrew T, Chen Z, Harari A,
Barris DM, Viswanathan S, Rodriguez AC, Castle P, Herrero R,
Schiffman M and Burk RD: The cervical microbiome over 7 years and a
comparison of methodologies for its characterization. PLoS One.
7:e404252012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J,
Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich
JK, Gordon JI, et al: QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput
community sequencing data. Nat Methods. 7:335–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Edgar RC: Search and clustering orders of
magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics. 1:2460–2461. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Matsen FA, Kodner RB and Armbrust EV:
Pplacer: Linear time maximum-likelihood and Bayesian phylogenetic
placement of sequences onto a fixed reference tree. BMC Bioinform.
11:5382010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Org E, Blum Y, Kasela S, Mehrabian M,
Kuusisto J, Kangas AJ, Soininen P, Wang Z, Ala-Korpela M, Hazen SL,
et al: Relationships between gut microbiota, plasma metabolites,
and metabolic syndrome traits in the METSIM cohort. Genome Biol.
18:702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pak CY: Kidney stones. Lancet.
351:1797–1801. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Parks BW, Nam E, Org E, Kostem E, Norheim
F, Hui ST, Pan C, Civelek M, Rau CD, Bennett BJ, et al: Genetic
control of obesity and gut microbiota composition in response to
high-fat, high-sucrose diet in mice. Cell Metab. 17:141–152. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu GD, Chen J, Hoffmann C, Bittinger K,
Chen YY, Keilbaugh SA, Bewtra M, Knights D, Walters WA, Knight R,
et al: Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial
enterotypes. Science. 334:105–108. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Daniel H, Gholami AM, Berry D,
Desmarchelier C, Hahne H, Loh G, Mondot S, Lepage P, Rothballer M,
Walker A, et al: High-fat diet alters gut microbiota physiology in
mice. ISME J. 8:295–308. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
David LA, Maurice CF, Carmody RN,
Gootenberg DB, Button JE, Wolfe BE, Ling AV, Devlin AS, Varma Y,
Fischbach MA, et al: Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human
gut microbiome. Nature. 505:559–563. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Palsson R, Indridason OS, Edvardsson VO
and Oddsson A: Genetics of common complex kidney stone disease:
Insights from genome-wide association studies. Urolithiasis.
47:11–21. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ratajczak W, Rył A, Mizerski A,
Walczakiewicz K, Sipak O and Laszczyńska M: Immunomodulatory
potential of gut microbiome-derived short-chain fatty acids
(SCFAs). Acta Biochim Pol. 66:1–12. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Okada A, Yasui T, Fujii Y, Niimi K,
Hamamoto S, Hirose M, Kojima Y, Itoh Y, Tozawa K, Hayashi Y and
Kohri K: Renal macrophage migration and crystal phagocytosis via
inflammatory-related gene expression during kidney stone formation
and elimination in mice: Detection by association analysis of
stone-related gene expression and microstructural observation. J
Bone Miner Res. 12:2701–2711. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Fakhoury MQ, Gordon B, Shorter B, Renson
A, Borofsky MS, Cohn MR, Cabezon E, Wysock JS and Bjurlin MA:
Perceptions of dietary factors promoting and preventing
nephrolithiasis: A cross-sectional survey. World J Urol.
37:1723–1731. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lim MY, Rho M, Song YM, Lee K, Sung J and
Ko G: Stability of gut enterotypes in Korean monozygotic twins and
their association with biomarkers and diet. Sci Rep. 4:73482014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Teixeira TF, Grzeskowiak L, Franceschini
SC, Bressan J, Ferreira CL and Peluzio MC: Higher level of faecal
SCFA in women correlates with metabolic syndrome risk factors. Br J
Nutr. 109:914–919. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Winter SE and Baumler AJ: Why related
bacterial species bloom simultaneously in the gut: Principles
underlying the ‘like will to like’ concept. Cell Microbiol.
16:179–184. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Winter SE and Baumler AJ: Dysbiosis in the
inflamed intestine: Chance favors the prepared microbe. Gut
Microbes. 5:71–73. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee JA and Stern JM: Understanding the
link between gut microbiome and urinary stone disease. Curr Urol
Rep. 20:192019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|