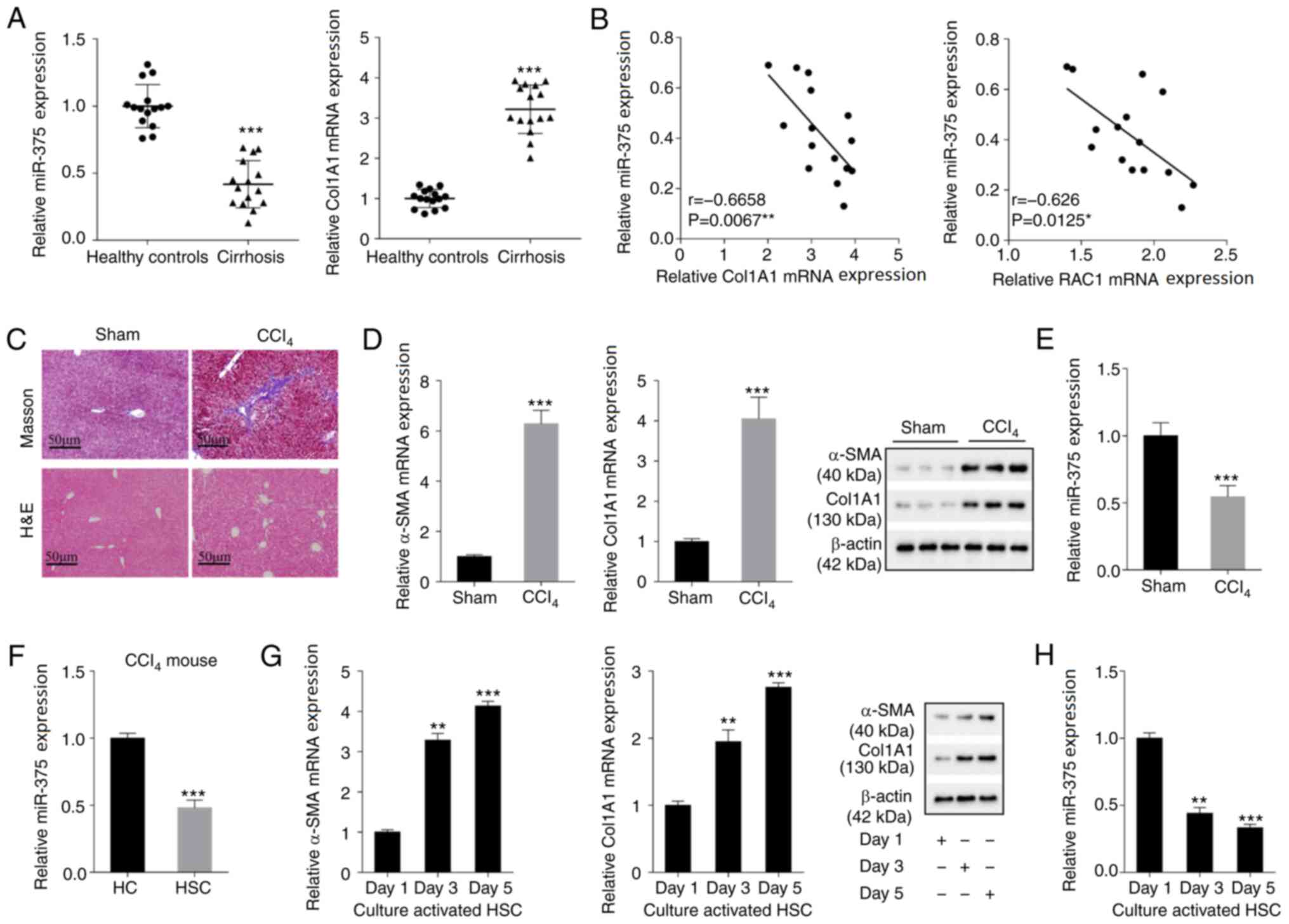
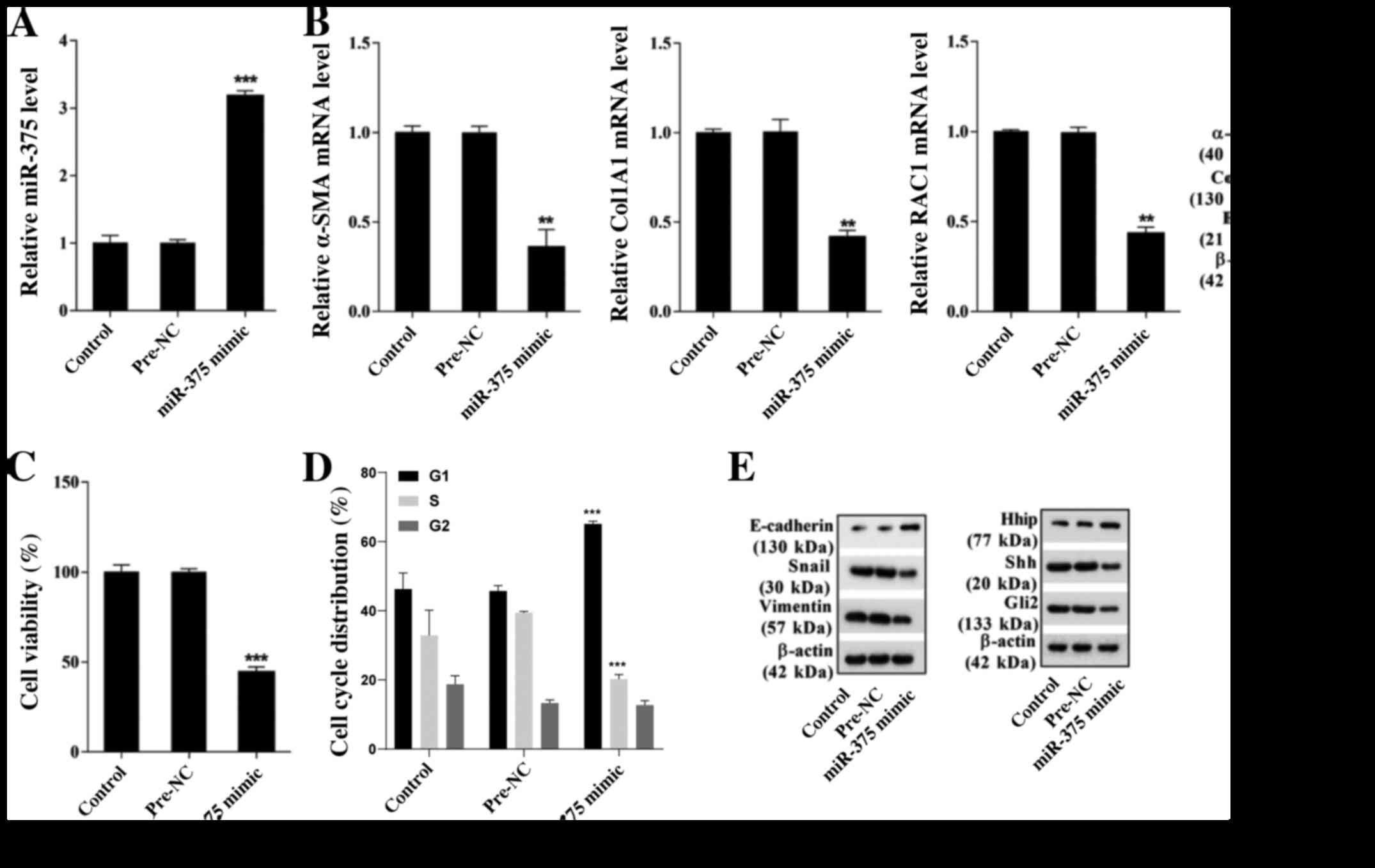
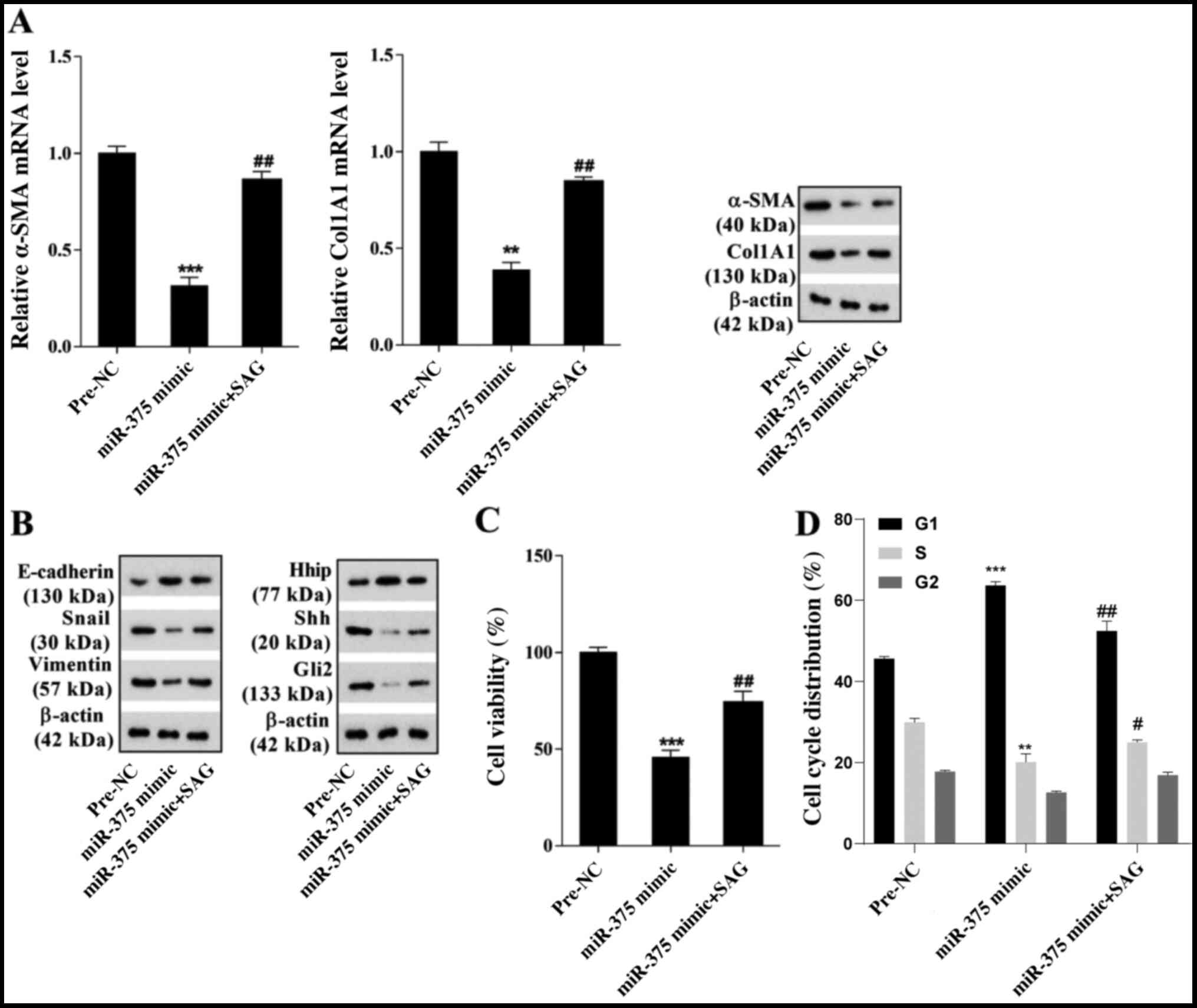
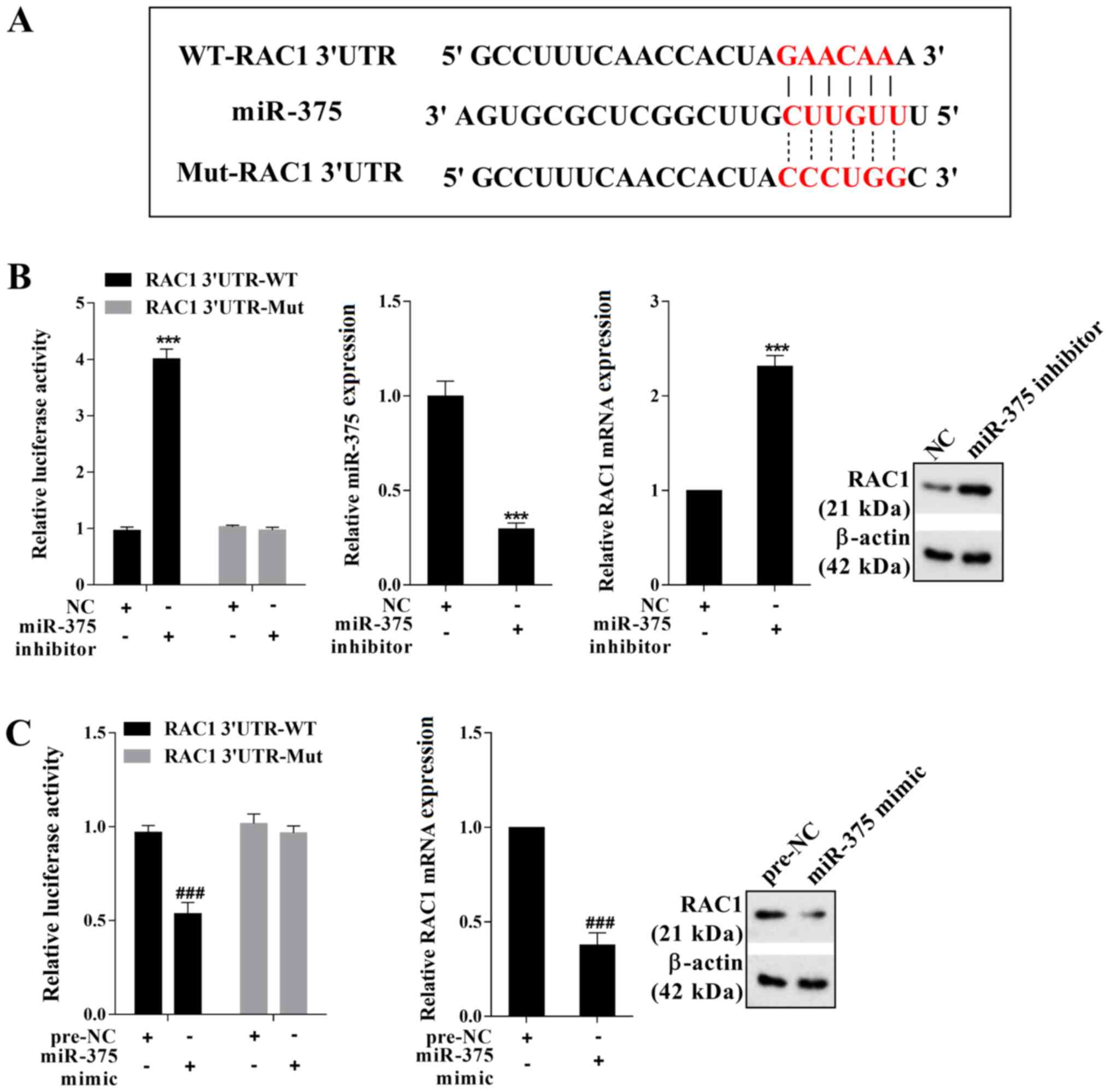
|
1
|
Breitkopf-Heinlein K, Meyer C, König C,
Gaitantzi H, Addante A, Thomas M, Wiercinska E, Cai C, Li Q, Wan F,
et al: BMP-9 interferes with liver regeneration and promotes liver
fibrosis. Gut. 66:939–954. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hernandez-Gea V and Friedman SL:
Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:425–456. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li W, Zhou C, Fu Y, Chen T, Liu X, Zhang Z
and Gong T: Targeted delivery of hyaluronic acid nanomicelles to
hepatic stellate cells in hepatic fibrosis rats. Acta Pharm Sin B.
10:693–710. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yu F, Geng W, Dong P, Huang Z and Zheng J:
LncRNA-MEG3 inhibits activation of hepatic stellate cells through
SMO protein and miR-212. Cell Death Dis. 9:10142018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Choi SS, Syn WK, Karaca GF, Omenetti A,
Moylan CA, Witek RP, Agboola KM, Jung Y, Michelotti GA and Diehl
AM: Leptin promotes the myofibroblastic phenotype in hepatic
stellate cells by activating the hedgehog pathway. J Biol Chem.
285:36551–36560. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu F, Zheng Y, Hong W, Chen B, Dong P and
Zheng J: MicroRNA-200a suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition in rat hepatic stellate cells via GLI family zinc finger
2. Mol Med Rep. 12:8121–8128. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu F, Lu Z, Chen B, Wu X, Dong P and Zheng
J: Salvianolic acid B-induced microRNA-152 inhibits liver fibrosis
by attenuating DNMT1-mediated Patched1 methylation. J Cell Mol Med.
19:2617–2632. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang C, Luo J, Chen Z, Ye M, Hong Y, Liu
J, Nie J, Zhao Q and Chang Y: MiR-375 impairs the invasive
capabilities of hepatoma cells by targeting HIF1α under hypoxia.
Dig Dis Sci. Mar 25–2020.(Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1007/s10620-020-06202-9. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yang YZ, Zhao XJ, Xu HJ, Wang SC, Pan Y,
Wang SJ, Xu Q, Jiao RQ, Gu HM and Kong LD: Magnesium
isoglycyrrhizinate ameliorates high fructose-induced liver fibrosis
in rat by increasing miR-375-3p to suppress JAK2/STAT3 pathway and
TGF-β1/Smad signaling. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 40:879–894. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ungefroren H, Witte D and Lehnert H: The
role of small GTPases of the Rho/Rac family in TGF-β-induced EMT
and cell motility in cancer. Dev Dyn. 247:451–461. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Choi SS, Sicklick JK, Ma Q, Yang L, Huang
J, Qi Y, Chen W, Li YX, Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ and Diehl AM:
Sustained activation of Rac1 in hepatic stellate cells promotes
liver injury and fibrosis in mice. Hepatology. 44:1267–1277. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Choi SS, Witek RP, Yang L, Omenetti A, Syn
WK, Moylan CA, Jung Y, Karaca GF, Teaberry VS, Pereira TA, et al:
Activation of Rac1 promotes hedgehog-mediated acquisition of the
myofibroblastic phenotype in rat and human hepatic stellate cells.
Hepatology. 52:278–290. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ge B, Wu H, Shao D, Li S and Li F:
Interfering with miR-24 alleviates rotenone-induced dopaminergic
neuron injury via enhancing autophagy by up-regulating DJ-1. Aging
Pathobiol Ther. 1:17–24. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu F, Chen B, Dong P and Zheng J: HOTAIR
epigenetically modulates PTEN expression via MicroRNA-29b: A novel
mechanism in regulation of liver fibrosis. Mol Ther. 25:205–217.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou X, Xiong J, Lu S, Luo L, Chen ZL,
Yang F, Jin F, Wang Y, Ma Q, Luo YY, et al: Inhibitory effect of
corilagin on miR-21-regulated hepatic fibrosis signaling pathway.
Am J Chin Med. 47:1541–1569. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu JC, Chen R, Luo X, Li ZH, Luo SZ and Xu
MY: MicroRNA-194 inactivates hepatic stellate cells and alleviates
liver fibrosis by inhibiting AKT2. World J Gastroenterol.
25:4468–4480. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li BB, Li DL, Chen C, Liu BH, Xia CY, Wu
HJ, Wu CQ, Ji GQ, Liu S, Ni W, et al: Potentials of the elevated
circulating miR-185 level as a biomarker for early diagnosis of
HBV-related liver fibrosis. Sci Rep. 6:341572016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wei S, Wang Q, Zhou H, Qiu J, Li C, Shi C,
Zhou S, Liu R and Lu L: miR-455-3p alleviates hepatic stellate cell
activation and liver fibrosis by suppressing HSF1 expression. Mol
Ther Nucleic Acids. 16:758–769. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang L, Dong C, Yang J, Yang L, Chang N,
Qi C and Li L: MicroRNA-26b-5p inhibits mouse liver fibrogenesis
and angiogenesis by targeting PDGF receptor-beta. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 16:206–217. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zou Y, Li S, Li Z, Song D, Zhang S and Yao
Q: MiR-146a attenuates liver fibrosis by inhibiting transforming
growth factor-β1 mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
hepatocytes. Cell Signal. 58:1–8. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kikuchi M, Sekiya M, Hara N, Miyashita A,
Kuwano R, Ikeuchi T, Iijima KM and Nakaya A: Disruption of a
RAC1-centred network is associated with Alzheimer's disease
pathology and causes age-dependent neurodegeneration. Hum Mol
Genet. 29:817–833. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kai Y, Kon R, Ikarashi N, Chiba Y, Kamei J
and Sakai H: Role of Rac1 in augmented endothelin-1-induced
bronchial contraction in airway hyperresponsive mice. J Pharmacol
Sci. 141:106–110. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bopp A, Wartlick F, Henninger C, Kaina B
and Fritz G: Rac1 modulates acute and subacute genotoxin-induced
hepatic stress responses, fibrosis and liver aging. Cell Death Dis.
4:e5582013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Venugopal SK, Jiang J, Kim TH, Li Y, Wang
SS, Torok NJ, Wu J and Zern MA: Liver fibrosis causes
downregulation of miRNA-150 and miRNA-194 in hepatic stellate
cells, and their overexpression causes decreased stellate cell
activation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 298:G101–G106.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|