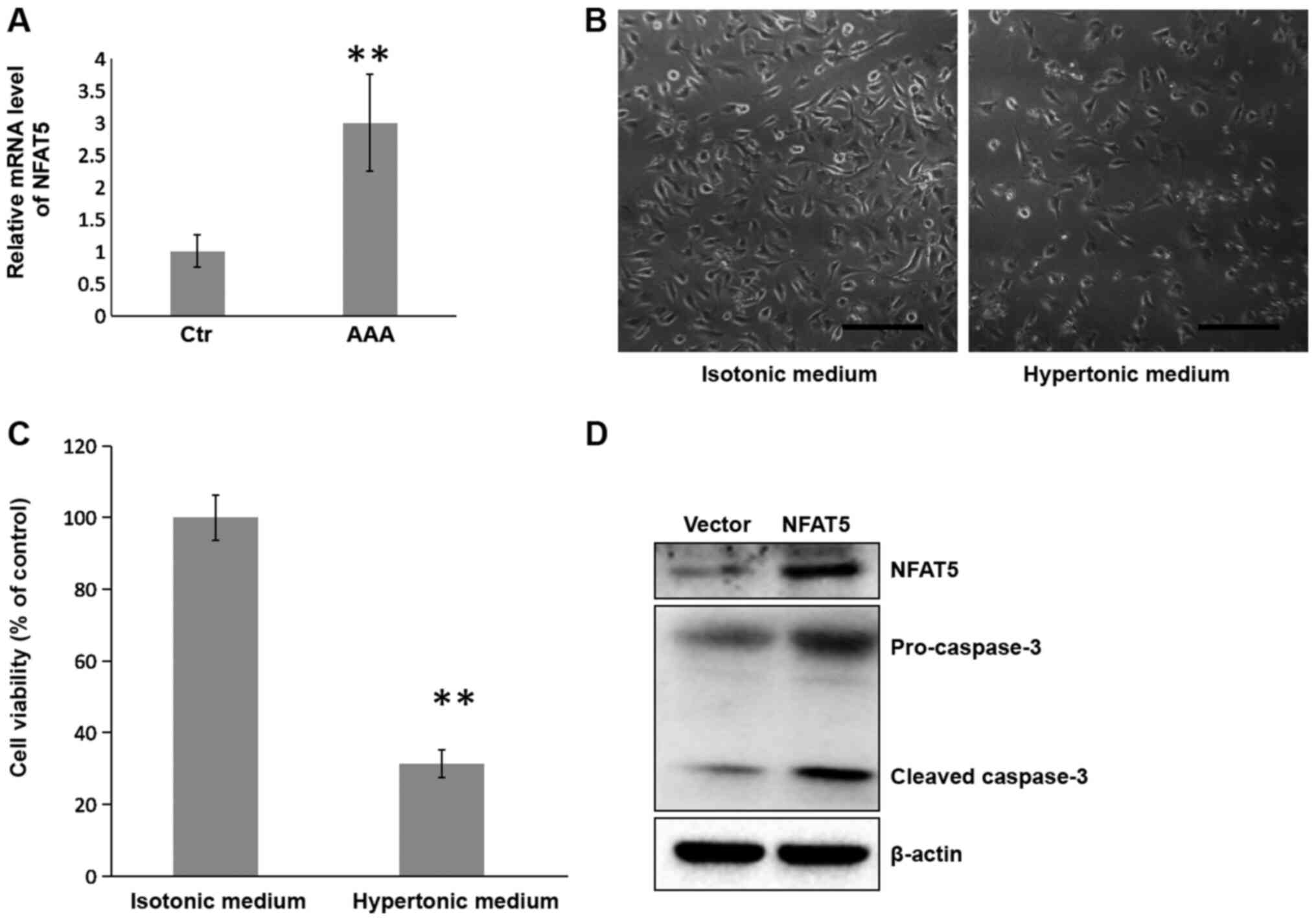
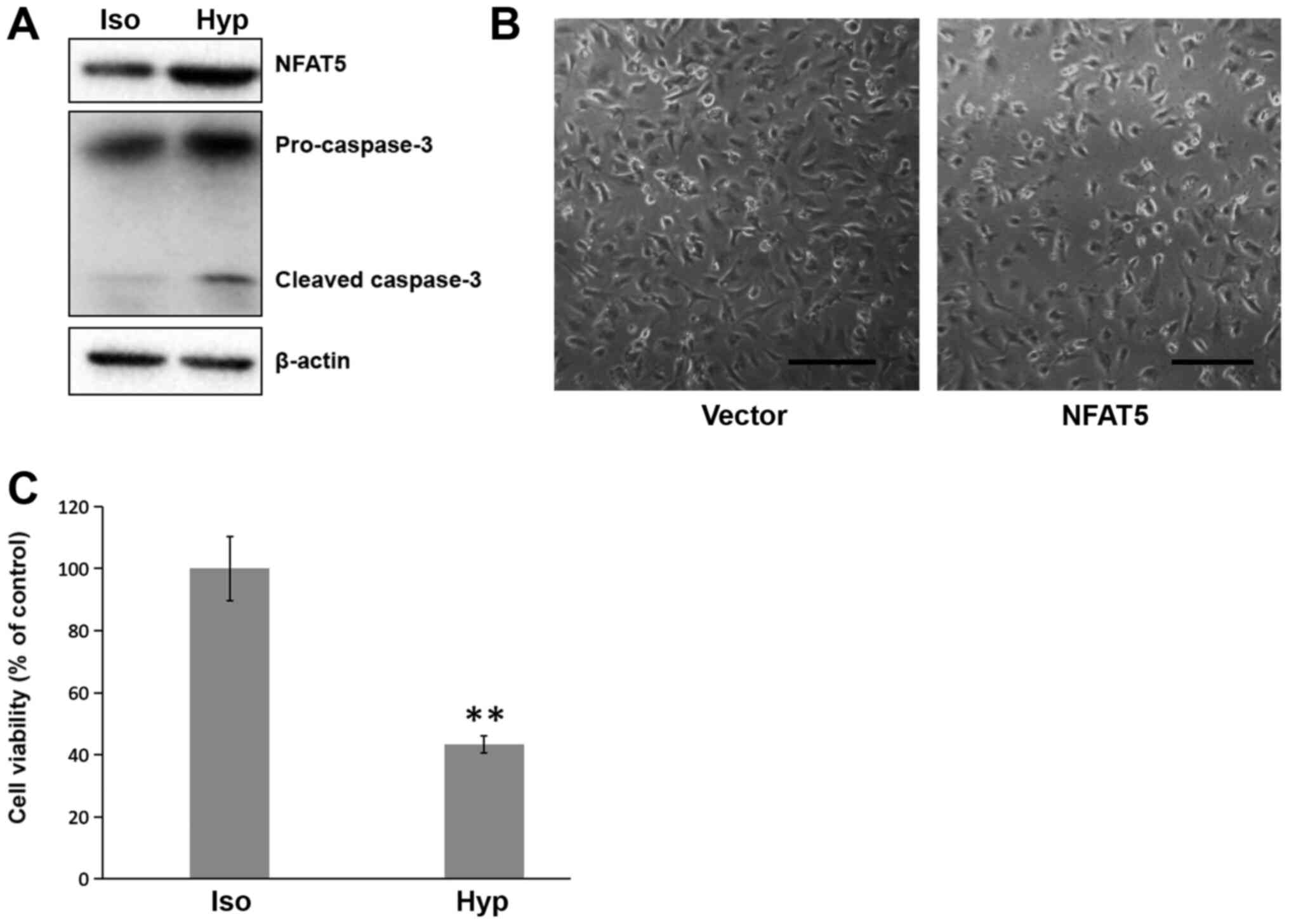
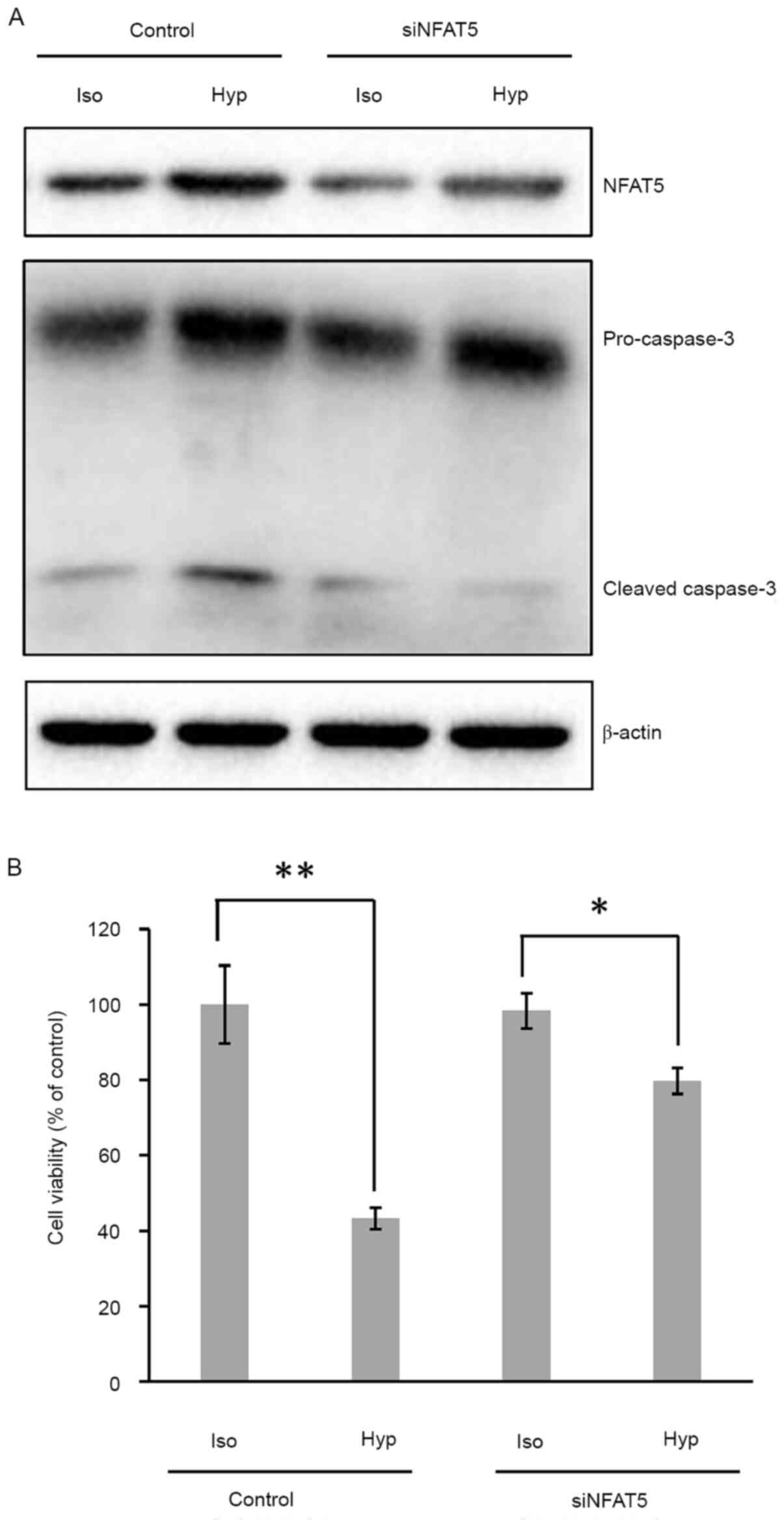
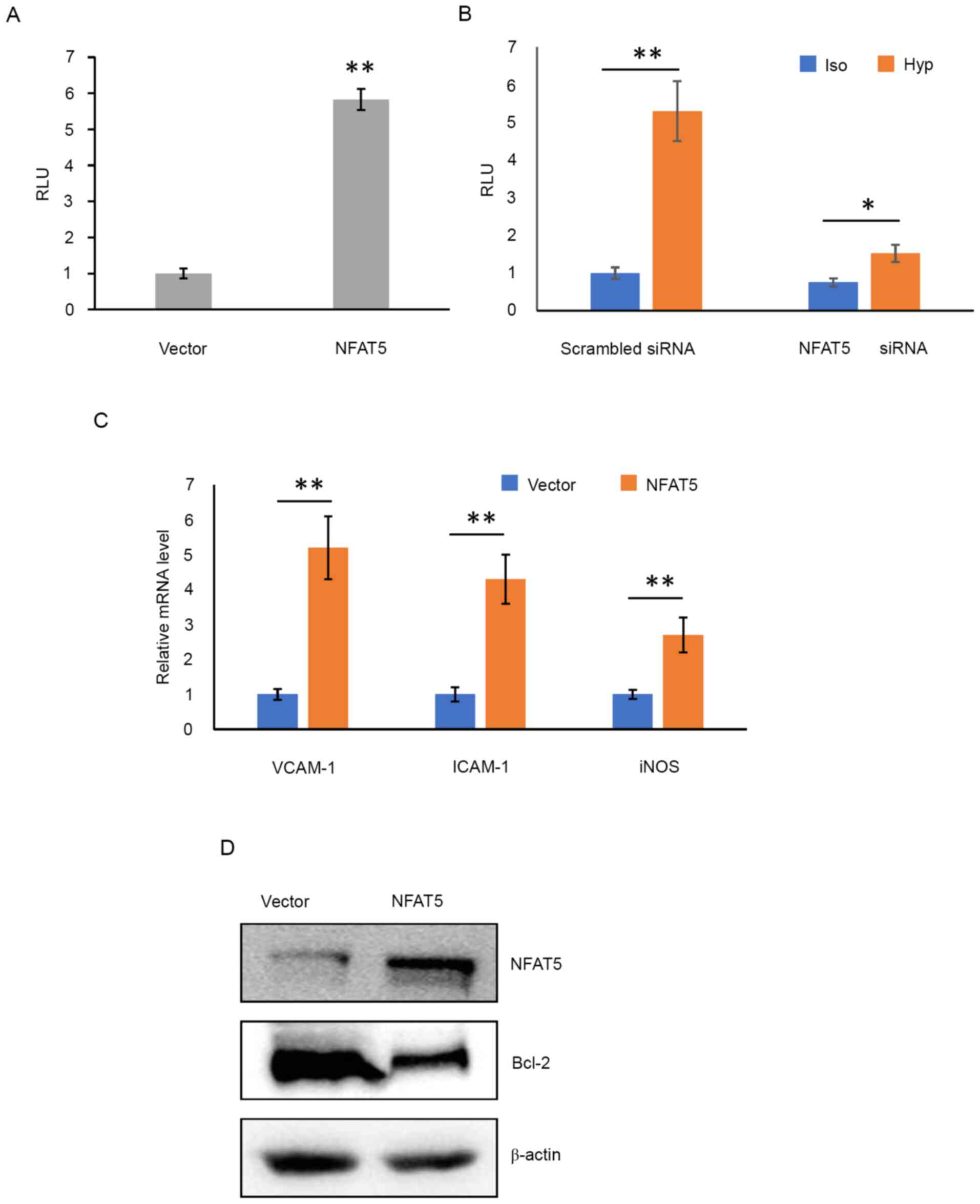
|
1
|
Kent KC: Clinical practice. Abdominal
aortic aneurysms. N Eng J Med. 371:2101–2108. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Spangler R, Van Pham T, Khoujah D and
Martinez JP: Abdominal emergencies in the geriatric patient. Int J
Emerg Med. 7:432014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Golledge J, Hankey GJ, Yeap BB, Almeida
OP, Flicker L and Norman PE: Reported high salt intake is
associated with increased prevalence of abdominal aortic aneurysm
and larger aortic diameter in older men. PLoS One. 9:e1025782014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu S, Gong MC and Guo Z: A new mouse
model for introduction of aortic aneurysm by implantation of
deoxycorticosterone acetate pellets or aldosterone infusion in the
presence of high salt. Methods Mol Biol. 1614:155–163. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Siasos G, Mourouzis K, Oikonomou E,
Tsalamandris S, Tsigkou V, Vlasis K, Vavuranakis M, Zografos T,
Dimitropoulos S, Papaioannou TG, et al: The role of endothelial
dysfunction in aortic aneurysms. Curr Pharm Des. 21:4016–4034.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Krischek B, Kasuya H, Tajima A, Akagawa H,
Sasaki T, Yoneyama T, Ujiie H, Kubo O, Bonin M, Takakura K, et al:
Network-based gene expression analysis of intracranial aneurysm
tissue reveals role of antigen presenting cells. Neuroscience.
154:1398–1407. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ishibashi R, Aoki T, Nishimura M,
Hashimoto N and Miyamoto S: Contribution of mast cells to cerebral
aneurysm formation. Curr Neurovasc Res. 7:113–124. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cao Y, Gong Y, Liu L, Zhou Y, Fang X,
Zhang C, Li Y and Li J: The use of human umbilical vein endothelial
cells (HUVECs) as an in vitro model to assess the toxicity of
nanoparticles to endothelium: A review. J Appl Toxicol.
37:1359–1369. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen G, Chen Y, Chen H, Li L, Yao J, Jiang
Q, Lin X, Wen J and Lin L: The effect of NF-κB pathway on
proliferation and apoptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial
cells induced by intermittent high glucose. Mol Cell Biochem.
347:127–133. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lopez-Rodríguez C, Aramburu J, Rakeman AS
and Rao A: NFAT5, a constitutively nuclear NFAT protein that does
not cooperate with Fos and Jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
96:7214–7219. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rondon-Berrios H, Argyropoulos C, Ing TS,
Raj DS, Malhotra D, Agaba EI, Rohrscheib M, Khitan ZJ, Murata GH,
Shapiro JI and Tzamaloukas AH: Hypertonicity: Clinical entities,
manifestations and treatment. World J Nephrol. 6:1–13. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Roth I, Leroy V, Kwon HM, Martin PY,
Féraille E and Hasler U: Osmoprotective transcription factor
NFAT5/TonEBP modulates nuclear factor-kappaB activity. Mol Biol
Cell. 21:3459–3474. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qiu Y, Ye X, Zhang HM, Hanson P, Zhao G,
Tong L, Xie R and Yang D: Cleavage of osmosensitive transcriptional
factor NFAT5 by Coxsackieviral protease 2A promotes viral
replication. PLoS Pathog. 13:e10067442017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jauliac S, Lopez-Rodriguez C, Shaw LM,
Brown LF, Rao A and Toker A: The role of NFAT transcription factors
in integrin-mediated carcinoma invasion. Nat Cell Biol. 4:540–544.
2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou W, Pal AS, Hsu AY, Gurol T, Zhu X,
Wirbisky-Hershberger SE, Freeman JL, Kasinski AL and Deng Q:
MicroRNA-223 suppresses the canonical NF-κB pathway in basal
keratinocytes to dampen neutrophilic inflammation. Cell Rep.
22:1810–1823. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Parodi FE, Mao D, Ennis TL, Bartoli MA and
Thompson RW: Suppression of experimental abdominal aortic aneurysms
in mice by treatment with pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate, an
antioxidant inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB. J Vasc Surg.
41:479–489. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death
Collaborators: Global, regional, and national life expectancy,
all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of
death, 1980–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of
Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 388:1459–1544. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death
Collaborators Global, regional, and national age-sex specific
all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death,
1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease
Study 2013. Lancet. 385:117–171. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sakalihasan N, Limet R and Defawe OD:
Abdominal aortic aneurysm. Lancet. 365:1577–1589. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Keisler B and Carter C: Abdominal aortic
aneurysm. Am Fam Physician. 91:538–543. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Greenhalgh RM and Powell JT: Endovascular
repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. N Engl J Med. 358:494–501.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao X, Yang X, Zhang X, Li Y, Zhao X, Ren
L, Wang L, Gu C, Zhu Z and Han Y: Dietary salt intake and coronary
atherosclerosis in patients with prehypertension. J Clin Hypertens
(Greenwich). 16:575–580. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ketonen J, Merasto S, Paakkari I and
Mervaala EM: High sodium intake increases vascular superoxide
formation and promotes atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein
E-deficient mice. Blood Press. 14:373–382. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Halterman JA, Kwon HM and Wamhoff BR:
Tonicity-independent regulation of the osmosensitive transcription
factor TonEBP (NFAT5). Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 302:C1–C8. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ko BC, Turck CW, Lee KW, Yang Y and Chung
SS: Purification, identification, and characterization of an
osmotic response element binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 270:52–61. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ito T, Fujio Y, Hirata M, Takatani T,
Matsuda T, Muraoka S, Takahashi K and Azuma J: Expression of
taurine transporter is regulated through the TonE
(tonicity-responsive element)/TonEBP (TonE-binding protein) pathway
and contributes to cytoprotection in HepG2 cells. Biochem J.
382:177–182. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Miyakawa H, Woo SK, Dahl SC, Handler JS
and Kwon HM: Tonicity-responsive enhancer binding protein, a
rel-like protein that stimulates transcription in response to
hypertonicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:2538–2542. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bosman DK, Deutz NE, Maas MA, van Eijk HM,
Smit JJ, de Haan JG and Chamuleau RA: Amino acid release from
cerebral cortex in experimental acute liver failure, studied by in
vivo cerebral cortex microdialysis. J Neurochem. 59:591–599. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rim JS, Atta MG, Dahl SC, Berry GT,
Handler JS and Kwon HM: Transcription of the sodium/myo-inositol
cotransporter gene is regulated by multiple tonicity-responsive
enhancers spread over 50 kilobase pairs in the 5′-flanking region.
J Biol Chem. 273:20615–20621. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Woo SK, Lee SD, Na KY, Park WK and Kwon
HM: TonEBP/NFAT5 stimulates transcription of HSP70 in response to
hypertonicity. Mol Cell Biol. 22:5753–5760. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kojima R, Randall JD, Ito E, Manshio H,
Suzuki Y and Gullans SR: Regulation of expression of the stress
response gene, Osp94: Identification of the tonicity response
element and intracellular signalling pathways. Biochem J.
380:783–794. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sheikh MS and Huang Y: Death receptor
activation complexes: It takes two to activate TNF receptor 1. Cell
Cycle. 2:550–552. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yeung F, Hoberg JE, Ramsey CS, Keller MD,
Jones DR, Frye RA and Mayo MW: Modulation of NF-kappaB-dependent
transcription and cell survival by the SIRT1 deacetylase. EMBO J.
23:2369–2380. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Qin X, Wang Y, Li J, Xiao Y and Liu Z:
NFAT5 inhibits invasion and promotes apoptosis in hepatocellular
carcinoma associated with osmolality. Neoplasma. 64:502–510. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mak MC, Lam KM, Chan PK, Lau YB, Tang WH,
Yeung PK, Ko BC, Chung SM and Chung SK: Embryonic lethality in mice
lacking the nuclear factor of activated T cells 5 protein due to
impaired cardiac development and function. PLoS One. 6:e191862011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
López-Rodríguez C, Aramburu J, Jin L,
Rakeman AS, Michino M and Rao A: Bridging the NFAT and NF-kappaB
families: NFAT5 dimerization regulates cytokine gene transcription
in response to osmotic stress. Immunity. 15:47–58. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Go WY, Liu X, Roti MA, Liu F and Ho SN:
NFAT5/TonEBP mutant mice define osmotic stress as a critical
feature of the lymphoid microenvironment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:10673–10678. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Trama J, Go WY and Ho SN: The
osmoprotective function of the NFAT5 transcription factor in T cell
development and activation. J Immunol. 169:5477–5488. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kuper C, Beck FX and Neuhofer W:
Generation of a conditional knockout allele for the NFAT5 gene in
mice. Front Physiol. 5:5072014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Grigoryants V, Hannawa KK, Pearce CG,
Sinha I, Roelofs KJ, Ailawadi G, Deatrick KB, Woodrum DT, Cho BS,
Henke PK, et al: Tamoxifen up-regulates catalase production,
inhibits vessel wall neutrophil infiltration, and attenuates
development of experimental abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc
Surg. 41:108–114. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|