|
1
|
Kahraman BO, Savci S, Ozsoy I, Baran A,
Acar S, Ozpelit E, Balci A, Sevinc C and Akdeniz B: Effects of
neuromuscular electrical stimulation in patients with pulmonary
arterial hypertension: A randomized controlled pilot study. J
Cardiol. 75:702–708. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hiraide T, Kataoka M, Suzuki H, Aimi Y,
Chiba T, Isobe S, Katsumata Y, Goto S, Kanekura K, Yamada Y, et al:
Poor outcomes in carriers of the RNF213 variant (p.Arg4810Lys) with
pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Heart Lung Transplant.
39:103–112. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang L, Wang Y, Wu G, Rao L, Wei Y, Yue
H, Yuan T, Yang P, Xiong F, Zhang S, et al: Blockade of JAK2
protects mice against hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial
hypertension by repressing pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell
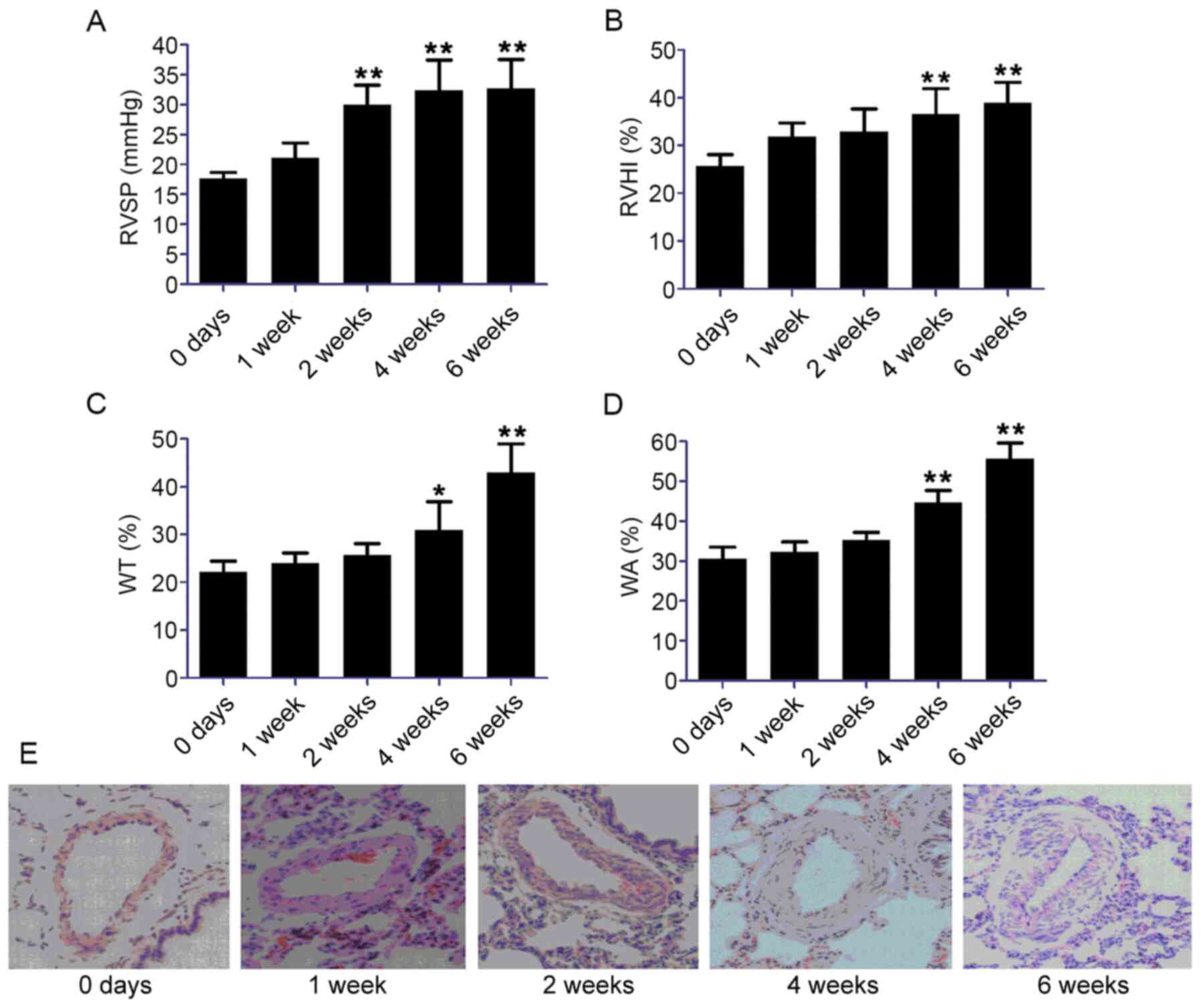
proliferation. Cell Prolif. 53:e127422020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Luo F, Wang X, Luo X, Li B, Zhu D, Sun H
and Tang Y: Invasive hemodynamic assessment for the right
ventricular system and hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial
hypertension in mice. J Vis Exp. 152:e600902019.
|
|
5
|
Zhou W, Negash S, Liu J and Raj JU:
Modulation of pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype in
hypoxia: Role of cGMP-dependent protein kinase and myocardin. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 296:L780–L789. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Humbert M, Sitbon O, Chaouat A, Bertocchi
M, Habib G, Gressin V, Yaïci A, Weitzenblum E, Cordier JF, Chabot
F, et al: Survival in patients with idiopathic, familial, and
anorexigen-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension in the modern
management era. Circulation. 122:156–163. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ren ZP, Hou XB, Tian XD, Guo JT, Zhang LB,
Xue ZQ, Deng JQ, Zhang SW, Pan JY and Chu XY: Identification of
nine microRNAs as potential biomarkers for lung adenocarcinoma.
FEBS Open Bio. 9:315–327. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Peng XX, Yu R, Wu X, Wu SY, Pi C, Chen ZH,
Zhang XC, Gao CY, Shao YW, Liu L, et al: Correlation of plasma
exosomal microRNAs with the efficacy of immunotherapy in EGFR/ALK
wild-type advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Immunother Cancer.
8:e0003762020.Erratum in: J Immunother Cancer 8: e000376corr1,
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim D and Kim Y and Kim Y: Effects of
β-carotene on expression of selected micrornas, histone
acetylation, and DNA methylation in colon cancer stem cells. J
Cancer Prev. 24:224–232. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Moloney BM, Gilligan KE, Joyce DP, O'Neill
CP, O'Brien KP, Khan S, Glynn CL, Waldron RM, Maguire CM, Holian E,
et al: Investigating the potential and pitfalls of EV-encapsulated
microRNAs as circulating biomarkers of breast cancer. Cells.
9:1412020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhao L, Shan Y, Liu B, Li Y and Jia L:
Functional screen analysis reveals miR-3142 as central regulator in
chemoresistance and proliferation through activation of the
PTEN-AKT pathway in CML. Cell Death Dis. 8:e28302017.Retraction in:
Cell Death Dis 11: 121, 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhu TT, Zhang WF, Yin YL, Liu YH, Song P,
Xu J, Zhang MX and Li P: MicroRNA-140-5p targeting tumor necrosis
factor-α prevents pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Cell Physiol.
234:9535–9550. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Babicheva A, Ayon RJ, Zhao T, Ek Vitorin
JF, Pohl NM, Yamamura A, Yamamura H, Quinton BA, Ba M, Wu L, et al:
MicroRNA-mediated downregulation of K+ channels in pulmonary
arterial hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
318:L10–L26. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mohsenin V: The emerging role of microRNAs
in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Sleep Breath.
20:1059–1067. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang P, Xu J, Hou Z, Wang F, Song Y, Wang
J, Zhu H and Jin H: miRNA-34a promotes proliferation of human
pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells by targeting PDGFRA. Cell
Prolif. 49:484–493. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tang BI, Tang MM, Xu QM, Guo JL, Xuan L,
Zhou J, Wang XJ, Zhang H and Kang PF: MicroRNA-143-5p modulates
pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells functions in hypoxic pulmonary
hypertension through targeting HIF-1α. J Biosci. 45:372020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
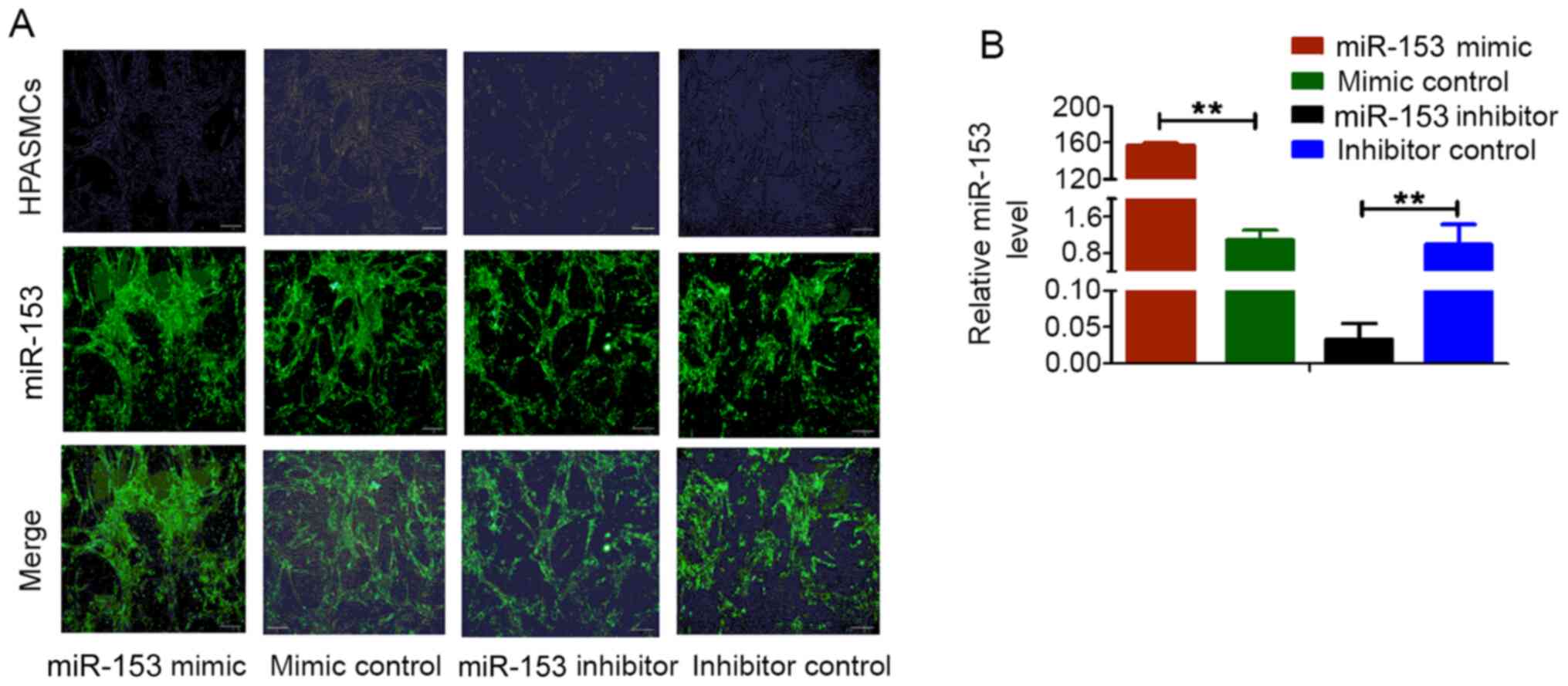
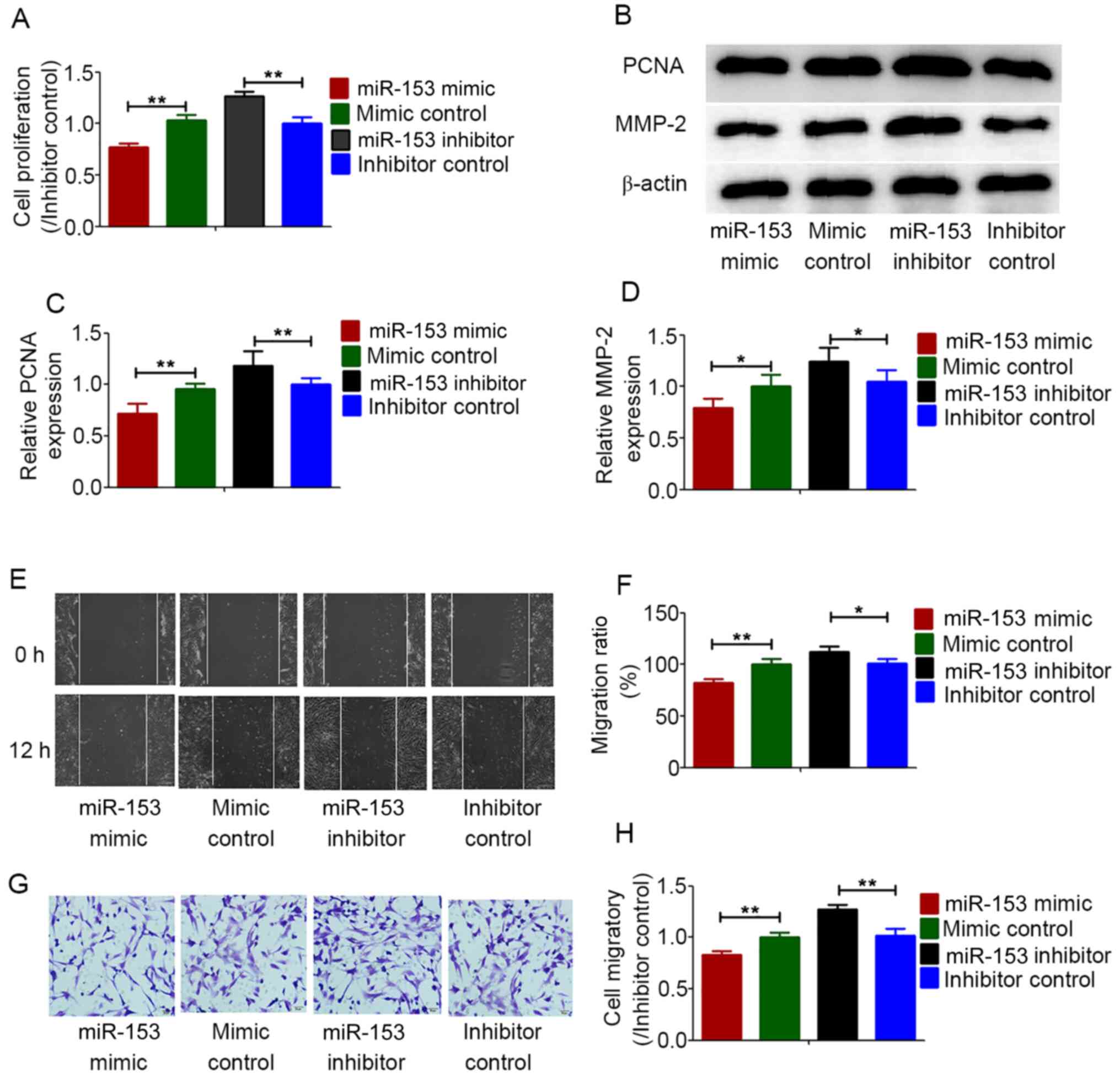
Shan N, Shen L, Wang J, He D and Duan C:
MiR-153 inhibits migration and invasion of human non-small-cell
lung cancer by targeting ADAM19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
456:385–391. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang L, Lv X, Fu X, Su L, Yang T and Xu P:
MiR-153 inhibits the resistance of lung cancer to gefitinib via
modulating expression of ABCE1. Cancer Biomark. 25:361–369. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liang C, Li X, Zhang L, Cui D, Quan X and
Yang W: The anti-fibrotic effects of microRNA-153 by targeting
TGFBR-2 in pulmonary fibrosis. Exp Mol Pathol. 99:279–285. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liang H, Xiao J, Zhou Z, Wu J, Ge F, Li Z,
Zhang H, Sun J, Li F, Liu R, et al: Hypoxia induces miR-153 through
the IRE1α-XBP1 pathway to fine tune the HIF1α/VEGFA axis in breast
cancer angiogenesis. Oncogene. 37:1961–1975. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu WH, Xu XH, Luo Q, Zhang HL, Wang Y, Xi
QY, Zhao ZH and Liu ZH: Inhibition of the RhoA/Rho-associated,
coiled-coil-containing protein kinase-1 pathway is involved in the
therapeutic effects of simvastatin on pulmonary arterial
hypertension. Clin Exp Hypertens. 40:224–230. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang M, Chang Z, Zhang P, Jing Z, Yan L,
Feng J, Hu Z, Xu Q, Zhou W, Ma P, et al: Protective effects of
18β-glycyrrhetinic acid on pulmonary arterial hypertension via
regulation of Rho A/Rho kinsase pathway. Chem Biol Interact.
311:1087492019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
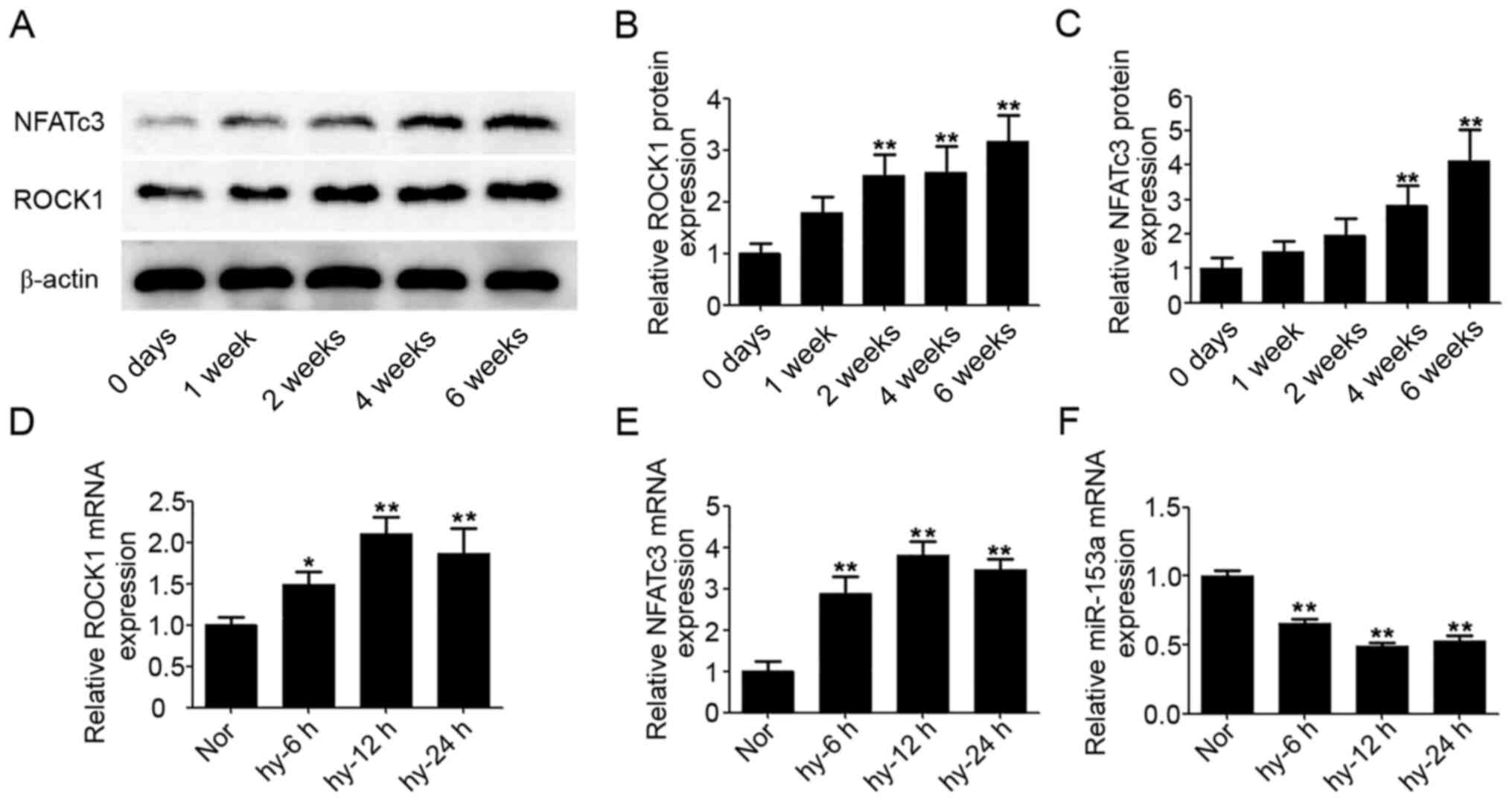
Zhu J, Liu C, Wang B, Tong X and Li Z:
Qibai Pingfei capsule medicated serum inhibits the proliferation of
hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells via the
Ca2+/calcineurin/nuclear factor of activated T-cells 3 pathway. J
Tradit Chin Med. 37:466–474. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kang K, Peng X, Zhang X, Wang Y, Zhang L,
Gao L, Weng T, Zhang H, Ramchandran R, Raj JU, et al: MicroRNA-124
suppresses the transactivation of nuclear factor of activated T
cells by targeting multiple genes and inhibits the proliferation of
pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 288:25414–25427.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hasnat AK, van der Velde ET, Hon JKF and
Yacoub MH: Reproducible model of post-infarction left ventricular
dysfunction: haemodynamic characterization by conductance catheter.
Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 24:98–104. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4:e050052015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhao M, Chen N, Li X, Lin L and Chen X:
miR-19a modulates hypoxia-mediated cell proliferation and migration
via repressing PTEN in human pulmonary arterial smooth muscle. Life
Sci. 239:1169282019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Siddique MAH, Satoh K, Kurosawa R, Kikuchi
N, Elias-Al-Mamun M, Omura J, Satoh T, Nogi M, Sunamura S, Miyata
S, et al: Identification of emetine as a therapeutic agent for
pulmonary arterial hypertension: novel effects of an old drug.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 39:2367–2385. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Han J, Tian H, Liu Y and Fan F:
Sarpogrelate attenuates pulmonary arterial hypertension via
calcium/calcineurin axis. Front Biosci. 24:607–615. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yu L, Quinn DA, Garg HG and Hales CA:
Deficiency of the NHE1 gene prevents hypoxia-induced pulmonary
hypertension and vascular remodeling. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
177:1276–1284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu J, Pan W, Wang C, Dong H, Xing L, Hou
J, Fang S, Li H, Yang F and Yu B: H2S attenuates
endoplasmic reticulum stress in hypoxia-induced pulmonary artery
hypertension. Biosci Rep. 39:BSR201903042019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu W, Li Y and Xu DQ: Role of ROS/Kv/HIF
Axis in the development of hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension.
Chin Med Sci J. 32:253–259. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang Y, Duo D, Yan Y, He R and Wu X:
Magnesium lithospermate B ameliorates hypobaric hypoxia-induced
pulmonary arterial hypertension by inhibiting
endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and its potential targets.
Biomed Pharmacother. 130:1105602020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Bierer R, Nitta CH, Friedman J, Codianni
S, de Frutos S, Dominguez-Bautista JA, Howard TA, Resta TC and Bosc
LV: NFATc3 is required for chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary
hypertension in adult and neonatal mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 301:L872–L880. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shao H, Dong D and Shao F: Long non-coding
RNA TUG1-mediated down-regulation of KLF4 contributes to metastasis
and the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer
by miR-153-1. Cancer Manag Res. 11:8699–8710. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xiao L, He Y, Peng F, Yang J and Yuan C:
Endometrial cancer cells promote M2-like macrophage polarization by
delivering exosomal miRNA-21 under hypoxia condition. J Immunol
Res. 2020:97310492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang Y, Qu A, Wu Q, Zhang X, Wang L, Li C,
Dong Z, Du L and Wang C: Prognostic value of a hypoxia-related
microRNA signature in patients with colorectal cancer. Aging
(Albany NY). 12:35–52. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Miao R, Liu W, Qi C, Song Y, Zhang Y, Fu
Y, Liu W, Lang Y, Zhang Y and Zhang Z: miR-18a-5p contributes to
enhanced proliferation and migration of PASMCs via targeting Notch2
in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Life Sci. 257:1179192020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Peng Y and Wang HH: Cir-ITCH inhibits
gastric cancer migration, invasion and proliferation by regulating
the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Sci Rep. 10:174432020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Luo Y, Teng X, Zhang L, Chen J, Liu Z,
Chen X, Zhao S, Yang S, Feng J and Yan X: CD146-HIF-1α hypoxic
reprogramming drives vascular remodeling and pulmonary arterial
hypertension. Nat Commun. 10:35512019.Erratum in: Nat Commun 10:
4098, 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cui Z, Luo Z, Lin Z, Shi L, Hong Y and Yan
C: Long non-coding RNA TTN-AS1 facilitates tumorigenesis of
papillary thyroid cancer through modulating the miR-153-3p/ZNRF2
axis. J Gene Med. 21:e30832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zuo Z, Ye F, Liu Z, Huang J and Gong Y:
MicroRNA-153 inhibits cell proliferation, migration, invasion and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer via direct
targeting of RUNX2. Exp Ther Med. 17:4693–4702. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang J, Liang S and Duan X: Molecular
mechanism of miR-153 inhibiting migration, invasion and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer by regulating
transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway. J Cell
Biochem. 120:9539–9546. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ma H, Tian T, Liu X, Xia M, Chen C, Mai L,
Xie S and Yu L: Upregulated circ_0005576 facilitates cervical
cancer progression via the miR-153/KIF20A axis. Biomed
Pharmacother. 118:1093112019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
He RL, Wu ZJ, Liu XR, Gui LX, Wang RX and
Lin MJ: Calcineurin/NFAT signaling modulates pulmonary artery
smooth muscle cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis in
monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension rats. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 49:172–189. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Huetsch JC, Walker J, Undem C, Lade J, Yun
X, Baksh S, Jiang H, Lai N and Shimoda LA: Rho kinase and Na+/H+
exchanger mediate endothelin-1-induced pulmonary arterial smooth
muscle cell proliferation and migration. Physiol Rep. 6:e136982018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|