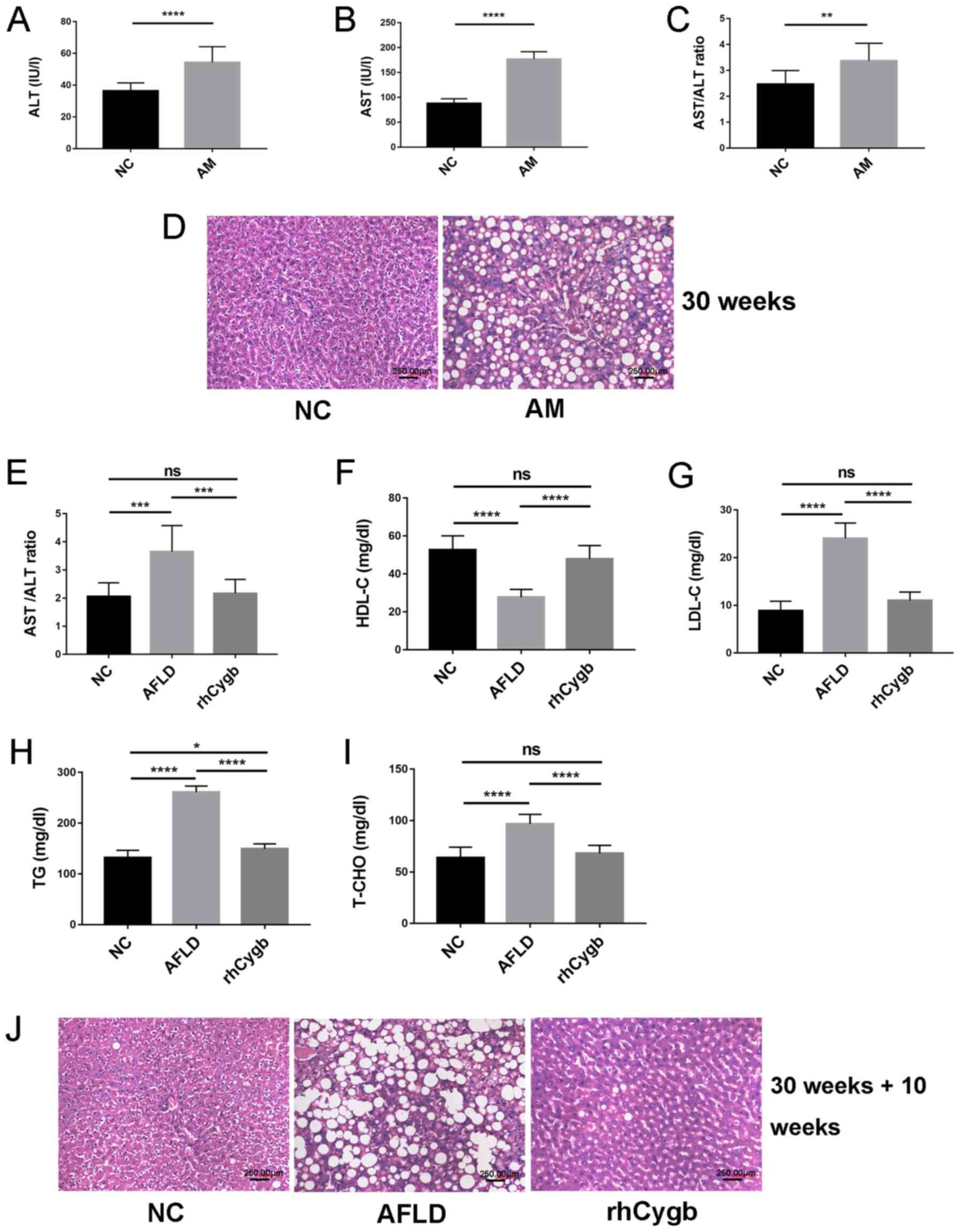
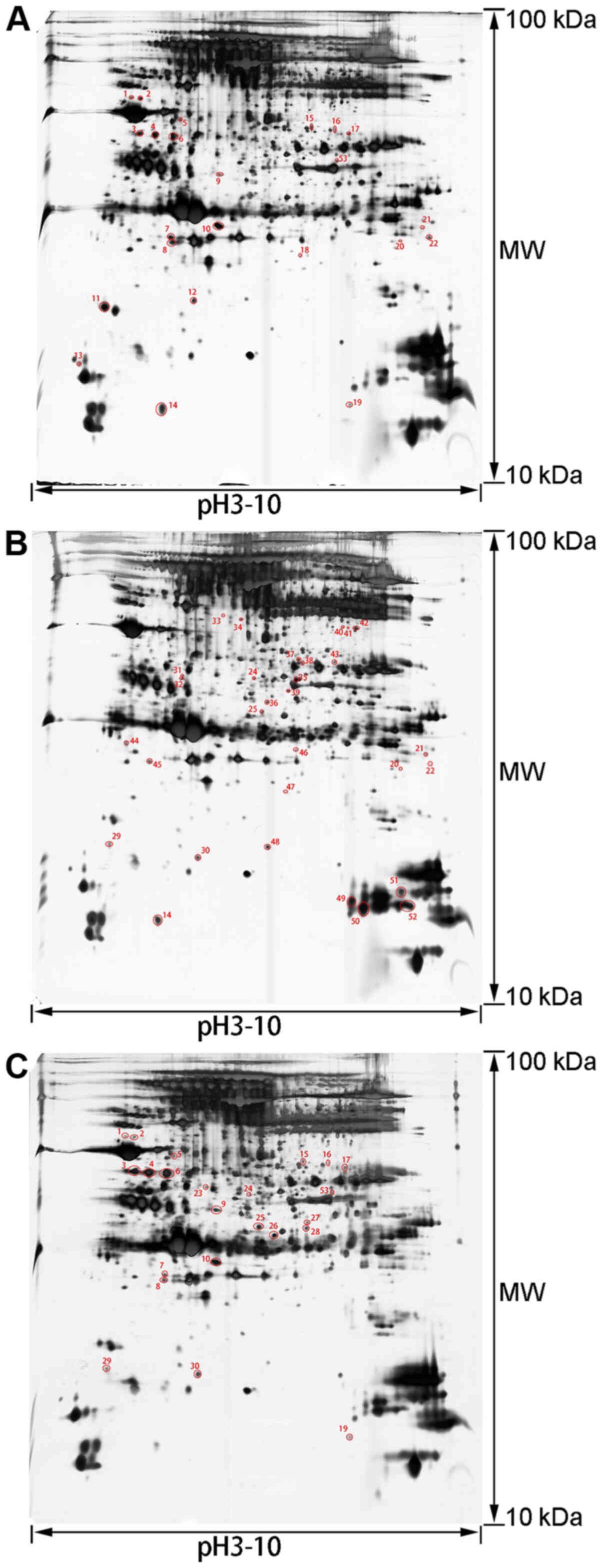
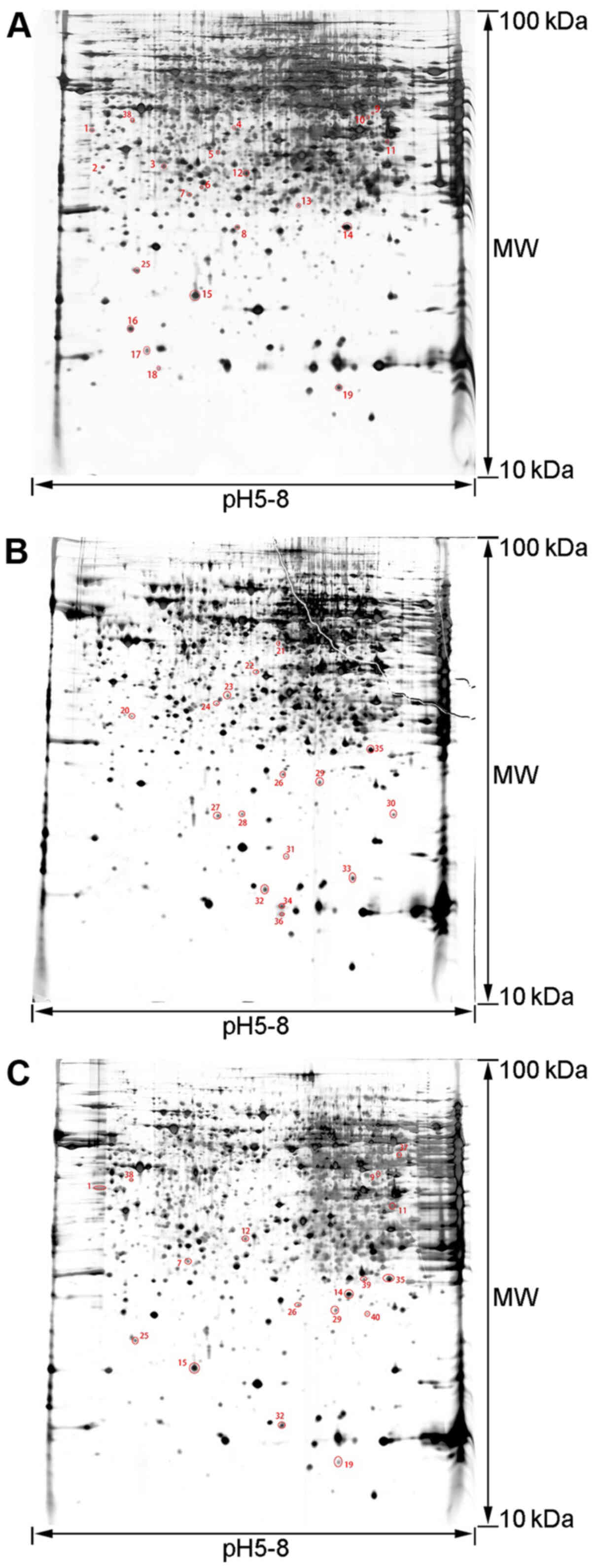
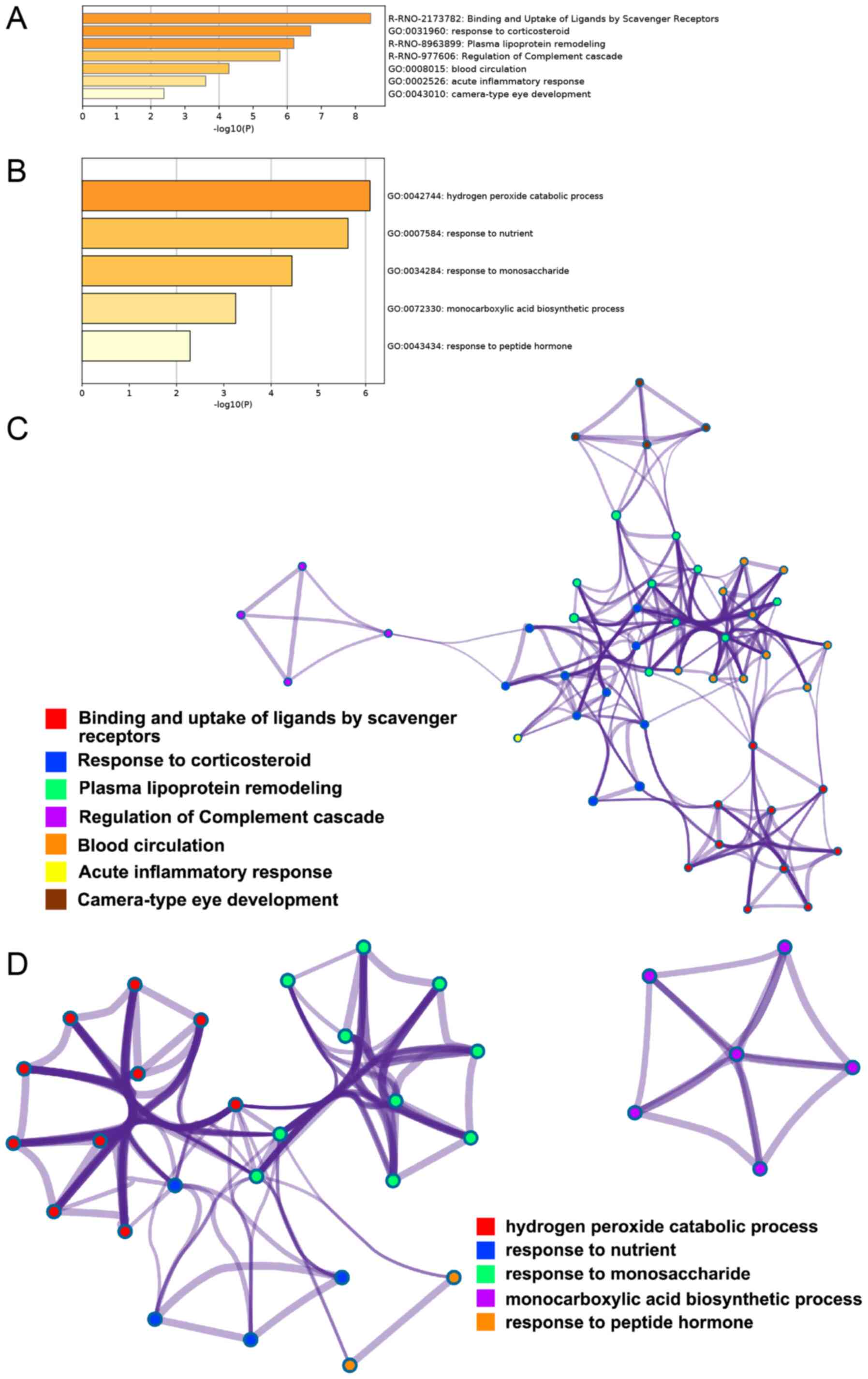
|
1
|
Basra S and Anand BS: Definition,
epidemiology and magnitude of alcoholic hepatitis. World J Hepatol.
3:108–113. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gaggini M, Morelli M, Buzzigoli E,
DeFronzo RA, Bugianesi E and Gastaldelli A: Non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease (NAFLD) and its connection with insulin resistance,
dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease.
Nutrients. 5:1544–1560. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jung UJ and Choi MS: Obesity and its
metabolic complications: The role of adipokines and the
relationship between obesity, inflammation, insulin resistance,
dyslipidemia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Sci.
15:6184–6223. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fon Tacer K and Rozman D: Nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease: Focus on lipoprotein and lipid deregulation. J
Lipids. 2011:7839762011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Suk KT, Kim MY and Baik SK: Alcoholic
liver disease: Treatment. World J Gastroenterol. 20:12934–12944.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kawada N, Kristensen DB, Asahina K,
Nakatani K, Minamiyama Y, Seki S and Yoshizato K: Characterization
of a stellate cell activation-associated protein (STAP) with
peroxidase activity found in rat hepatic stellate cells. J Biol
Chem. 276:25318–25323. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Burmester T, Ebner B, Weich B and Hankeln
T: Cytoglobin: A novel globin type ubiquitously expressed in
vertebrate tissues. Mol Biol Evol. 19:416–421. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yoshizato K, Thuy le TT, Shiota G and
Kawada N: Discovery of cytoglobin and its roles in physiology and
pathology of hepatic stellate cells. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol
Sci. 92:77–97. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fordel E, Thijs L, Moens L and Dewilde S:
Neuroglobin and cytoglobin expression in mice. Evidence for a
correlation with reactive oxygen species scavenging. FEBS J.
274:1312–1317. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gardner AM, Cook MR and Gardner PR:
Nitric-oxide dioxygenase function of human cytoglobin with cellular
reductants and in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 285:23850–23857.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li Z, Wei W, Chen B, Cai G, Li X, Wang P,
Tang J and Dong W: The effect of rhCygb on CCl4-induced hepatic
fibrogenesis in rat. Sci Rep. 6:235082016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wen J, Wu Y, Wei W, Li Z, Wang P, Zhu S
and Dong W: Protective effects of recombinant human cytoglobin
against chronic alcohol-induced liver disease in vivo and in vitro.
Sci Rep. 7:416472017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Y, Liang X, Yang J, Wang H, Tan D,
Chen S, Cheng J, Chen Y, Sun J, Rong F, et al: Improved performance
of quantitative collagen parameters versus standard histology in
longitudinal assessment of nonadvanced liver fibrosis for chronic
hepatitis B. J Viral Hepat. 25:598–607. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou J, Li J, Yu Y, Liu Y, Li H, Liu Y,
Wang J, Zhang L, Lu X, Chen Z and Zuo D: Mannan-binding lectin
deficiency exacerbates sterile liver injury in mice through
enhancing hepatic neutrophil recruitment. J Leukoc Biol.
105:177–186. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
He WQ, Chen XJ, Wen YQ, Li YZ, He H and
Chen Q: Detection of hepatitis B virus-like nucleotide sequences in
liver samples from murine rodents and asian house shrews. Vector
Borne Zoonotic Dis. 19:781–783. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fagoonee S, Gburek J, Hirsch E, Marro S,
Moestrup SK, Laurberg JM, Christensen EI, Silengo L, Altruda F and
Tolosano E: Plasma protein haptoglobin modulates renal iron
loading. Am J Pathol. 166:973–983. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ou L, Li X, Chen B, Ge Z, Zhang J, Zhang
Y, Cai G, Li Z, Wang P and Dong W: Recombinant human cytoglobin
prevents atherosclerosis by regulating lipid metabolism and
oxidative stress. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 23:162–173. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qi X, Ng KT, Lian QZ, Liu XB, Li CX, Geng
W, Ling CC, Ma YY, Yeung WH, Tu WW, et al: Clinical significance
and therapeutic value of glutathione peroxidase 3 (GPx3) in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 5:11103–11120. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Arthur JR: The glutathione peroxidases.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 57:1825–1835. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lubos E, Loscalzo J and Handy DE:
Glutathione peroxidase-1 in health and disease: From molecular
mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal.
15:1957–1997. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dich J, Hansen SE and Thieden HI: Effect
of albumin concentration and colloid osmotic pressure on albumin
synthesis in the perfused rat liver. Acta Physiol Scand.
89:352–358. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rock KL, Gramm C, Rothstein L, Clark K,
Stein R, Dick L, Hwang D and Goldberg AL: Inhibitors of the
proteasome block the degradation of most cell proteins and the
generation of peptides presented on MHC class I molecules. Cell.
78:761–771. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen B, Retzlaff M, Roos T and Frydman J:
Cellular strategies of protein quality control. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 3:a0043742011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Voges D, Zwickl P and Baumeister W: The
26S proteasome: A molecular machine designed for controlled
proteolysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 68:1015–1068. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rodriguez KA, Edrey YH, Osmulski P,
Gaczynska M and Buffenstein R: Altered composition of liver
proteasome assemblies contributes to enhanced proteasome activity
in the exceptionally long-lived naked mole-rat. PLoS One.
7:e358902012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fujito NT and Nonaka M: Highly divergent
dimorphic alleles of the proteasome subunit beta type-8 (PSMB8)
gene of the bichir Polypterus senegalus: Implication for evolution
of the PSMB8 gene of jawed vertebrates. Immunogenetics. 64:447–453.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
da Fonseca PC, He J and Morris EP:
Molecular model of the human 26S proteasome. Mol Cell. 46:54–66.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang L and Colón W: The interaction
between apolipoprotein serum amyloid A and high-density
lipoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 317:157–161. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
de Beer MC, Yuan T, Kindy MS, Asztalos BF,
Roheim PS and de Beer FC: Characterization of constitutive human
serum amyloid A protein (SAA4) as an apolipoprotein. J Lipid Res.
36:526–534. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Uhlar CM and Whitehead AS: Serum amyloid
A, the major vertebrate acute-phase reactant. Eur J Biochem.
265:501–523. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Eklund KK, Niemi K and Kovanen PT: Immune
functions of serum amyloid A. Crit Rev Immunol. 32:335–348. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mayilyan KR: Complement genetics,
deficiencies, and disease associations. Protein Cell. 3:487–496.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Birmingham DJ and Hebert LA: The
complement system in lupus nephritis. Semin Nephrol. 35:444–454.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hugli TE, Marceau F and Lundberg C:
Effects of complement fragments on pulmonary and vascular smooth
muscle. Am Rev Respir Dis. 135:S9–S13. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mahley RW, Innerarity TL, Rall SC Jr and
Weisgraber KH: Plasma lipoproteins: Apolipoprotein structure and
function. J Lipid Res. 25:1277–1294. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|