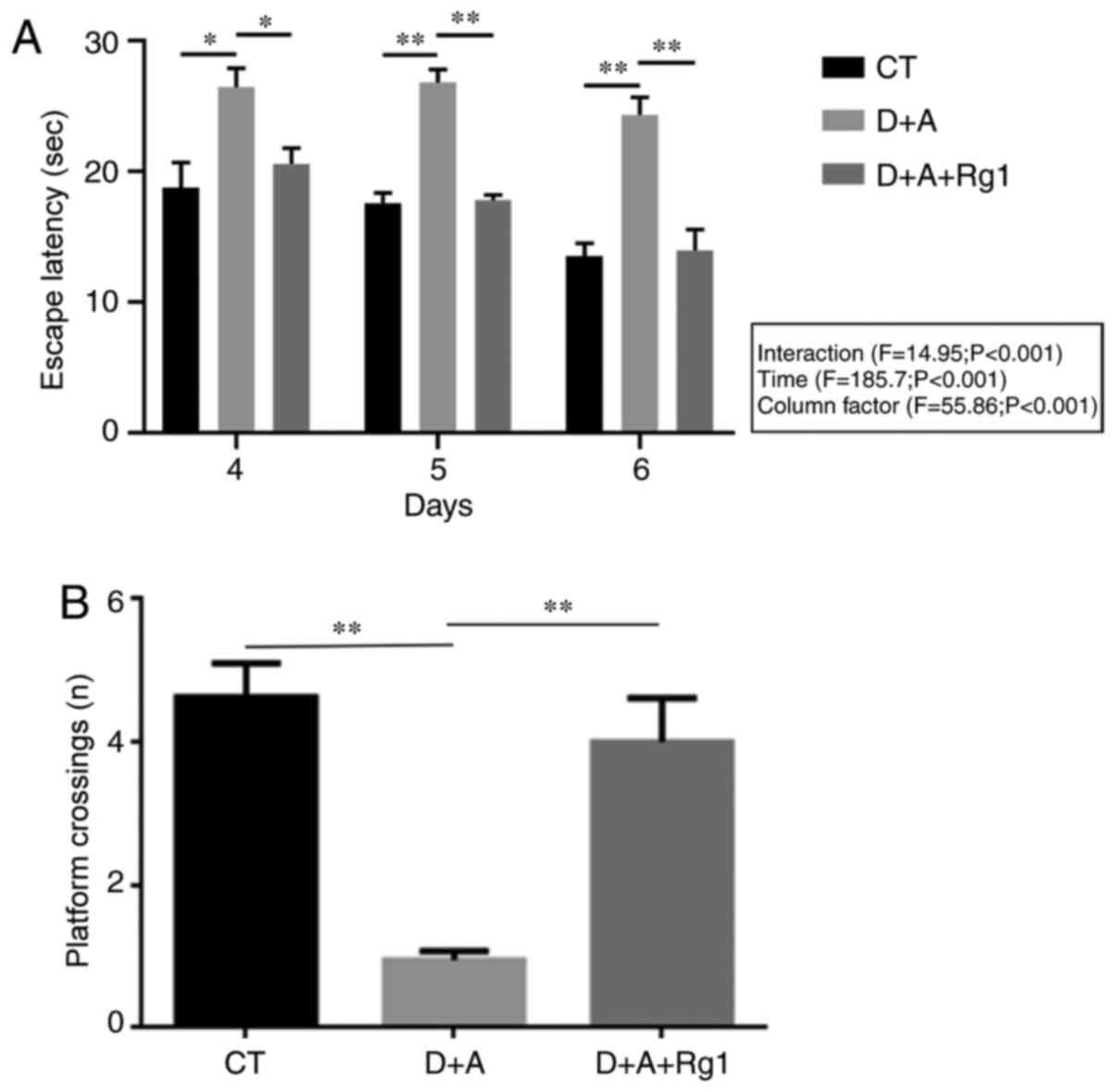
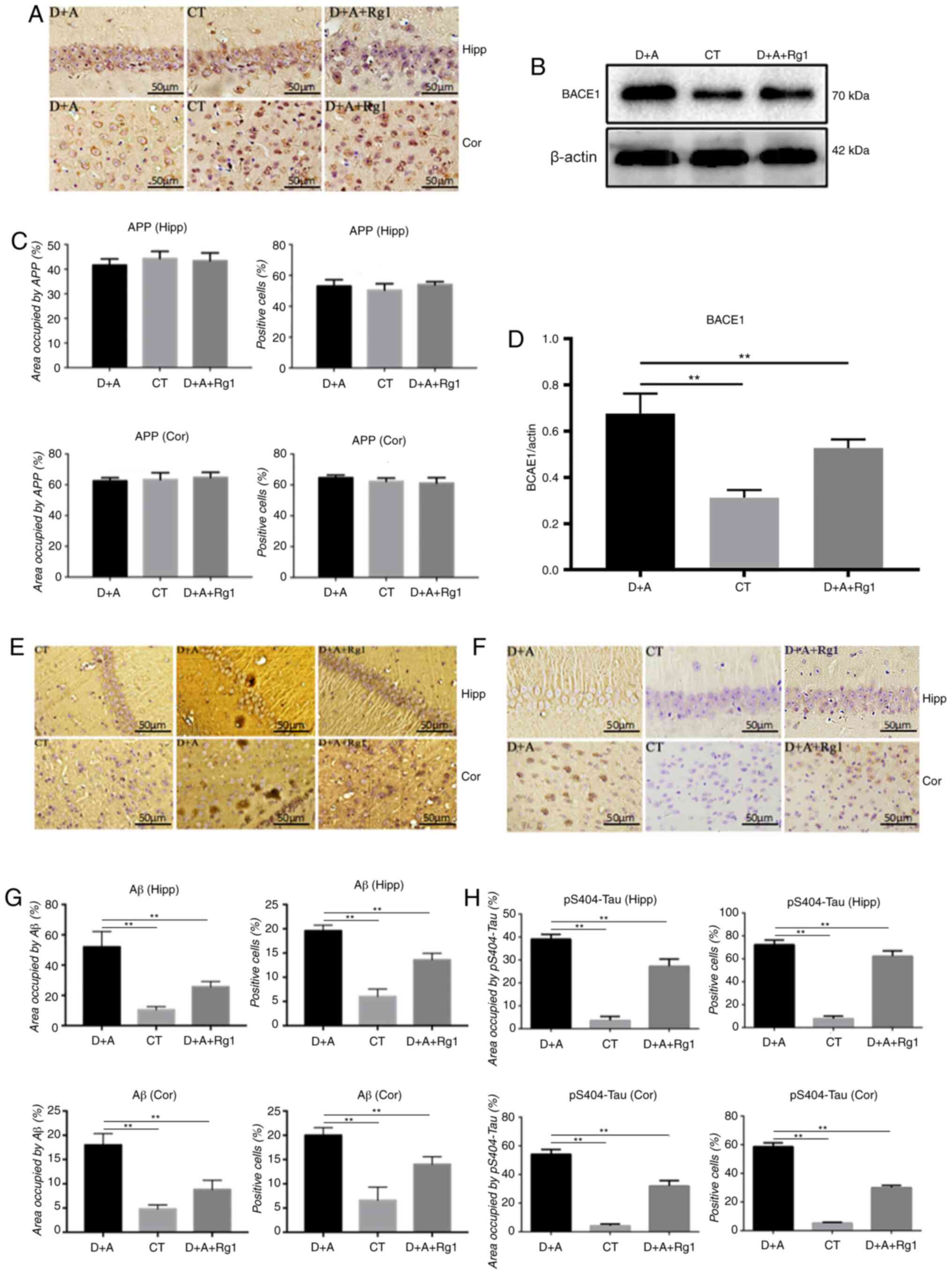
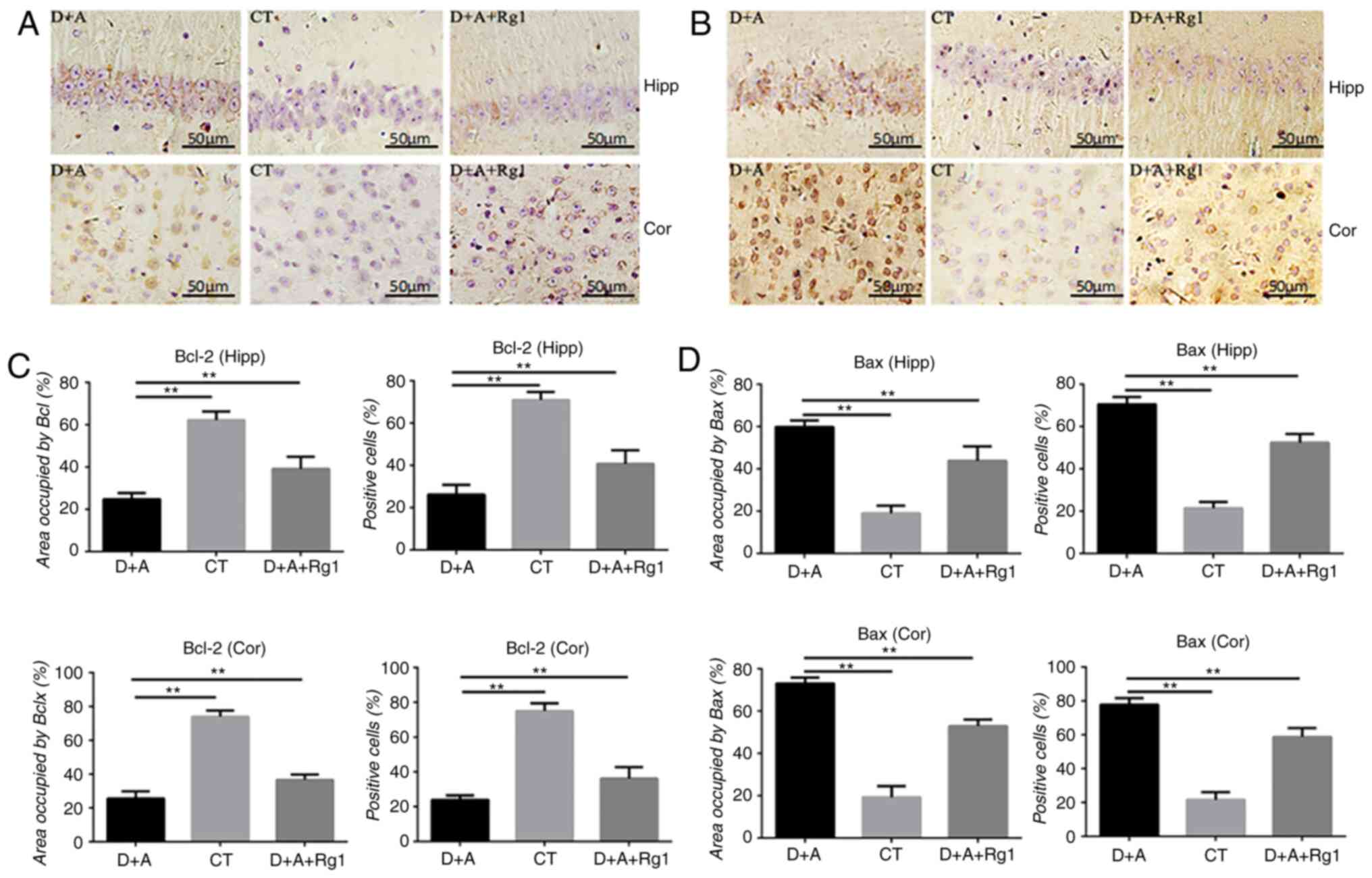
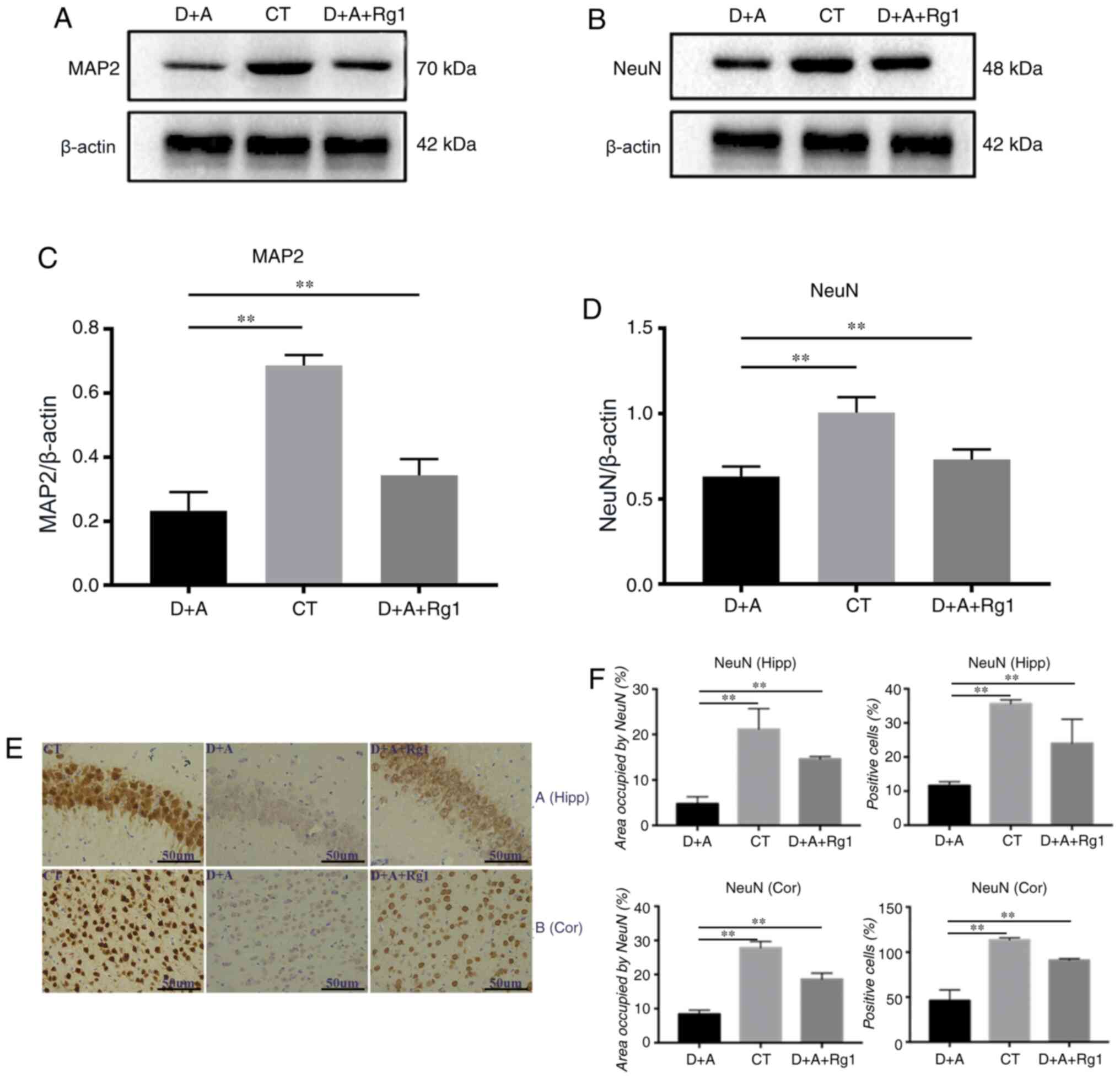
|
1
|
Quigley EMM: Microbiota-brain-gut axis and
neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 17:942017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lecouvey G, Morand A, Gonneaud J, Piolino
P, Orriols E, Pélerin A, Ferreira Da Silva L, de La Sayette V,
Eustache F and Desgranges B: An impairment of prospective memory in
mild Alzheimer's disease: A ride in a virtual town. Front Psychol.
10:241. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Manso-Calderón R, Cacabelos-Pérez P,
Sevillano-García MD, Herrero-Prieto ME and González-Sarmiento R:
The impact of vascular burden on behavioural and psychological
symptoms in older adults with dementia: The BEVASDE study. Neurol
Sci. 41:165–174. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ratno Budiarto B and Chan WH: Oxidative
stresses-mediated apoptotic effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on pre- and
post-implantation mouse embryos in vitro and in vivo. Environ
Toxicol. 32:1990–2003. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tian W, Chen L, Zhang L, Wang B, Li XB,
Fan KR, Ai CH, Xia X, Li SD and Li Y: Effects of ginsenoside Rg1 on
glucose metabolism and liver injury in streptozotocin-induced type
2 diabetic rats. Genet Mol Res. 16:March 30–2017, https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr16019463
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ong WY, Farooqui T, Koh HL, Farooqui AA
and Ling EA: Protective effects of ginseng on neurological
disorders. Front Aging Neurosci. 7:1292015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen LM, Lin N, Zhang J, Zhu YG and Chen
XC: Mechanism of ginsenoside Rg1 regulating the activity of β
secretase in N2a/APP695 cells. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 92:330–335.
2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang L, Wang Y, Xiayu X, Shi C, Chen W,
Song N, Fu X, Zhou R, Xu YF, Huang L, et al: Altered gut microbiota
in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimer's Dis.
60:1241–1257. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Claesson MJ, Cusack S, OSullivan O,
Greene-Diniz R, de Weerd H, Flannery E, Marchesi JR, Falush D,
Dinan T, Fitzgerald G, et al: Composition, variability, and
temporal stability of the intestinal microbiota of the elderly.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108 (Suppl 1):4586–4591. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Claesson MJ, Jeffery IB, Conde S, Power
SE, OConnor EM, Cusack S, Harris HMB, Coakley M, Lakshminarayanan
B, OSullivan O, et al: Gut microbiota composition correlates with
diet and health in the elderly. Nature. 488:178–184. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Odamaki T, Kato K, Sugahara H, Hashikura
N, Takahashi S, Xiao JZ, Abe F and Osawa R: Age-related changes in
gut microbiota composition from newborn to centenarian: A
cross-sectional study. BMC Microbiol. 16:902016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
McElhanon BO, McCracken C, Karpen S and
Sharp WG: Gastrointestinal symptoms in autism spectrum disorder: A
meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 133:872–883. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pfeiffer RF: Gastrointestinal dysfunction
in Parkinsons disease. Lancet Neurol. 2:107–116. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Severance EG, Yolken RH and Eaton WW:
Autoimmune diseases, gastrointestinal disorders and the microbiome
in schizophrenia: More than a gut feeling. Schizophr Res.
176:23–35. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Doraiswamy PM, Leon J, Cummings JL, Marin
D and Neumann PJ: Prevalence and impact of medical comorbidity in
Alzheimer's disease. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 57:M173–M177.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kowalski K and Mulak A:
Brain-gut-microbiota axis in Alzheimer's disease. J
Neurogastroenterol Motil. 25:48–60. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mosher KI and Wyss-Coray T: Microglial
dysfunction in brain aging and Alzheimer's disease. Biochem
Pharmacol. 88:594–604. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen SG, Stribinskis V, Rane MJ, Demuth
DR, Gozal E, Roberts AM, Jagadapillai R, Liu R, Choe K, Shivakumar
B, et al: Exposure to the functional bacterial amyloid protein
curli enhances alpha-synuclein aggregation in aged fischer 344 rats
and Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci Rep. 6:34477. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Minter MR, Zhang C, Leone V, Ringus DL,
Zhang X, Oyler-Castrillo P, Musch MW, Liao F, Ward JF, Holtzman DM,
et al: Antibiotic-induced perturbations in gut microbial diversity
influences neuro-inflammation and amyloidosis in a murine model of
Alzheimer's disease. Sci Rep. 6:30028. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Harach T, Marungruang N, Duthilleul N,
Cheatham V, Mc Coy KD, Frisoni G, Neher JJ, Fåk F, Jucker M, Lasser
T, et al: Reduction of Abeta amyloid pathology in APPPS1 transgenic
mice in the absence of gut microbiota. Sci Rep. 7:41802. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang CH, Sheng JQ, Sarsaiya S, Shu FX,
Liu TT, Tu XY, Ma GQ, Xu GL, Zheng HX and Zhou LF: The
anti-diabetic activities, gut microbiota composition, the
anti-inflammatory effects of Scutellaria-coptis herb couple against
insulin resistance-model of diabetes involving the toll-like
receptor 4 signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 237:202–214. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun YF, Zhang X, Wang XY and Jia W: Effect
of long-term intake of ginseng extracts on gut microbiota in rats.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 43:3927–3932. 2018.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cheng D, Chang H, Ma S, Guo J, She G,
Zhang F, Li L, Li X and Lu Y: Tiansi liquid modulates gut
microbiota composition and tryptophan-kynurenine metabolism in rats
with hydrocortisone-induced depression. Molecules. 23:28322018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Xiao J, Liu R and Chen CS: Tree shrew
(Tupaia belangeri) as a novel laboratory disease animal
model. Zool Res. 38:127–137. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fan Y, Luo R, Su LY, Xiang Q, Yu D, Xu L,
Chen JQ, Bi R, Wu DD, Zheng P, et al: Does the genetic feature of
the Chinese Tree Shrew (Tupaia belangeri chinensis) support
its potential as a viable model for Alzheimer's disease research? J
Alzheimer's Dis. 61:1015–1028. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zheng H, Niu S, Zhao H, Li S and Jiao J:
Donepezil improves the cognitive impairment in a tree shrew model
of Alzheimer's disease induced by amyloid-β1–40 via activating the
BDNF/TrkB signal pathway. Metab Brain Dis. 33:1961–1974. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Römer S, Bender H, Knabe W, Zimmermann E,
Rübsamen R, Seeger J and Fietz SA: Neural progenitors in the
developing Neocortex of the Northern Tree Shrew (Tupaia
belangeri) show a closer relationship to gyrencephalic primates
than to lissencephalic rodents. Front Neuroanat. 12:292018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Health N: Guide for the care and use of
laboratory animals. NIH contract No No1-RR-2-2135. 1985.11–28
|
|
29
|
Ghumatkar PJ, Patil SP, Peshattiwar V,
Vijaykumar T, Dighe V, Vanage G and Sathaye S: The modulatory role
of phloretin in Aβ25–35 induced sporadic Alzheimer's disease in rat
model. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 392:327–339. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chao A: Non-parametric estimation of the
classes in a population. Scand J Stat. 11:265–270. 1984.
|
|
31
|
Du H, Guo L, Zhang W, Rydzewska M and Yan
S: Cyclophilin D deficiency improves mitochondrial function and
learning/memory in aging Alzheimer disease mouse model. Neurobiol
Aging. 32:398–406. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Feng L, Liao YT, He JC, Xie CL, Chen SY,
Fan HH, Su ZP and Wang Z: Plasma long non-coding RNA BACE1 as a
novel biomarker for diagnosis of Alzheimer disease. BMC Neurol.
18:42018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mulder SD, van der Flier WM, Verheijen JH,
Mulder C, Scheltens P, Blankenstein MA, Hack CE and Veerhuis R:
BACE1 activity in cerebrospinal fluid and its relation to markers
of AD pathology. J Alzheimer's Dis. 20:253–260. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dash R, Emran TB, Uddin MMN, Islam A and
Junaid M: Molecular docking of fisetin with AD associated AChE,
ABAD and BACE1 proteins. Bioinformation. 10:562–568. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Song XY, Hu JF, Chu SF, Zhang Z, Xu S,
Yuan YH, Han N, Liu Y, Niu F, He X, et al: Ginsenoside Rg1
attenuates okadaic acid induced spatial memory impairment by the
GSK3β/tau signaling pathway and the Aβ formation prevention in
rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 710:29–38. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Manczak M, Kandimalla R, Yin X and Reddy
PH: Hippocampal mutant APP and amyloid beta-induced cognitive
decline, dendritic spine loss, defective autophagy, mitophagy and
mitochondrial abnormalities in a mouse model of Alzheimer's
disease. Hum Mol Genet. 27:1332–1342. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jiang S, Nandy P, Wang W, Ma X, Hsia J,
Wang C, Wang Z, Niu M, Siedlak SL, Torres S, et al: Mfn2 ablation
causes an oxidative stress response and eventual neuronal death in
the hippocampus and cortex. Mol Neurodegener. 13:52018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lax N, Fainstein N, Nishri Y, Ben-Zvi A
and Ben-Hur T: Systemic microbial TLR2 agonists induce
neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease mice. J Neuroinflammation.
17:552020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kandimalla R, Manczak M, Yin X, Wang R and
Reddy PH: Hippocampal phosphorylated tau induced cognitive decline,
dendritic spine loss and mitochondrial abnormalities in a mouse
model of Alzheimer's disease. Hum Mol Genet. 27:30–40. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Koo YS, Kim H, Park JH, Kim MJ, Shin YI,
Choi BT, Lee SY and Shin HK: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-dependent
neurotoxic kynurenine metabolism contributes to poststroke
depression Induced in mice by ischemic stroke along with spatial
restraint stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018:24138412018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Leplus A, Lauritzen I, Melon C,
Kerkerian-Le Goff L, Fontaine D and Checler F: Chronic fornix deep
brain stimulation in a transgenic Alzheimer's rat model reduces
amyloid burden, inflammation, and neuronal loss. Brain Struct
Funct. 224:363–372. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lu J, Lu L, Yu Y, Cluette-Brown J, Martin
CR and Claud EC: Effects of intestinal microbiota on brain
development in humanized gnotobiotic mice. Sci Rep. 8:54432018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhong L, Tong Y, Chuan J, Bai L, Shi J and
Zhu Y: Protective effect of ethyl vanillin against Aβ-induced
neurotoxicity in PC12 cells via the reduction of oxidative stress
and apoptosis. Exp Ther Med. 17:2666–2674. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hu J, Gu Y and Fan W: Rg1 protects rat
bone marrow stem cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell
apoptosis through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Mol Med Rep. 14:406–412.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jin M, Zhang H, Zhao K, Xu C, Shao D,
Huang Q, Shi J and Yang H: Responses of intestinal iucosal barrier
functions of rats to simulated eeightlessness. Front Physiol.
9:7292018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sharon G, Sampson TR, Geschwind DH and
Mazmanian SK: The central nervous system and the gut microbiome.
Cell. 167:915–932. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Vogt NM, Kerby RL, Dill-McFarland KA,
Harding SJ, Merluzzi AP, Johnson SC, Carlsson CM, Asthana S,
Zetterberg H, Blennow K, et al: Gut microbiome alterations in
Alzheimer's disease. Sci Rep. 7:13537. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Heiss CN and Olofsson LE: The role of the
gut microbiota in development, function and disorders of the
central nervous system and the enteric nervous system. J
Neuroendocrinol. 31:e126842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini
V, Mardis ER and Gordon JI: An obesity-associated gut microbiome
with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature. 444:1027–1031.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Preidis GA, Ajami NJ, Wong MC, Bessard BC,
Conner ME and Petrosino JF: Microbial-derived metabolites reflect
an altered intestinal microbiota during catch-up growth in
undernourished neonatal mice. J Nutr. 146:940–948. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Rezaeiasl Z, Salami M and Sepehri G: The
effects of probiotic Lactobacillus and
Bifidobacterium strains on memory and learning behavior,
long-term potentiation (LTP), and some biochemical parameters in
β-amyloid-induced rats model of Alzheimer's disease. Prev Nutr Food
Sci. 24:265–273. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tan FHP, Liu G, Lau SA, Jaafar MH, Park
YH, Azzam G, Li Y and Liong MT: Lactobacillus probiotics improved
the gut microbiota profile of a Drosophila melanogaster
Alzheimer's disease model and alleviated neurodegeneration in the
eye. Benef Microbes. 11:79–89. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhao Y, Zhao L, Zheng X, Fu T, Guo H and
Ren F: Lactobacillus salivarius strain FDB89 induced
longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans by dietary restriction.
J Microbiol. 51:183–188. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|