|
1
|
Bao J, Tang C, Li J, Zhang Y, Bhetwal BP,
Zheng H and Yan W: RAN-binding protein 9 is involved in alternative
splicing and is critical for male germ cell development and male
fertility. PLoS Genet. 10:e10048252014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lehti MS and Sironen A: Formation and
function of the manchette and flagellum during spermatogenesis.
Reproduction. 151:R43–R54. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li RK, Tan JL, Chen LT, Feng JS, Liang WX,
Guo XJ, Liu P, Chen Z, Sha JH, Wang YF, et al: Iqcg is essential
for sperm flagellum formation in mice. PLoS One. 9:e980532014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nishimura H and LHernault SW:
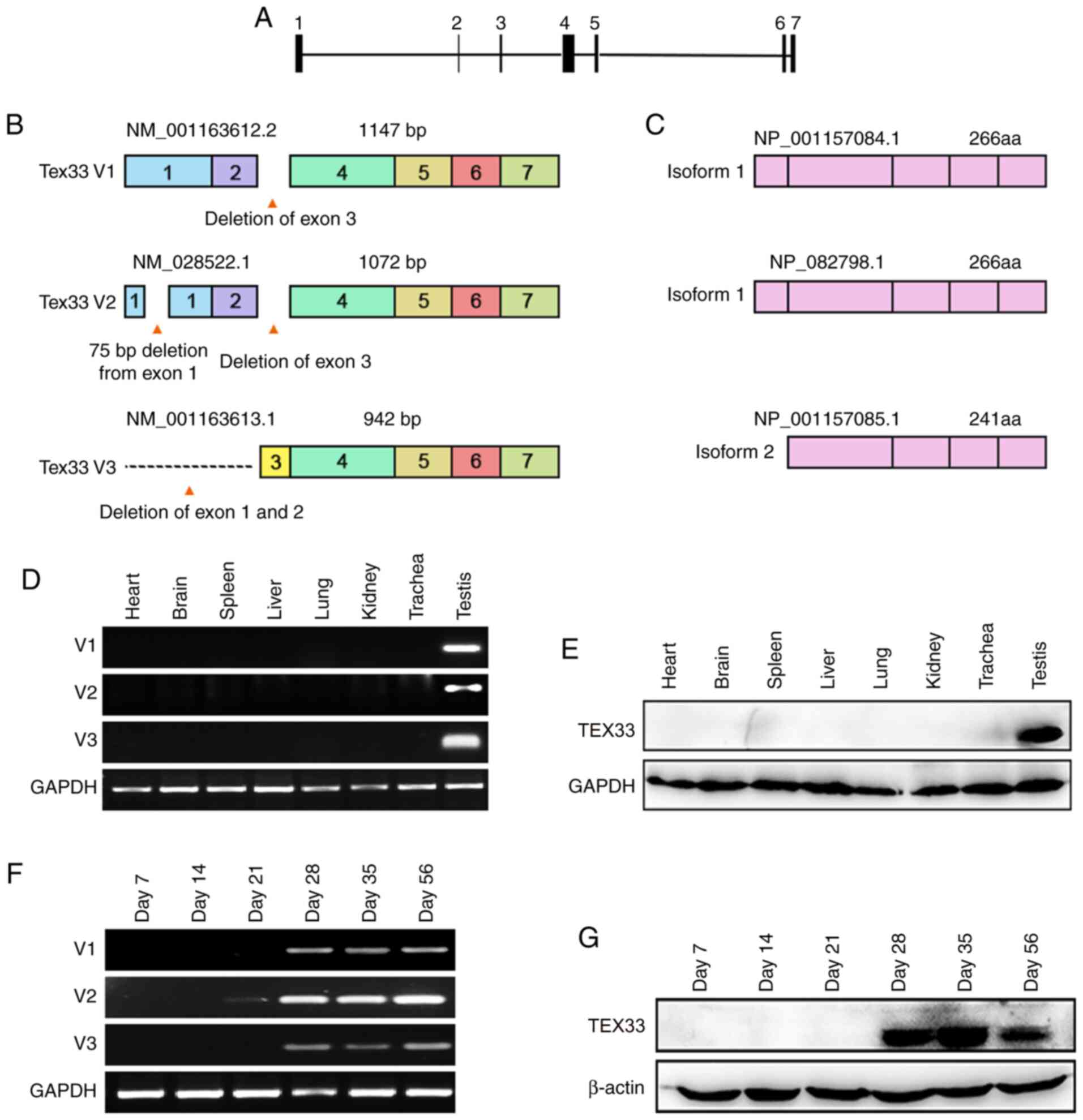
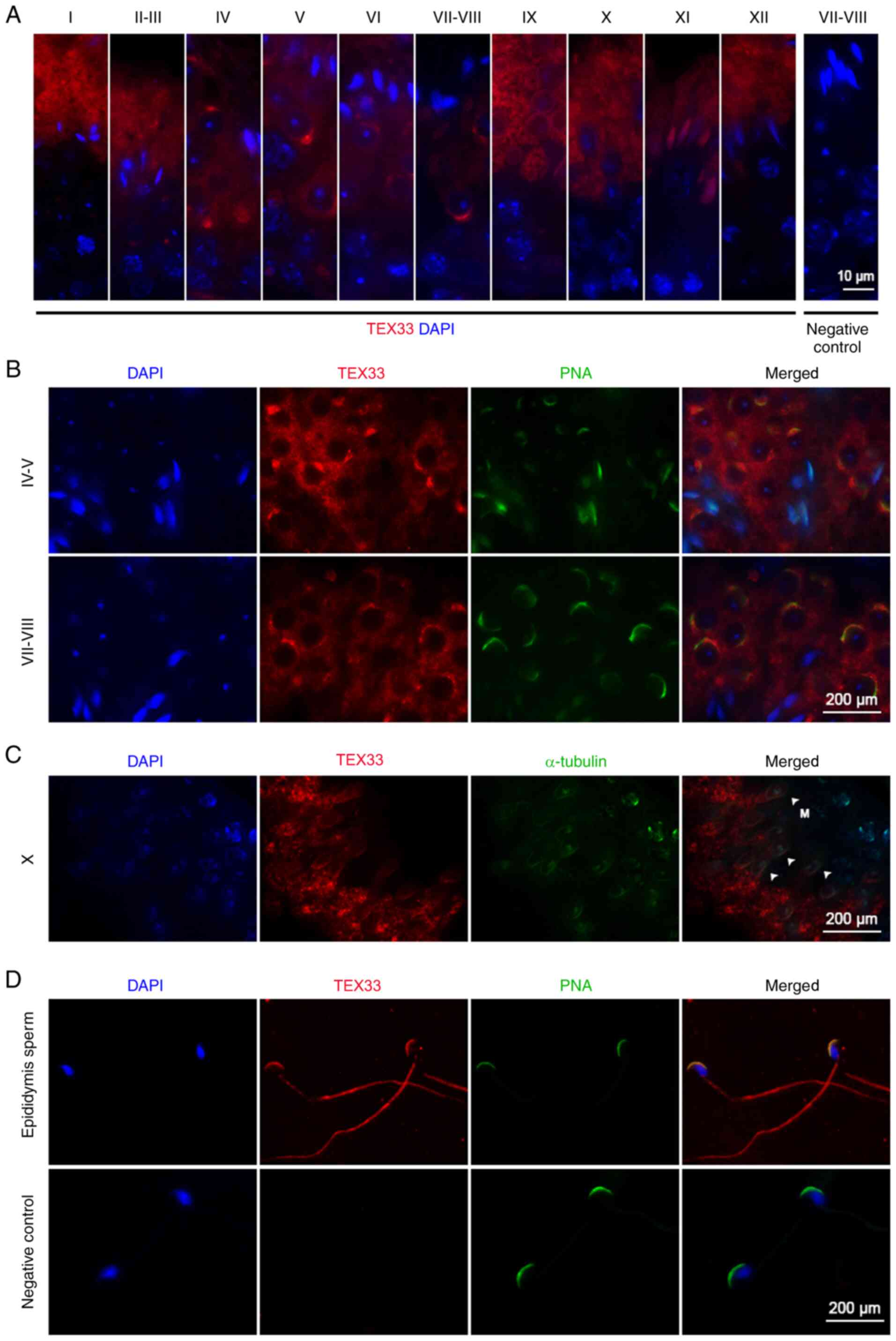
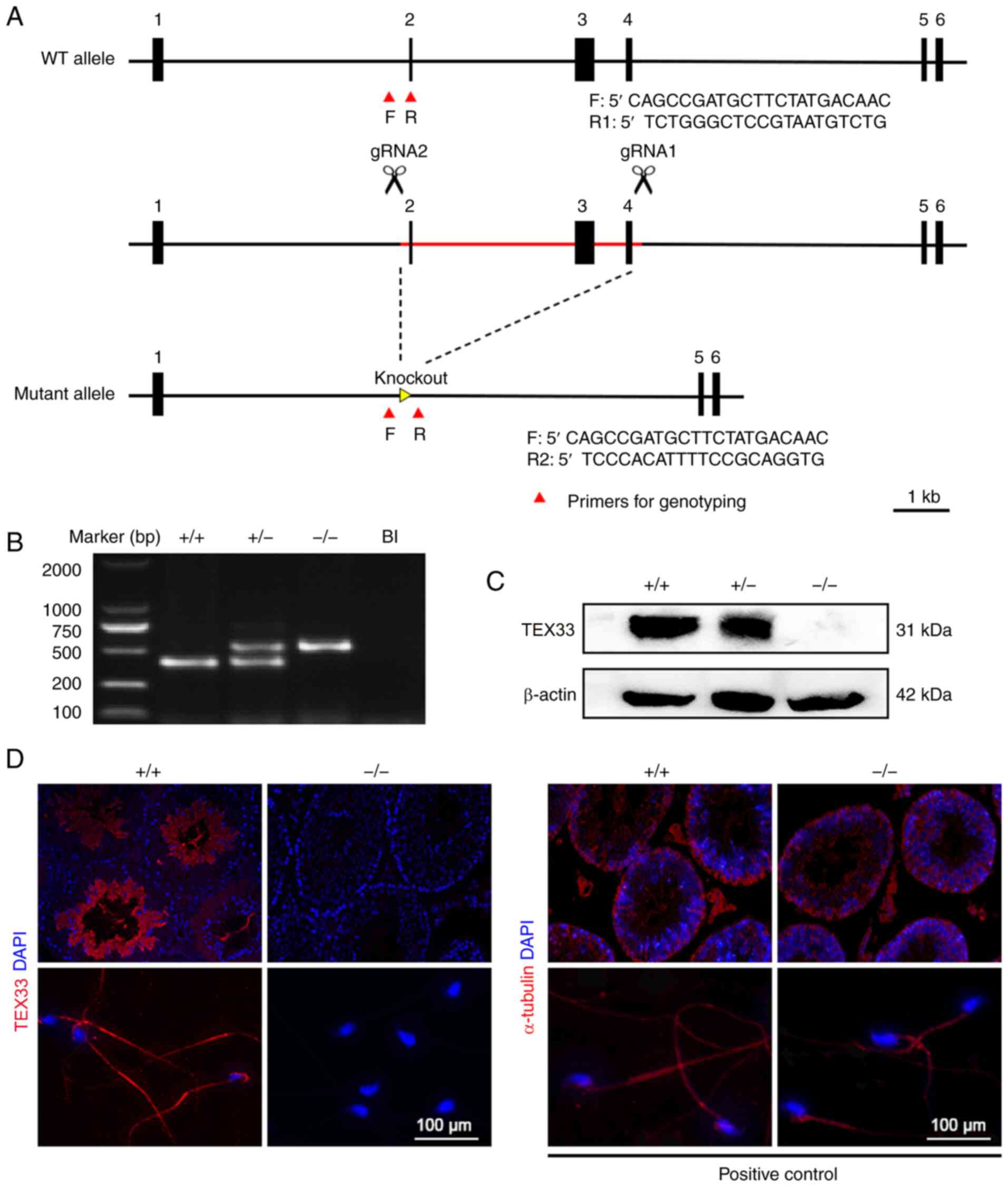
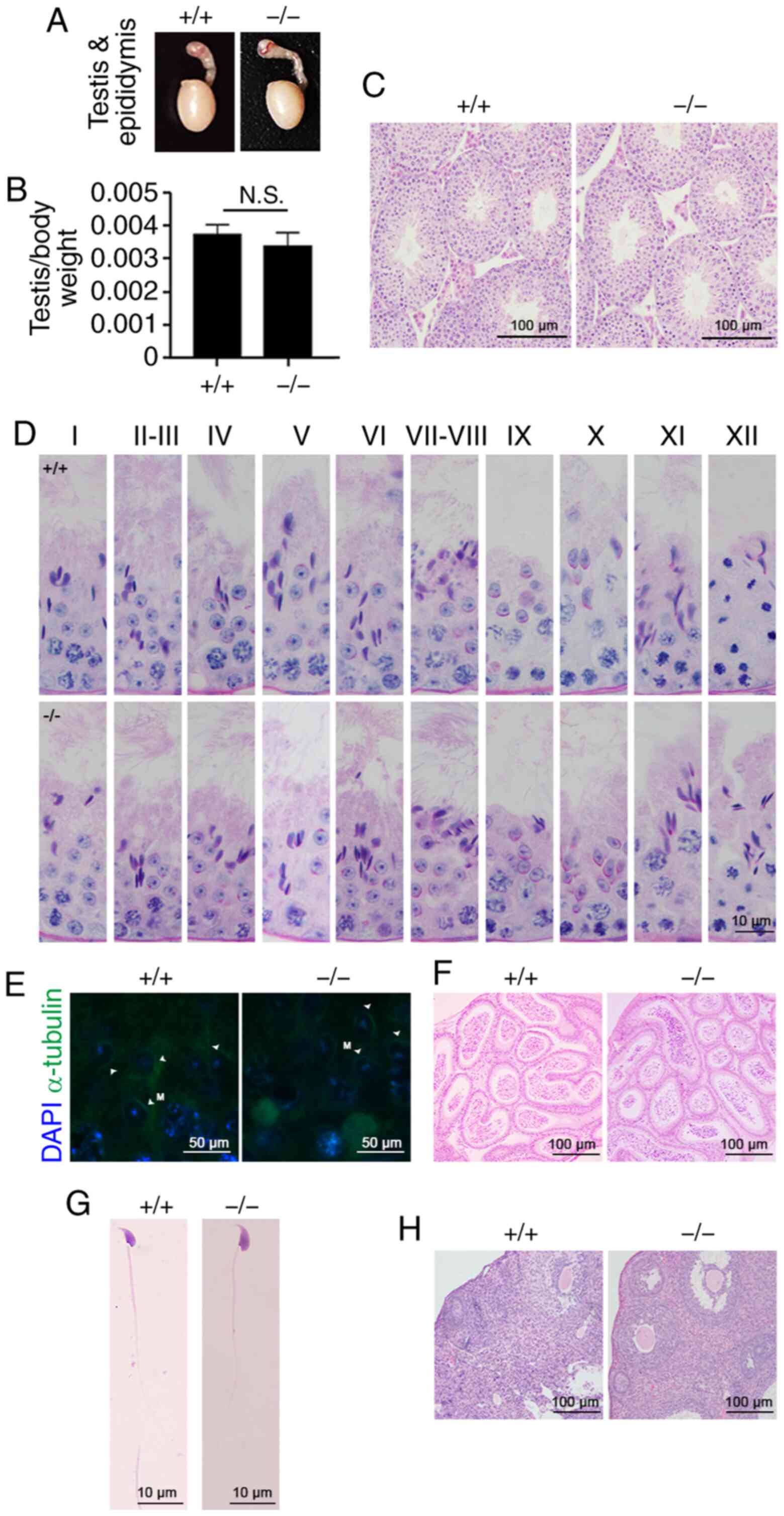
Spermatogenesis. Curr Biol. 27:R988–R994. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kazarian E, Son H, Sapao P, Li W, Zhang Z,
Strauss JF III and Teves ME: SPAG17 is required for male germ cell
differentiation and fertility. Int J Mol Sci. 19:12522018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bryant JM, Donahue G, Wang X, Meyer-Ficca
M, Luense LJ, Weller AH, Bartolomei MS, Blobel GA, Meyer RG, Garcia
BA, et al: Characterization of BRD4 during mammalian postmeiotic
sperm development. Mol Cell Biol. 35:1433–1448. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kistler WS, Baas D, Lemeille S, Paschaki
M, Seguin-Estevez Q, Barras E, Ma W, Duteyrat JL, Morlé L, Durand
B, et al: RFX2 is a major transcriptional regulator of
spermiogenesis. PLoS Genet. 11:e10053682015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang H, Wan H, Li X, Liu W, Chen Q, Wang
Y, Yang L, Tang H, Zhang X, Duan E, et al: Atg7 is required for
acrosome biogenesis during spermatogenesis in mice. Cell Res.
24:852–869. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu C, Song Z, Wang L, Yu H, Liu W, Shang
Y, Xu Z, Zhao H, Gao F, Wen J, et al: Sirt1 regulates acrosome
biogenesis by modulating autophagic flux during spermiogenesis in
mice. Development. 144:441–451. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Khawar MB, Gao H and Li W: Mechanism of
acrosome biogenesis in mammals. Front Cell Dev Biol. 7:1952019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Okuda H, DeBoer K, OConnor AE, Merriner
DJ, Jamsai D and OBryan MK: LRGUK1 is part of a multiprotein
complex required for manchette function and male fertility. FASEB
J. 31:1141–1152. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Martins LR, Bung RK, Koch S, Richter K,
Schwarzmüller L, Terhardt D, Kurtulmus B, Niehrs C, Rouhi A,
Lohmann I, et al: Stk33 is required for spermatid differentiation
and male fertility in mice. Dev Biol. 433:84–93. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schultz N, Hamra FK and Garbers DL: A
multitude of genes expressed solely in meiotic or postmeiotic
spermatogenic cells offers a myriad of contraceptive targets. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:12201–12206. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nozawa K, Zhang Q, Miyata H, Devlin DJ, Yu
Z, Oura S, Koyano T, Matsuyama M, Ikawa M and Matzuk MM: Knockout
of serine-rich single-pass membrane protein 1 (Ssmem1) causes
globozoospermia and sterility in male mice. Biol Reprod.
103:244–253. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Da Costa R, Bordessoules M, Guilleman M,
Carmignac V, Lhussiez V, Courot H, Bataille A, Chlémaire A, Bruno
C, Fauque P, et al: Vps13b is required for acrosome biogenesis
through functions in Golgi dynamic and membrane trafficking. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 77:511–529. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Paiardi C, Pasini ME, Gioria M and Berruti
G: Failure of acrosome formation and globozoospermia in the wobbler
mouse, a Vps54 spontaneous recessive mutant. Spermatogenesis.
1:52–62. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dunleavy JEM, Okuda H, OConnor AE,
Merriner DJ, ODonnell L, Jamsai D, Bergmann M and OBryan MK:
Katanin-like 2 (KATNAL2) functions in multiple aspects of haploid
male germ cell development in the mouse. PLoS Genet.
13:e10070782017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lehti MS, Zhang FP, Kotaja N and Sironen
A: SPEF2 functions in microtubule-mediated transport in elongating
spermatids to ensure proper male germ cell differentiation.
Development. 144:2683–2693. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schwarz T, Prieler B, Schmid JA, Grzmil P
and Neesen J: Ccdc181 is a microtubule-binding protein that
interacts with Hook1 in haploid male germ cells and localizes to
the sperm tail and motile cilia. Eur J Cell Biol. 96:276–288. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu Z, Miyata H, Kaneda Y, Castaneda JM, Lu
Y, Morohoshi A, Yu Z, Matzuk MM and Ikawa M: CIB4 is essential for
the haploid phase of spermatogenesis in mice. Biol Reprod.
103:235–243. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Z, Kostetskii I, Tang W,
Haig-Ladewig L, Sapiro R, Wei Z, Patel AM, Bennett J, Gerton GL,
Moss SB, et al: Deficiency of SPAG16L causes male infertility
associated with impaired sperm motility. Biol Reprod. 74:751–759.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Y, Ou Y, Cheng M, Saadi HS,
Thundathil JC and van der Hoorn FA: KLC3 is involved in sperm tail
midpiece formation and sperm function. Dev Biol. 366:101–110. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kuo YC, Shen YR, Chen HI, Lin YH, Wang YY,
Chen YR, Wang CY and Kuo PL: SEPT12 orchestrates the formation of
mammalian sperm annulus by organizing core octameric complexes with
other SEPT proteins. J Cell Sci. 128:923–934. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Moretti E, Collodel G, Mazzi L, Russo I
and Giurisato E: Ultrastructural study of spermatogenesis in KSR2
deficient mice. Transgenic Res. 24:741–751. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang X, Wei Y, Fu G, Li H, Saiyin H, Lin
G, Wang Z, Chen S and Yu L: Tssk4 is essential for maintaining the
structural integrity of sperm flagellum. Mol Hum Reprod.
21:136–145. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
McClintock TS, Glasser CE, Bose SC and
Bergman DA: Tissue expression patterns identify mouse cilia genes.
Physiol Genomics. 32:198–206. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xia M, Xia J, Yang D, Liu M, Niu C, Shen
X, Sun H and Zheng Y: Preparation and application of rabbit
polyclonal antibody against mouse Tex33. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi
Xue Za Zhi. 34:643–649. 2018.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Busada JT, Velte EK, Serra N, Cook K,
Niedenberger BA, Willis WD, Goulding EH, Eddy EM and Geyer CB:
Rhox13 is required for a quantitatively normal first wave of
spermatogenesis in mice. Reproduction. 152:379–388. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee MC and Damjanov I: Lectin binding
sites on human sperm and spermatogenic cells. Anat Rec.
212:282–287. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Arya M and Vanha-Perttula T: Comparison of
lectin-staining pattern in testis and epididymis of gerbil, guinea
pig, mouse, and nutria. Am J Anat. 175:449–469. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wakayama T, Nakata H, Kumchantuek T,
Gewaily MS and Iseki S: Identification of
5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine-labeled cells during mouse spermatogenesis
by heat-induced antigen retrieval in lectin staining and
immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 63:190–205. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fàbrega A, Puigmulé M, Dacheux JL, Bonet S
and Pinart E: Glycocalyx characterisation and glycoprotein
expression of Sus domesticus epididymal sperm surface samples.
Reprod Fertil Dev. 24:619–630. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu Y, Zhong A, Zheng H, Jiang M, Xia Z, Yu
J, Chen L and Huang X: Expression of flotilin-2 and acrosome
biogenesis are regulated by MiR-124 during spermatogenesis. PLoS
One. 10:e01366712015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhong L, Yang M, Zou X, Du T, Xu H and Sun
J: Human umbilical cord multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells
alleviate acute ischemia-reperfusion injury of spermatogenic cells
via reducing inflammatory response and oxidative stress. Stem Cell
Res Ther. 11:2942020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang Q, Liu H, Zeng J, Li W, Zhang S,
Zhang L, Song S, Zhou T, Sutovsky M, Sutovsky P, et al: COP9
signalosome complex subunit 5, an IFT20 binding partner, is
essential to maintain male germ cell survival and acrosome
biogenesis. Biol Reprod. 102:233–247. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Anawalt BD: Approach to male infertility
and induction of spermatogenesis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
98:3532–3542. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
García-Vázquez FA, Gadea J, Matás C and
Holt WV: Importance of sperm morphology during sperm transport and
fertilization in mammals. Asian J Androl. 18:844–850.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Morohoshi A, Miyata H, Shimada K, Nozawa
K, Matsumura T, Yanase R, Shiba K, Inaba K and Ikawa M:
Nexin-Dynein regulatory complex component DRC7 but not FBXL13 is
required for sperm flagellum formation and male fertility in mice.
PLoS Genet. 16:e10085852020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Oura S, Kazi S, Savolainen A, Nozawa K,
Castañeda J, Yu Z, Miyata H, Matzuk RM, Hansen JN, Wachten D, et
al: Cfap97d1 is important for flagellar axoneme maintenance and
male mouse fertility. PLoS Genet. 16:e10089542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Miyata H, Shimada K, Morohoshi A, Oura S,
Matsumura T, Xu Z, Oyama Y and Ikawa M: Testis-enriched kinesin
KIF9 is important for progressive motility in mouse spermatozoa.
FASEB J. 34:5389–5400. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang L, Zhen J, Huang Q, Liu H, Li W,
Zhang S, Min J, Li Y, Shi L, Woods J, et al: Mouse
spermatogenesis-associated protein 1 (SPATA1), an IFT20 binding
partner, is an acrosomal protein. Dev Dyn. 249:543–555. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lehti MS and Sironen A: Formation and
function of sperm tail structures in association with sperm
motility defects. Biol Reprod. 97:522–536. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang ET, Sandberg R, Luo S, Khrebtukova I,
Zhang L, Mayr C, Kingsmore SF, Schroth GP and Burge CB: Alternative
isoform regulation in human tissue transcriptomes. Nature.
456:470–476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Miyata H, Castaneda JM, Fujihara Y, Yu Z,
Archambeault DR, Isotani A, Kiyozumi D, Kriseman ML, Mashiko D,
Matsumura T, et al: Genome engineering uncovers 54 evolutionarily
conserved and testis-enriched genes that are not required for male
fertility in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:7704–7710. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang Y, Liu H, Li W, Zhang Z, Zhang S,
Teves ME, Stevens C, Foster JA, Campbell GE, Windle JJ, et al:
Intraflagellar transporter protein 140 (IFT140), a component of
IFT-A complex, is essential for male fertility and spermiogenesis
in mice. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 75:70–84. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kobayashi K, Endo T, Matsumura T, Lu Y, Yu
Z, Matzuk MM and Ikawa M: Prss55 but not Prss51 is required for
male fertility in mice. Biol Reprod. 103:223–234. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wu XL, Yun DM, Gao S, Liang AJ, Duan ZZ,
Wang HS, Wang GS and Sun F: The testis-specific gene 1700102P08Rik
is essential for male fertility. Mol Reprod Dev. 87:231–240. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Krakauer DC and Plotkin JB: Redundancy,
antiredundancy, and the robustness of genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:1405–1409. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Khan M, Jabeen N, Khan T, Hussain HMJ, Ali
A, Khan R, Jiang L, Li T, Tao Q, Zhang X, et al: The evolutionarily
conserved genes: Tex37, Ccdc73, Prss55 and Nxt2 are dispensable for
fertility in mice. Sci Rep. 8:49752018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Holcomb RJ, Oura S, Nozawa K, Kent K, Yu
Z, Robertson MJ, Coarfa C, Matzuk MM, Ikawa M and Garcia TX: The
testis-specific serine proteases PRSS44, PRSS46, and PRSS54 are
dispensable for male mouse fertility. Biol Reprod. 102:84–91.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|