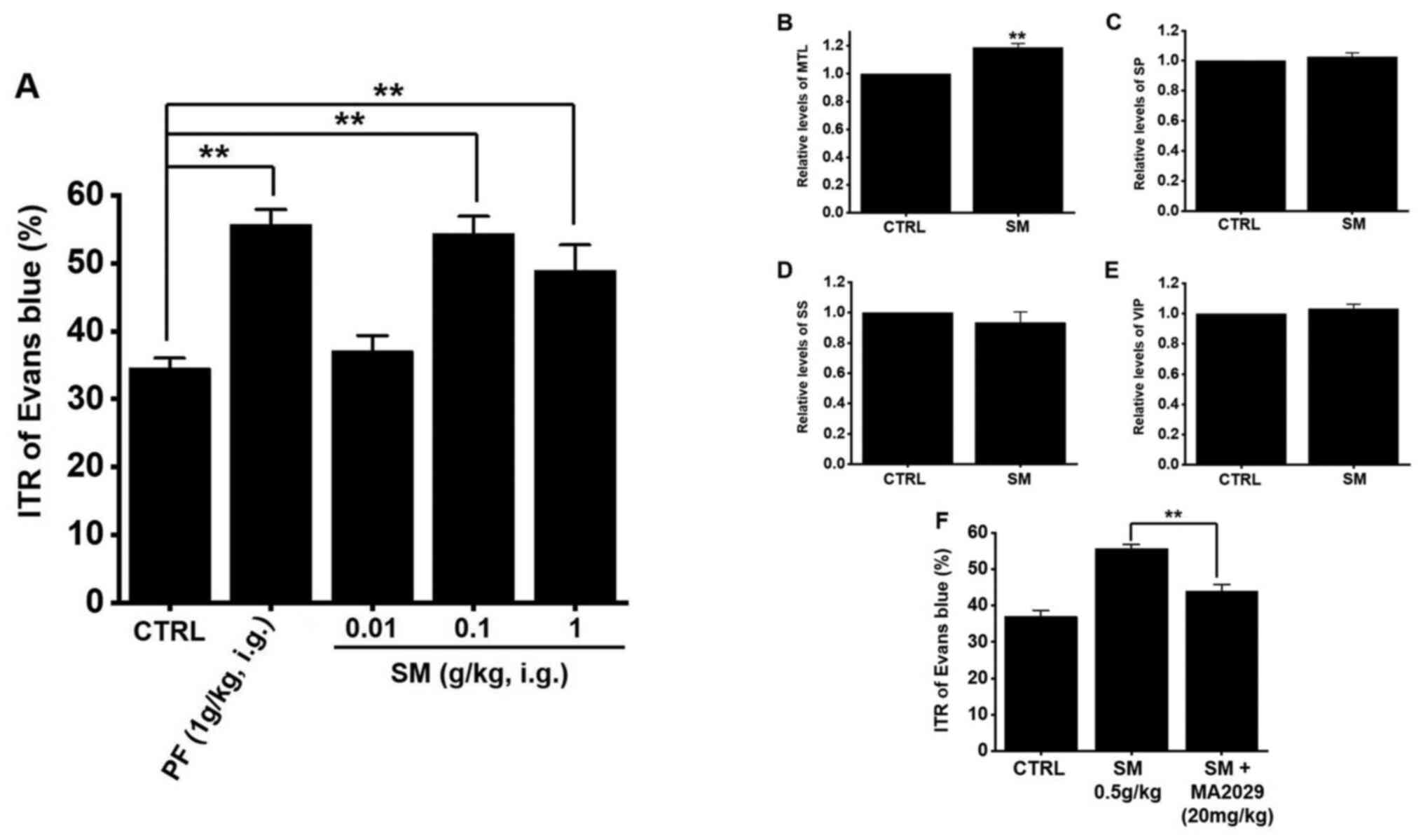
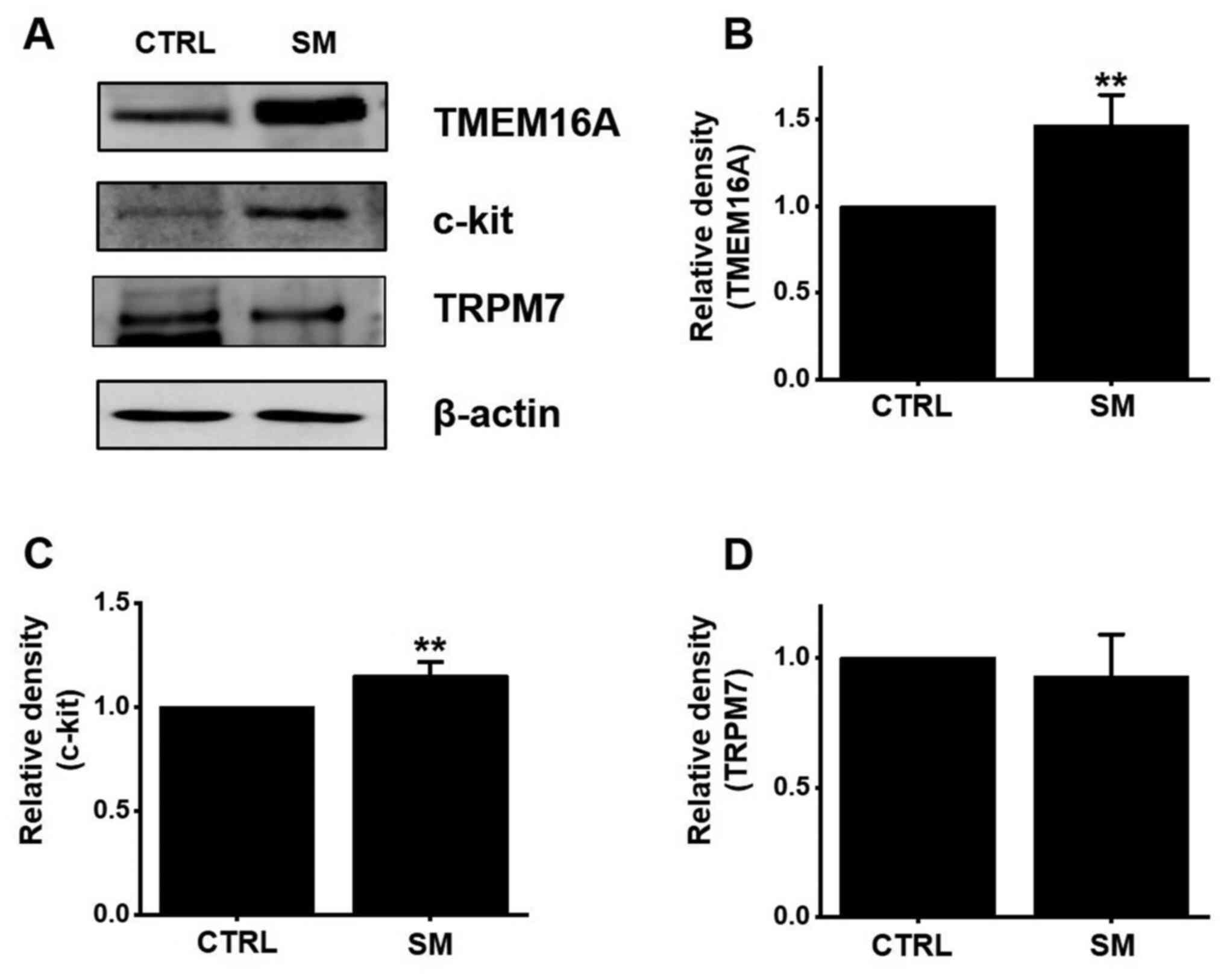
|
1
|
Kim SY, Moon TC, Chang HW, Son KH, Kang SS
and Kim HP: Effects of tanshinone I isolated from Salvia
miltiorrhiza bunge on arachidonic acid metabolism and in vivo
inflammatory responses. Phytother Res. 16:616–620. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wu YJ, Hong CY, Lin SJ, Wu P and Shiao MS:
Increase of vitamin E content in LDL and reduction of
atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed rabbits by a water-soluble
antioxidant-rich fraction of Salvia miltiorrhiza.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 18:481–486. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Guo Y, Li Y, Xue L, Severino RP, Gao S,
Niu J, Qin LP, Zhang D and Bromme D: Salvia miltiorrhiza: An
ancient Chinese herbal medicine as a source for antiosteoporotic
drugs. J Ethnopharmacol. 155:1401–1416. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ji XY, Tan BK and Zhu YZ: Salvia
miltiorrhiza and ischemic diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
21:1089–1094. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chan K, Chui SH, Wong DY, Ha WY, Chan CL
and Wong RN: Protective effects of danshensu from the aqueous
extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen) against
homocysteine-induced endothelial dysfunction. Life Sci.
75:3157–3171. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang ZY, Chen XP and Lu QP: Effect of
Salvia miltiorrhiza pretreatment on the CCK and VIP
expression in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion-induced digestive tract
congestion. Front Med China. 4:317–322. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wen XD, Wang CZ, Yu C, Zhang Z, Calway T,
Wang Y, Li P and Yuan CS: Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen)
significantly ameliorates colon inflammation in dextran sulfate
sodium induced colitis. Am J Chin Med. 41:1097–1108. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xiping Z, Yan P, Xinmei H, Guanghua F,
Meili M, Jie N and Fangjie Z: Effects of dexamethasone and
Salvia miltiorrhizae on the small intestine and immune
organs of rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Inflammation.
33:259–266. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsai CC, Huang SC, Liu JK, Wang HC, Tsai
TR, Tsai PJ, Liu CW and Chang LC: Salvia miltiorrhiza causes
tonic contraction in rat ileum through Ca2+-calmodulin
pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 142:694–699. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tsai CC, Chang LC, Huang SC, Tey SL, Hsu
WL, Su YT, Liu CW and Tsai TR: Salvia miltiorrhiza induces
tonic contraction of the lower esophageal sphincter in rats via
activation of extracellular Ca2+ influx. Molecules.
20:14504–14521. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang X, Guo Y, He J, Zhang F, Sun X, Yang
S and Dong H: Estrogen and estrogen receptors in the modulation of
gastrointestinal epithelial secretion. Oncotarget. 8:97683–97692.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang JM, Li J, Liu EW, Wang H, Fan GW,
Wang YF, Zhu Y, Ma SW and Gao XM: Danshen enhanced the estrogenic
effects of qing E formula in ovariectomized rats. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 16:1812016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fan G, Zhu Y, Guo H, Wang X, Wang H and
Gao X: Direct vasorelaxation by a novel phytoestrogen tanshinone
IIA is mediated by nongenomic action of estrogen receptor through
endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation and calcium
mobilization. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 57:340–347. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Evans RM: The steroid and thyroid hormone
receptor superfamily. Science. 240:889–895. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yasar P, Ayaz G, User SD, Güpür G and
Muyan M: Molecular mechanism of estrogen-estrogen receptor
signaling. Reprod Med Biol. 16:4–20. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mapplebeck JC, Beggs S and Salter MW: Sex
differences in pain: A tale of two immune cells. Pain. 157
(Suppl):S2–S6. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mulak A and Bonaz B: Irritable bowel
syndrome: A model of the brain-gut interactions. Med Sci Monit.
10:RA55–RA62. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sorge RE, Mapplebeck JC, Rosen S, Beggs S,
Taves S, Alexander JK, Martin LJ, Austin JS, Sotocinal SG, Chen D,
et al: Different immune cells mediate mechanical pain
hypersensitivity in male and female mice. Nat Neurosci.
18:1081–1083. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meleine M and Matricon J: Gender-Related
differences in irritable bowel syndrome: Potential mechanisms of
sex hormones. World J Gastroenterol. 20:6725–6743. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huizinga JD, Thuneberg L, Klüppel M,
Malysz J, Mikkelsen HB and Bernstein A: W/kit gene required for
interstitial cells of cajal and for intestinal pacemaker activity.
Nature. 373:347–349. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim BJ, Lim HH, Yang DK, Jun JY, Chang IY,
Park CS, So I, Stanfield PR and Kim KW: Melastatin-Type transient
receptor potential channel 7 is required for intestinal pacemaking
activity. Gastroenterology. 129:1504–1517. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sanders KM, Ward SM and Koh SD:
Interstitial cells: Regulators of smooth muscle function. Physiol
Rev. 94:859–907. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen X, Guo J, Bao J, Lu J and Wang Y: The
anticancer properties of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (Danshen): a
systematic review. Med Res Rev. 34:768–794. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care Use of Laboratory Animals:
Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th edition.
National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
25
|
Kim JH and Kim BJ: Depolarization of
pacemaker potentials by caffeic acid phenethyl ester in
interstitial cells of cajal from the murine small intestine. Can J
Physiol Pharmacol. 98:201–210. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hwang M, Kim JN, Lee JR, Kim SC and Kim
BJ: Effects of Chaihu-Shugan-san on small intestinal interstitial
cells of Cajal in mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 43:707–715. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Koh SD, Sanders KM and Ward SM:
Spontaneous electrical rhythmicity in cultured interstitial cells
of cajal from the murine small intestine. J Physiol. 513:203–213.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Komori S, Kawai M, Takewaki T and Ohashi
H: GTP-Binding protein involvement in membrane currents evoked by
carbachol and histamine in guinea-pig ileal muscle. J Physiol.
450:105–126. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ogata R, Inoue Y, Nakano H, Ito Y and
Kitamura K: Oestradiol-Induced relaxation of rabbit basilar artery
by inhibition of voltage-dependent Ca channels through GTP-binding
protein. Br J Pharmacol. 117:351–359. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ward SM: Interstitial cells of cajal in
enteric neurotransmission. Gut. 47:40–43. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liao QS, Du Q, Lou J, Xu JY and Xie R:
Roles of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger 1 in digestive
system physiology and pathophysiology. World J Gastroenterol.
25:287–299. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim H, Kim I, Lee MC, Kim HJ, Lee GS, Kim
H and Kim BJ: Effects of hwangryunhaedok-tang on gastrointestinal
motility function in mice. World J Gastroenterol. 23:2705–2715.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huang F, Rock JR, Harfe BD, Cheng T, Huang
X, Jan YN and Jan LY: Studies on expression and function of the
TMEM16A calcium-activated chloride channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:21413–21418. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu MH, Kim TW, Ro S, Yan W, Ward SM, Koh
SD and Sanders KM: A Ca(2+)-activated Cl(−)conductance in
interstitial cells of cajal linked to slow wave currents and
pacemaker activity. J Physiol. 587:4905–4918. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sanders KM, Koh SD, Ro S and Ward SM:
Regulation of gastrointestinal motility-insights from smooth muscle
biology. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 9:633–645. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lam FFY, Deng SY, Ng ESK, Yeung JHK, Kwan
YW, Lau CBS, Loon JCM, Zhou L, Zuo Z, Leung PC and Fung KP:
Mechanisms of the relaxant effect of a danshen and gegen
formulation on rat isolated cerebral basilar artery. J
Ethnopharmacol. 132:186–192. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Eyster KM: The estrogen receptors: An
overview from different perspectives. Methods Mol Biol. 1366:1–10.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li Y, Xu J, Jiang F, Jiang Z, Liu C, Li L,
Luo Y, Lu R, Mu Y, Liu Y and Xue B: G protein-coupled estrogen
receptor is involved in modulating colonic motor function via
nitric oxide release in C57BL/6 female mice. Neurogastroenterol
Motil. 28:432–442. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vivacqua A, Bonofiglio D, Recchia AG,
Musti AM, Ando DPS and Maggiolini M: The G protein-coupled receptor
GPR30 mediates the proliferative effects induced by
17beta-estradiol and hydroxytamoxifen in endometrial cancer cells.
Mol Endocrinol. 20:631–646. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zielińska M, Fichna J, Bashashati M,
Habibi S, Sibaev A, Timmermans JP and Storr M: G protein-coupled
estrogen receptor and estrogen receptor ligands regulate colonic
motility and visceral pain. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 29:1–11.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhu MH, Sung IK, Zheng H, Sung TS, Britton
FC, O'Driscoll K, Koh SD and Sanders KM: Muscarinic activation of
Ca2+-activated Cl− current in interstitial
cells of cajal. J Physiol. 589:4565–4582. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhu MH, Sung TS, O'Driscoll K, Koh SD and
Sanders KM: Intracellular Ca(2+) release from endoplasmic reticulum
regulates slow wave currents and pacemaker activity of interstitial
cells of cajal. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 308:C608–C620. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Drumm BT, Hennig GW, Battersby MJ,
Cunningham EK, Sung TS, Ward SM, Sanders KM and Baker SA:
Clustering of Ca2+ transients in interstitial cells of
cajal defines slow wave duration. J Gen Physiol. 149:703–725. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jun JY, Choi S, Yeum CH, Chang IY, You HJ,
Park CK, Kim MY, Kong ID, Kim MJ, Lee KP, et al: Substance P
induces inward current and regulates pacemaker currents through
tachykinin NK1 receptor in cultured interstitial cells of cajal of
murine small intestine. Eur J Pharmacol. 495:35–42. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zheng H, Drumm BT, Zhu MH, Xie Y,
O'Driscoll KE, Baker SA, Perrino BA, Koh SD and Sanders KM:
Na+/Ca2 + exchange and pacemaker activity of
interstitial cells of cajal. Front Physiol. 11:2302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ahmed M and Ahmed S: Functional,
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Aspects of Gastrointestinal Hormones.
Gastroenterology Res. 12:233–244. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Thomas PA, Akwari OE and Kelly KA:
Hormonal control of gastrointestinal motility. World J Surg.
3:545–552. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Peeters TL: Gastrointestinal hormones and
gut motility. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 22:9–13. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Rehfeld JF: The new biology of
gastrointestinal hormones. Physiol Rev. 78:1087–1108. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Dockray GJ: Gastrointestinal hormones and
the dialogue between gut and brain. J Physiol. 592:2927–2941. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hirst GD, Bramich NJ, Teramoto N, Suzuki H
and Edwards FR: Regenerative component of slow waves in the
guinea-pig gastric antrum involves a delayed increase in
[Ca(2+)](i) and Cl(−) channels. J Physiol. 540:907–919. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hwang SJ, Blair PJ, Britton FC, O'Driscoll
KE, Hennig G, Bayguinov YR, Rock JR, Harfe BD, Sanders KM and Ward
SM: Expression of anoctamin 1/TMEM16A by interstitial cells of
cajal is fundamental for slow wave activity in gastrointestinal
muscles. J Physiol. 587:4887–4904. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Maeda H, Yamagata A and Nishikawa S,
Yoshinaga K, Kobayashi S, Nishi K and Nishikawa S: Requirement of
c-kit for development of intestinal pacemaker system. Development.
116:369–753. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Torihashi S, Ward SM, Nishikawa S, Nishi
K, Kobayashi S and Sanders KM: C-Kit-Dependent development of
interstitial cells and electrical activity in the murine
gastrointestinal tract. Cell Tissue Res. 280:97–111. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|