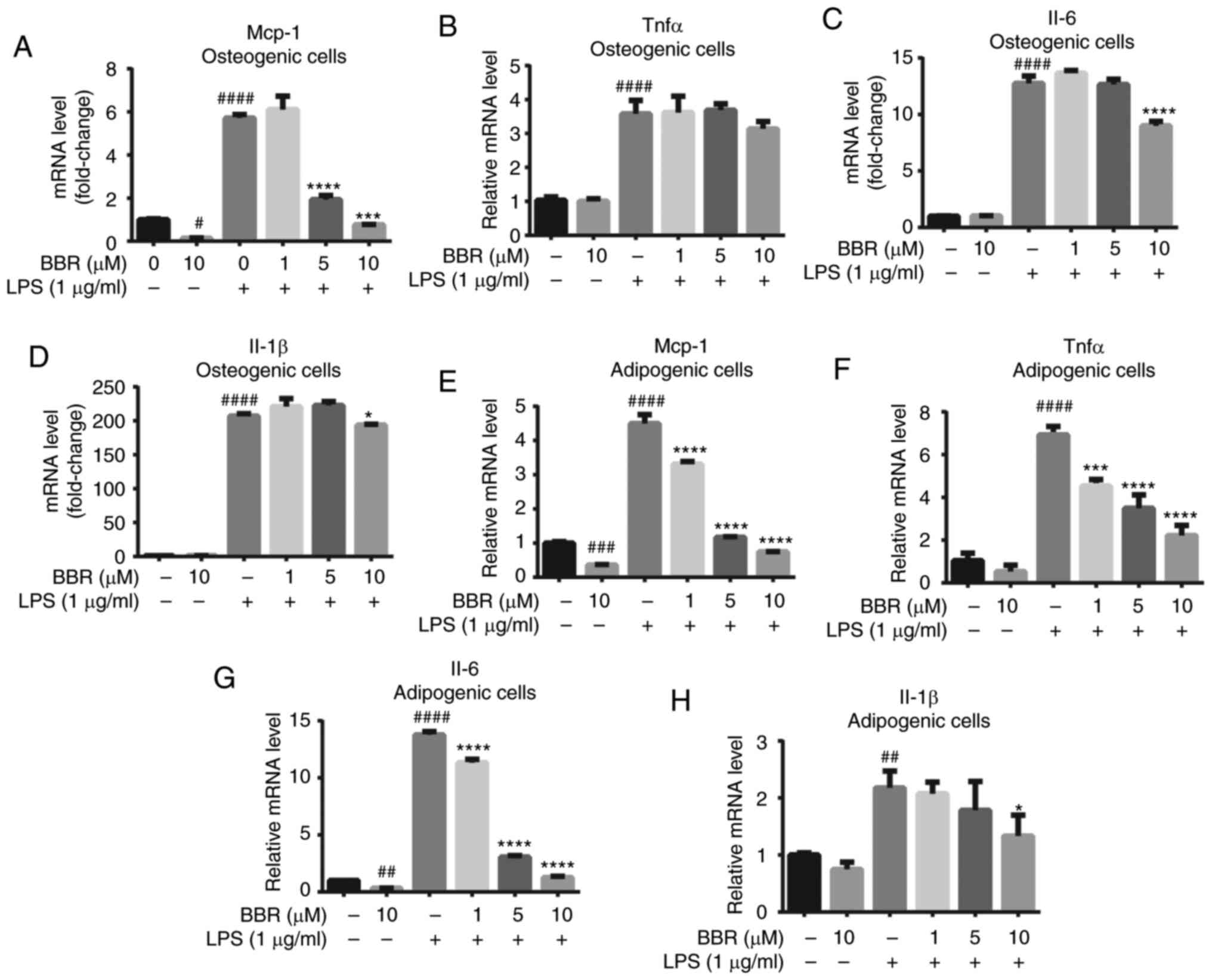
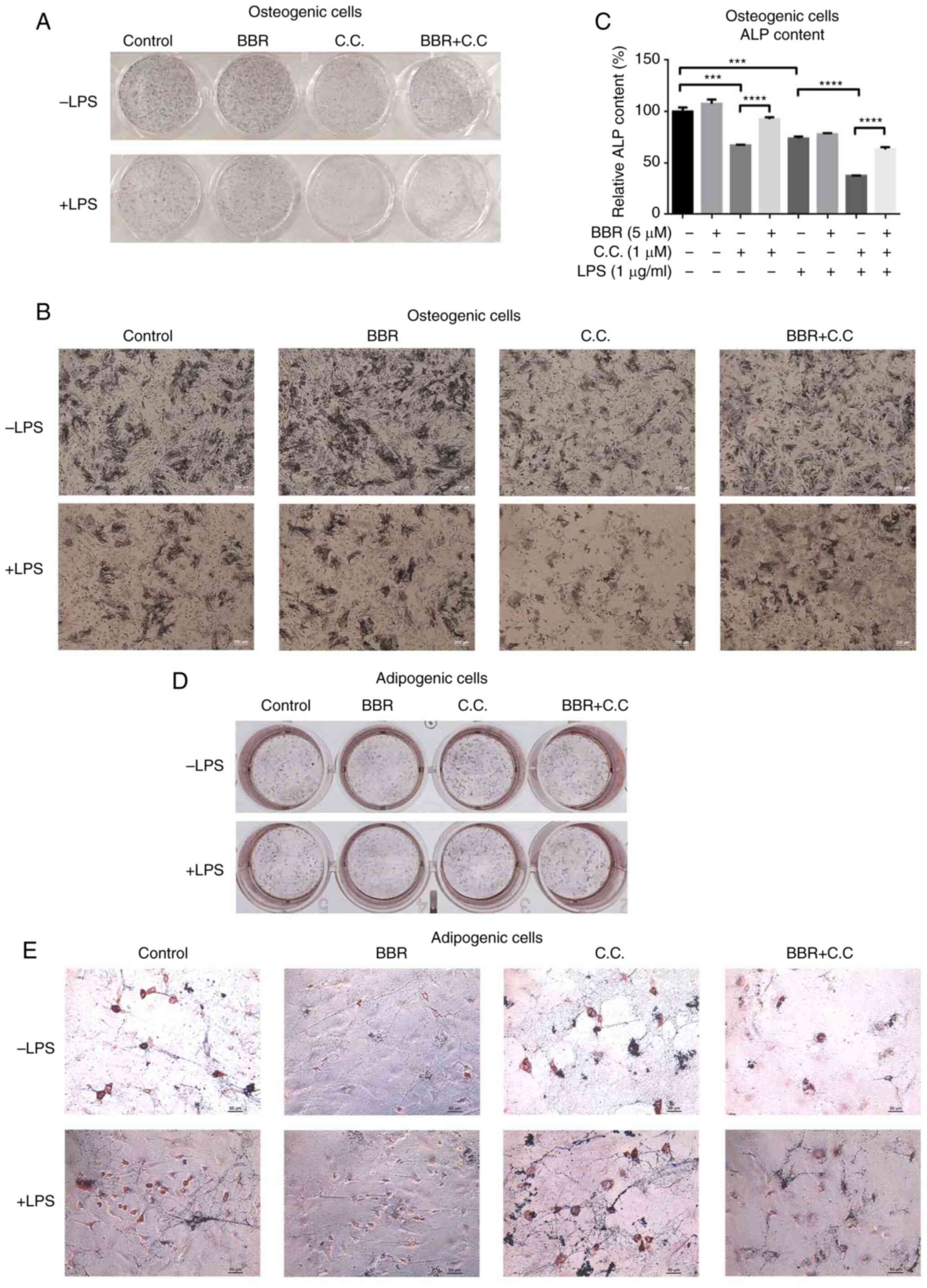
|
1
|
Dreyer H, Grischke J, Tiede C, Eberhard J,
Schweitzer A, Toikkanen SE, Glöckner S, Krause G and Stiesch M:
Epidemiology and risk factors of peri-implantitis: A systematic
review. J Periodontal Res. 53:657–681. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Heitz-Mayfield LJ: Diagnosis and
management of peri-implant diseases. Aust Dent J. 53 (Suppl
1):S43–S48. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Daubert DM, Weinstein BF, Bordin S, Leroux
BG and Flemming TF: Prevalence and predictive factors for
peri-implant disease and implant failure: A cross-sectional
analysis. J Periodontol. 86:337–347. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mishler OP and Shiau HJ: Management of
peri-implant disease: A current appraisal. J Evid Based Dent Pract.
14 (Suppl):53–59. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Salvi GE, Cosgarea R and Sculean A:
Prevalence and mechanisms of peri-implant diseases. J Dent Res.
96:31–37. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Derks J and Tomasi C: Peri-implant health
and disease. A systematic review of current epidemiology. J Clin
Periodontol. 42 (Suppl 16):S158–S171. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Figuero E, Graziani F, Sanz I, Herrera D
and Sanz M: Management of peri-implant mucositis and
peri-implantitis. Periodontol 2000. 66:255–273. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hentenaar DFM, De Waal YCM, Van Winkelhoff
AJ, Meijer HJA and Raghoebar GM: Non-surgical peri-implantitis
treatment using a pocket irrigator device; clinical,
microbiological, radiographical and patient-centred outcomes-A
pilot study. Int J Dent Hyg. 18:403–412. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Takeuchi O, Hoshino K, Kawai T, Sanjo H,
Takada H, Ogawa T, Takeda K and Akira S: Differential roles of TLR2
and TLR4 in recognition of gram-negative and gram-positive
bacterial cell wall components. Immunity. 11:443–451. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cui L, Feng L, Zhang ZH and Jia XB: The
anti-inflammation effect of baicalin on experimental colitis
through inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB pathway activation. Int
Immunopharmacol. 23:294–303. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Park H, Noh AL, Kang JH, Sim JS, Lee DS
and Yim M: Peroxiredoxin II negatively regulates
lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoclast formation and bone loss via
JNK and STAT3. Antioxid Redox Signal. 22:63–77. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sul OJ, Park HJ, Son HJ and Choi HS:
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced autophagy is responsible for
enhanced osteoclastogenesis. Mol Cells. 40:880–887. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bonsignore LA, Anderson JR, Lee Z,
Goldberg VM and Greenfield EM: Adherent lipopolysaccharide inhibits
the osseointegration of orthopedic implants by impairing osteoblast
differentiation. Bone. 52:93–101. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nouneh RA, Wataha JC, Hanes PJ and
Lockwood PE: Effect of lipopolysaccharide contamination on the
attachment of osteoblast-like cells to titanium and titanium alloy
in vitro. J Oral Implantol. 27:174–179. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Insua A, Monje A, Wang HL and Miron RJ:
Basis of bone metabolism around dental implants during
osseointegration and peri-implant bone loss. J Biomed Mater Res A.
105:2075–2089. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen Q, Shou P, Zheng C, Jiang M, Cao G,
Yang Q, Cao J, Xie N, Velletri T, Zhang X, et al: Fate decision of
mesenchymal stem cells: Adipocytes or osteoblasts? Cell Death
Differ. 23:1128–1139. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen KY, Chung CM, Chen YS, Bau DT and Yao
CH: Rat bone marrow stromal cells-seeded porous gelatin/tricalcium
phosphate/oligomeric proanthocyanidins composite scaffold for bone
repair. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 7:708–719. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhu J, Tang H, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Qiu C,
Zhang L, Huang P and Li F: Kaempferol slows intervertebral disc
degeneration by modifying LPS-induced osteogenesis/adipogenesis
imbalance and inflammation response in BMSCs. Int Immunopharmacol.
43:236–242. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pirillo A and Catapano AL: Berberine, a
plant alkaloid with lipid- and glucose-lowering properties: From in
vitro evidence to clinical studies. Atherosclerosis. 243:449–461.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee HW, Suh JH, Kim HN, Kim AY, Park SY,
Shin CS, Choi JY and Kim JB: Berberine promotes osteoblast
differentiation by Runx2 activation with p38 MAPK. J Bone Miner
Res. 23:1227–1237. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Han SY and Kim YK: Berberine Suppresses
RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation by inhibiting c-Fos and
NFATc1 expression. Am J Chin Med. 47:439–455. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu JP, Nishishita K, Sakai E, Yoshida H,
Kato Y, Tsukuba T and Okamoto K: Berberine inhibits RANKL-induced
osteoclast formation and survival through suppressing the NF-kappaB
and Akt pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 580:70–79. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shanbhag S, Mohamed-Ahmed S, Lunde THF,
Suliman S, Bolstad AI, Hervig T and Mustafa K: Influence of
platelet storage time on human platelet lysates and platelet
lysate-expanded mesenchymal stromal cells for bone tissue
engineering. Stem Cell Res Ther. 11:3512020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang Y, Hou Q, Su H, Chen D, Luo Y and
Jiang T: miR-488 negatively regulates osteogenic differentiation of
bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by psoralen by targeting
Runx2. Mol Med Rep. 20:3746–3754. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee YC, Chan YH, Hsieh SC, Lew WZ and Feng
SW: Comparing the osteogenic potentials and bone regeneration
capacities of bone marrow and dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells in
a rabbit calvarial bone defect model. Int J Mol Sci. 20:50152019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhang J, Zheng Y, Luo Y, Du Y, Zhang X and
Fu J: Curcumin inhibits LPS-induced neuroinflammation by promoting
microglial M2 polarization via TREM2/ TLR4/ NF-κB pathways in BV2
cells. Mol Immunol. 116:29–37. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zou K, Li Z, Zhang Y, Zhang HY, Li B, Zhu
WL, Shi JY, Jia Q and Li YM: Advances in the study of berberine and
its derivatives: A focus on anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor
effects in the digestive system. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 38:157–167.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yan Q, Li Y, Cheng N, Sun W and Shi B:
Effect of retinoic acid on the function of
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated bone marrow stromal cells grown on
titanium surfaces. Inflamm Res. 64:63–70. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stermitz FR, Lorenz P, Tawara JN, Zenewicz
LA and Lewis K: Synergy in a medicinal plant: Antimicrobial action
of berberine potentiated by 5′-methoxyhydnocarpin, a multidrug pump
inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:1433–1437. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang H, Shan Y, Wu Y, Xu C, Yu X, Zhao J,
Yan J and Shang W: Berberine suppresses LPS-induced inflammation
through modulating Sirt1/NF-κB signaling pathway in RAW264.7 cells.
Int Immunopharmacol. 52:93–100. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liang Y, Fan C, Yan X, Lu X, Jiang H, Di
S, Ma Z, Feng Y, Zhang Z, Feng P, et al: Berberine ameliorates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via the PERK-mediated
Nrf2/HO-1 signaling axis. Phytother Res. 33:130–148. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tao K, Xiao D, Weng J, Xiong A, Kang B and
Zeng H: Berberine promotes bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem
cells osteogenic differentiation via canonical Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway. Toxicol Lett. 240:68–80. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fiedler T, Salamon A, Adam S, Herzmann N,
Taubenheim J and Peters K: Impact of bacteria and bacterial
components on osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of
adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res.
319:2883–2892. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chu M, Ding R, Chu ZY, Zhang MB, Liu XY,
Xie SH, Zhai YJ and Wang YD: Role of berberine in anti-bacterial as
a high-affinity LPS antagonist binding to TLR4/MD-2 receptor. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 14:892014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nagai Y, Akashi S, Nagafuku M, Ogata M,
Iwakura Y, Akira S, Kitamura T, Kosugi A, Kimoto M and Miyake K:
Essential role of MD-2 in LPS responsiveness and TLR4 distribution.
Nat Immunol. 3:667–672. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gu C, Yin Z, Nie H, Liu Y, Yang J, Huang
G, Shen J, Chen L and Fei J: Identification of berberine as a novel
drug for the treatment of multiple myeloma via targeting UHRF1. BMC
Biol. 8:332020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Sabatino L, Fucci A, Pancione M, Carafa V,
Nebbioso A, Pistore C, Babbio F, Votino C, Laudanna C, Ceccarelli
M, et al: UHRF1 coordinates peroxisome proliferator activated
receptor gamma (PPARG) epigenetic silencing and mediates colorectal
cancer progression. Oncogene. 31:5061–5072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Simonin MA, Bordji K, Boyault S, Bianchi
A, Gouze E, Bécuwe P, Dauça M, Netter P and Terlain B: PPAR-gamma
ligands modulate effects of LPS in stimulated rat synovial
fibroblasts. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 282:C125–C133. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Qu R-N and Qu W: Metformin inhibits
LPS-induced inflammatory response in VSMCs by regulating TLR4 and
PPAR-γ. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:4988–4995. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sun H, Kim JK, Mortensen R, Mutyaba LP,
Hankenson KD and Krebsbach PH: Osteoblast-targeted suppression of
PPARγ increases osteogenesis through activation of mTOR signaling.
Stem Cells. 31:2183–2192. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sergeeva MG, Aleshin SE, Grabeklis S and
Reiser G: PPAR activation has dichotomous control on the expression
levels of cytosolic and secretory phospholipase A2 in astrocytes;
inhibition in naïve, untreated cells and enhancement in
LPS-stimulated cells. J Neurochem. 115:399–410. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Huang X, Wang P, Li T, Tian X, Guo W, Xu
B, Huang G, Cai D, Zhou F, Zhang H, et al: Self-assemblies based on
traditional medicine berberine and cinnamic acid for
adhesion-induced inhibition multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus
aureus. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 12:227–237. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|