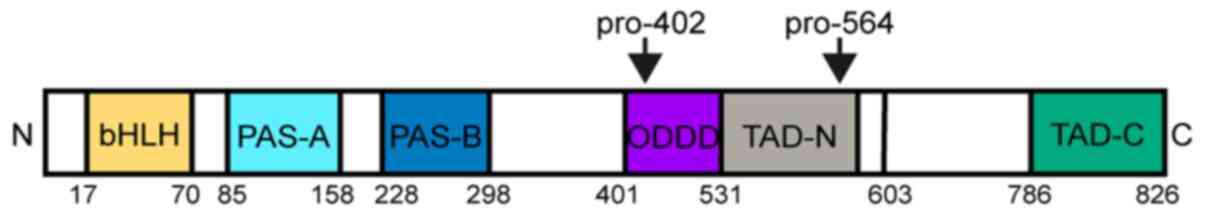
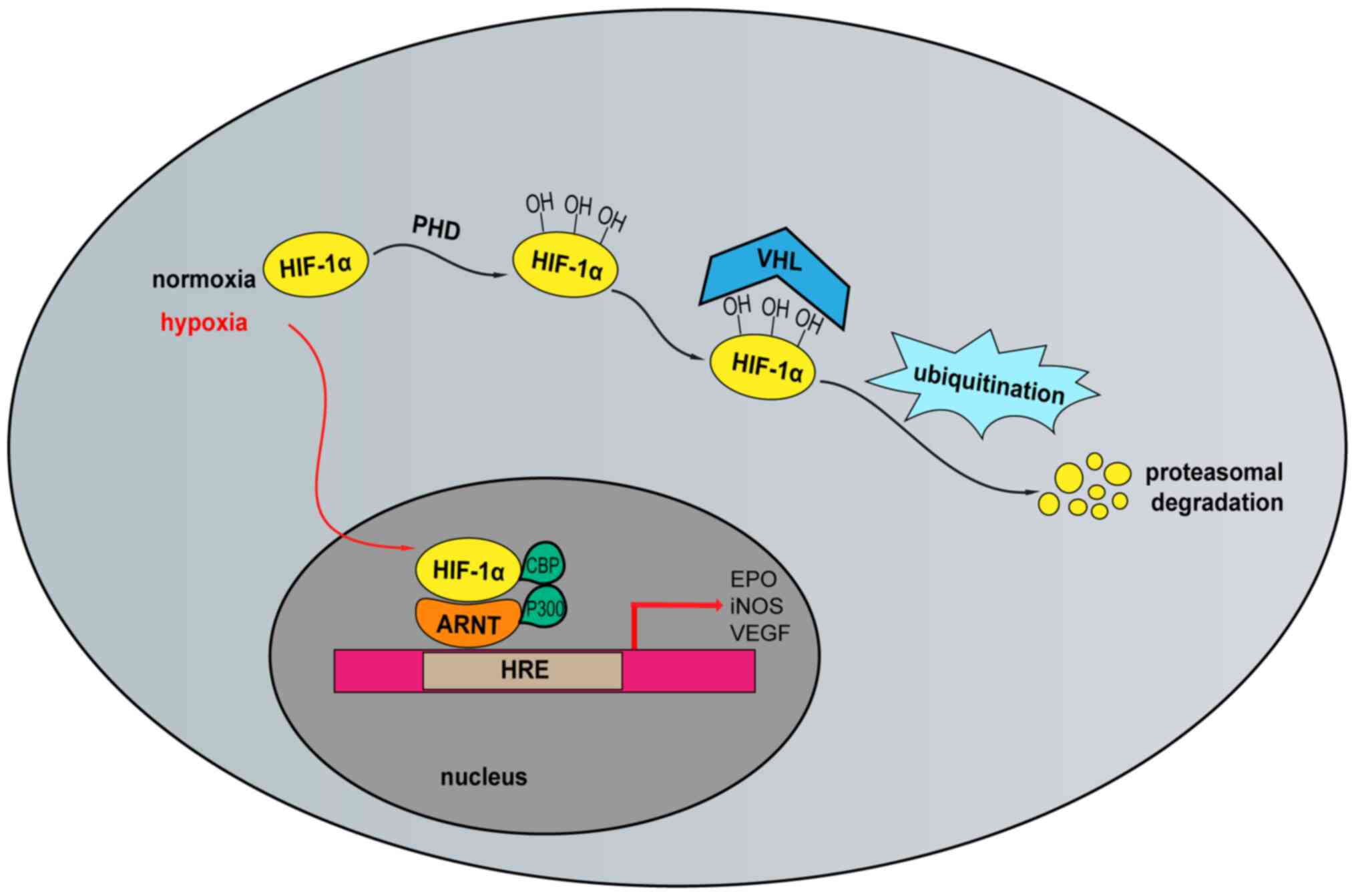
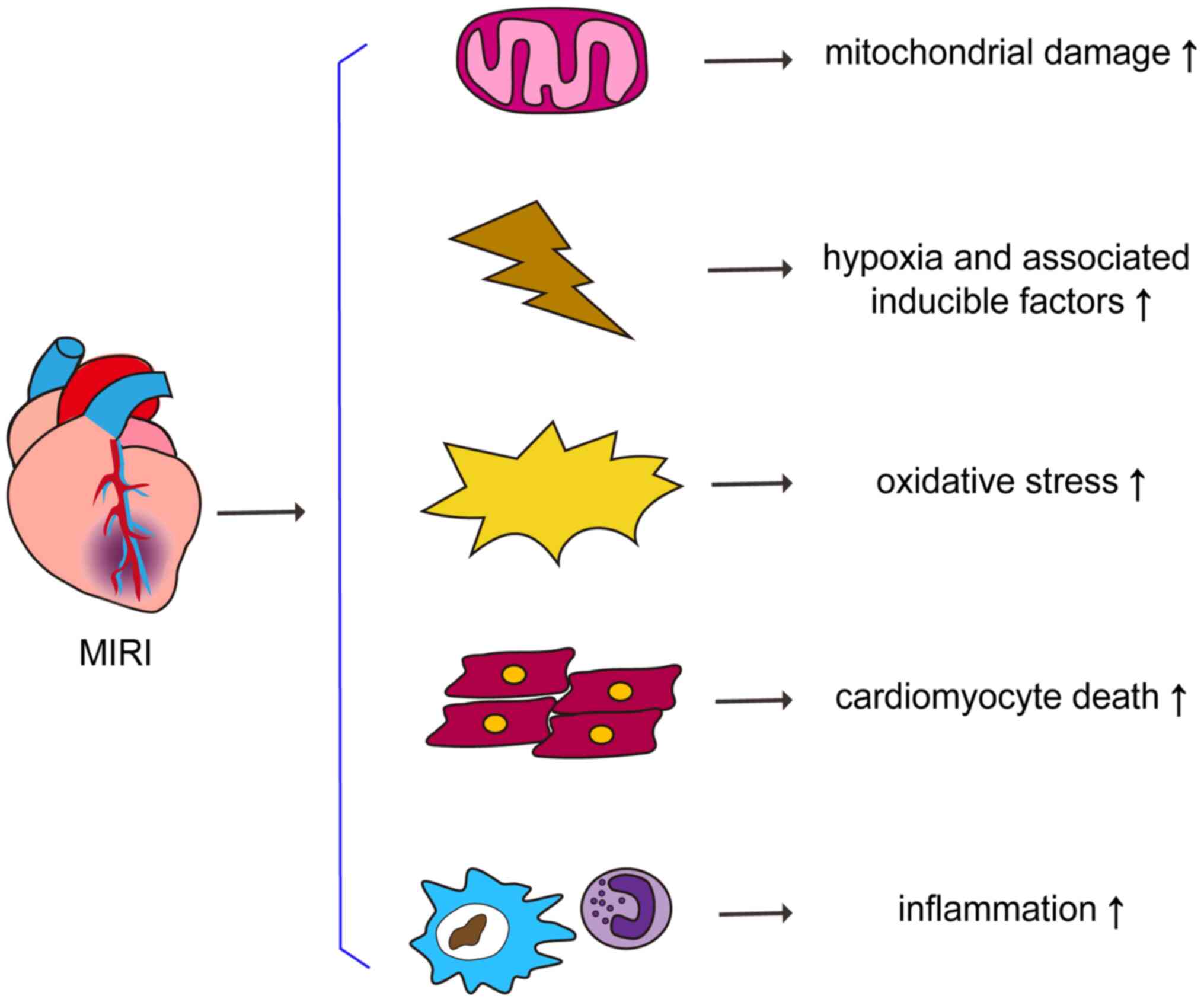
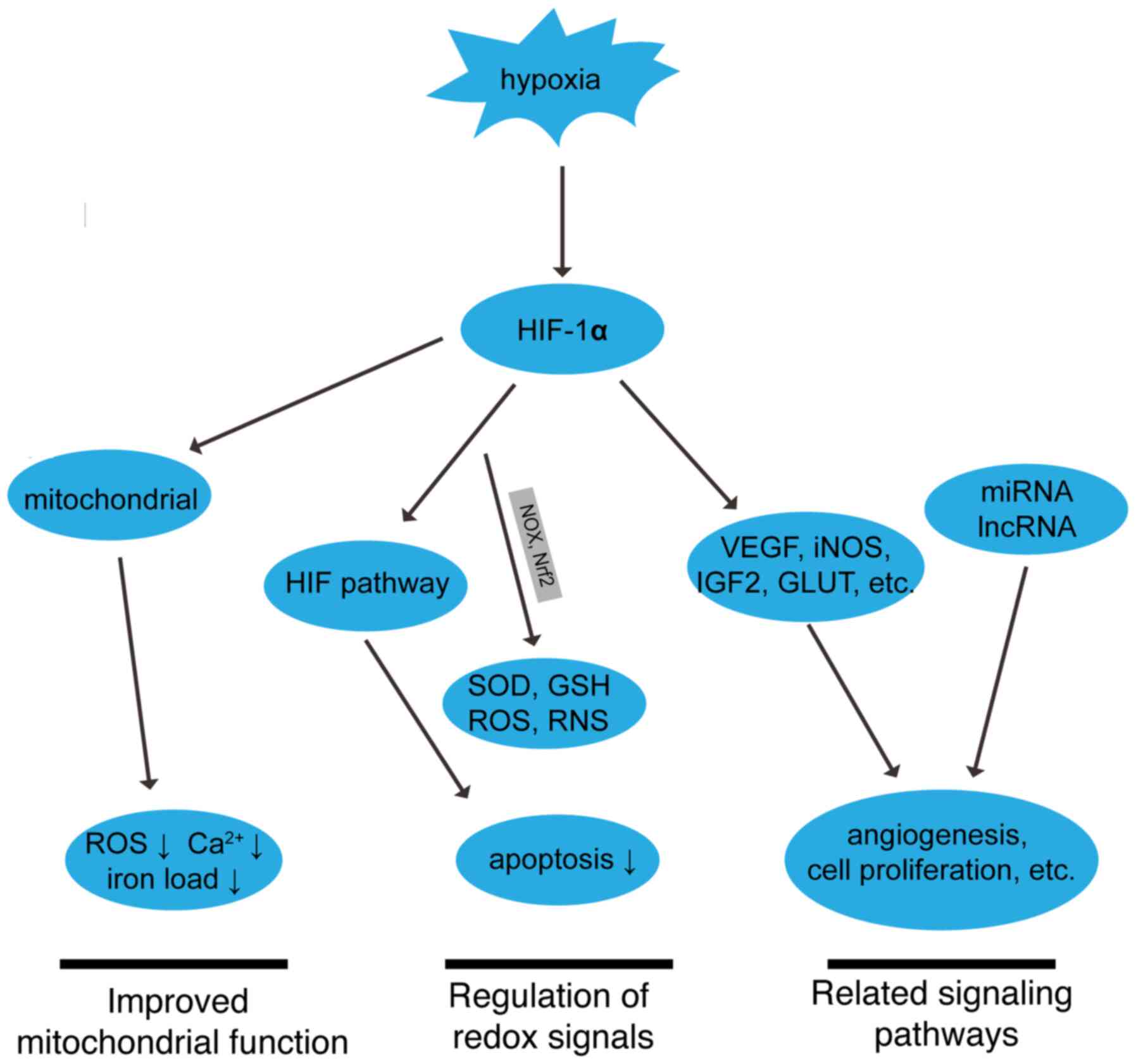
|
1
|
Kaski JC, Crea F, Gersh BJ and Camici PG:
Reappraisal of ischemic heart disease. Circulation. 138:1463–1480.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ma LY, Chen WW, Gao RL, Liu LS, Zhu ML,
Wang YJ, Wu ZS, Li HJ, Gu DF, Yang YJ, et al: China cardiovascular
diseases report 2018: An updated summary. J Geriatr Cardiol.
17:1–8. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhao D, Liu J, Wang M, Zhang X and Zhou M:
Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in China: Current features
and implications. Nat Rev Cardiol. 16:203–212. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Patel MR, Calhoon JH, Dehmer GJ, Grantham
JA, Maddox TM, Maron DJ and Smith PK:
ACC/AATS/AHA/ASE/ASNC/SCAI/SCCT/STS 2017 appropriate use criteria
for coronary revascularization in patients with stable ischemic
heart disease: A report of the American college of cardiology
appropriate use criteria task force, American association for
thoracic surgery, American heart association, American society of
echocardiography, American society of nuclear cardiology, society
for cardiovascular angiography and interventions, society of
cardiovascular computed tomography, and society of thoracic
surgeons. J Am Coll Cardiol. 69:2212–2241. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ibáñez B, Heusch G, Ovize M and Van de
Werf F: Evolving therapies for myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury. J Am Coll Cardiol. 65:1454–1471. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bellanti F: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in
myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Acta Physiol (Oxf).
221:93–94. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Choudhry H and Harris AL: Advances in
hypoxia-inducible factor biology. Cell Metab. 27:281–298. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Semenza GL, Nejfelt MK, Chi SM and
Antonarakis SE: Hypoxia-inducible nuclear factors bind to an
enhancer element located 3′ to the human erythropoietin gene. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 88:5680–5684. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chee NT, Lohse I and Brothers SP:
mRNA-to-protein translation in hypoxia. Mol Cancer. 18:49. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Masoud GN and Li W: HIF-1α pathway: Role,
regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B.
5:378–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Majmundar AJ, Wong WJ and Simon MC:
Hypoxia-inducible factors and the response to hypoxic stress. Mol
Cell. 40:294–309. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Eckle T, Köhler D, Lehmann R, El Kasmi K
and Eltzschig HK: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 is central to
cardioprotection: A new paradigm for ischemic preconditioning.
Circulation. 118:166–175. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang BH, Rue E, Wang GL, Roe R and
Semenza GL: Dimerization, DNA binding, and transactivation
properties of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem.
271:17771–17778. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang GL and Semenza GL: Purification and
characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem.
270:1230–1237. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sousa Fialho MDL, Abd Jamil AH, Stannard
GA and Heather LC: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 signalling,
metabolism and its therapeutic potential in cardiovascular disease.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1865:831–843. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ong SG and Hausenloy DJ: Hypoxia-inducible
factor as a therapeutic target for cardioprotection. Pharmacol
Ther. 136:69–81. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mole DR, Blancher C, Copley RR, Pollard
PJ, Gleadle JM, Ragoussis J and Ratcliffe PJ: Genome-wide
association of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and HIF-2alpha
DNA binding with expression profiling of hypoxia-inducible
transcripts. J Biol Chem. 284:16767–16775. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee JW, Bae SH, Jeong JW, Kim SH and Kim
KW: Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1)alpha: Its protein stability
and biological functions. Exp Mol Med. 36:1–12. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Singh L, Aldosary S, Saeedan AS, Ansari MN
and Kaithwas G: Prolyl hydroxylase 2: A promising target to inhibit
hypoxia-induced cellular metabolism in cancer cells. Drug Discov
Today. 23:1873–1882. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Abe H, Semba H and Takeda N: The roles of
hypoxia signaling in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases. J
Atheroscler Thromb. 24:884–894. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Matsushima S, Kuroda J, Ago T, Zhai P,
Ikeda Y, Oka S, Fong GH, Tian R and Sadoshima J: Broad suppression
of NADPH oxidase activity exacerbates ischemia/reperfusion injury
through inadvertent downregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
and upregulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α.
Circ Res. 112:1135–1149. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou YH, Han QF, Wang LH, Liu T, Meng XY,
Wu L, Li T, Jiao YR, Yao HC and Zhang DY: High mobility group box 1
protein attenuates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury via
inhibition of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling
pathway. Exp Ther Med. 14:1582–1588. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu N, Li J, Li Y, Zhang Y, Du Q, Hao P,
Li J, Cao X and Li L: Berberine protects against simulated
ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced H9C2 cardiomyocytes apoptosis
in vitro and myocardial ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis in
vivo by regulating the mitophagy-mediated HIF-1α/BNIP3 pathway.
Front Pharmacol. 11:3672020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lesnefsky EJ, Chen Q, Tandler B and Hoppel
CL: Mitochondrial dysfunction and myocardial ischemia-reperfusion:
Implications for novel therapies. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.
57:535–565. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hausenloy DJ, Garcia-Dorado D, Bøtker HE,
Davidson SM, Downey J, Engel FB, Jennings R, Lecour S, Leor J,
Madonna R, et al: Novel targets and future strategies for acute
cardioprotection: Position paper of the european society of
cardiology working group on cellular biology of the heart.
Cardiovasc Res. 113:564–585. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bernardi P and Di Lisa F: The
mitochondrial permeability transition pore: Molecular nature and
role as a target in cardioprotection. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
78:100–106. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jang S, Lewis TS, Powers C, Khuchua Z,
Baines CP, Wipf P and Javadov S: Elucidating mitochondrial electron
transport chain supercomplexes in the heart during
ischemia-reperfusion. Antioxid Redox Signal. 27:57–69. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chowdhury A, Aich A, Jain G, Wozny K,
Lüchtenborg C, Hartmann M, Bernhard O, Balleiniger M, Alfar EA,
Zieseniss A, et al: Defective mitochondrial cardiolipin remodeling
dampens HIF-1α expression in hypoxia. Cell Rep. 25:561–570. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nanayakkara G, Alasmari A, Mouli S,
Eldoumani H, Quindry J, McGinnis G, Fu X, Berlin A, Peters B, Zhong
J and Amin R: Cardioprotective HIF-1α-frataxin signaling against
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
309:H867–H879. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fuhrmann DC and Brüne B: Mitochondrial
composition and function under the control of hypoxia. Redox Biol.
12:208–215. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cadenas S: ROS and redox signaling in
myocardial isch-emia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection. Free
Radic Biol Med. 117:76–89. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Deshwal S, Antonucci S, Kaludercic N and
Di Lisa F: Measurement of mitochondrial ROS formation. Methods Mol
Biol. 1782:403–418. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Garlick PB, Davies MJ, Hearse DJ and
Slater TF: Direct detection of free radicals in the reperfused rat
heart using electron spin resonance spectroscopy. Circ Res.
61:757–760. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Boengler K, Bornbaum J, Schlüter KD and
Schulz R: P66shc and its role in ischemic cardiovascular diseases.
Basic Res Cardiol. 114:292019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Boengler K, Lochnit G and Schulz R:
Mitochondria ‘THE’ target of myocardial conditioning. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 315:H1215–H1231. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen J, Luo Y, Wang S, Zhu H and Li D:
Roles and mechanisms of SUMOylation on key proteins in myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 134:154–164. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kurian GA, Rajagopal R, Vedantham S and
Rajesh M: The role of oxidative stress in myocardial ischemia and
reperfusion injury and remodeling: Revisited. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016:16564502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bertero E and Maack C: Calcium signaling
and reactive oxygen species in mitochondria. Circ Res.
122:1460–1478. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cadenas S: ROS and redox signaling in
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection. Free
Radic Biol Med. 117:76–89. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jiang L, Zeng H, Ni L, Qi L, Xu Y, Xia L,
Yu Y, Liu B, Yang H, Hao H and Li P: HIF-1α preconditioning
potentiates antioxidant activity in ischemic injury: The role of
sequential administration of dihydrotanshinone I and protocatechuic
aldehyde in cardioprotection. Antioxid Redox Signal. 31:227–242.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible factors:
Coupling glucose metabolism and redox regulation with induction of
the breast cancer stem cell phenotype. EMBO J. 36:252–259. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Thomas LW and Ashcroft M: Exploring the
molecular interface between hypoxia-inducible factor signalling and
mitochondria. Cell Mol Life Sci. 76:1759–1777. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Adeyemi OS, Eseola AO, Plass W, Otuechere
CA and Elebiyo TC: New imidazoles cause cellular toxicity by
impairing redox balance, mitochondrial membrane potential, and
modulation of HIF-1α expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
529:23–27. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gyongyosi A, Terraneo L, Bianciardi P,
Tosaki A, Lekli I and Samaja M: The impact of moderate chronic
hypoxia and hyperoxia on the level of apoptotic and autophagic
proteins in myocardial tissue. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2018:57867422018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Watanabe Y, Cohen RA and Matsui R: Redox
regulation of ischemic angiogenesis-another aspect of reactive
oxygen species. Circ J. 80:1278–1284. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tang WH, Wu S, Wong TM, Chung SK and Chung
SS: Polyol pathway mediates iron-induced oxidative injury in
ischemic-reperfused rat heart. Free Radic Biol Med. 45:602–610.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang S, Ma K, Liu Y, Pan X, Chen Q, Qi L
and Li S: Stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor by DMOG
inhibits development of chronic hypoxia-induced right ventricular
remodeling. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 67:68–75. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lee JW, Ko J, Ju C and Eltzschig HK:
Hypoxia signaling in human diseases and therapeutic targets. Exp
Mol Med. 51:1–13. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Dong J, Xu M, Zhang W and Che X: Effects
of sevoflurane pretreatment on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury through the Akt/hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha
(HIF-1α)/vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling
pathway. Med Sci Monit. 25:3100–3107. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li J, Zhou W, Chen W, Wang H, Zhang Y and
Yu T: Mechanism of the hypoxia inducible factor 1/hypoxic response
element pathway in rat myocardial ischemia/diazoxide
post-conditioning. Mol Med Rep. 21:1527–1536. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wu N, Zhang X, Du S, Chen D and Che R:
Upregulation of miR-335 ameliorates myocardial ischemia reperfusion
injury via targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha subunit
inhibitor. Am J Transl Res. 10:4082–4094. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Si J, Wang N, Wang H, Xie J, Yang J, Yi H,
Shi Z, Ma J, Wang W, Yang L, et al: HIF-1α signaling activation by
post-ischemia treatment with astragaloside IV attenuates myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury. PLoS One. 9:e1078322014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhang Y, Liu D, Hu H, Zhang P, Xie R and
Cui W: HIF-1α/BNIP3 signaling pathway-induced-autophagy plays
protective role during myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Biomed Pharmacother. 120:1094642019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Liu DW, Zhang YN, Hu HJ, Zhang PQ and Cui
W: Downregulation of microRNA-199a-5p attenuates
hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cytotoxicity in cardiomyocytes by
targeting the HIF-1α-GSK3β-mPTP axis. Mol Med Rep. 19:5335–5344.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Adluri RS, Thirunavukkarasu M, Dunna NR,
Zhan L, Oriowo B, Takeda K, Sanchez JA, Otani H, Maulik G, Fong GH
and Maulik N: Disruption of hypoxia-inducible transcription
factor-prolyl hydroxylase domain-1 (PHD-1−/−) attenuates
ex vivo myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α transcription factor and its target
genes in mice. Antioxid Redox Signal. 15:1789–1797. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yao HC, Zhou M, Zhou YH, Wang LH, Zhang
DY, Han QF, Liu T, Wu L, Tian KL and Zhang M: Intravenous high
mobility group box 1 upregulates the expression of HIF-1α in the
myocardium via a protein kinase B-dependent pathway in rats
following acute myocardial ischemia. Mol Med Rep. 13:1211–1219.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Tekin D, Dursun AD and Xi L:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) and cardioprotection. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 31:1085–1094. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Correia de Sousa M, Gjorgjieva M, Dolicka
D, Sobolewski C and Foti M: Deciphering miRNAs' action through
miRNA editing. Int J Mol Sci. 20:62492019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Sheng Z, Lu W, Zuo Z, Wang D, Zuo P, Yao Y
and Ma G: MicroRNA-7b attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced H9C2
cardiomyocyte apoptosis via the hypoxia-inducible factor-1/p-p38
pathway. J Cell Biochem. 120:9947–9955. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Liu Y, Zou J, Liu X and Zhang Q:
MicroRNA-138 attenuates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury
through inhibiting mitochondria-mediated apoptosis by targeting
HIF1-α. Exp Ther Med. 18:3325–3332. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Serocki M, Bartoszewska S,
Janaszak-Jasiecka A, Ochocka RJ, Collawn JF and Bartoszewski R:
miRNAs regulate the HIF switch during hypoxia: A novel therapeutic
target. Angiogenesis. 21:183–202. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wu L, Chen Y, Chen Y, Yang W, Han Y, Lu L,
Yang K and Cao J: Effect of HIF-1α/miR-10b-5p/PTEN on
hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. J Am Heart Assoc.
8:e0119482019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wu K, Hu M, Chen Z, Xiang F, Chen G, Yan
W, Peng Q and Chen X: Asiatic acid enhances survival of human AC16
cardiomyocytes under hypoxia by upregulating miR-1290. IUBMB Life.
69:660–667. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Bavelloni A, Ramazzotti G, Poli A, Piazzi
M, Focaccia E, Blalock W and Faenza I: MiRNA-210: A current
overview. Anticancer Res. 37:6511–6521. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Long B, Li N, Xu XX, Li XX, Xu XJ, Guo D,
Zhang D, Wu ZH and Zhang SY: Long noncoding RNA FTX regulates
cardiomyocyte apoptosis by targeting miR-29b-1-5p and Bcl2l2.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 495:312–318. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kopp F and Mendell JT: Functional
classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs.
Cell. 172:393–407. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Jiang X and Ning Q: The emerging roles of
long noncoding RNAs in common cardiovascular diseases. Hypertens
Res. 38:375–379. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ong SB, Katwadi K, Kwek XY, Ismail NI,
Chinda K, Ong SG and Hausenloy DJ: Non-coding RNAs as therapeutic
targets for preventing myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 22:247–261. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ren L, Chen S, Liu W, Hou P, Sun W and Yan
H: Downregulation of long non-coding RNA nuclear enriched abundant
transcript 1 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits cell
apoptosis by targeting miR-193a in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 19:1922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Li X, Luo S, Zhang J, Yuan Y, Jiang W, Zhu
H, Ding X, Zhan L, Wu H, Xie Y, et al: lncRNA H19 alleviated
myocardial I/RI via suppressing miR-877-3p/Bcl-2-mediated
mitochondrial apoptosis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 17:297–309. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Yang F, Zhang H, Mei Y and Wu M:
Reciprocal regulation of HIF-1α and lincRNA-p21 modulates the
Warburg effect. Mol Cell. 53:88–100. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yue X, Wang R, Li W, Wang C, Lu H and
Zhang J: Research progress of long chain non-coding RNA H19 in
anoxic environment mechanism. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.
43:1151–1158. 2018.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Xue X and Luo L: LncRNA HIF1A-AS1
contributes to ventricular remodeling after myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury by adsorption of microRNA-204 to
regulating SOCS2 expression. Cell Cycle. 18:2465–2480. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Liu XW, Lu MK, Zhong HT, Wang LH and Fu
YP: Panax notoginseng saponins attenuate myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury through the HIF-1α/BNIP3 pathway of
autophagy. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 73:92–99. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Shen K, Ji L, Gong C, Ma Y, Yang L, Fan Y,
Hou M and Wang Z: Notoginsenoside Ft1 promotes angiogenesis via
HIF-1α mediated VEGF secretion and the regulation of PI3K/AKT and
Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathways. Biochem Pharmacol. 84:784–792.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Huang X, Zuo L, Lv Y, Chen C, Yang Y, Xin
H, Li Y and Qian Y: Asiatic acid attenuates myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury via Akt/GSK-3β/HIF-1α signaling in rat
H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Molecules. 21:12482016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Veloso CD, Belew GD, Ferreira LL, Grilo
LF, Jones JG, Portincasa P, Sardão VA and Oliveira PJ: A
mitochondrial approach to cardiovascular risk and disease. Curr
Pharm Des. 25:3175–3194. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Guo H, Zheng M, Jiao YB and Zheng H:
Paclitaxel enhances the protective effect of myocardial ischemia
preconditioning on ischemia/reperfusion injury in aged rat.
Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 46:719–724. 2018.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Cai Z, Zhong H, Bosch-Marce M, Fox-Talbot
K, Wang L, Wei C, Trush MA and Semenza GL: Complete loss of
ischaemic preconditioning-induced cardioprotection in mice with
partial deficiency of HIF-1 alpha. Cardiovasc Res. 77:463–470.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Jia P, Wu X, Dai Y, Teng J, Fang Y, Hu J,
Zou J, Liang M and Ding X: MicroRNA-21 is required for local and
remote ischemic preconditioning in multiple organ protection
against sepsis. Crit Care Med. 45:e703–e710. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Yu X, Ge L, Niu L, Lian X, Ma H and Pang
L: The dual role of inducible nitric oxide synthase in myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury: Friend or foe? Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2018:83648482018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Cai Z, Luo W, Zhan H and Semenza GL:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is required for remote ischemic
preconditioning of the heart. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:17462–17467. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Chen H, Jing XY, Shen YJ, Wang TL, Ou C,
Lu SF, Cai Y, Li Q, Chen X, Ding YJ, et al: Stat5-dependent
cardioprotection in late remote ischaemia preconditioning.
Cardiovasc Res. 114:679–689. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Wan DY, Zhang Z and Yang HH:
Cardioprotective effect of miR-214 in myocardial ischemic
postconditioning by down-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1,
alpha subunit inhibitor. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 61:1–6.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Wang C, Zuo B and Wu X: The role of
macrophage migration inhibitory factor in remote ischemic
postconditioning. Can J Cardiol. 35:501–510. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Davidson SM, Ferdinandy P, Andreadou I,
Bøtker HE, Heusch G, Ibáñez B, Ovize M, Schulz R, Yellon DM,
Hausenloy DJ, et al: Multitarget strategies to reduce myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury: JACC review topic of the week. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 73:89–99. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Li D, Ni H, Rui Q, Gao R and Chen G: Mst1:
Function and mechanism in brain and myocardial ischemia reperfusion
injury. Curr Neuropharmacol. 16:1358–1364. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Wang S, Shao X, Li X, Su X, Huo Y and Yang
C: HIF-1α may provide only short-term protection against
ischemia-reperfusion injury in Sprague-Dawley myocardial cultures.
Mol Clin Oncol. 4:579–583. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Chen C, Hu Q, Yan J, Yang X, Shi X, Lei J,
Chen L, Huang H, Han J, Zhang JH and Zhou C: Early inhibition of
HIF-1alpha with small interfering RNA reduces ischemic-reperfused
brain injury in rats. Neurobiol Dis. 33:509–517. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|