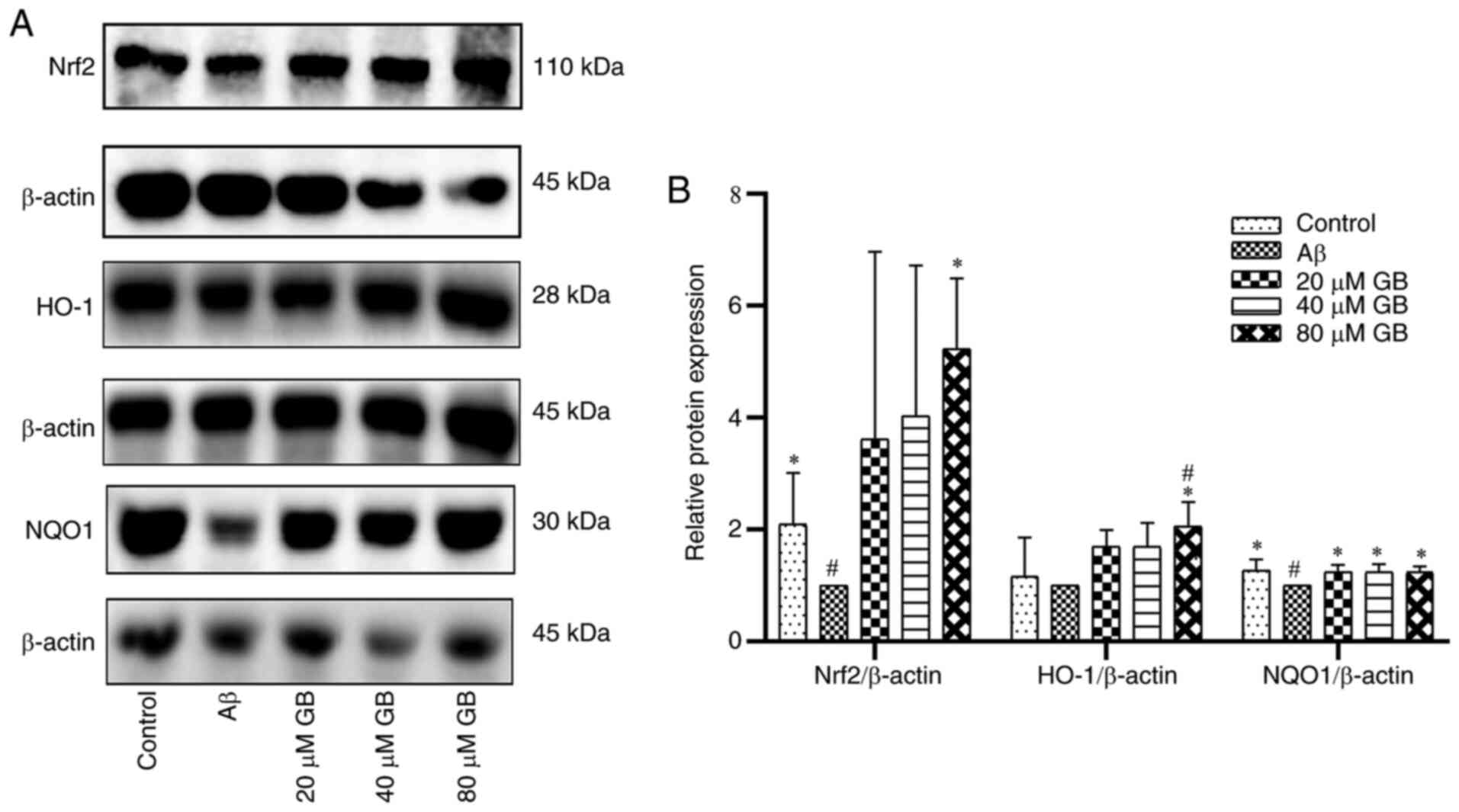
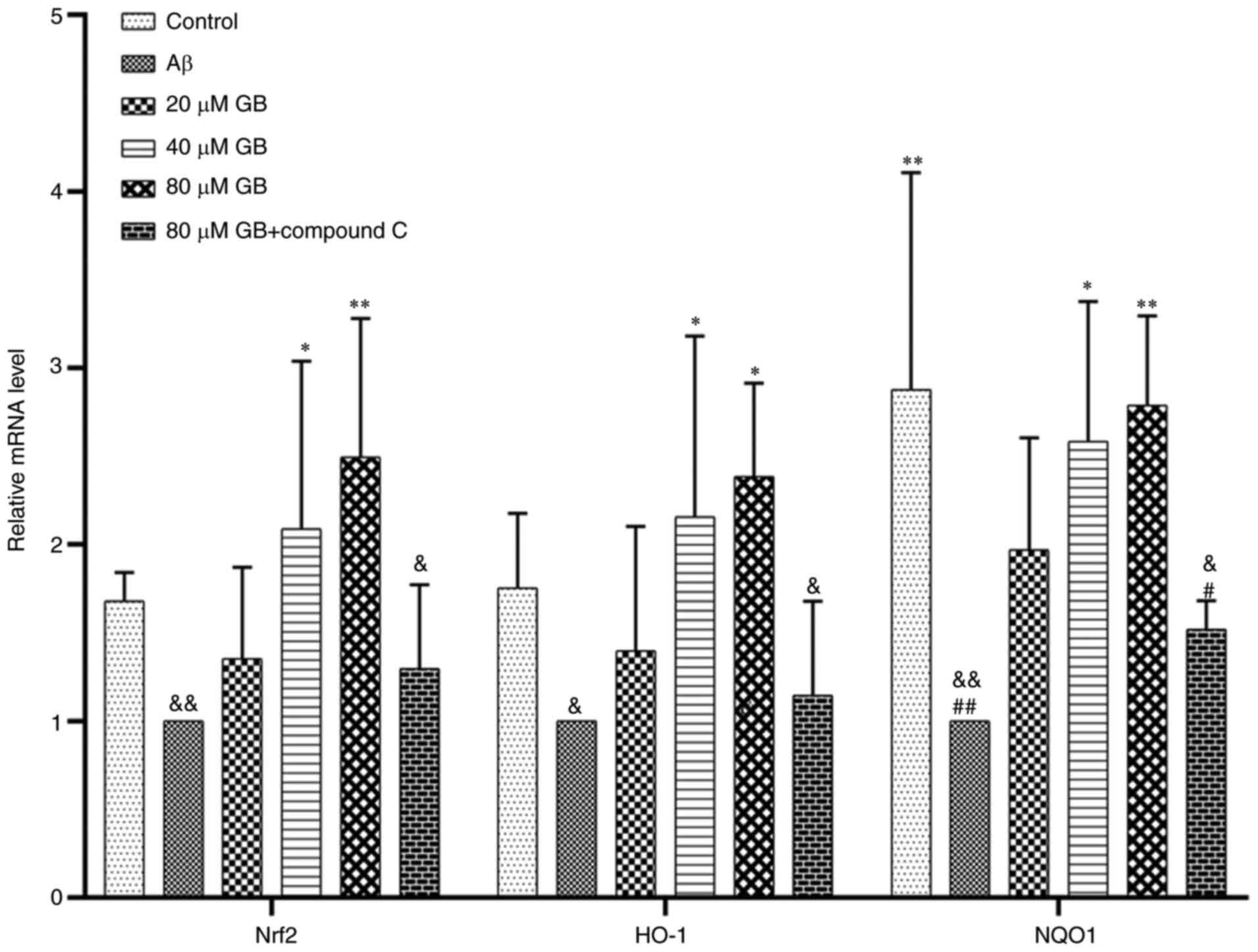
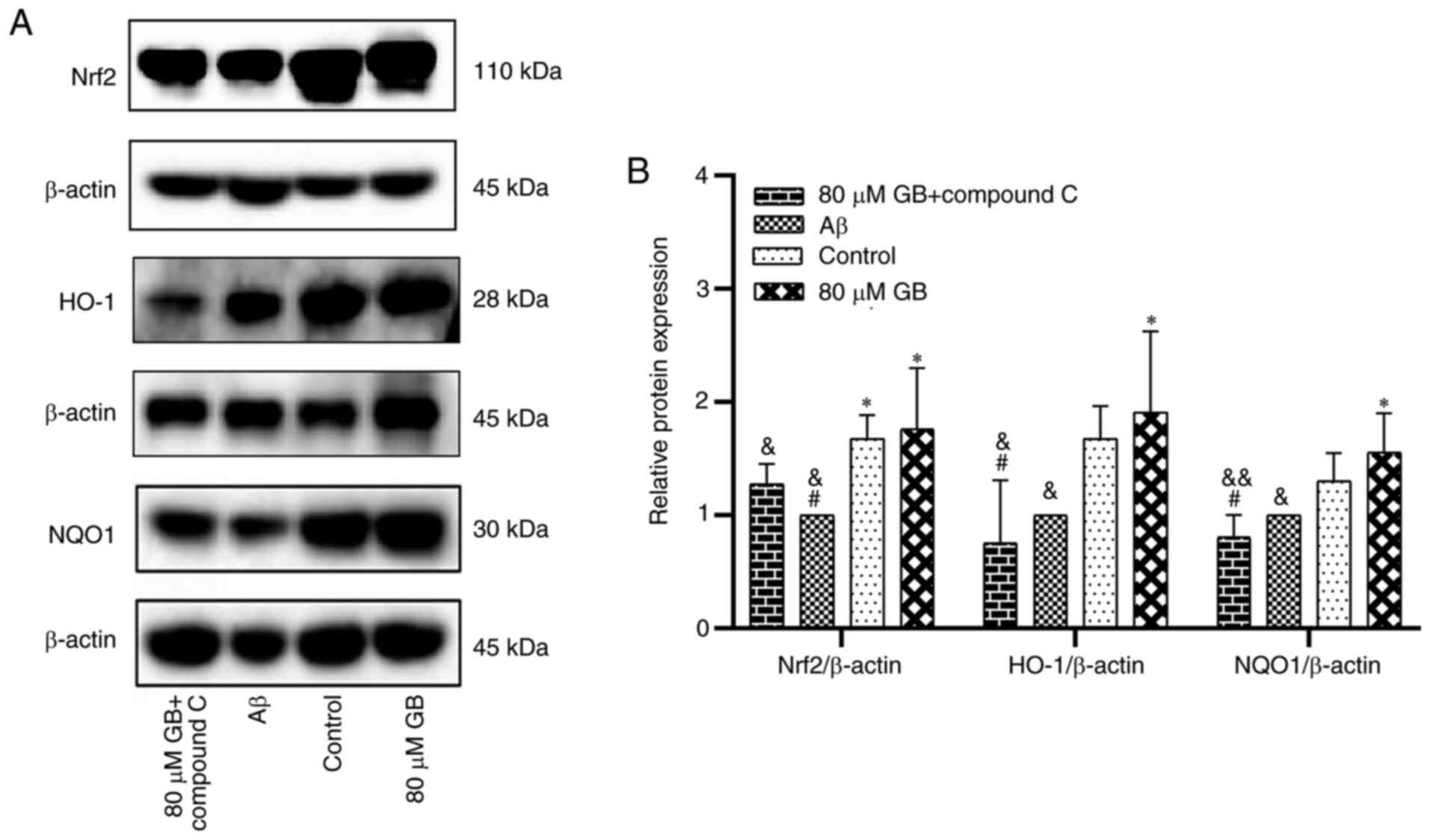
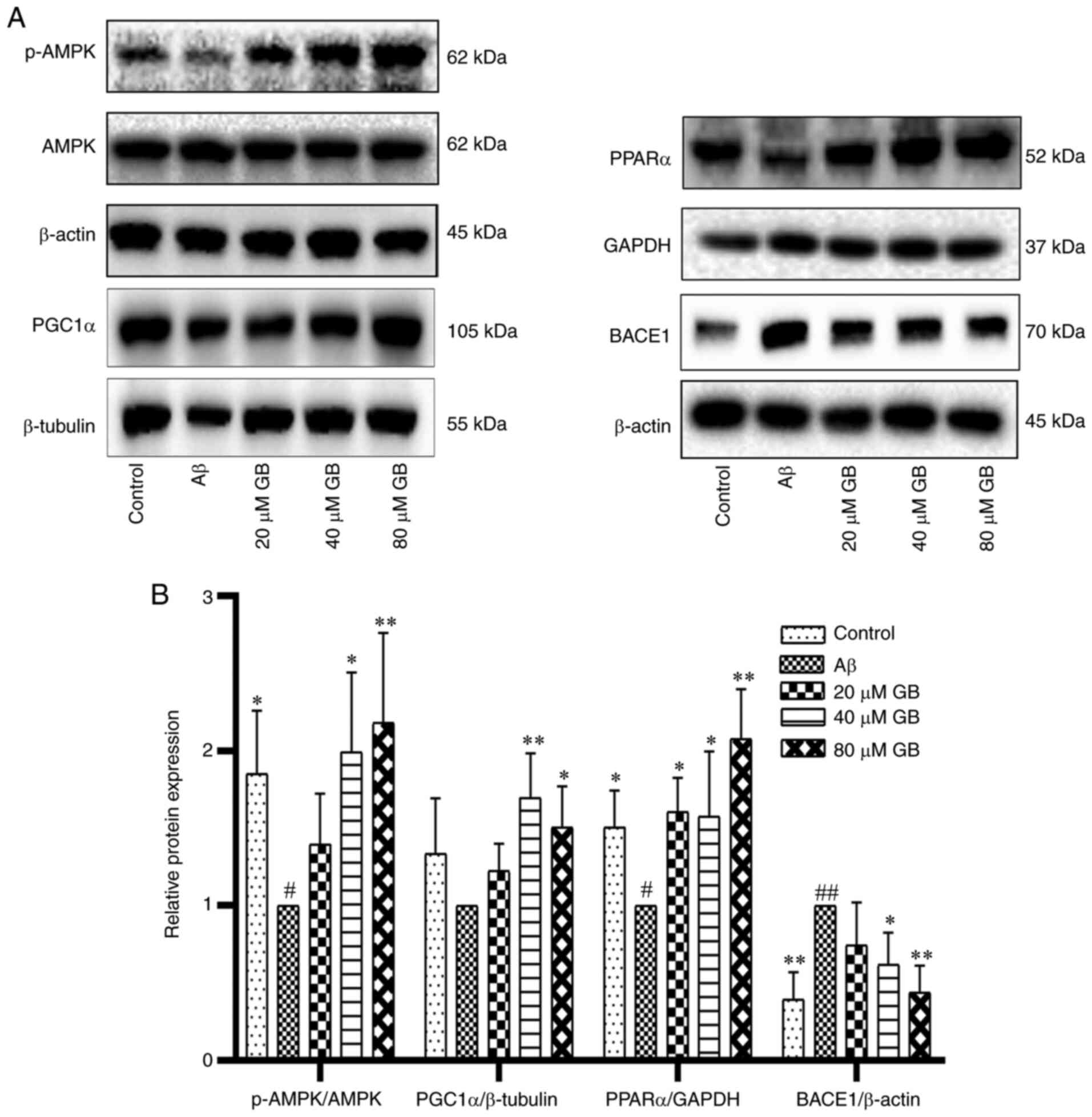
|
1
|
Maclennan KM, Darlington CL and Smith PF:
The CNS effects of Ginkgo biloba extracts and ginkgolide B. Prog
Neurobiol. 67:235–257. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang P, Cai X, Zhou K, Lu C and Chen W: A
novel oil-body nanoemulsion formulation of Ginkgolide B:
Pharmacokinetics study and in vivo pharmacodynamics evaluations. J
Pharm Sci. 103:1075–1084. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bate C, Tayebi M and Williams A:
Ginkgolides protect against amyloid-β1-42-mediated synapse damage
in vitro. Mol Neurodegener. 3:12008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Werneke U, Turner T and Priebe S:
Complementary medicines in psychiatry: Review of effectiveness and
safety. Br J Psychiatry. 188:109–121. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jean NS, Kathy GW, Pauline M and Stacy H:
Dysgraphia in Alzheimer's disease: A review for clinical and
research purposes. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 49:1313–1330. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nobuyuki K: Diabetes mellitus induces
Alzheimer's disease pathology: Histopathological evidence from
animal models. Int J Mol Sci. 17:5032016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ballard C, Gauthier S, Corbett A, Brayne C
and Jones E: Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 377:1019–1031. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shankar GM, Li S, Mehta TH, Garcia-Munoz
A, Shepardson NE, Smith I, Brett FM, Farrell MA, Rowan MJ, Lemere
CA, et al: Amyloid-β protein dimers isolated directly from
Alzheimer's brains impair synaptic plasticity and memory. Nat Med.
14:837–842. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wyss-Coray T, Loike JD, Brionne TC, Lu E
and Husemann J: Adult mouse astrocytes degrade amyloid-beta in
vitro and in situ. Nat Med. 9:453–457. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nielsen HM, Veerhuis R, Bo H and
Janciauskiene S: Binding and uptake of Abeta1-42 by
primary human astrocytes in vitro. Glia. 57:978–988. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Basak JM, Verghese PB, Yoon H, Kim J and
Holtzman DM: Low-density lipoprotein receptor represents an
apolipoprotein E-independent pathway of Aβ uptake and degradation
by astrocytes. J Biol Chem. 287:13959–13971. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Thal DR, Schultz C, Dehghani F, Yamaguchi
H, Braak H and Braak E: Amyloid beta-protein (Abeta)-containing
astrocytes are located preferentially near N-terminal-truncated
Abeta deposits in the human entorhinal cortex. Acta Neuropathol.
100:608–617. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang ZZ, Li J, Li SX, Feng W and Wang H:
Effect of ginkgolide B on striatal extracellular amino acids in
middle cerebral artery occluded rats. J Ethnopharmacol.
136:117–122. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Poon WW, Carlos AJ, Aguilar BL, Berchtold
NC, Kawano CK, Zograbyan V, Yaopruke T, Shelanski M and Cotman CW:
β-Amyloid (Aβ) oligomers impair brain-derived neurotrophic factor
retrograde trafficking by down-regulating ubiquitin C-terminal
hydrolase, UCH-L1. J Biol Chem. 288:16937–16948. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ihara Y, Morishima-Kawashima M and Nixon
R: The ubiquitin-proteasome system and the autophagic-lysosomal
system in Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med.
2:a0063612012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Iurlaro R and Muñoz-Pinedo C: Cell death
induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. FEBS J. 283:2640–2652.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li HH, Lu FJ, Hung HC, Liu GY, Lai TJ and
Lin CL: Humic acid increases amyloid β-induced cytotoxicity by
induction of ER stress in human SK-N-MC neuronal cells. Int J Mol
Sci. 16:10426–10442. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li JQ, Tai YJ, Jiang T and Tan L:
Endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. Mol
Neurobiol. 51:383–395. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Umeda T, Tomiyama T, Sakama N, Tanaka S,
Lambert MP, Klein WL and Mori H: Intraneuronal amyloid-beta
oligomers cause cell death via endoplasmic reticulum stress,
endosomal/lysosomal leakage, and mitochondrial dysfunction in vivo.
J Neurosci Res. 89:1031–1042. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hoozemans JJ, van Haastert ES, Nijholt DA,
Rozemuller AJ, Eikelenboom P and Scheper W: The unfolded protein
response is activated in pretangle neurons in Alzheimer's disease
hippocampus. Am J Pathol. 110:165–172. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Araki E, Oyadomari S and Mori M:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress and diabetes mellitus. Intern Med.
42:7–14. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Verri M, Pastoris O, Dossena M, Aquilani R
and Bongiorno AI: Mitochondrial alterations, oxidative stress and
neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease. Int J Immunopathol
Pharmacol. 25:345–353. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Su X, Wu W, Huang Z, Hu J, Lei P, Yu C,
Zhao YF and Li Y: Hydrogen peroxide can be generated by tau in the
presence of Cu(II). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 358:661–665. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cha M, Han S, Son S, Hong H, Cha Y, Byun J
and Inhee M: Mitochondria-specific accumulation of amyloid β
induces mitochondrial dysfunction leading to apoptotic cell death.
PLoS One. 7:e349292012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Borghi R, Patriarca S, Traverso N, Piccini
A, Storace D, Garuti A, Cirmena G, Odetti P and Tabaton M: The
increased activity of BACE1 correlates with oxidative stress in
Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 28:1009–1014. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ribeiro MF, Genebra T, Rego AC, Rodrigues
CMP and Solá S: Amyloid β peptide compromises neural stem cell fate
by irreversibly disturbing mitochondrial oxidative state and
blocking mitochondrial biogenesis and dynamics. Mol Neurobiol.
56:3922–3936. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jahanshahi M, Sadeghi Y, Hosseini A,
Naghdi N and Marjani A: The effect of spatial learning on the
number of astrocytes in the CA3 subfield of the rat hippocampus.
Singapore Med J. 49:388–391. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kawano H, Oyabu K, Yamamoto H, Eto K,
Adaniya Y, Kubota K, Watanabe T, Hiranoiwata A, Nabekura J,
Katsurabayashi S and Iwasaki K: Astrocytes with previous chronic
exposure to amyloid β-peptide fragment 1–40 suppress excitatory
synaptic transmission. J Neurochem. 143:624–634. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang N, Xiong WW, Yuan X and Zhang W:
Culture method of rat fetal hippocampal neurons and astrocytes.
Acta Neuropharmacol. 7:24–28. 2017.
|
|
30
|
Aguirre-Rueda D, Guerra-Ojeda S, Aldasoro
M, Iradi A, Obrador E, Ortega A, Mauricio MD, Vila JM and Valles
SL: Astrocytes protect neurons from Aβ1-42 peptide-induced
neurotoxicity increasing TFAM and PGC-1 and decreasing PPAR-γ and
SIRT-1. International Journal of Medical ences. 12:48–56.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hardy J and Higgins G: Alzheimer's
disease: The amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science. 256:184–185.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jan A, Gokce O, Luthi-Carter R and Lashuel
HA: The ratio of monomeric to aggregated forms of Abeta40 and
Abeta42 is an important determinant of amyloid-beta aggregation,
fibrillogenesis, and toxicity. J Biol Chem. 283:28176–28189. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mulder SD, Veerhuis R, Blankenstein MA and
Nielsen HM: The effect of amyloid associated proteins on the
expression of genes involved in amyloid-β clearance by adult human
astrocytes. Exp Neurol. 233:373–379. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Paris D, Beaulieu-Abdelahad D, Bachmeier
C, Reed J, Ait-Ghezala G, Bishop A, Chao J, Mathura V, Crawford F
and Mullan M: Anatabine lowers Alzheimer's Aβ production in vitro
and in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 670:384–391. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mohamed A and Chaves EPd: Aβ
internalization by neurons and glia. Int J Alzheimers Dis.
2011:1279842011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fan J, Donkin J and Wellington C: Greasing
the wheels of Abeta clearance in Alzheimer's disease: The role of
lipids and apolipoprotein E. Biofactors. 35:239–248. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Phillips EC, Croft CL, Kurbatskaya K,
O'Neill MJ, Hutton ML, Hanger DP, Garwood CJ and Noble W:
Astrocytes and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease. Biochem
Soc Trans. 42:1321–1325. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Unterberger U, Höftberger R, Gelpi E,
Flicker H, Budka H and Voigtländer T: Endoplasmic reticulum stress
features are prominent in Alzheimer disease but not in prion
diseases in vivo. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 65:348–357. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Doyle KM, Kennedy D, Gorman AM, Gupta S,
Healy S and Samali A: Unfolded proteins and endoplasmic reticulum
stress in neurodegenerative disorders. J Cell Mol Med.
15:2025–2039. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lindholm D, Wootz H and Korhonen L: ER
stress and neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Death Differ.
3:385–392. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Torres L, Quaglio NB, de Souza GT, Garcia
RT, Dati LM, Moreira WL, Loureiro AP, de Souza-Talarico JN, Smid J,
Porto CS, et al: Peripheral oxidative stress biomarkers in mild
cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimer's Dis.
26:59–68. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Smith CD, Carney JM, Tatsumo T, Stadtman
ER, Floyd RA and Markesbery WR: Protein oxidation in aging brain.
Ann N Y Acad Sci. 663:110–119. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Choi D, Lee Y, Hong JT and Lee H:
Antioxidant properties of natural polyphenols and their therapeutic
potentials for Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res Bull. 87:144–153.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Silva DF, Selfridge JE, Lu J, Lezi E and
Swerdlow RH: Mitochondrial abnormalities in Alzheimer's Disease.
Possible targets for therapeutic intervention. Adv Pharmacol.
64:83–126. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Darvesh AS, Carroll RT, Bishayee A,
Geldenhuys WJ and Van der Schyf CJ: Oxidative stress and
Alzheimer's disease: Dietary polyphenols as potential therapeutic
agents. Expert Rev Neurother. 10:729–745. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Aliev G, Palacios HH, Walrafen B, Lipsitt
AE, Obrenovich ME and Morales L: Brain mitochondria as a primary
target in the development of treatment strategies for Alzheimer
disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 41:1989–2004. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Milton NG: Role of hydrogen peroxide in
the aetiology of Alzheimer's disease: Implications for treatment.
Drugs Aging. 21:81–100. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kontush A: Amyloid-beta: An antioxidant
that becomes a pro-oxidant and critically contributes to
Alzheimer's disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 31:1120–1131. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Perry G, Cash AD and Smith MA: Alzheimer
disease and oxidative stress. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2:120–123. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Honda K, Smith MA, Zhu X, Baus D, Merrick
WC, Tartakoff AM, Hattier T, Harris PL, Siedlak SL, Fujioka H, et
al: Ribosomal RNA in Alzheimer disease is oxidized by bound
redox-active iron. J Biol Chem. 280:20978–20986. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Casley CS, Canevari L, Land JM, Clark JB
and Sharpe MA: Beta-amyloid inhibits integrated mitochondrial
respiration and key enzyme activities. J Neurochem. 80:91–100.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gegg ME, Clark JB and Heales SJ:
Co-culture of neurones with glutathione deficient astrocytes leads
to increased neuronal susceptibility to nitric oxide and increased
glutamate-cysteine ligase activity. Brain Res. 1036:1–6. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Tian Y, Wang W, Xu L, Li H, Wei Y, Wu Q
and Jia J: Activation of Nrf2/ARE pathway alleviates the cognitive
deficits in PS1V97L-Tg mouse model of Alzheimer's disease through
modulation of oxidative stress. J Neurosci Res. 97:492–505. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Mccubrey JA, Lahair MM and Franklin RA:
Reactive oxygen species-induced activation of the MAP kinase
signaling pathways. Antioxid Redox Signal. 8:1775–1789. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Eckert A, Hauptmann S, Scherping I, Rhein
V, Mullerspahn F, Gotz J and Muller WE: Soluble beta-amyloid leads
to mitochondrial defects in amyloid precursor protein and tau
transgenic mice. Neurodegener Dis. 5:157–159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Schmidt C, Lepsverdize E, Chi SL, Das AM
and Schachner M: Amyloid precursor protein and amyloid beta-peptide
bind to ATP synthase and regulate its activity at the surface of
neural cells. Mol Psychiatry. 13:953–969. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Coskuner O and Murray IV: Adenosine
triphosphate (ATP) reduces amyloid-β protein misfolding in vitro. J
Alzheimers Dis Jad. 41:561–574. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Müller WEG, Wang S, Ackermann M, Neufurth
M, Steffen R, Mecja E, Muñoz-Espí R, Feng Q, Schröder HC and Wang
X: Rebalancing β-amyloid-induced decrease of ATP level by amorphous
nano/micro polyphosphate: Suppression of the neurotoxic effect of
amyloid β-protein fragment 25–35. Int J Mol Sci. 18:21542017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Du H and Yan SS: Mitochondrial
permeability transition pore in Alzheimer's disease: Cyclophilin D
and amyloid beta. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1802:198–204. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ke R, Xu Q, Li C, Luo L and Huang D:
Mechanisms of AMPK in the maintenance of ATP balance during energy
metabolism. Cell Biol Int. 42:384–392. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ou Z, Kong X, Sun X, He X, Zhang L, Gong
Z, Huang J, Xu B, Long D, Li J, et al: Metformin treatment prevents
amyloid plaque deposition and memory impairment in APP/PS1 mice.
Brain Behav Immun. 69:351–363. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Sun X, He G and Song W: BACE2, as a novel
APP theta-secretase, is not responsible for the pathogenesis of
Alzheimer's disease in Down syndrome. FASEB J. 20:1369–1376. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Coimbra JRM, Marques DFF, Baptista SJ,
Pereira CMF, Moreira PI, Dinis TCP, Santos AE and Salvador JAR:
Highlights in BACE1 inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease treatment.
Front Chem. 6:1782018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Jeon SM: Regulation and function of AMPK
in physiology and diseases. Exp Mol Med. 48:e2452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Finck BN and Kelly DP: PGC-1 coactivators:
Inducible regulators of energy metabolism in health and disease. J
Clin Invest. 116:615–622. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Tiraby C and Langin D: Conversion from
white to brown adipocytes: A strategy for the control of fat mass?
Trends Endocrinol Metab. 14:439–441. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Austin S and St-Pierre J: PGC1α and
mitochondrial metabolism-emerging concepts and relevance in ageing
and neurodegenerative disorders. J Cell Sci. 125:4963–4971. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ettcheto M, Petrov D, Pedros I, Alva N,
Carbonell T, Beaszarate C, Pallas M, Auladell C, Folch J and Camins
A: Evaluation of neuropathological effects of a high-fat diet in a
presymptomatic Alzheimer's disease stage in APP/PS1 mice. J
Alzheimer's Dis. 54:233–251. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Li Z, Li H, Zhao CH, Lv C, Zhong CJ, Xin
WF and Zhang WS: Protective effect of Notoginsenoside R1 on an
APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease by up-regulating insulin
degrading enzyme and inhibiting Aβ accumulation. CNS Neurol Disord
Drug Targets. 14:360–369. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Camacho IE, Serneels L, Spittaels K,
Merchiers P, Dominguez D and De Strooper B: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma induces a clearance mechanism
for the amyloid-beta peptide. J Neurosci. 24:10908–10917. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Mamelak M: Energy and the Alzheimer brain.
Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 75:297–313. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Biswas J, Gupta S, Verma DK and Singh S:
Streptozotocin alters glucose transport, connexin expression and
endoplasmic reticulum functions in neurons and astrocytes.
Neuroscience. 356:151–166. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Park-York MJ, Kim Y and York DA: Cage food
location alters energy balance and endoplasmic reticulum stress in
the brain of mice. Physiol Behav. 106:158–163. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Grahame Hardie D: AMP-activated protein
kinase: A key regulator of energy balance with many roles in human
disease. J Intern Med. 276:543–559. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Boß M, Newbatt Y, Gupta S, Collins I,
Brüne B and Namgaladze D: AMPK-independent inhibition of human
macrophage ER stress response by AICAR. Sci Rep. 6:321112016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Yeh CH, Chen TP, Wang YC, Lin YM and Fang
SW: AMP-activated protein kinase activation during
cardioplegia-induced hypoxia/reoxygenation injury attenuates
cardiomyocytic apoptosis via reduction of endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Mediators Inflamm. 2010:1306362010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Gao F, Chen J and Zhu H: A potential
strategy for treating atherosclerosis: Improving endothelial
function via AMP-activated protein kinase. Sci China Life Sci.
61:1024–1029. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Cao SS and Kaufman RJ: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress and oxidative stress in cell fate decision and
human disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 21:396–413. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Zheng W, Wang B, Si M, Zou H, Song R, Gu
J, Yuan Y, Liu X, Zhu G, Bai J, et al: Zearalenone altered the
cytoskeletal structure via ER stress-autophagy-oxidative stress
pathway in mouse TM4 Sertoli cells. Sci Rep. 8:33202018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Wu P, Yan Y, Ma L, Hou B, He Y, Zhang L,
Niu Z, Song J, Pang X and Yang X: Effects of the Nrf2 modulator
salvianolic acid A alone or combined with metformin on
diabetes-associated macrovascular and renal injury. J Biol Chem.
291:22288–22301. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|