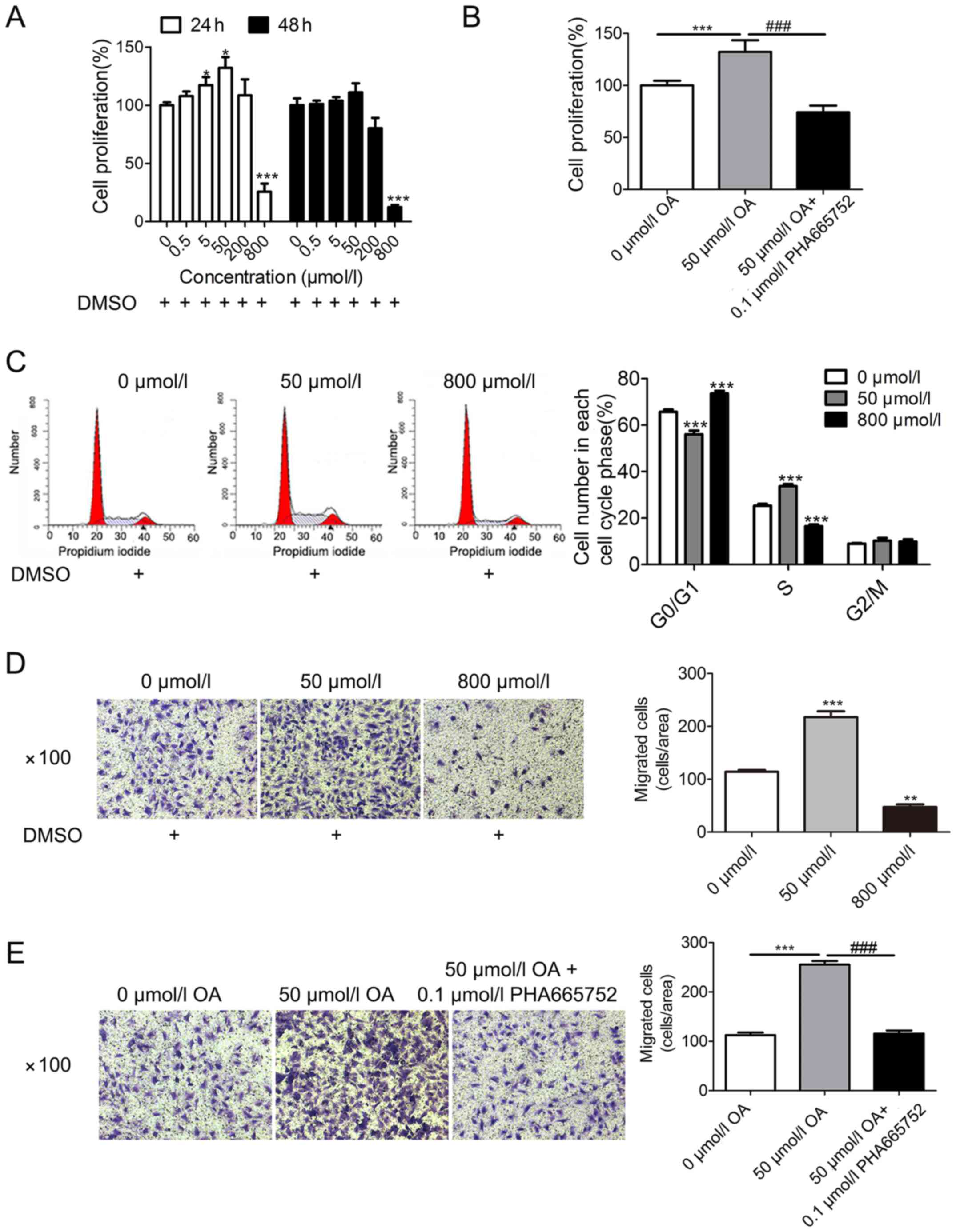
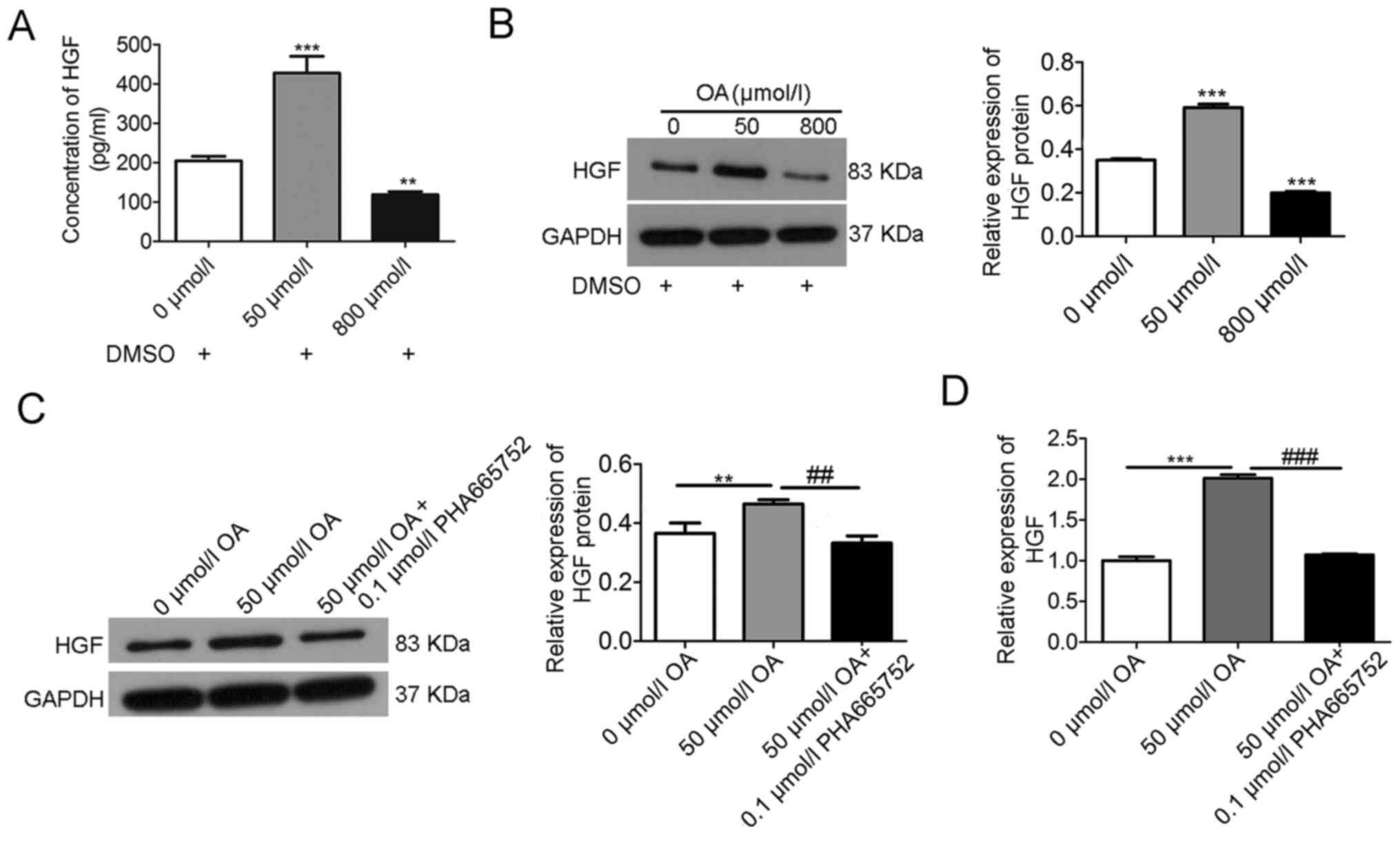
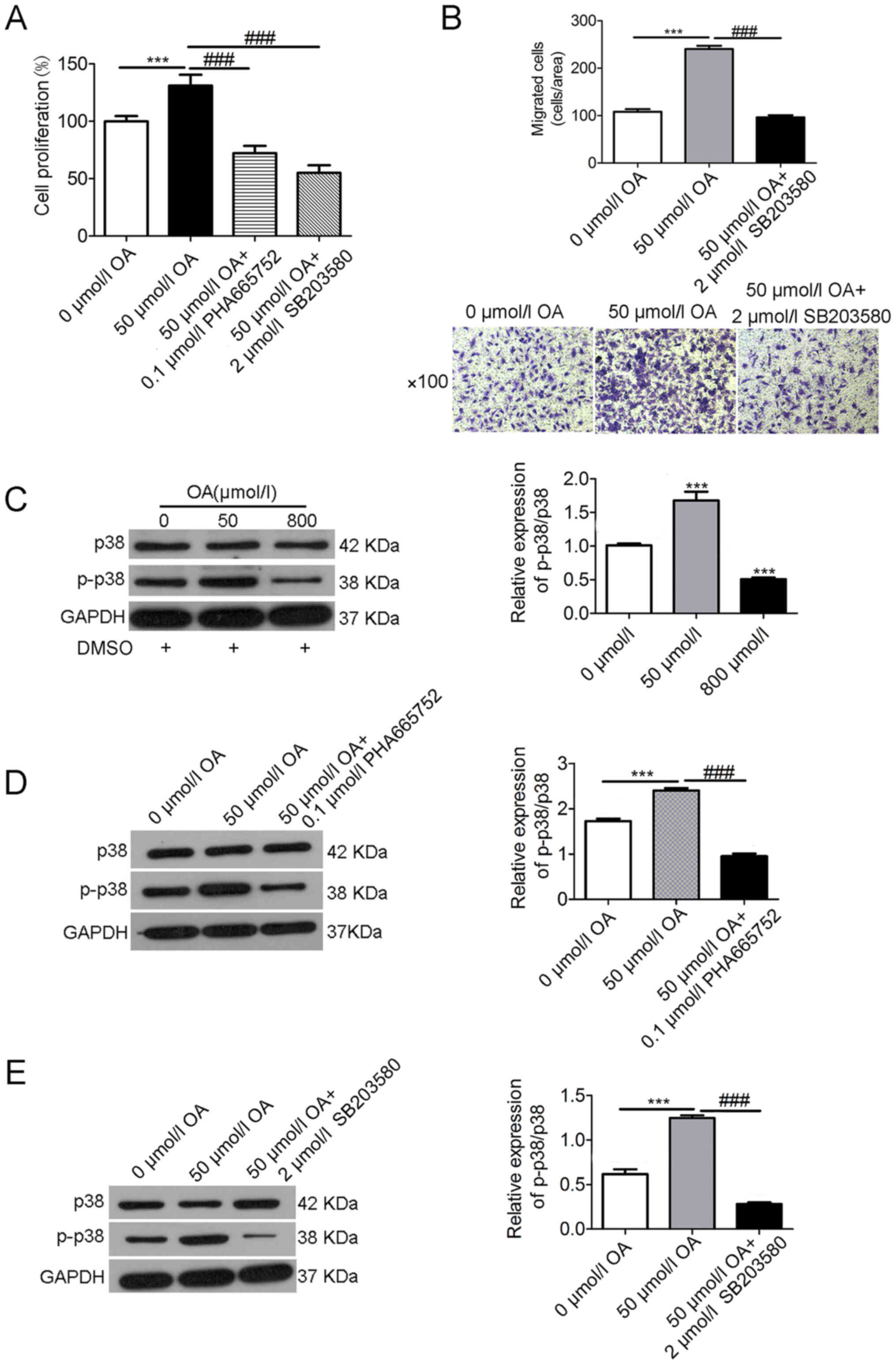
|
1
|
Zhao WH, Zhang J, You Y, Man QQ, Li H,
Wang CR, Zhai Y, Li Y, Jin SG and Yang XG: Epidemiologic
characteristics of dyslipidemia in people aged 18 years and over in
China. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 39:306–310. 2005.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Després JP and Lemieux I: Abdominal
obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature. 444:881–887. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Xie C, Wang ZC, Liu XF and Yang MS: The
common biological basis for common complex diseases: Evidence from
lipoprotein lipase gene. Eur J Hum Genet. 18:3–7. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hardy S, Langelier Y and Prentki M: Oleate
activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and promotes proliferation
and reduces apoptosis of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells, whereas
palmitate has opposite effects. Cancer Res. 60:6353–6358.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sargsyan E, Artemenko K, Manukyan L,
Bergquist J and Bergsten P: Oleate protects beta-cells from the
toxic effect of palmitate by activating pro-survival pathways of
the ER stress response. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1861:1151–1160. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ross R: The pathogenesis of
atherosclerosis - an updata. N Engl J Med. 314:488–500. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Basatemur GL, Jørgensen HF, Clarke MCH,
Bennett MR and Mallat Z: Vascular smooth muscle cells in
atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. 16:727–744. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bennett MR, Sinha S and Owens GK: Vascular
smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 118:692–702.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou XX, Zhou XH, Yang HM and Su PQ: High
triglyceride serum promotes the proliferation of vascular smooth
muscle cells. Chin J Cardiol. 28:3162000.(In Chinese).
doi:10.3760/j:issn:0253-3758.2000.04.024.
|
|
10
|
Yin Z, Gao HK, Li LS, Luan RH and Wang HC:
Effects of atorvastatin on hyperlipemic serum induced proliferation
of vascular smooth muscle cells in rats. Chin Hear J. 20:180–183.
2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Mattern HM and Hardin CD: Vascular
metabolic dysfunction and lipotoxicity. Physiol Res. 56:149–158.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang YQ and Yang MS: Effects of glyceryl
trioleate on the proliferation of rat aortic smooth muscle cells. J
Chongqing Med Univ. 39:1384–1390. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Yang MS and Wang YQ: Bidirectional effects
of medium chain triglyceride on the proliferation of vascular
smooth muscle cells. Chin J Arterioscler. 24:551–556. 2016.(In
Chinese). doi: 10.13406/jcnki.cyxb.001052. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liotti A, Cosimato V, Mirra P, Calì G,
Conza D, Secondo A, Luongo G, Terracciano D, Formisano P, Beguinot
F, et al: Oleic acid promotes prostate cancer malignant phenotype
via the G protein-coupled receptor FFA1/GPR40. J Cell Physiol.
233:7367–7378. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang C, Lim W, Bazer FW and Song G: Oleic
acid stimulation of motility of human extravillous trophoblast
cells is mediated by stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 activity. Mol Hum
Reprod. 23:755–770. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nakamura T, Sakai K, Nakamura T and
Matsumoto K: Hepatocyte growth factor twenty years on: Much more
than a growth factor. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26 (Suppl
1):S188–S202. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Forte G, Minieri M, Cossa P, Antenucci D,
Sala M, Gnocchi V, Fiaccavento R, Carotenuto F, De Vito P, Baldini
PM, et al: Hepatocyte growth factor effects on mesenchymal stem
cells: Proliferation, migration, and differentiation. Stem Cells.
24:23–33. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Greene EL, Lu G, Zhang D and Egan BM:
Signaling events mediating the additive effects of oleic acid and
angiotensin II on vascular smooth muscle cell migration.
Hypertension. 37:308–312. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wan Q, Liu Z and Yang Y: Puerarin inhibits
vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation induced by fine
particulate matter via suppressing of the p38 MAPK signaling
pathway. BMC Complement Altern Med. 18:1462018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kyriakis JM and Avruch J: Mammalian MAPK
signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation:
A 10-year update. Physiol Rev. 92:689–737. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cuenda A and Rousseau S: p38 MAP-kinases
pathway regulation, function and role in human diseases. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1773:1358–1375. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Karin M and Gallagher E: From JNK to pay
dirt: Jun kinases, their biochemistry, physiology and clinical
importance. IUBMB Life. 57:283–295. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jacob T, Ascher E, Alapat D, Olevskaia Y
and Hingorani A: Activation of p38MAPK signaling cascade in a VSMC
injury model: Role of p38MAPK inhibitors in limiting VSMC
proliferation. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 29:470–478. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Awasthi V and King RJ: PKC, p42/p44 MAPK,
and p38 MAPK are required for HGF-induced proliferation of H441
cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 279:L942–L949. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chattopadhyay N, Tfelt-Hansen J and Brown
EM: PKC, p42/44 MAPK and p38 MAPK regulate hepatocyte growth factor
secretion from human astrocytoma cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res.
102:73–82. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yao J, Ke J, Zhou Z, Tan G, Yin Y, Liu M,
Chen J and Wu W: Combination of HGF and IGF-1 promotes connexin 43
expression and improves ventricular arrhythmia after myocardial
infarction through activating the MAPK/ERK and MAPK/p38 signaling
pathways in a rat model. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 9:346–354. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Christensen JG, Schreck R, Burrows J,
Kuruganti P, Chan E, Le P, Chen J, Wang X, Ruslim L, Blake R, et
al: A selective small molecule inhibitor of c-Met kinase inhibits
c-Met-dependent phenotypes in vitro and exhibits cytoreductive
antitumor activity in vivo. Cancer Res. 63:7345–7355.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yun MR, Lee JY, Park HS, Heo HJ, Park JY,
Bae SS, Hong KW, Sung SM and Kim CD: Oleic acid enhances vascular
smooth muscle cell proliferation via phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Pharmacol Res. 54:97–102. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qi W, Ding D and Salvi RJ: Cytotoxic
effects of dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) on cochlear organotypic
cultures. Hear Res. 236:52–60. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xiang Q, Zhen Z, Deng DY, Wang J and Chen
Y, Li J, Zhang Y, Wang F, Chen N, Chen H and Chen Y: Tivantinib
induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis by disrupting tubulin
polymerization in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
34:1182015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sreekanth GP, Chuncharunee A,
Sirimontaporn A, Panaampon J, Noisakran S, Yenchitsomanus PT and
Limjindaporn T: SB203580 modulates p38 MAPK signaling and dengue
virus-induced liver injury by reducing MAPKAPK2, HSP27, and ATF2
phosphorylation. PLoS One. 11:e01494862016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
He T, Liu S, Chen S, Ye J, Wu X, Bian Z
and Chen X: The p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 abrogates tumor
necrosis factor-induced proliferative expansion of mouse
CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. Front Immunol.
9:15562018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu T, Li Q, Sun Q, Zhang Y, Yang H, Wang
R, Chen L and Wang W: MET inhibitor PHA-665752 suppresses the
hepatocyte growth factor-induced cell proliferation and
radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 449:49–54. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xiang QF, Zhan MX, Li Y, Liang H, Hu C,
Huang YM, Xiao J, He X, Xin YJ, Chen MS and Lu LG: Activation of
MET promotes resistance to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells via the AKT/ERK1/2-EGR1 pathway. Artif Cells Nanomed
Biotechnol. 47:83–89. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bielinski SJ, Berardi C, Decker PA, Larson
NB, Bell EJ, Pankow JS, Sale MM, Tang W, Hanson NQ, Wassel CL, et
al: Hepatocyte growth factor demonstrates racial heterogeneity as a
biomarker for coronary heart disease. Heart. 103:1185–1193. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bell EJ, Larson NB, Decker PA, Pankow JS,
Tsai MY, Hanson NQ, Wassel CL, Longstreth WT Jr and Bielinski SJ:
Hepatocyte growth factor is positively associated with risk of
stroke: The MESA (multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis). Stroke.
47:2689–2694. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gallo S, Sala V, Gatti S and Crepaldi T:
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of HGF/Met in the cardiovascular
system. Clin Sci (Lond). 129:1173–1193. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bell EJ, Decker PA, Tsai MY, Pankow JS,
Hanson NQ, Wassel CL, Larson NB, Cohoon KP, Budoff MJ, Polak JF, et
al: Hepatocyte growth factor is associated with progression of
atherosclerosis: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA).
Atherosclerosis. 272:162–167. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nakamura T and Mizuno S: The discovery of
hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and its significance for cell
biology, life sciences and clinical medicine. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B
Phys Biol Sci. 86:588–610. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Smolen GA, Sordella R, Muir B, Mohapatra
G, Barmettler A, Archibald H, Kim WJ, Okimoto RA, Bell DW, Sgroi
DC, et al: Amplification of MET may identify a subset of cancers
with extreme sensitivity to the selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor
PHA-665752. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2316–2321. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mukohara T, Civiello G, Davis IJ, Taffaro
ML, Christensen J, Fisher DE, Johnson BE and Jänne PA: Inhibition
of the met receptor in mesothelioma. Clin Cancer Res. 11:8122–8130.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lu G, Meier KE, Jaffa AA, Rosenzweig SA
and Egan BM: Oleic acid and angiotensin II induce a synergistic
mitogenic response in vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertension.
31:978–985. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lu G, Greene EL, Nagai T and Egan BM:
Reactive oxygen species are critical in the oleic acid-mediated
mitogenic signaling pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells.
Hypertension. 32:1003–1010. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ahn HJ, Park J, Song JS, Ju MK, Kim MS, Ha
H, Song KH and Kim YS: Mycophenolic acid inhibits oleic
acid-induced vascular smooth muscle cell activation by inhibiting
cellular reactive oxygen species. Transplantation. 84:634–638.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ou TT, Lin MC, Wu CH, Lin WL and Wang CJ:
Gallic acid attenuates oleic acid-induced proliferation of vascular
smooth muscle cell through regulation of AMPK-eNOS-FAS signaling.
Curr Med Chem. 20:3944–3953. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lin MC, Ou TT, Chang CH, Chan KC and Wang
CJ: Protocatechuic acid inhibits oleic acid-induced vascular smooth
muscle cell proliferation through activation of AMP-activated
protein kinase and cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase. J Agric Food
Chem. 63:235–241. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhu Y, Schwarz S, Ahlemeyer B, Grzeschik
S, Klumpp S and Krieglstein J: Oleic acid causes apoptosis and
dephosphorylates Bad. Neurochem Int. 46:127–135. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Carrillo C, Cavia Mdel M and Alonso-Torre
SR: Antitumor effect of oleic acid; mechanisms of action: A review.
Nutr Hosp. 27:1860–1865. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Cheng CI, Lee YH, Chen PH, Lin YC, Chou MH
and Kao YH: Free fatty acids induce autophagy and LOX-1
upregulation in cultured aortic vascular smooth muscle cells. J
Cell Biochem. 118:1249–1261. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Artwohl M, Lindenmair A, Roden M,
Waldhäusl WK, Freudenthaler A, Klosner G, Ilhan A, Luger A and
Baumgartner-Parzer SM: Fatty acids induce apoptosis in human smooth
muscle cells depending on chain length, saturation, and duration of
exposure. Atherosclerosis. 202:351–362. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang C, Wang W, Lin J, Xiao J and Tian Y:
lncRNA CCAT1 promotes bladder cancer cell proliferation, migration
and invasion. Int Braz J Urol. 45:549–559. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Belal SA, Sivakumar AS, Kang DR, Cho S,
Choe HS and Shim KS: Modulatory effect of linoleic and oleic acid
on cell proliferation and lipid metabolism gene expressions in
primary bovine satellite cells. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul).
22:324–333. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|