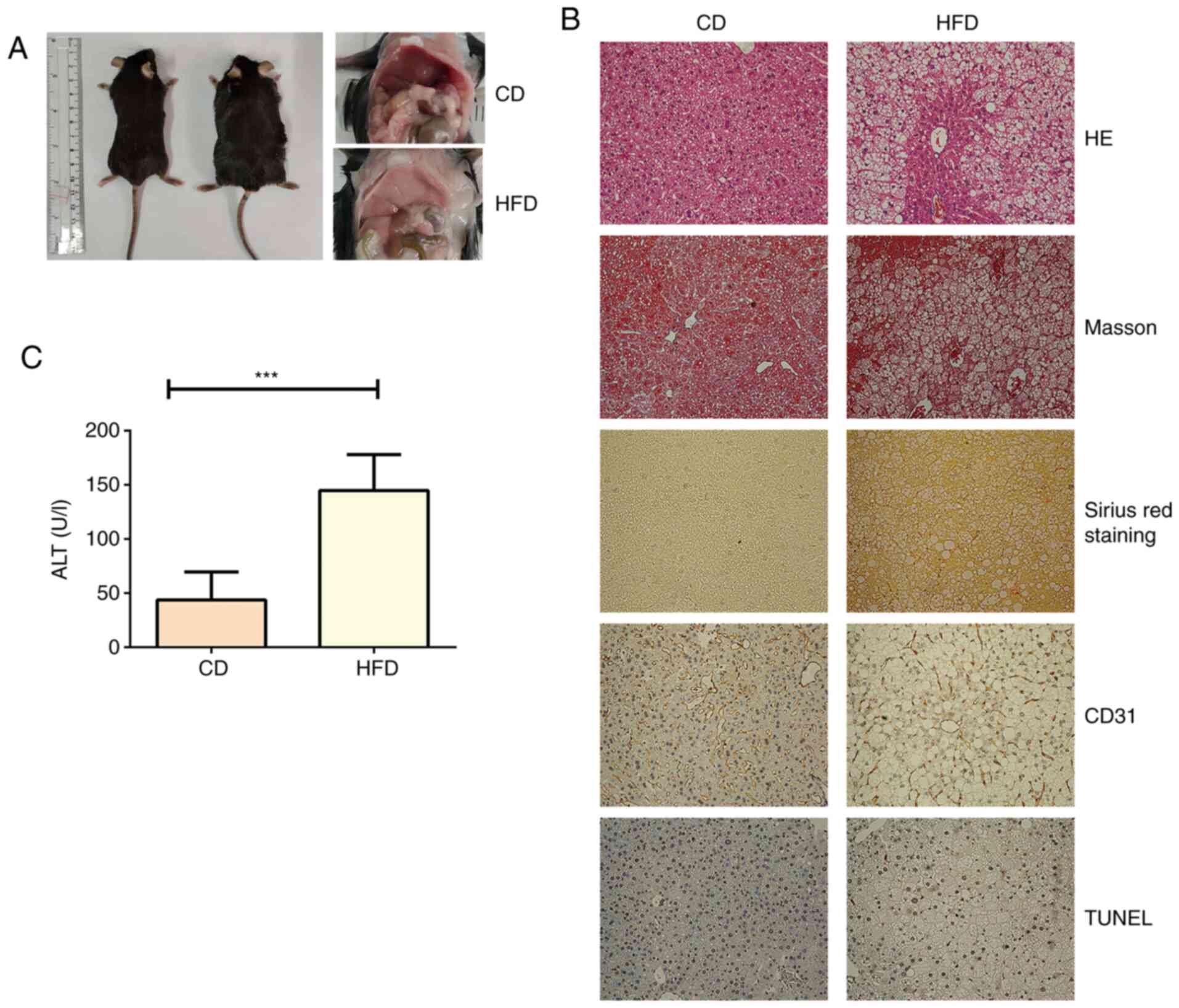
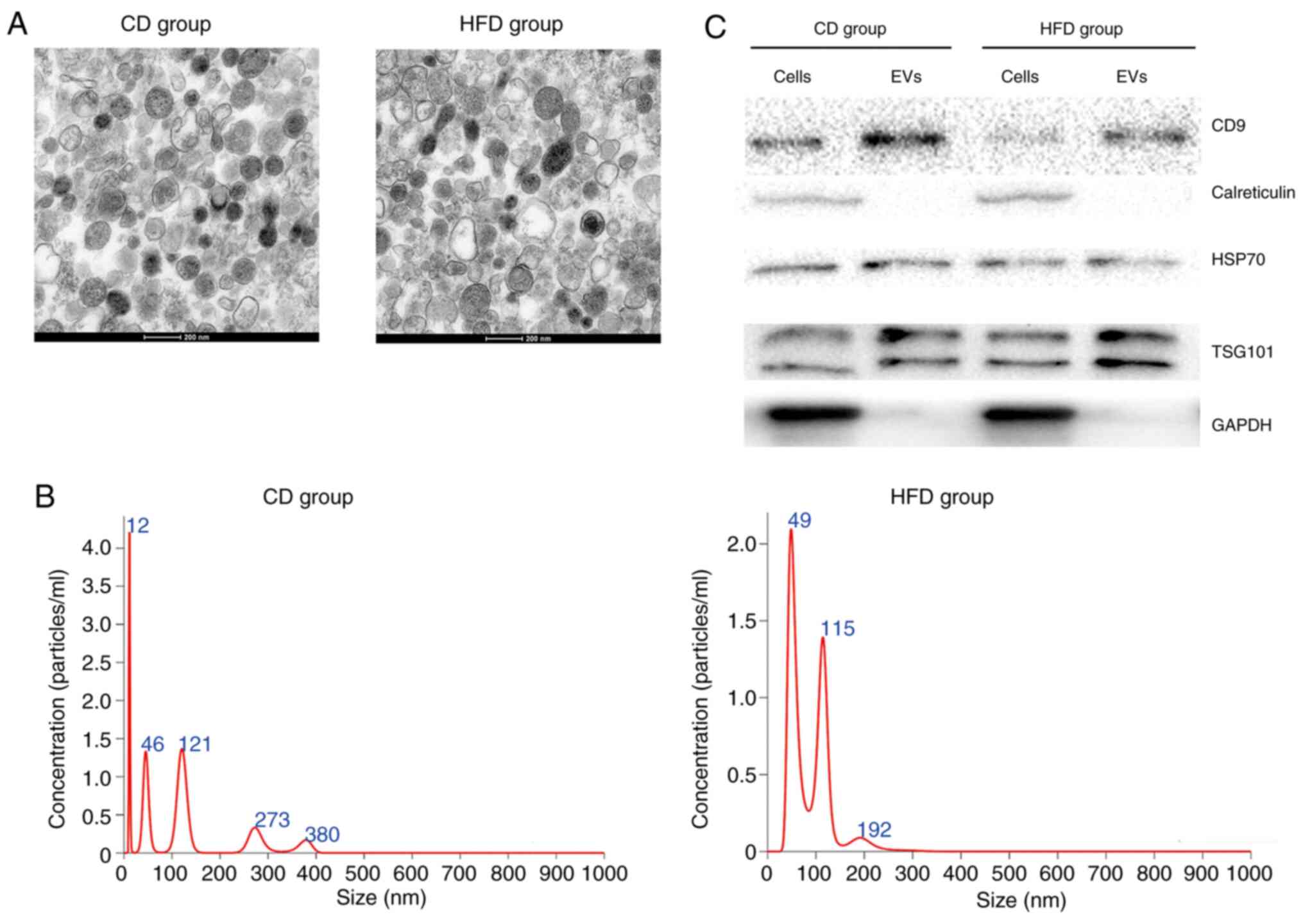
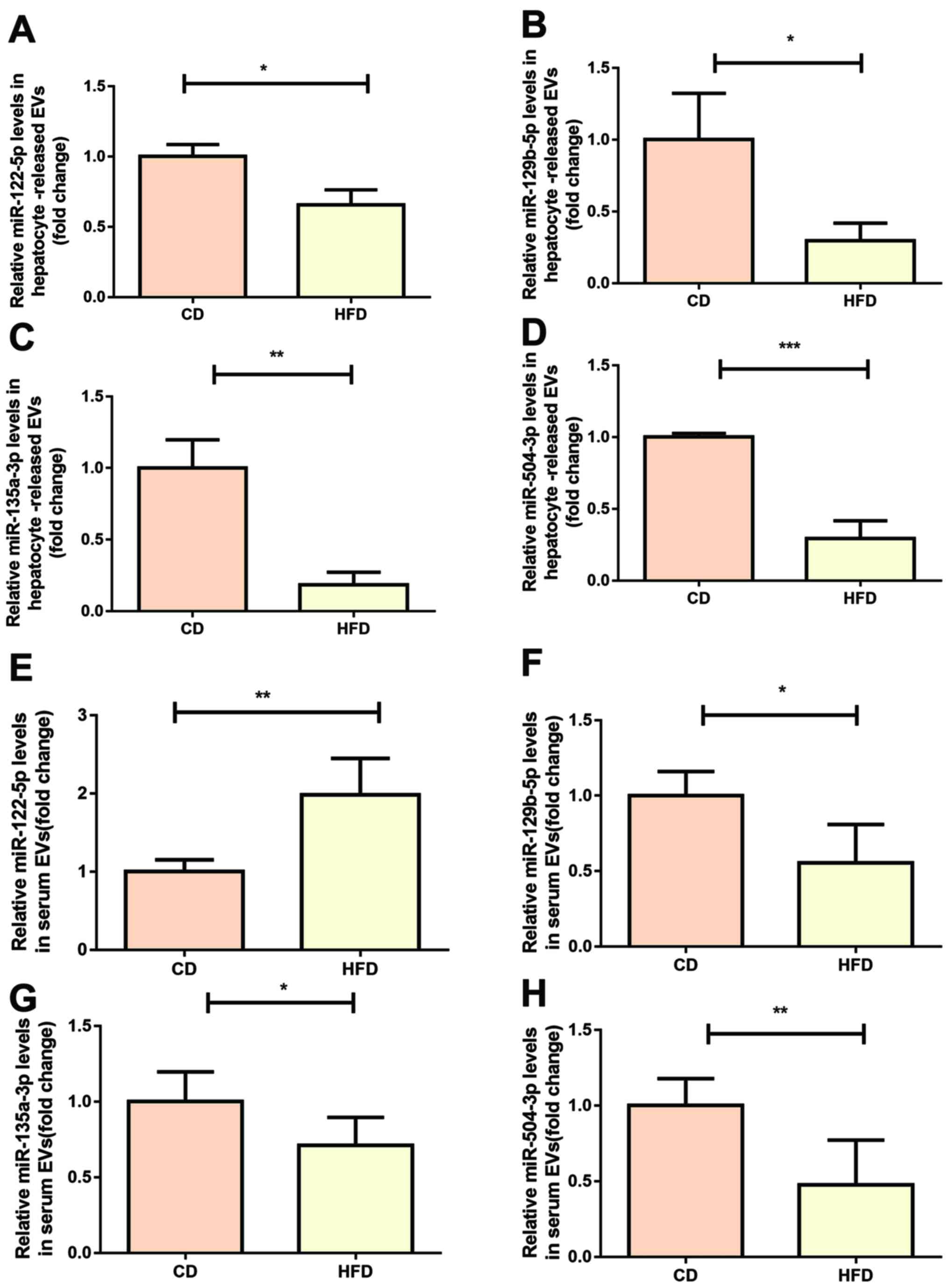
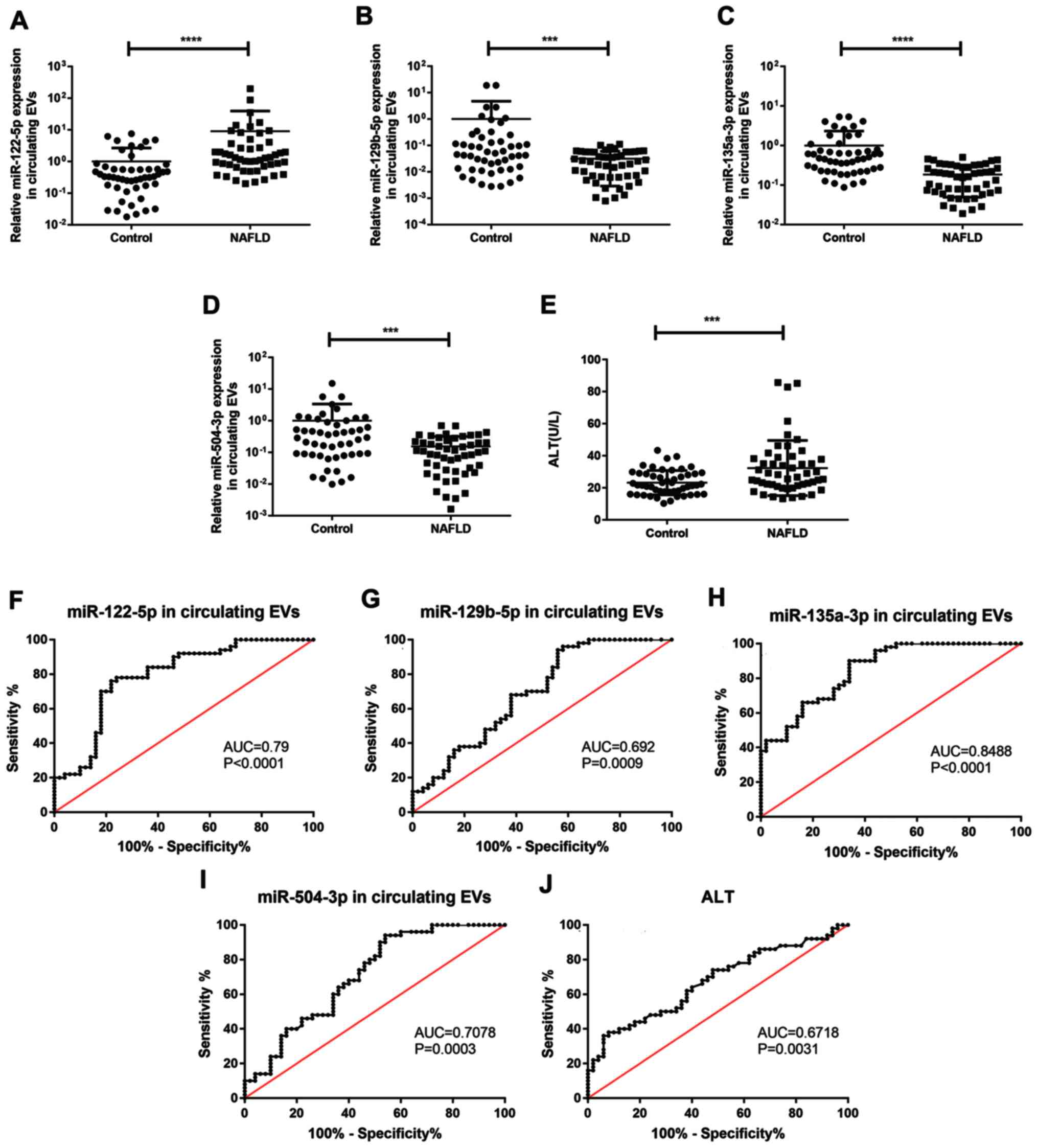
|
1
|
Albhaisi S and Sanyal A: Recent advances
in understanding and managing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
F1000Res. 7:F1000 Faculty Rev-720. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lucas C, Lucas G, Lucas N, Krzowska-Firych
J and Tomasiewicz K: A systematic review of the present and future
of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Exp Hepatol. 4:165–174.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Younossi Z: Non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease-A global public health perspective. J Hepatol. 70:531–544.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fan JG and Farrell GC: Epidemiology of
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in China. J Hepatol. 50:204–210.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fan JG: Epidemiology of alcoholic and
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in China. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
28 (Suppl 1):S11–S17. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Adams LA, Harmsen S, St Sauver JL,
Charatcharoenwitthaya P, Enders FB, Therneau T and Angulo P:
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease increases risk of death among
patients with diabetes: A community-based cohort study. Am J
Gastroenterol. 105:1567–1573. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Katsiki N, Athyros VG, Karagiannis A and
Mikhailidis DP: Managing the combination of non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease and metabolic syndrome. Expert Opin Pharmacother.
13:287–290. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Byrne CD and Targher G: NAFLD: A
multisystem disease. J Hepatol. 62 (1 Suppl):S47–S64. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mazhar K: The future of nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease treatment. Med Clin North Am. 103:57–69. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
He Z, Yang JJ, Zhang R, Li HT, Wu L, Jiang
F, Jia WP and Hu C: Circulating miR-29b positively correlates with
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a Chinese population. J Dig
Dis. 20:189–195. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
DiStefano JK and Gerhard GS: Circulating
microRNAs in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:161–163. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yamada H, Suzuki K, Ichino N, Ando Y,
Sawada A, Osakabe K, Sugimoto K, Ohashi K, Teradaira R, Inoue T, et
al: Associations between circulating microRNAs (miR-21, miR-34a,
miR-122 and miR-451) and non-alcoholic fatty liver. Clin Chim Acta.
424:99–103. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu CH, Ampuero J, Gil-Gomez A,
Montero-Vallejo R, Rojas Á, Muñoz-Hernández R, Gallego-Durán R and
Romero-Gómez M: miRNAs in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol.
69:1335–1348. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tan Y, Ge G, Pan T, Wen D and Gan J: A
pilot study of serum microRNAs panel as potential biomarkers for
diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS One.
9:e1051922014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Afonso MB, Rodrigues PM, Simao AL and
Castro RE: Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers in
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Clin Med. 5:302016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
He Y, Deng F, Yang S, Wang D, Chen X,
Zhong S, Zhao J and Tang J: Exosomal microRNA: A novel biomarker
for breast cancer. Biomark Med. 12:177–188. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang G, Lin G, Zhu Y, Duan W and Jin D:
Emerging technologies for profiling extracellular vesicle
heterogeneity. Lab Chip. 20:2423–2437. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ibáñez F, Ureña-Peralta JR, Costa-Alba P,
Torres JL, Laso FJ, Marcos M, Guerri C and Pascual M: Circulating
MicroRNAs in extracellular vesicles as potential biomarkers of
alcohol-induced neuroinflammation in adolescence: Gender
differences. Int J Mol Sci. 21:67302020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Nedaeinia R, Manian M, Jazayeri MH,
Ranjbar M, Salehi R, Sharifi M, Mohaghegh F, Goli M, Jahednia SH,
Avan A and Ghayour-Mobarhan M: Circulating exosomes and exosomal
microRNAs as biomarkers in gastrointestinal cancer. Cancer Gene
Ther. 24:48–56. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Takahasi K, Iinuma H, Wada K, Minezaki S,
Kawamura S, Kainuma M, Ikeda Y, Shibuya M, Miura F and Sano K:
Usefulness of exosome-encapsulated microRNA-451a as a minimally
invasive biomarker for prediction of recurrence and prognosis in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci.
25:155–161. 2018. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yoshikawa M, Iinuma H, Umemoto Y,
Yanagisawa T, Matsumoto A and Jinno H: Exosome-encapsulated
microRNA-223-3p as a minimally invasive biomarker for the early
detection of invasive breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 15:9584–9592.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang W, Ni M, Su Y, Wang H, Zhu S, Zhao A
and Li G: MicroRNAs in serum exosomes as potential biomarkers in
clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol Focus. 4:412–419. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fu Q, Li Y, Jiang H, Shen Z, Gao R, He Y,
Liu Y, Xu K and Yang T: Hepatocytes derived extracellular vesicles
from high-fat diet induced obese mice modulate genes expression and
proliferation of islet β cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
516:1159–1166. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tessitore A, Cicciarelli G, Del Vecchio F,
Gaggiano A, Verzella D, Fischietti M, Mastroiaco V, Vetuschi A,
Sferra R, Barnabei R, et al: MicroRNA expression analysis in high
fat diet-induced NAFLD-NASH-HCC progression: Study on C57BL/6J
mice. BMC Cancer. 16:32016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tasci I, Mas MR, Vural SA, Deveci S,
Comert B, Alcigir G, Mas N, Akay C, Bozdayi M, Yurdaydin C, et al:
Pegylated interferon-alpha plus taurine in treatment of rat liver
fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol. 13:3237–3244. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Brunt EM, Kleiner DE, Wilson LA, Belt P
and Neuschwander-Tetri BA; NASH Clinical Research Network (CRN), :
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) activity score and the
histopathologic diagnosis in NAFLD: Distinct clinicopathologic
meanings. Hepatology. 53:810–820. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pigeon C, Ilyin G, Courselaud B, Leroyer
P, Turlin B, Brissot P and Loréal O: A new mouse liver-specific
gene, encoding a protein homologous to human antimicrobial peptide
hepcidin, is overexpressed during iron overload. J Biol Chem.
276:7811–7819. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Angulo P: GI epidemiology: Nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 25:883–889. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mofrad P, Contos MJ, Haque M, Sargeant C,
Fisher RA, Luketic VA, Sterling RK, Shiffman ML, Stravitz RT and
Sanyal AJ: Clinical and histologic spectrum of nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease associated with normal ALT values. Hepatology.
37:1286–1292. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vogel A, Cervantes A, Chau I, Daniele B,
Llovet JM, Meyer T, Nault JC, Neumann U, Ricke J, Sangro B, et al:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for
diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 30:871–873. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Deffieux T, Gennisson JL, Bousquet L,
Corouge M, Cosconea S, Amroun D, Tripon S, Terris B, Mallet V,
Sogni P, et al: Investigating liver stiffness and viscosity for
fibrosis, steatosis and activity staging using shear wave
elastography. J Hepatol. 62:317–324. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Khov N, Sharma A and Riley TR: Bedside
ultrasound in the diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
World J Gastroenterol. 20:6821–6825. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Myers RP, Pomier-Layrargues G, Kirsch R,
Pollett A, Beaton M, Levstik M, Duarte-Rojo A, Wong D, Crotty P and
Elkashab M: Discordance in fibrosis staging between liver biopsy
and transient elastography using the FibroScan XL probe. J Hepatol.
56:564–570. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Myers RP, Pomier-Layrargues G, Kirsch R,
Pollett A, Duarte-Rojo A, Wong D, Beaton M, Levstik M, Crotty P and
Elkashab M: Feasibility and diagnostic performance of the FibroScan
XL probe for liver stiffness measurement in overweight and obese
patients. Hepatology. 55:199–208. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Angulo P: Long-term mortality in
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Is liver histology of any
prognostic significance? Hepatology. 51:373–375. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dongiovanni P, Meroni M, Longo M, Fargion
S and Fracanzani AL: miRNA Signature in NAFLD: A turning point for
a non-invasive diagnosis. Int J Mol Sci. 19:39662018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dorairaj V, Sulaiman S, Abu N and Abdul
Murad N: Extracellular vesicles in the development of the
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An update. Biomolecules.
10:14942020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Banales JM, Feldstein AE, Sanger H,
Lukacs-Kornek V, Szabo G and Kornek M: Extracellular vesicles in
liver diseases: Meeting report from the international liver
congress 2018. Hepatol Commun. 3:305–315. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Garcia-Martinez I, Alen R, Rada P and
Valverde AM: Insights into extracellular vesicles as biomarker of
NAFLD pathogenesis. Front Med (Lausanne). 7:3952020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Otsuka M, Kishikawa T, Yoshikawa T,
Yamagami M, Ohno M, Takata A, Shibata C, Ishibashi R and Koike K:
MicroRNAs and liver disease. J Hum Genet. 62:75–80. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Povero D, Eguchi A, Li H, Johnson CD,
Papouchado BG, Wree A, Messer K and Feldstein AE: Circulating
extracellular vesicles with specific proteome and liver microRNAs
are potential biomarkers for liver injury in experimental fatty
liver disease. PLoS One. 9:e1136512014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Povero D, Eguchi A, Niesman IR, Andronikou
N, de Mollerat du Jeu X, Mulya A, Berk M, Lazic M, Thapaliya S,
Parola M, et al: Lipid-induced toxicity stimulates hepatocytes to
release angiogenic microparticles that require Vanin-1 for uptake
by endothelial cells. Sci Signal. 6:ra882013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Csak T, Bala S, Lippai D, Satishchandran
A, Catalano D, Kodys K and Szabo G: microRNA-122 regulates
hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and vimentin in hepatocytes and
correlates with fibrosis in diet-induced steatohepatitis. Liver
Int. 35:532–541. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Madhavan D, Zucknick M, Wallwiener M, Cuk
K, Modugno C, Scharpff M, Schott S, Heil J, Turchinovich A, Yang R,
et al: Circulating miRNAs as surrogate markers for circulating
tumor cells and prognostic markers in metastatic breast cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 18:5972–5982. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Mori MA, Ludwig RG, Garcia-Martin R,
Brando BB and Kahn CR: Extracellular miRNAs: From biomarkers to
mediators of physiology and disease. Cell Metab. 30:656–673. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Jiang F, Chen Q, Wang W, Ling Y, Yan Y and
Xia P: Hepatocyte-derived extracellular vesicles promote
endothelial inflammation and atherogenesis via microRNA-1. J
Hepatol. 72:156–166. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cermelli S, Ruggieri A, Marrero JA,
Ioannou GN and Beretta L: Circulating microRNAs in patients with
chronic hepatitis C and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS
One. 6:e239372011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cheung O, Puri P, Eicken C, Contos MJ,
Mirshahi F, Maher JW, Kellum JM, Min H, Luketic VA and Sanyal AJ:
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is associated with altered hepatic
MicroRNA expression. Hepatology. 48:1810–1820. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lv LL, Cao YH, Ni HF, Xu M, Liu D, Liu H,
Chen PS and Liu BC: MicroRNA-29c in urinary exosome/microvesicle as
a biomarker of renal fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
305:F1220–F1227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Murakami Y, Toyoda H, Tanahashi T, Tanaka
J, Kumada T, Yoshioka Y, Kosaka N, Ochiya T and Taguchi YH:
Comprehensive miRNA expression analysis in peripheral blood can
diagnose liver disease. PLoS One. 7:e483662012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Devhare PB and Ray RB: Extracellular
vesicles: Novel mediator for cell to cell communications in liver
pathogenesis. Mol Aspects Med. 60:115–122. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Quan H, Li B and Yang J: MicroRNA-504
functions as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma through
inhibiting Frizzled-7-mediated-Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Biomed
Pharmacother. 107:754–762. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Tian Y, Mok MT, Yang P and Cheng AS:
Epigenetic activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in
NAFLD-associated hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancers (Basel). 8:762016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Li C, Miao R, Zhang J, Qu K and Liu C:
Long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 mediates the growth of hepatocellular
carcinoma by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-504.
Int J Oncol. 52:1603–1612. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Duan S, Dong X, Hai J, Jiang J, Wang W,
Yang J, Zhang W and Chen C: MicroRNA-135a-3p is downregulated and
serves as a tumour suppressor in ovarian cancer by targeting CCR2.
Biomed Pharmacother. 107:712–720. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Inamoto T, Uehara H, Akao Y, Ibuki N,
Komura K, Takahara K, Takai T, Uchimoto T, Saito K, Tanda N, et al:
A Panel of MicroRNA signature as a tool for predicting survival of
patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Dis Markers.
2018:54686722018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Esquejo RM, Salatto CT, Delmore J,
Albuquerque B, Reyes A, Shi Y, Moccia R, Cokorinos E, Peloquin M,
Monetti M, et al: Activation of Liver AMPK with PF-06409577
Corrects NAFLD and lowers cholesterol in rodent and primate
preclinical models. EBioMedicine. 31:122–132. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Watt MJ, Miotto PM, De Nardo W and
Montgomery MK: The liver as an endocrine organ-linking NAFLD and
insulin resistance. Endoc Rev. 40:1367–1393. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|