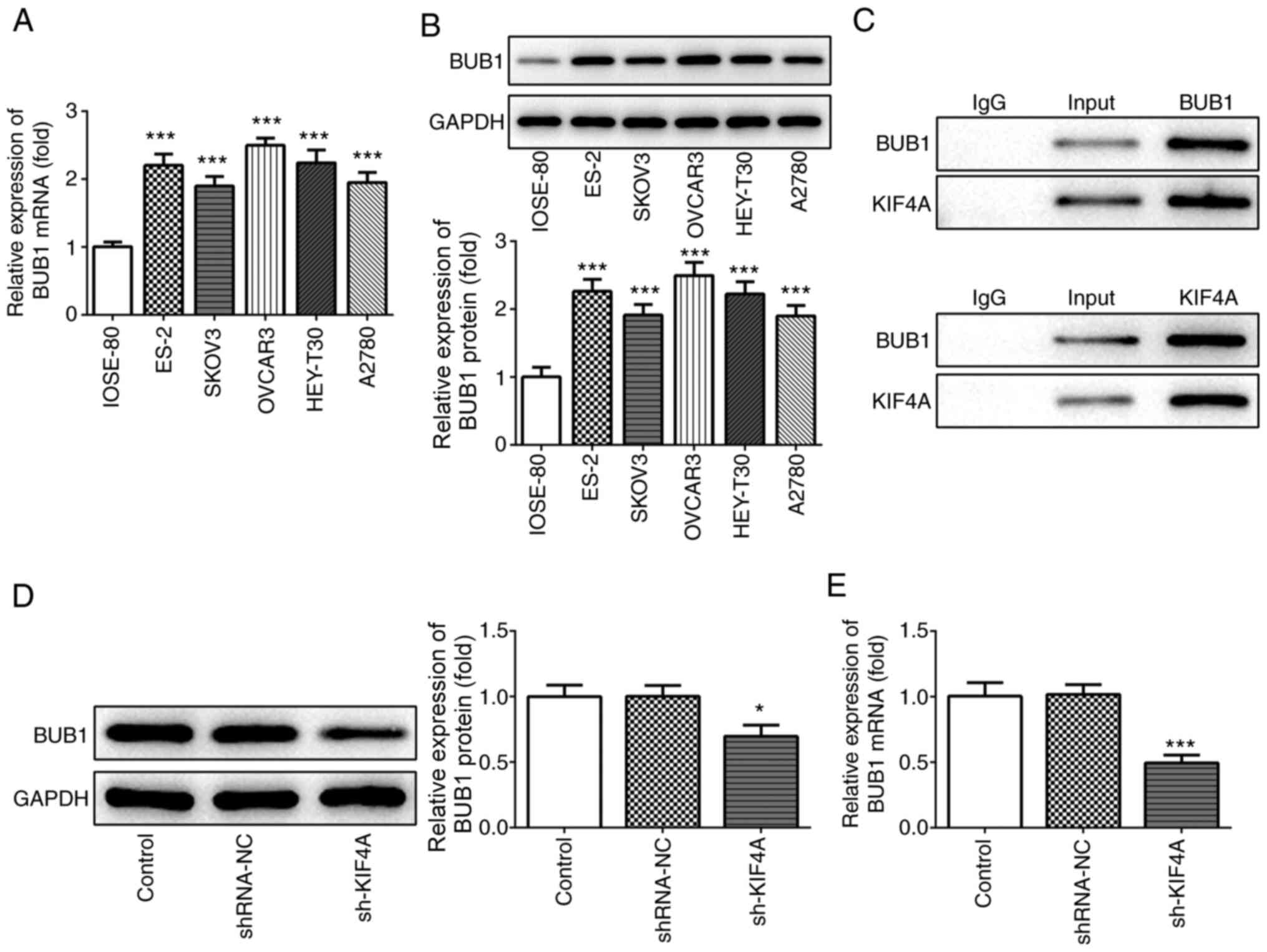
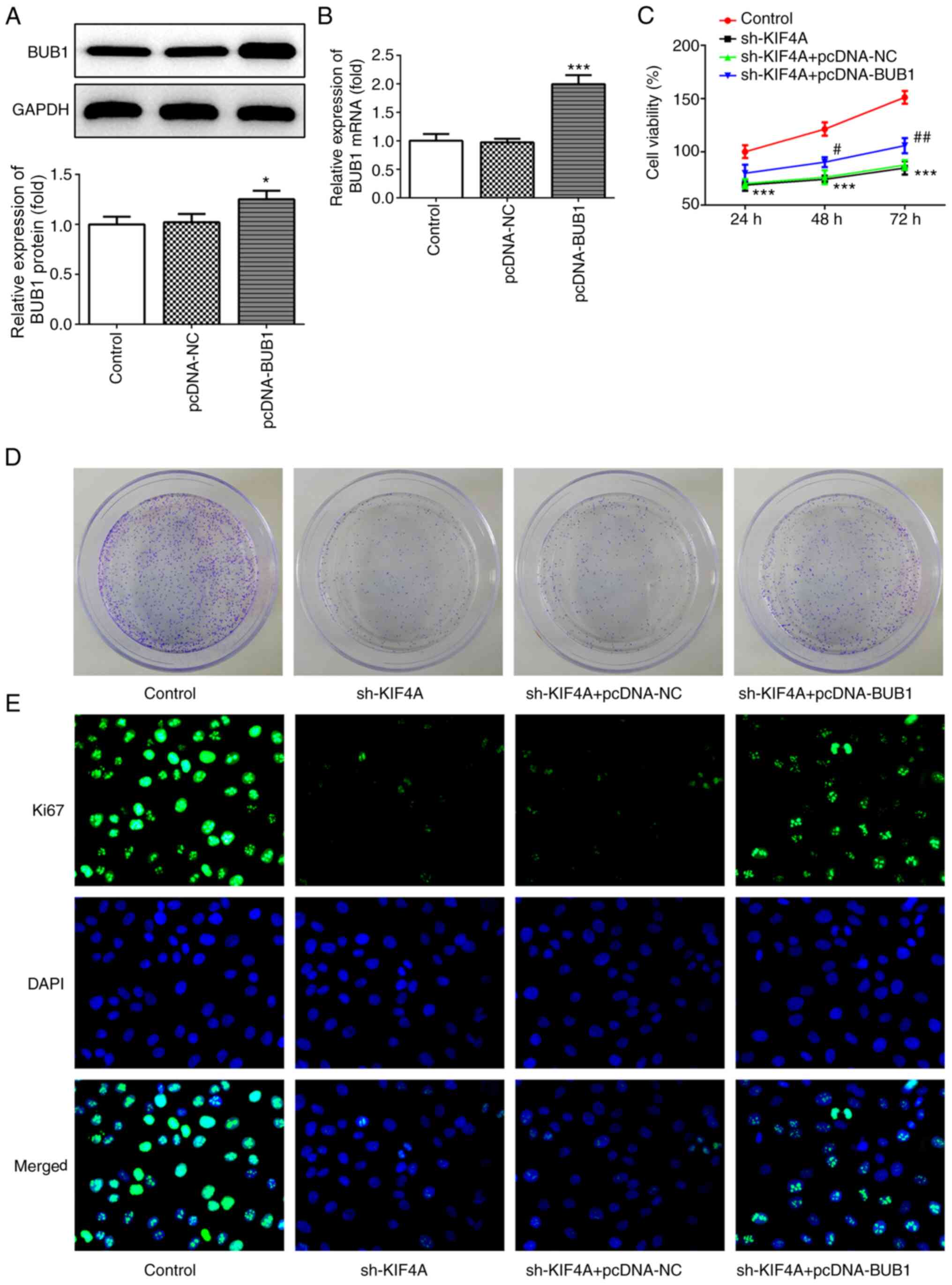
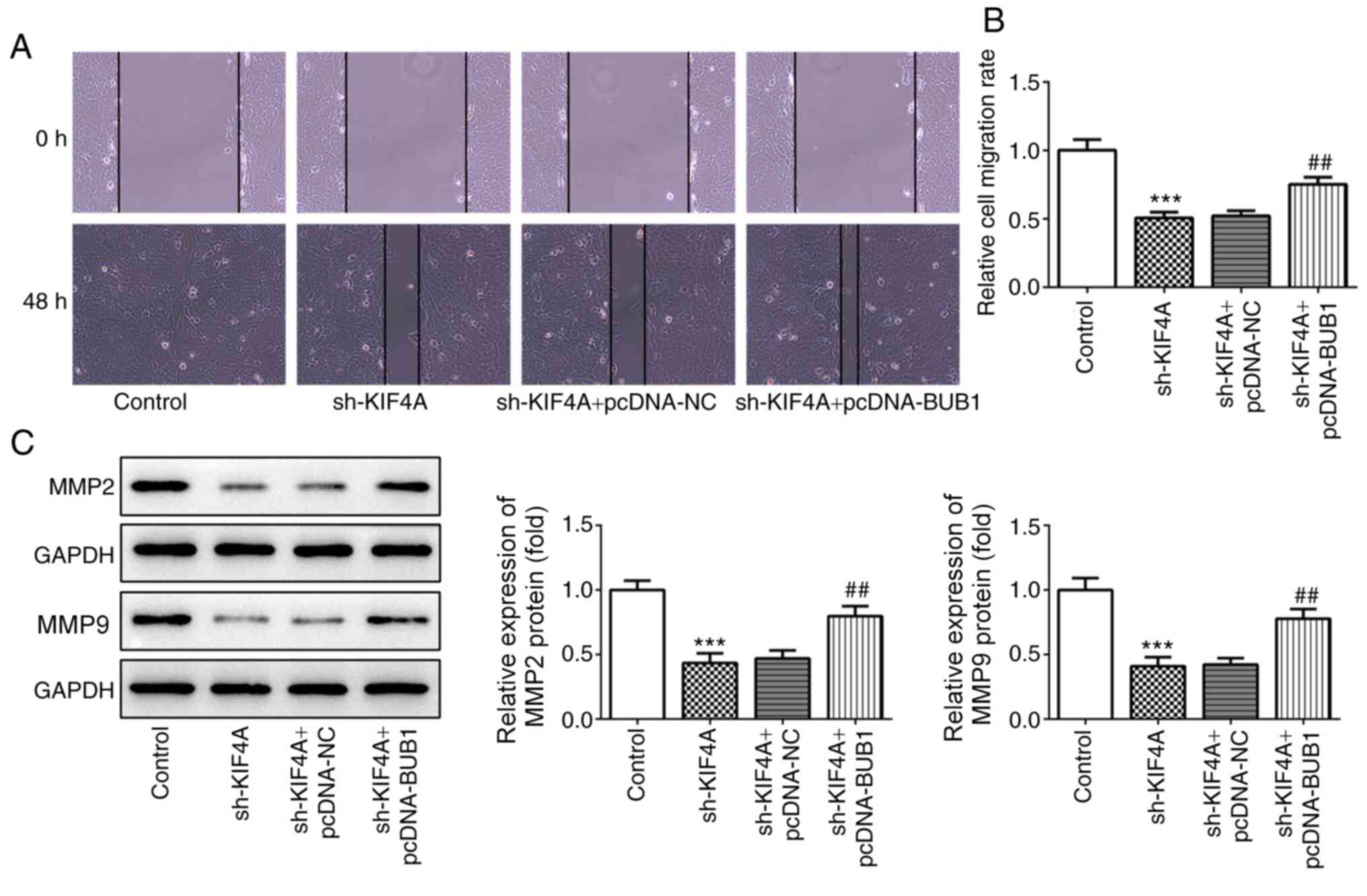
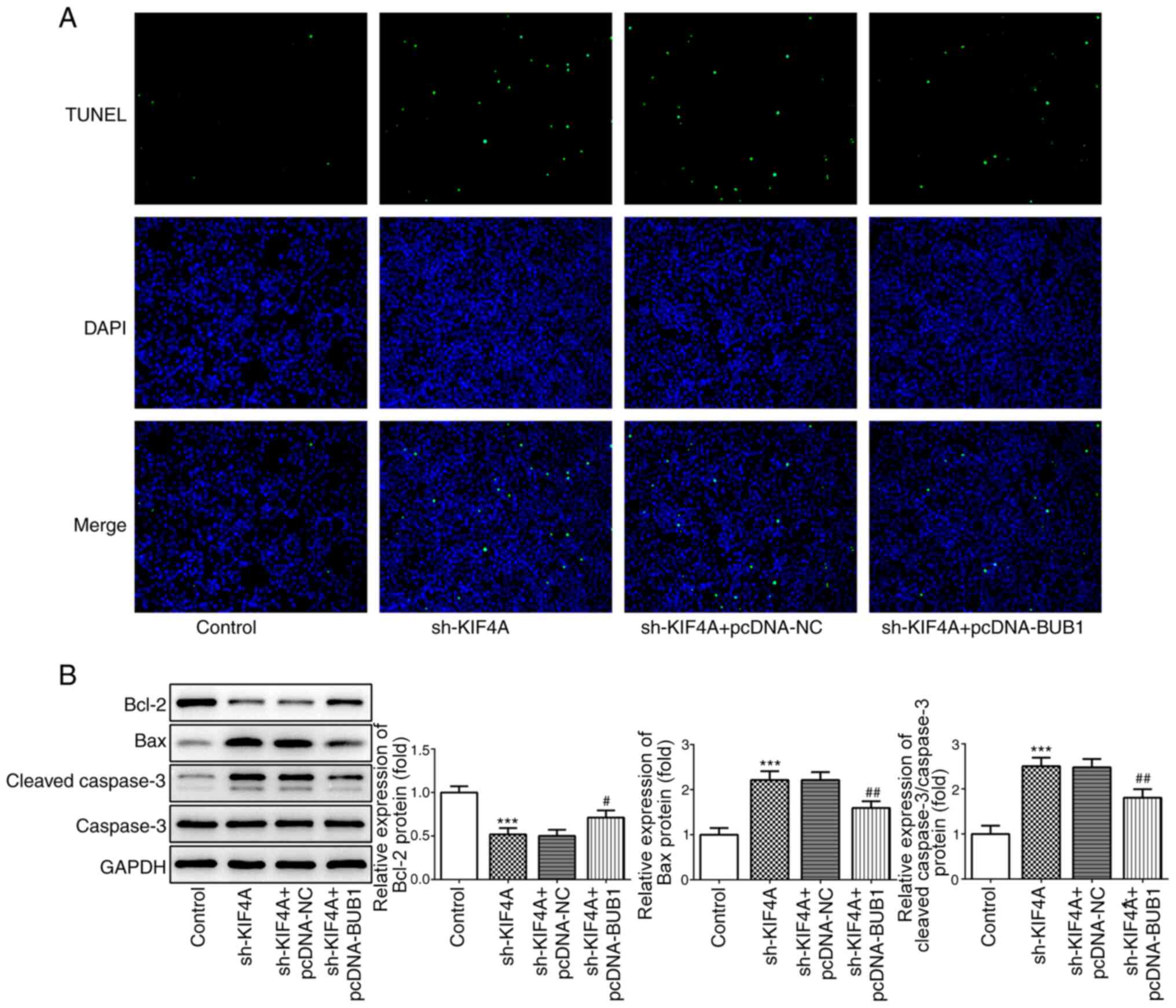
|
1
|
Webb PM and Jordan SJ: Epidemiology of
epithelial ovarian cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol.
41:3–14. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stewart C, Ralyea C and Lockwood S:
Ovarian Cancer: An Integrated Review. Semin Oncol Nurs. 35:151–156.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vargas AN: Natural history of ovarian
cancer. Ecancermedicalscience. 8:4652014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang L, Yan W, Li X, Liu Z, Tian T, Chen
T, Zou L and Cui Z: S100A10 silencing suppresses proliferation,
migration and invasion of ovarian cancer cells and enhances
sensitivity to carboplatin. J Ovarian Res. 12:1132019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rath O and Kozielski F: Kinesins and
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:527–539. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ha MJ, Yoon J, Moon E, Lee YM, Kim HJ and
Kim W: Assignment of the kinesin family member 4 genes (KIF4A and
KIF4B) to human chromosome bands Xq13.1 and 5q33.1 by in situ
hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 88:41–42. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mazumdar M, Sundareshan S and Misteli T:
Human chromokinesin KIF4A functions in chromosome condensation and
segregation. J Cell Biol. 166:613–620. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hu CK, Coughlin M, Field CM and Mitchison
TJ: KIF4 regulates midzone length during cytokinesis. Curr Biol.
21:815–824. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kurasawa Y, Earnshaw WC, Mochizuki Y,
Dohmae N and Todokoro K: Essential roles of KIF4 and its binding
partner PRC1 in organized central spindle midzone formation. EMBO
J. 23:3237–3248. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hou PF, Jiang T, Chen F, Shi PC, Li HQ,
Bai J and Song J: KIF4A facilitates cell proliferation via
induction of p21-mediated cell cycle progression and promotes
metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 9:4772018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xue D, Cheng P, Han M, Liu X, Xue L, Ye C,
Wang K and Huang J: An integrated bioinformatical analysis to
evaluate the role of KIF4A as a prognostic biomarker for breast
cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 11:4755–4768. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gao H, Chen X, Cai Q, Shang Z and Niu Y:
Increased KIF4A expression is a potential prognostic factor in
prostate cancer. Oncol Lett. 15:7941–7947. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hou G, Dong C, Dong Z, Liu G, Xu H, Chen
L, Liu L, Wang H and Zhou W: Upregulate KIF4A Enhances
Proliferation, Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Indicates
poor prognosis Across Human Cancer Types. Sci Rep. 7:41482017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang D, He Y, Wu B, Deng Y, Wang N, Li M
and Liu Y: Integrated bioinformatics analysis for the screening of
hub genes and therapeutic drugs in ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res.
13:102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bolanos-Garcia VM and Blundell TL: BUB1
and BUBR1: Multifaceted kinases of the cell cycle. Trends Biochem
Sci. 36:141–150. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fu X, Chen G, Cai ZD, Wang C, Liu ZZ, Lin
ZY, Wu YD, Liang YX, Han ZD, Liu JC, et al: Overexpression of BUB1B
contributes to progression of prostate cancer and predicts poor
outcome in patients with prostate cancer. OncoTargets Ther.
9:2211–2220. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Stahl D, Braun M, Gentles AJ, Lingohr P,
Walter A, Kristiansen G and Gütgemann I: Low BUB1 expression is an
adverse prognostic marker in gastric adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget.
8:76329–76339. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
von Mering C, Huynen M, Jaeggi D, Schmidt
S, Bork P and Snel B: STRING: A database of predicted functional
associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:258–261. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Feng H, Gu ZY, Li Q, Liu QH, Yang XY and
Zhang JJ: Identification of significant genes with poor prognosis
in ovarian cancer via bioinformatical analysis. J Ovarian Res.
12:352019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang X and Chen T: CUL4A regulates
endometrial cancer cell proliferation, invasion and migration by
interacting with CSN6. Mol Med Rep. 23:232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Y, Yang X, Ge X and Zhang F:
Puerarin attenuates neurological deficits via Bcl-2/Bax/cleaved
caspase-3 and Sirt3/SOD2 apoptotic pathways in subarachnoid
hemorrhage mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 109:726–733. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Holschneider CH and Berek JS: Ovarian
cancer: Epidemiology, biology, and prognostic factors. Semin Surg
Oncol. 19:3–10. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Maringe C, Walters S, Butler J, Coleman
MP, Hacker N, Hanna L, Mosgaard BJ, Nordin A, Rosen B, Engholm G,
et al ICBP Module 1 Working Group, : Stage at diagnosis and ovarian
cancer survival: Evidence from the International Cancer
Benchmarking Partnership. Gynecol Oncol. 127:75–82. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu B, Xu T, Liu H, Min Q, Wang S and Song
Q: MiR-490-5p suppresses cell proliferation and invasion by
targeting BUB1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Pharmacology.
100:269–282. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tang D, Zhao X, Zhang L, Wang Z and Wang
C: Identification of hub genes to regulate breast cancer metastasis
to brain by bioinformatics analyses. J Cell Biochem. 120:9522–9531.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pabla S, Conroy JM, Nesline MK, Glenn ST,
Papanicolau-Sengos A, Burgher B, Hagen J, Giamo V, Andreas J, Lenzo
FL, et al: Proliferative potential and resistance to immune
checkpoint blockade in lung cancer patients. J Immunother Cancer.
7:272019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|