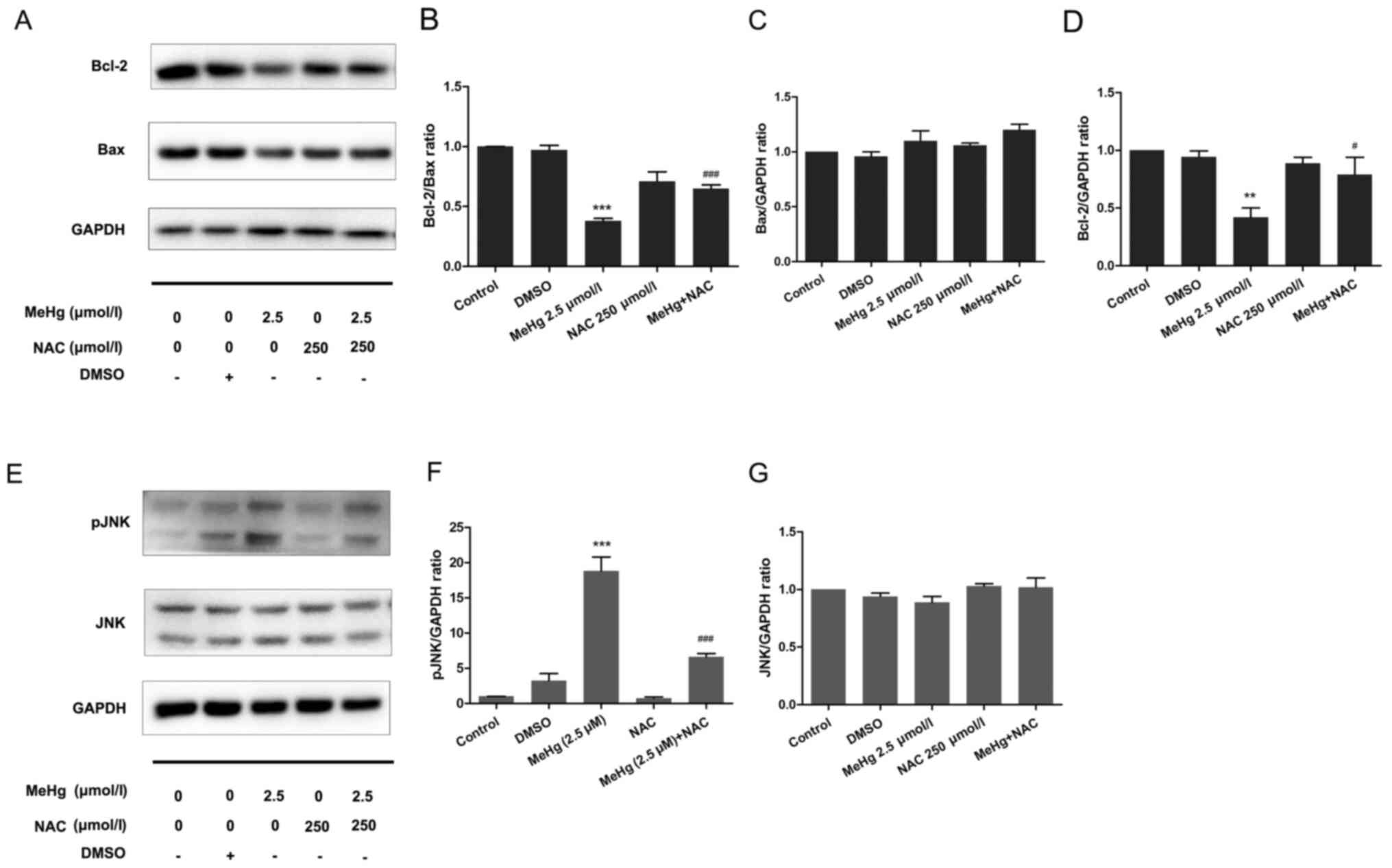
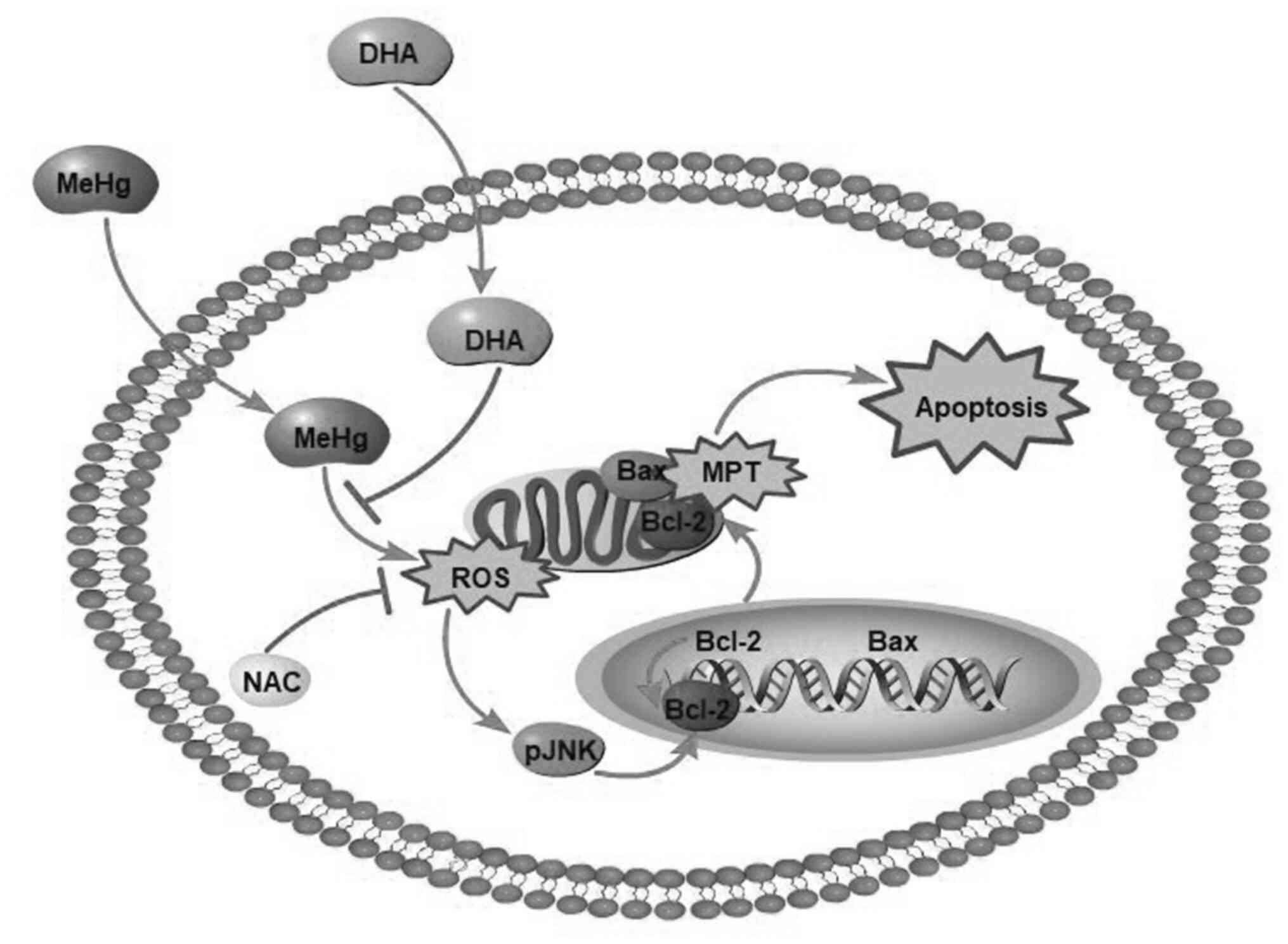
|
1
|
Jacobs S, Sioen I, Jacxsens L, Domingo JL,
Sloth JJ, Marques A and Verbeke W: Risk assessment of methylmercury
in five European countries considering the national seafood
consumption patterns. Food Chem Toxicol. 104:26–34. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hylander LD: Global Mercury Pollution and
its Expected Decrease after a Mercury Trade Ban. Water Air Soil
Pollut. 125:331–344. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Borowska S and Brzóska MM: Metals in
cosmetics: Implications for human health. J Appl Toxicol.
35:551–572. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim W, Kim DW, Yoo DY, Jung HY, Kim JW,
Kim DW, Choi JH, Moon SM, Yoon YS and Hwang IK: Antioxidant effects
of Dendropanax morbifera Léveille extract in the hippocampus
of mercury-exposed rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 15:2472015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Clarkson TW, Magos L and Myers GJ: The
toxicology of mercury - current exposures and clinical
manifestations. N Engl J Med. 349:1731–1737. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Syversen T and Kaur P: The toxicology of
mercury and its compounds. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 26:215–226. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bellinger DC, Devleesschauwer B, O'Leary K
and Gibb HJ: Global burden of intellectual disability resulting
from prenatal exposure to methylmercury, 2015. Environ Res.
170:416–421. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sheehan MC, Burke TA, Navas-Acien A,
Breysse PN, McGready J and Fox MA: Global methylmercury exposure
from seafood consumption and risk of developmental neurotoxicity: A
systematic review. Bull World Health Organ. 92:F254–F269. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ke T, Gonçalves FM, Gonçalves CL, dos
Santos AA, Rocha JBT, Farina M, Skalny A, Tsatsakis A, Bowman AB
and Aschner M: Post-translational modifications in MeHg-induced
neurotoxicity. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1865:2068–2081.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ying Z, Chen K, Zheng L, Wu Y, Li L, Wang
R, Long Q, Yang L, Guo J, Yao D, et al: Transient Activation of
Mitoflashes Modulates Nanog at the Early Phase of Somatic Cell
Reprogramming. Cell Metab. 23:220–226. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu L, Liu Z, Qiu L, Hao L and Guo J:
Ipatasertib sensitizes colon cancer cells to TRAIL-induced
apoptosis through ROS-mediated caspase activation. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 519:812–818. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tan BL, Norhaizan ME and Chan LC:
ROS-Mediated Mitochondrial Pathway is Required for Manilkara
Zapota (L.) P. Royen Leaf Methanol Extract Inducing Apoptosis
in the Modulation of Caspase Activation and EGFR/NF-κ B Activities
of HeLa Human Cervical Cancer Cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2018:65786482018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mangali S, Bhat A, Udumula MP, Dhar I,
Sriram D and Dhar A: Inhibition of protein kinase R protects
against palmitic acid-induced inflammation, oxidative stress, and
apoptosis through the JNK/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway in cultured H9C2
cardiomyocytes. J Cell Biochem. 120:3651–3663. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen Y, Feng X, Hu X, Sha J, Li B, Zhang H
and Fan H: Dexmedetomidine Ameliorates Acute Stress-Induced Kidney
Injury by Attenuating Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis through
Inhibition of the ROS/JNK Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2018:40353102018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Niu S-L, Mitchell DC, Lim S-Y, Wen ZM, Kim
HY, Salem N Jr and Litman BJ: Reduced G protein-coupled signaling
efficiency in retinal rod outer segments in response to n-3 fatty
acid deficiency. J Biol Chem. 279:31098–31104. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Oken E, Wright RO, Kleinman KP, Bellinger
D, Amarasiriwardena CJ, Hu H, Rich-Edwards JW and Gillman MW:
Maternal fish consumption, hair mercury, and infant cognition in a
U.S. Cohort. Environ Health Perspect. 113:1376–1380. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Oken E, Østerdal ML, Gillman MW, Knudsen
VK, Halldorsson TI, Strøm M, Bellinger DC, Hadders-Algra M,
Michaelsen KF and Olsen SF: Associations of maternal fish intake
during pregnancy and breastfeeding duration with attainment of
developmental milestones in early childhood: A study from the
Danish National Birth Cohort. Am J Clin Nutr. 88:789–796. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cardoso C, Bernardo I, Bandarra NM, Louro
Martins L and Afonso C: Portuguese preschool children: Benefit
(EPA+DHA and Se) and risk (MeHg) assessment through the consumption
of selected fish species. Food Chem Toxicol. 115:306–314. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nøstbakken OJ, Bredal IL, Olsvik PA, Huang
TS and Torstensen BE: Effect of marine omega 3 fatty acids on
methylmercury-induced toxicity in fish and mammalian cells in
vitro. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012:4176522012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kaur P, Heggland I, Aschner M and Syversen
T: Docosahexaenoic acid may act as a neuroprotector for
methylmercury-induced neurotoxicity in primary neural cell
cultures. Neurotoxicology. 29:978–987. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Takanezawa Y, Nakamura R, Hamaguchi M,
Yamamoto K, Sone Y, Uraguchi S and Kiyono M: Docosahexaenoic acid
enhances methylmercury-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and
cell death and eicosapentaenoic acid potentially attenuates these
effects in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Toxicol Lett. 306:35–42.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Δ Δ C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang Y, Huang H, Wang S, Chen F and Zheng
G: Dehydrocorydaline inhibits the tumorigenesis of breast cancer
MDA MB 231 cells. Mol Med Rep. 22:43–50. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao L, Gu Q, Xiang L, Dong X, Li H, Ni J,
Wan L, Cai G and Chen G: Curcumin inhibits apoptosis by modulating
Bax/Bcl-2 expression and alleviates oxidative stress in testes of
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Ther Clin Risk Manag.
13:1099–1105. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
de Angelis C, Galdiero M, Pivonello C,
Salzano C, Gianfrilli D, Piscitelli P, Lenzi A, Colao A and
Pivonello R: The environment and male reproduction: The effect of
cadmium exposure on reproductive function and its implication in
fertility. Reprod Toxicol. 73:105–127. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang X, Wang M, Teng S and Wang D, Li X,
Wang X, Liao W and Wang D: Indolyl-chalcone derivatives induce
hepatocellular carcinoma cells apoptosis through oxidative stress
related mitochondrial pathway in vitro and in vivo. Chem Biol
Interact. 293:61–69. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kuo LM, Chen PJ, Sung PJ, Chang YC, Ho CT,
Wu YH and Hwang TL: The Bioactive Extract of Pinnigorgia sp.
Induces Apoptosis of Hepatic Stellate Cells via
ROS-ERK/JNK-Caspase-3 Signaling. Mar Drugs. 16(19)2018.
|
|
28
|
Ren X, Wang S, Zhang C, Hu X, Zhou L, Li Y
and Xu L: Selenium ameliorates cadmium-induced mouse leydig TM3
cell apoptosis via inhibiting the ROS/JNK /c-jun signaling pathway.
Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 192:1102662020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen X, Wu W, Gong B, Hou L, Dong X, Xu C,
Zhao R, Yu Q, Zhou Z, Huang S, et al: Metformin attenuates
cadmium-induced neuronal apoptosis in vitro via blocking
ROS-dependent PP5/AMPK-JNK signaling pathway. Neuropharmacology.
175:1080652020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang Z, Yu K, Hu Y, Su F, Gao Z, Hu T,
Yang Y, Cao X and Qian F: Schisantherin A induces cell apoptosis
through ROS/JNK signaling pathway in human gastric cancer cells.
Biochem Pharmacol. 173:1136732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zareba G, Cernichiari E, Hojo R, Nitt SM,
Weiss B, Mumtaz MM, Jones DE and Clarkson TW: Thimerosal
distribution and metabolism in neonatal mice: Comparison with
methyl mercury. J Appl Toxicol. 27:511–518. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Poling A and LeSage M: Evaluating
psychotropic drugs in people with mental retardation: Where are the
social validity data? Am J Ment Retard. 100:193–200.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Watanabe J, Nakamachi T, Ohtaki H,
Naganuma A, Shioda S and Nakajo S: Low dose of methylmercury (MeHg)
exposure induces caspase mediated-apoptosis in cultured neural
progenitor cells. J Toxicol Sci. 38:931–935. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Petroni D, Tsai J, Agrawal K, Mondal D and
George W: Low-dose methylmercury-induced oxidative stress,
cytotoxicity, and tau-hyperphosphorylation in human neuroblastoma
(SH-SY5Y) cells. Environ Toxicol. 27:549–555. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Calder PC: Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty
acids and inflammatory processes: nutrition or pharmacology? Br J
Clin Pharmacol. 75:645–662. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kuratko CN, Barrett EC, Nelson EB and
Salem N Jr: The relationship of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) with
learning and behavior in healthy children: a review. Nutrients.
5:2777–2810. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tan Q, Zhang M, Geng L, Xia Z, Li C, Usman
M, Du Y, Wei L and Bi H: Hormesis of methylmercury-human serum
albumin conjugate on N9 microglia via ERK/MAPKs and STAT3 signaling
pathways. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 362:59–66. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Iuchi K, Ema M, Suzuki M, Yokoyama C and
Hisatomi H: Oxidized unsaturated fatty acids induce apoptotic cell
death in cultured cells. Mol Med Rep. 19:2767–2773. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Srikanth M, Chandrasaharan K, Zhao X,
Chayaburakul K, Ong W-Y and Herr DR: Metabolism of Docosahexaenoic
Acid (DHA) Induces Pyroptosis in BV-2 Microglial Cells.
Neuromolecular Med. 20:504–514. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xue D-F, Pan S-T, Huang G and Qiu J-X: ROS
enhances the cytotoxicity of cisplatin by inducing apoptosis and
autophagy in tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 122:1057322020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hassani S, Ghaffari P, Chahardouli B,
Alimoghaddam K, Ghavamzadeh A, Alizadeh S and Ghaffari SH:
Disulfiram/copper causes ROS levels alteration, cell cycle
inhibition, and apoptosis in acute myeloid leukaemia cell lines
with modulation in the expression of related genes. Biomed
Pharmacother. 99:561–569. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu Z, Li C, Wu G, Li W, Zhang X, Zhou J,
Zhang L, Tao J, Shen M and Liu H: Involvement of JNK/FOXO1 pathway
in apoptosis induced by severe hypoxia in porcine granulosa cells.
Theriogenology. 154:120–127. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang Y, Li Y, Ma P, Chen J and Xie W:
Ficus carica leaves extract inhibited pancreatic β-cell apoptosis
by inhibiting AMPK/JNK/caspase-3 signaling pathway and
antioxidation. Biomed Pharmacother. 122:1096892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kalkavan H and Green DR: MOMP, cell
suicide as a BCL-2 family business. Cell Death Differ. 25:46–55.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Qi H, Jiang Y, Yin Z, Jiang K, Li L and
Shuai J: Optimal pathways for the assembly of the Apaf-1·cytochrome
c complex into apoptosome. Phys Chem Chem Phys.
20:1964–1973. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pouraminaei M, Mirzaiey MR, Khoshdel A,
Hajizadeh MR, Mahmoodi M and Fahmidehkar MA: The effect of Cressa
Cretica hydroalcoholic extract on apoptosis and the expression of
Bcl2, Bax and P53 genes in hepatoma cell line HepG2. Gene Rep.
20:1006922020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Hou D, Che Z, Chen P, Zhang W, Chu Y, Yang
D and Liu J: Suppression of AURKA alleviates p27 inhibition on Bax
cleavage and induces more intensive apoptosis in gastric cancer.
Cell Death Dis. 9:7812018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|