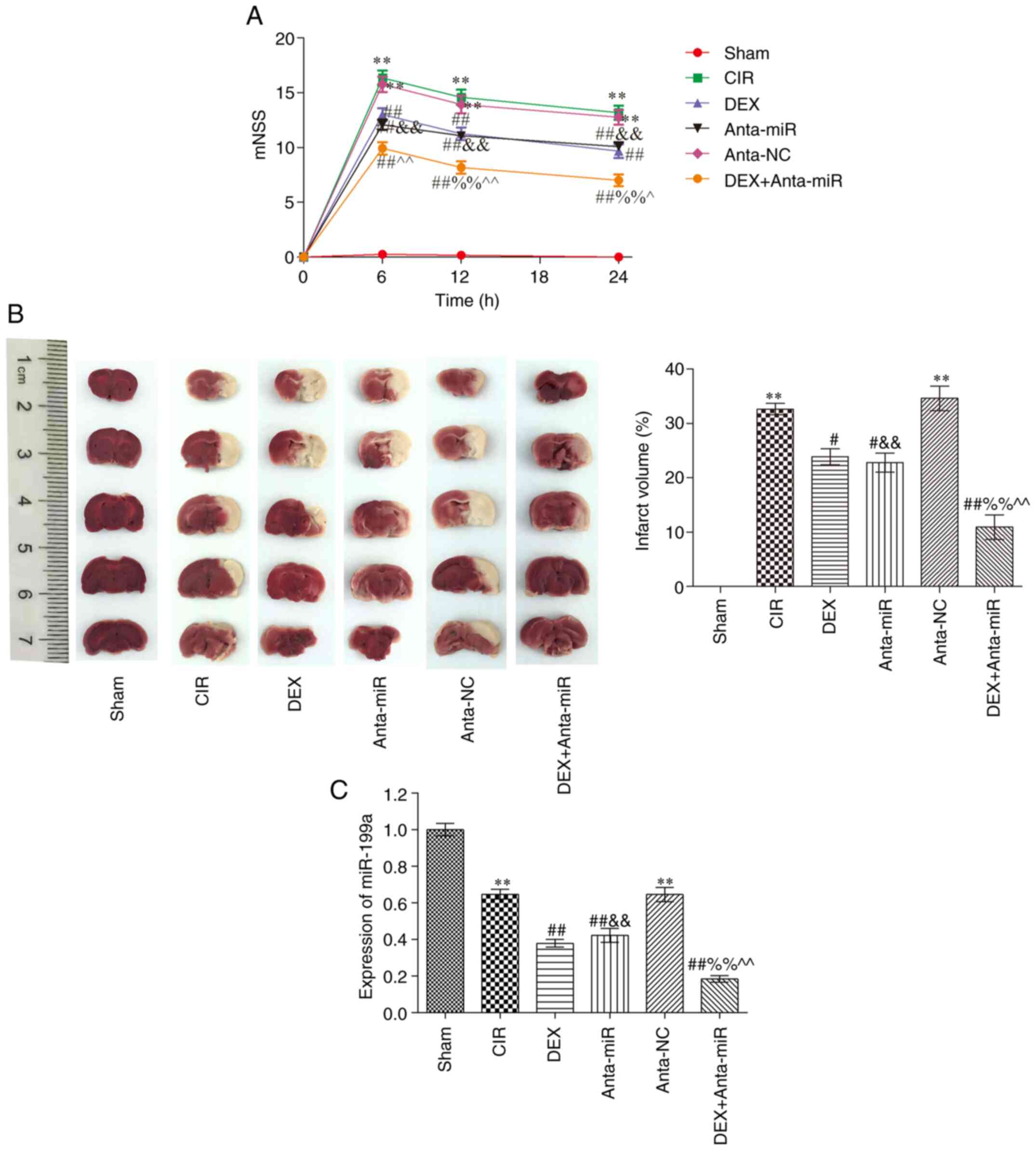
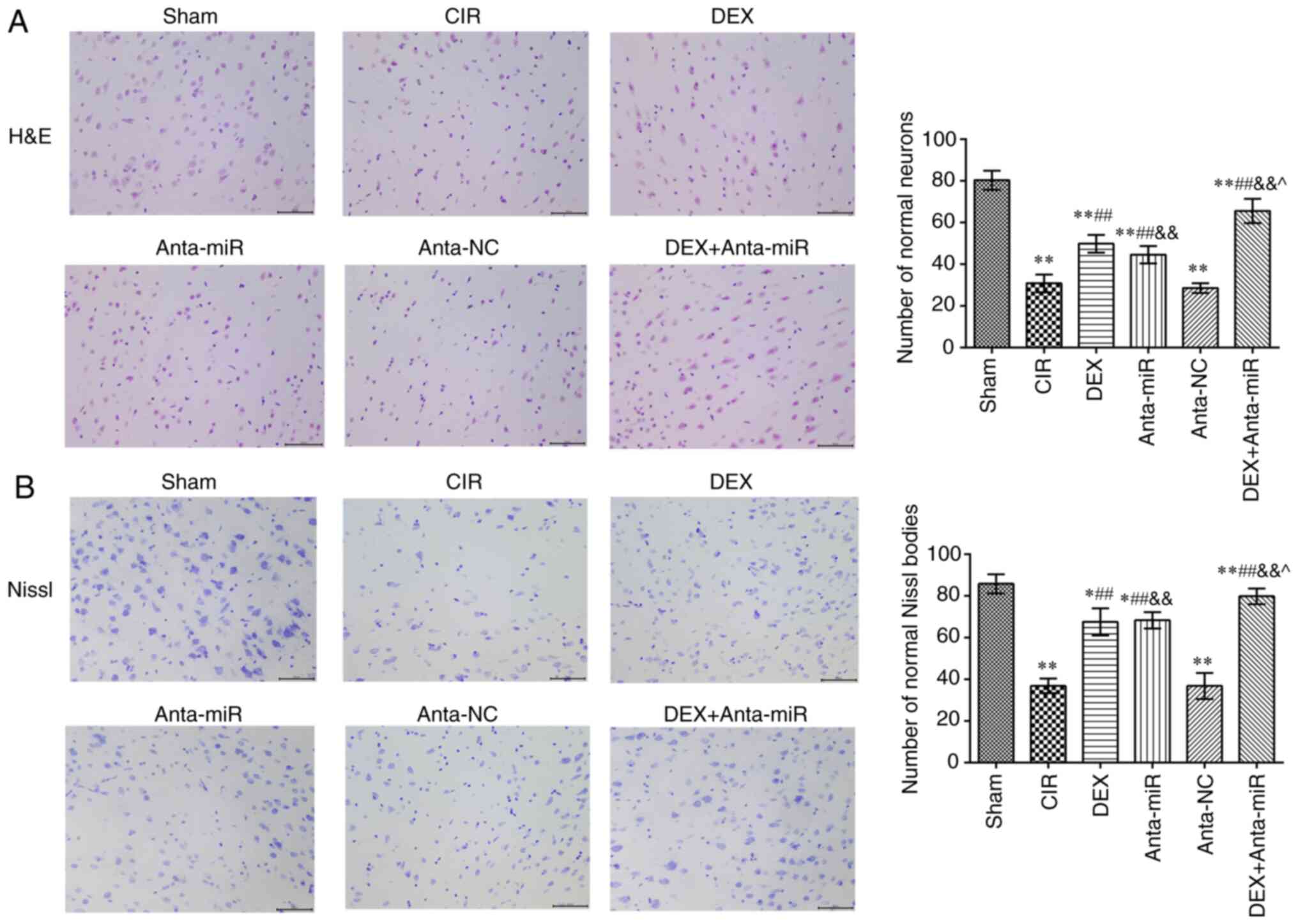
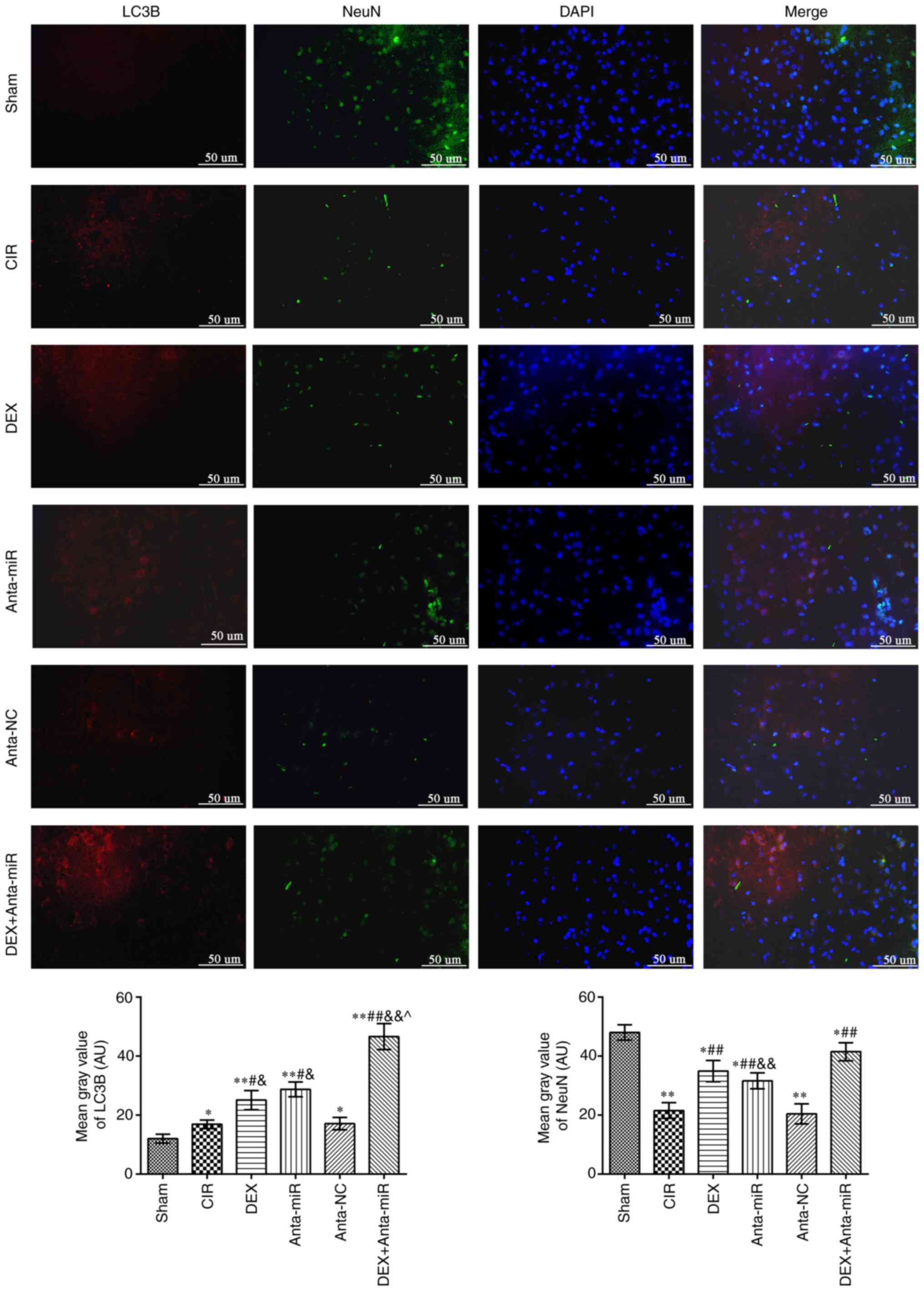
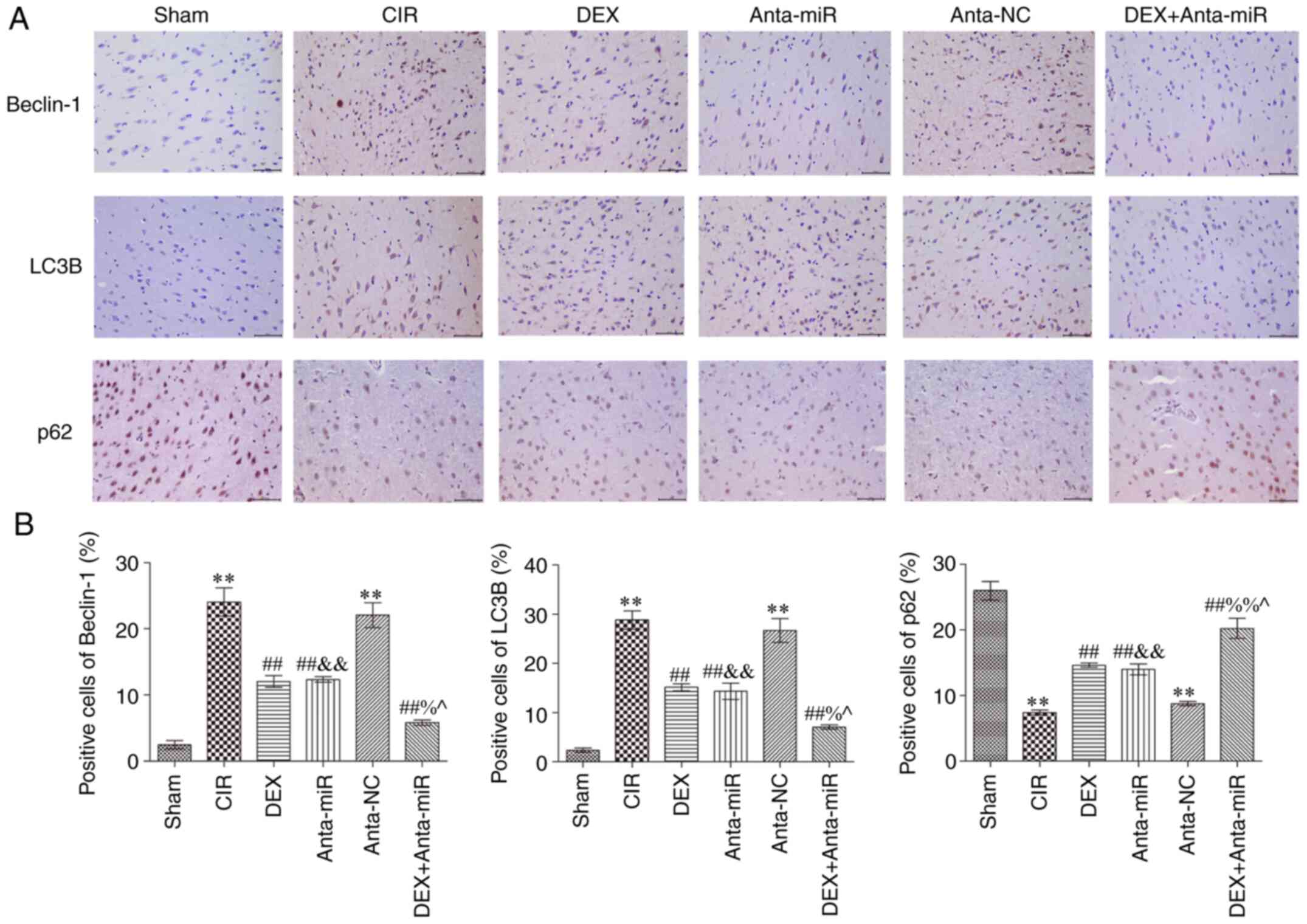
|
1
|
Paul S and Candelario-Jalil E: Emerging
neuroprotective strategies for the treatment of ischemic stroke: An
overview of clinical and preclinical studies. Exp Neurol.
335:1135182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Barteczek P, Li L, Ernst AS, Böhler LI,
Marti HH and Kunze R: Neuronal HIF-1α and HIF-2α deficiency
improves neuronal survival and sensorimotor function in the early
acute phase after ischemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
37:291–306. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Choi JI, Ha SK, Lim DJ, Kim SD and Kim SH:
S100ß, matrix metalloproteinase-9, D-dimer, and heat shock protein
70 are serologic biomarkers of acute cerebral infarction in a mouse
model of transient MCA occlusion. J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
61:548–558. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Doherty J and Baehrecke EH: Life, death
and autophagy. Nat Cell Biol. 20:1110–1117. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Carloni S, Albertini MC, Galluzzi L,
Buonocore G, Proietti F and Balduini W: Melatonin reduces
endoplasmic reticulum stress and preserves sirtuin 1 expression in
neuronal cells of newborn rats after hypoxia-ischemia. J Pineal
Res. 57:192–199. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang W and Zhang J: Dexmedetomidine
preconditioning protects against lung inju-ry induced by
ischemia-reperfusion through inhibition of autophagy. Exp Ther Med.
14:973–980. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang W, Zhang JQ, Meng FM and Xue FS:
Dexmedetomidine protects against lung ischemia-reperfusion injury
by the PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α signaling pathway. J Anesth. 30:826–833.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang YQ, Tang YF, Yang MK and Huang XZ:
Dexmedetomidine alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in
rats via inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. J Cell Biochem.
Nov 19–2018.(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1002/jcb.28058.
|
|
9
|
Begum G, Yan HQ, Li L, Singh A, Dixon CE
and Sun D: Docosahexaenoic acid reduces ER stress and abnormal
protein accumulation and improves neuronal function following
traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci. 34:3743–3755. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hetta DF, Kamal EE, Mahran AM, Ahmed DG,
Elawamy A and Abdelraouf AM: Efficacy of local dexmedetomidine
add-on for spermatic cord block anesthesia in patients undergoing
intrascrotal surgeries: Randomized controlled multicenter clinical
trial. J Pain Res. 10:2621–2628. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu C, Fu Q, Mu R, Wang F, Zhou C, Zhang
L, Yu B, Zhang Y, Fang T and Tian F: Dexmedetomidine alleviates
cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting endoplasmic
reticulum stress dependent apoptosis through the
PERK-CHOP-Caspase-11 pathway. Brain Res. 1701:246–254. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS and Bartel
DP: Mammalian microRNAs predom-inantly act to decrease target mRNA
levels. Nature. 466:835–840. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guo D, Ma J, Yan L, Li T, Li Z, Han X and
Shui S: Down-regulation of lncrna MALAT1 attenuates neuronal cell
death through suppressing beclin1-dependent autophagy by regulating
mir-30a in cerebral ischemic stroke. Cell Physiol Biochem.
43:182–194. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu P, Zuo X, Deng H, Liu X, Liu L and Ji
A: Roles of long noncoding RNAs in brain development, functional
diversification and neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Bull.
97:69–80. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang J, Yuan L, Zhang X, Hamblin MH, Zhu
T, Meng F, Li Y, Chen YE and Yin KJ: Altered long non-coding RNA
transcriptomic profiles in brain microvascular endothelium after
cerebral ischemia. Exp Neurol. 277:162–170. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ebert MS and Sharp PA: Roles for microRNAs
in conferring robustness to biolog-ical processes. Cell.
149:515–524. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu J, Wang F, Yang GH, Wang FL, Ma YN, Du
ZW and Zhang JW: Human microRNA clusters: Genomic organization and
expression profile in leukemia cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 349:59–68. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Calame K: MicroRNA-155 function in B
Cells. Immunity. 27:825–827. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yao S, Tang B, Li G, Fan R and Cao F:
miR-455 inhibits neuronal cell death by targeting TRAF3 in cerebral
ischemic stroke. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 12:3083–3092. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yin KJ, Deng Z, Huang H, Hamblin M, Xie C,
Zhang J and Chen YE: miR-497 regulates neuronal death in mouse
brain after transient focal cerebral ischemia. Neurobiol Dis.
38:17–26. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals, . Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th
edition. National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC: pp.
963–965. 2011
|
|
22
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sha R, Han X, Zheng C, Peng J, Wang L,
Chen L and Huang X: The effects of electroacupuncture in a rat
model of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury following middle
cerebral artery occlusion involves microRNA-223 and the PTEN
signaling pathway. Med Sci Monit. 25:10077–10088. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang D, Li Z, Zhang Y, Wang G, Wei M, Hu
Y, Ma S, Jiang Y, Che N, Wang X, et al: Targeting of
microRNA-199a-5p protects against pilocarpine-induced status
epilepticus and seizure damage via SIRT1-p53 cascade. Epilepsia.
57:706–716. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen J, Sanberg PR, Li Y, Wang L, Lu M,
Willing AE, Sanchez-Ramos J and Chopp M: Intravenous administration
of human umbilical cord blood reduces behavioral deficits after
stroke in rats. Stroke. 32:2682–2688. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hei C, Liu P, Yang X, Niu J and Li PA:
Inhibition of mTOR signaling confers protection against cerebral
ischemic injury in acute hyperglycemic rats. Int J Biol Sci.
13:878–887. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jiang M, Li J, Peng Q, Liu Y, Liu W, Luo
C, Peng J, Li J, Yung KK and Mo Z: Neuroprotective effects of
bilobalide on cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury are
associated with inhibition of pro-inflammatory mediator production
and down-regulation of JNK1/2 and p38 MAPK activation. J
Neuroinflammation. 11:1672014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Halestrap AP: Calcium, mitochondria and
reperfusion injury: A pore way to die. Biochem Soc Trans.
34:232–237. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Carloni S, Girelli S, Scopa C, Buonocore
G, Longini M and Balduini W: Activation of autophagy and Akt/CREB
signaling play an equivalent role in the neuroprotective effect of
rapamycin in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Autophagy. 6:366–377. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chu CT: Mechanisms of selective autophagy
and mitophagy: Implications for neurodegenerative diseases.
Neurobiol Dis. 122:23–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Descloux C, Ginet V, Clarke PG, Puyal J
and Truttmann AC: Neuronal death after perinatal cerebral
hypoxia-ischemia: Focus on autophagy-mediated cell death. Int J Dev
Neurosci. 45:75–85. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Qian X, Li X, Cai Q, Zhang C, Yu Q, Jiang
Y, Lee JH, Hawke D, Wang Y, Xia Y, et al: Phosphoglycerate kinase 1
phosphorylates beclin1 to induce autophagy. Mol Cell.
65:917–931.e6. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huang L, Chen C, Zhang X, Li X, Chen Z,
Yang C, Liang X, Zhu G and Xu Z: Neuroprotective Effect of Curcumin
against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion via mediating autophagy and
inflammation. J Mol Neurosci. 64:129–139. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Aryan HE, Box KW, Ibrahim D, Desiraju U
and Ames CP: Safety and efficacy of dexmedetomidine in
neurosurgical patients. Brain Inj. 20:791–798. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wu L, Xi Y and Kong Q: Dexmedetomidine
protects PC12 cells from oxidative damage through regulation of
miR-199a/HIF-1α. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 48:506–514. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yin D, Zhou S, Xu X, Gao W, Li F, Ma Y,
Sun D, Wu Y, Guo Q, Liu H, et al: Dexmedetomidine attenuated early
brain injury in rats with subarachnoid haemorrhage by suppressing
the inflammatory response: The TLR4/NF-κB pathway and the NLRP3
inflammasome may be involved in the mechanism. Brain Res.
1698:1–10. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang P, Liang J, Li Y and Li J, Yang X,
Zhang X, Han S, Li S and Li J: Down-regulation of miRNA-30a
alleviates cerebral ischemic injury through enhancing beclin
1-mediated autophagy. Neurochem Res. 39:1279–1291. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rane S, He M, Sayed D, Vashistha H,
Malhotra A, Sadoshima J, Vatner DE, Vat-ner SF and Abdellatif M:
Downregulation of miR-199a derepresses hypoxia-inducible
factor-1alpha and Sirtuin 1 and recapitulates hypoxia
preconditioning in cardiac myocytes. Circ Res. 104:879–886. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zuo Y, Wang Y, Hu H and Cui W:
Atorvastatin protects myocardium against ischemia-reperfusion
injury through inhibiting miR-199a-5p. Cell Physiol Biochem.
39:1021–1030. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xu WH, Yao XY, Yu HJ, Huang JW and Cui LY:
Downregulation of miR-199a may play a role in 3-nitropropionic acid
induced ischemic tolerance in rat brain. Brain Res. 1429:116–123.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|