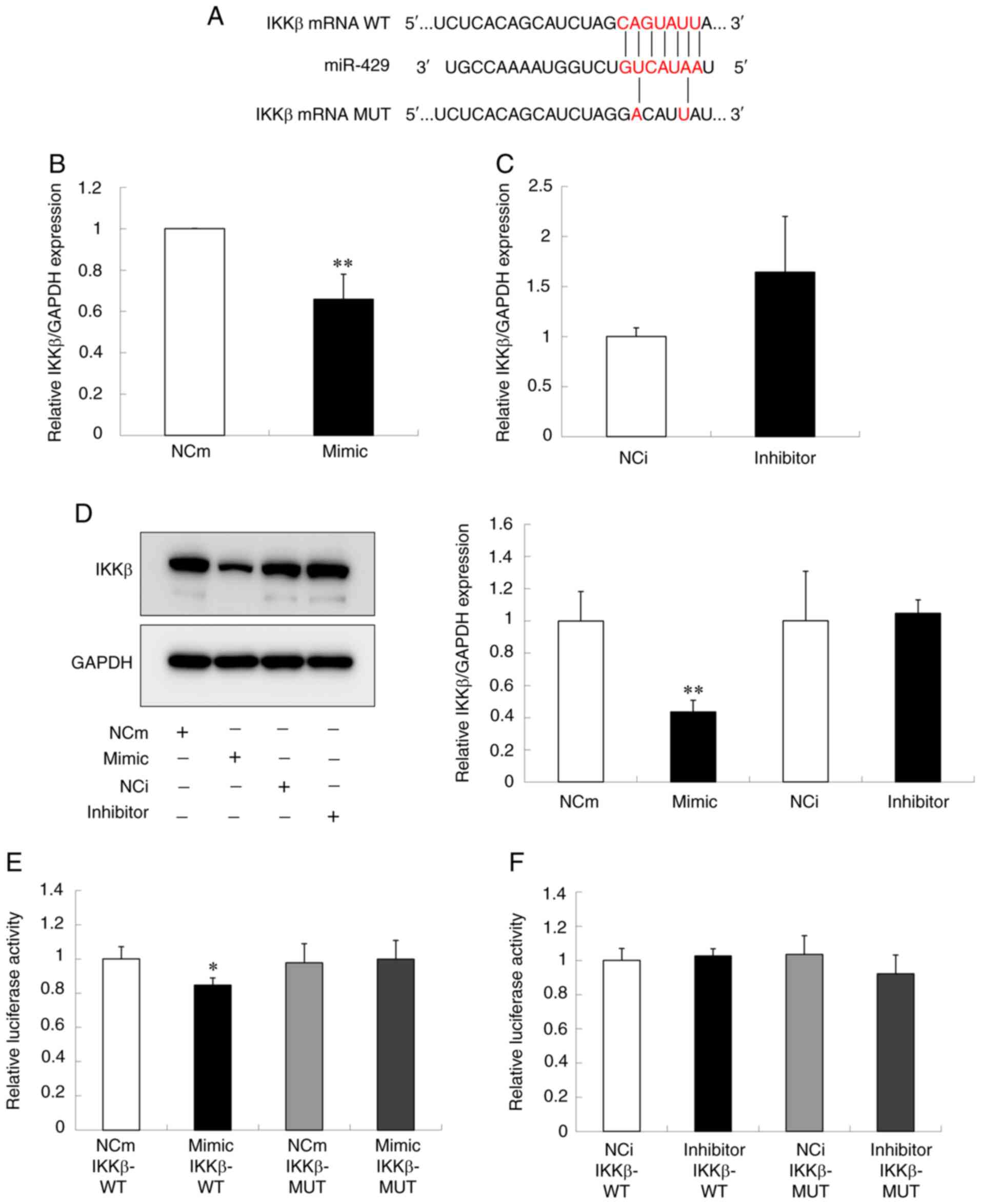
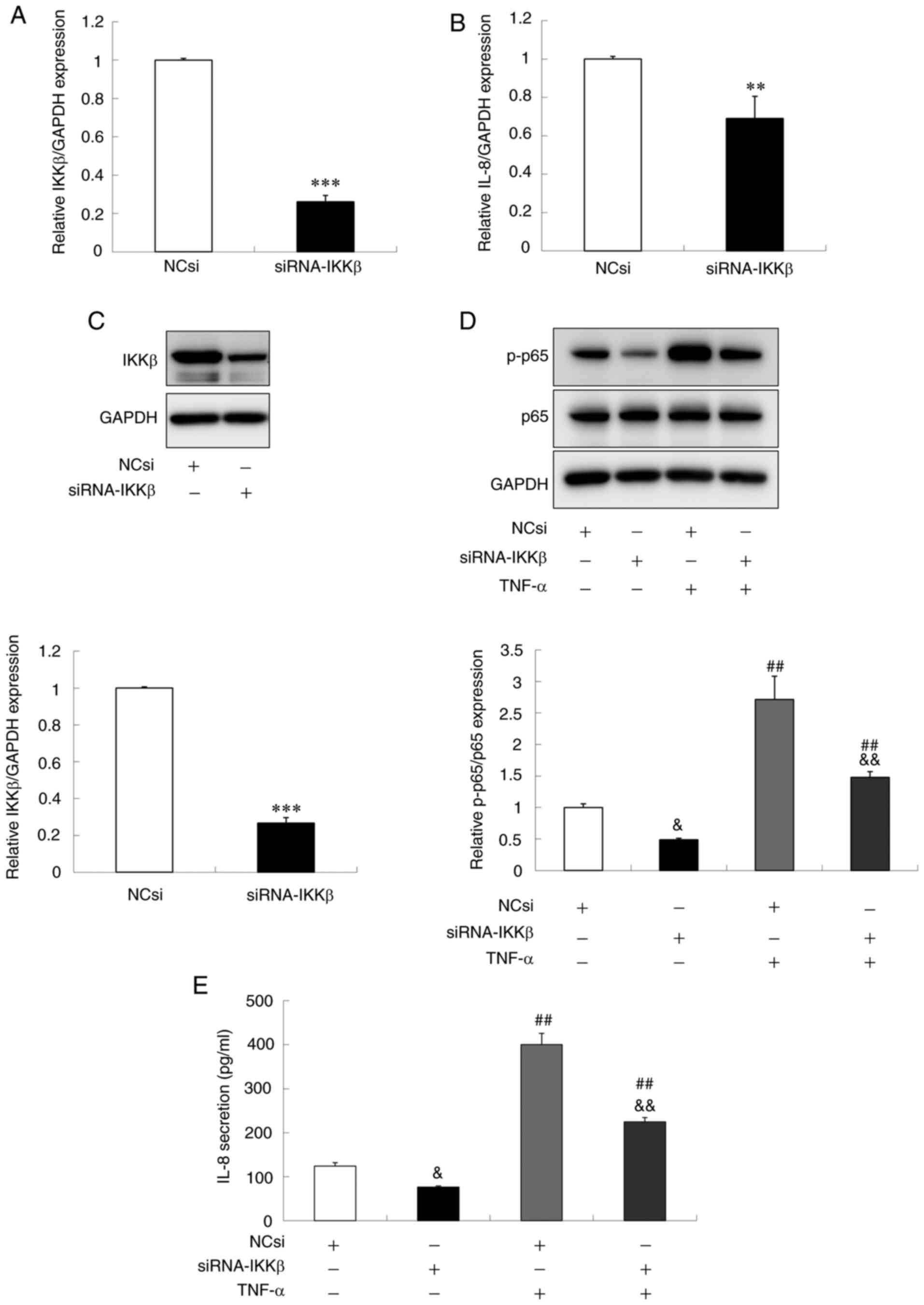
|
1
|
Hasturk H and Kantarci A: Activation and
resolution of periodontal inflammation and its systemic impact.
Periodontol. 69:255–273. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Darveau RP: Periodontitis: A polymicrobial
disruption of host homeostasis. Nat Rev Microbiol. 8:481–490. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hajishengallis G: Periodontitis: From
microbial immune subversion to systemic inflammation. Nat Rev
Immunol. 15:30–44. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pan W, Wang Q and Chen Q: The cytokine
network involved in the host immune response to periodontitis. Int
J Oral Sci. 11:302019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fujita T, Yoshimoto T, Kajiya M, Ouhara K,
Matsuda S, Takemura T, Akutagawa K, Takeda K, Mizuno N and Kurihara
H: Regulation of defensive function on gingival epithelial cells
can prevent periodontal disease. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 54:66–75. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lawrence T: The nuclear factor NF-kappaB
pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
1:a0016512009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Grimaldi A, Zarone MR, Irace C, Zappavigna
S, Lombardi A, Kawasaki H, Caraglia M and Misso G: Non-coding RNAs
as a new dawn in tumor diagnosis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 78:37–50.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Misso G, Zarone MR, Grimaldi A, Maria TDM,
Lombardi A, Kawasaki H, Paola S, Pierfrancesco T, Pierosandro T and
Caraglia M: Non coding RNAs: A new avenue for the self-tailoring of
blood cancer treatment. Curr Drug Targets. 18:35–55. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Takeuchi T, Kawasaki H, Luce A, Cossu AM,
Misso G, Scrima M, Bocchetti M, Ricciardiello F, Caraglia M and
Zappavigna S: Insight toward the MicroRNA profiling of laryngeal
cancers: Biological role and clinical impact. Int J Mol Sci.
21:36932020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Misso G, Zarone MR, Lombardi A, Grimaldi
A, Cossu AM, Ferri C, Russo M, Vuoso DC, Luce A, Kawasaki H, et al:
miR-125b upregulates miR-34a and sequentially activates stress
adaption and cell death mechanisms in multiple myeloma. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 16:391–406. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Maudet C, Mano M and Eulalio A: MicroRNAs
in the interaction between host and bacterial pathogens. FEBS Lett.
588:4140–4147. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kawasaki H, Takeuchi T, Ricciardiello F,
Lombardi A, Biganzoli E, Fornili M, De Bortoli D, Mesolella M,
Cossu AM, Scrima M, et al: Definition of miRNA signatures of nodal
metastasis in LCa: miR-449a targets notch genes and suppresses cell
migration and invasion. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 20:711–724. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR,
Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O'Briant
KC, Allen A, et al: Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based
markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:10513–10518. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Grassia V, Lombardi A, Kawasaki H, Ferri
C, Perillo L, Mosca L, Cave DD, Nucci L, Porcelli M and Caraglia M:
Salivary microRNAs as new molecular markers in cleft lip and
palate: A new frontier in molecular medicine. Oncotarget.
9:18929–18938. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Saito A, Horie M, Ejiri K, Akira A,
Katagiri S, Maekawa S, Suzuki S, Kong S, Yamauchi T, Yamaguchi Y,
et al: MicroRNA profiling in gingival crevicular fluid of
periodontitis-a pilot study. FEBS Open Bio. 7:981–994. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry
SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, Vadas MA, Khew-Goodall Y and Goodall GJ:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Park SM, Gaur AB, Lengyel E and Peter ME:
The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer
cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors. ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes
Dev. 22:894–907. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang P, Cao J, Liu S, Pan H, Liu X, Sui A,
Wang L, Yao R, Liu Z and Liang J: Upregulated microRNA-429 inhibits
the migration of HCC cells by targeting TRAF6 through the NF-κB
pathway. Oncol Rep. 37:2883–2890. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Arunkumar G, Deva Magendhra Rao AK,
Manikandan M, Prasanna Srinivasa Rao H, Subbiah S, Ilangovan R,
Murugan AK and Munirajan AK: Dysregulation of miR-200 family
microRNAs and epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 15:649–657. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chuang TD and Khorram O: miR-200c
regulates IL8 expression by targeting IKBKB: A potential mediator
of inflammation in leiomyoma pathogenesis. PLoS One. 9:e953702014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hong L, Sharp T, Khorsand B, Fischer C,
Eliason S, Salem A, Akkouch A, Brogden K and Amendt BA:
MicroRNA-200c represses IL-6, IL-8 and CCL-5 expression and
enhances osteogenic differentiation. PLoS One. 11:e01609152016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pecot CV, Rupaimoole R, Yang D, Akbani R,
Ivan C, Lu C, Wu S, Han HD, Shah MY, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, et al:
Tumour angiogenesis regulation by the miR-200 family. Nat Commun.
4:24272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shen Y, Zhou M, Yan J, Gong Z, Xiao Y,
Zhang C, Du P and Chen Y: miR-200b inhibits TNF-α-induced IL-8
secretion and tight junction disruption of intestinal epithelial
cells in vitro. Am J Physiol Liver Physiol. 312:G123–G132.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Matsui S, Zhou L, Nakayama Y, Mezawa M,
Kato A, Suzuki N, Tanabe N, Nakayama T, Suzuki Y, Kamio N, et al:
miR-200b attenuates IL-6 production through IKKβ and ZEB1 in human
gingival fibroblasts. Inflamm Res. 67:965–973. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou X, Lu H, Li F, Hao X, Han L, Dong Q
and Chen X: MicroRNA-429 inhibits neuroblastoma cell proliferation,
migration and invasion via the NF-κB pathway. Cell Mol Biol Lett.
25:52020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu H, Wang G, Wang Z, An S, Ye P and Luo
S: A negative feedback loop between miR-200b and the nuclear
factor-κB pathway via IKBKB/IKK-β in breast cancer cells. FEBS J.
283:2259–2271. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Song B, Zheng K, Ma H, Liu A, Jing W, Shao
C, Li G and Jin G: miR-429 determines poor outcome and inhibits
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma growth by targeting TBK1. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 35:1846–1856. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ohtani M and Nishimura T: Sulfur
containing amino acids in aged garlic extract inhibit inflammation
in human gingival epithelial cells by suppressing intercellular
adhesion molecule-1 expression and IL-6 secretion. Biomed Rep.
12:99–108. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Badr CE, Niers JM, Tjon-Kon-Fat LA, Noske
DP, Wurdinger T and Tannous BA: Real-time monitoring of nuclear
Factor kappaB activity in cultured cells and in animal models. Mol
Imaging. 8:278–290. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Catley MC, Chivers JE, Holden NS, Barnes
PJ and Newton R: Validation of IKK beta as therapeutic target in
airway inflammatory disease by adenoviral-mediated delivery of
dominant-negative IKK beta to pulmonary epithelial cells. Br J
Pharmacol. 145:114–122. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hirata Y, Maeda S, Ohmae T, Shibata W,
Yanai A, Ogura K, Yoshida H, Kawabe T and Omata M: Helicobacter
pylori induces IkappaB kinase alpha nuclear translocation and
chemokine production in gastric epithelial cells. Infect Immun.
74:1452–1461. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hernandez L, Hsu SC, Davidson B, Birrer
MJ, Kohn EC and Annunziata CM: Activation of NF-kappaB signaling by
inhibitor of NF-kappaB kinase β increases aggressiveness of ovarian
cancer. Cancer Res. 70:4005–4014. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Moutsopoulos NM and Konkel JE:
Tissue-specific immunity at the oral mucosal barrier. Trends
Immunol. 39:276–287. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Guo Y and Liao Y: miR-200bc/429 cluster
alleviates inflammation in IgA nephropathy by targeting TWEAK/Fn14.
Int Immunopharmacol. 52:150–155. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Leng J, Liu W, Li L, Wei FY, Tian M, Liu
HM and Guo W: MicroRNA-429/Cxcl1 axis protective against oxygen
glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced injury in brain
microvascular endothelial cells. Dose-Response.
18:15593258209137852020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bezzerri V, Borgatti M, Finotti A,
Tamanini A, Gambari R and Cabrini G: Mapping the transcriptional
machinery of the IL-8 gene in human bronchial epithelial cells. J
Immunol. 187:6069–6081. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Finoti LS, Nepomuceno R, Pigossi SC, Corbi
SC, Secolin R and Scarel-Caminaga RM: Association between
interleukin-8 levels and chronic periodontal disease. Medicine
(Baltimore). 96:e69322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nagahama Y, Obama T, Usui M, Kanazawa Y,
Iwamoto S, Suzuki K, Miyazaki A, Yamaguchi T, Yamamoto M and Itabe
H: Oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced periodontal
inflammation is associated with the upregulation of
cyclooxygenase-2 and microsomal prostaglandin synthase 1 in human
gingival epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 413:566–571.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Grimm D, Wang L, Lee JS, Schürmann N, Gu
S, Börner K, Storm TA and Kay MA: Argonaute proteins are key
determinants of RNAi efficacy, toxicity and persistence in the
adult mouse liver. J Clin Invest. 120:3106–3119. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Matsui M, Prakash TP and Corey DR:
Argonaute 2-dependent regulation of gene expression by
single-stranded miRNA mimics. Mol Ther. 24:946–955. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Poplutz MK, Wessels I, Rink L and
Uciechowski P: Regulation of the Interleukin-6 gene expression
during monocytic differentiation of HL-60 cells by chromatin
remodeling and methylation. Immunobiology. 219:619–626. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tanaka T, Narazaki M and Kishimoto T: IL-6
in inflammation, immunity and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Biol. 6:a0162952014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ruocco MG, Maeda S, Park JM, Lawrence T,
Hsu LC, Cao Y, Schett G, Wagner EF and Karin M: IκB kinase (IKK)β,
but not IKKα, is a critical mediator of osteoclast survival and is
required for inflammation-induced bone loss. J Exp Med.
201:1677–1687. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Groeger S, Jarzina F, Domann E and Meyle
J: Porphyromonas gingivalis activates NFκB and MAPK pathways in
human oral epithelial cells. BMC Immunol. 18:12017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gao Y and Yu Z: MicroRNA-16 inhibits
interleukin-13-induced inflammatory cytokine secretion and mucus
production in nasal epithelial cells by suppressing the IκB kinase
β/nuclear factor-κB pathway. Mol Med Rep. 18:4042–4050.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Khalife J, Ghose J, Martella M, Viola D,
Rocci A, Troadec E, Terrazas C, Satoskar AR, Gunes EG, Dona A, et
al: miR-16 regulates crosstalk in NF-κB tolerogenic inflammatory
signaling between myeloma cells and bone marrow macrophages. JCI
Insight. 4:e1293482019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Patel V, Carrion K, Hollands A, Hinton A,
Gallegos T, Dyo J, Sasik R, Leire E, Hardiman G, Mohamed SA, et al:
The stretch responsive microRNA miR-148a-3p is a novel repressor of
IKBKB, NF-κB signaling and inflammatory gene expression in human
aortic valve cells. FASEB J. 29:1859–1868. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chen R, Alvero AB, Silasi DA, Kelly MG,
Fest S, Visintin I, Leiser A, Schwartz PE, Rutherford T and Mor G:
Regulation of IKKβ by miR-199a affects NF-κB activity in ovarian
cancer cells. Oncogene. 27:4712–4723. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wei D, Shen B, Wang W, Zhou Y, Yang X, Lu
G, Yang J and Shao Y: MicroRNA-199a-5p functions as a tumor
suppressor in oral squamous cell carcinoma via targeting the
IKKβ/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 43:1585–1596.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Dai L, Gu L and Di W: miR-199a attenuates
endometrial stromal cell invasiveness through suppression of the
IKKβ/NF-κB pathway and reduced interleukin-8 expression. Mol Hum
Reprod. 18:136–145. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yamazaki-Takai M, Takai H, Iwai Y, Noda K,
Mezawa M, Tsuruya Y, Yamaguchi A, Nakayama Y and Ogata Y: miR-200b
suppresses TNF-α-induced AMTN production in human gingival
epithelial cells. Odontology. 109:403–410. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cao Y, Tang S, Nie X, Zhou Z, Ruan G, Han
W, Zhu Z and Ding C: Decreased miR-214-3p activates NF-κB pathway
and aggravates osteoarthritis progression. EBioMedicine.
65:1032832021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Niu D, Gong Z, Sun X, Yuan J, Zheng T,
Wang X, Fan X, Mao Y, Liu X, Tang B and Fu Y: miR-338-3p regulates
osteoclastogenesis via targeting IKKβ gene. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol
Anim. 55:243–251. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kong XJ, Duan LJ, Qian XQ, Xu D, Liu HL,
Zhu YJ and Qi J: Tumor-suppressive microRNA-497 targets IKKβ to
regulate NF-κB signaling pathway in human prostate cancer cells. Am
J Cancer Res. 5:1795–1804. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mechtler P, Singhal R, Kichina JV, Bard
JE, Buck MJ and Kandel ES: MicroRNA analysis suggests an additional
level of feedback regulation in the NF-κB signaling cascade.
Oncotarget. 6:17097–17106. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chen W, He LN, Liang Y, Zeng X, Wu CP, Su
MQ, Cheng Y and Liu JH: TERF1 downregulation promotes the migration
and invasion of the PC3 prostate cancer cell line as a target of
miR-155. Mol Med Rep. 22:5209–5218. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yang J, Meng X, Pan J, Jiang N, Zhou C, Wu
Z and Gong Z: CRISPR/Cas9-mediated noncoding RNA editing in human
cancers. RNA Biol. 15:35–43. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|