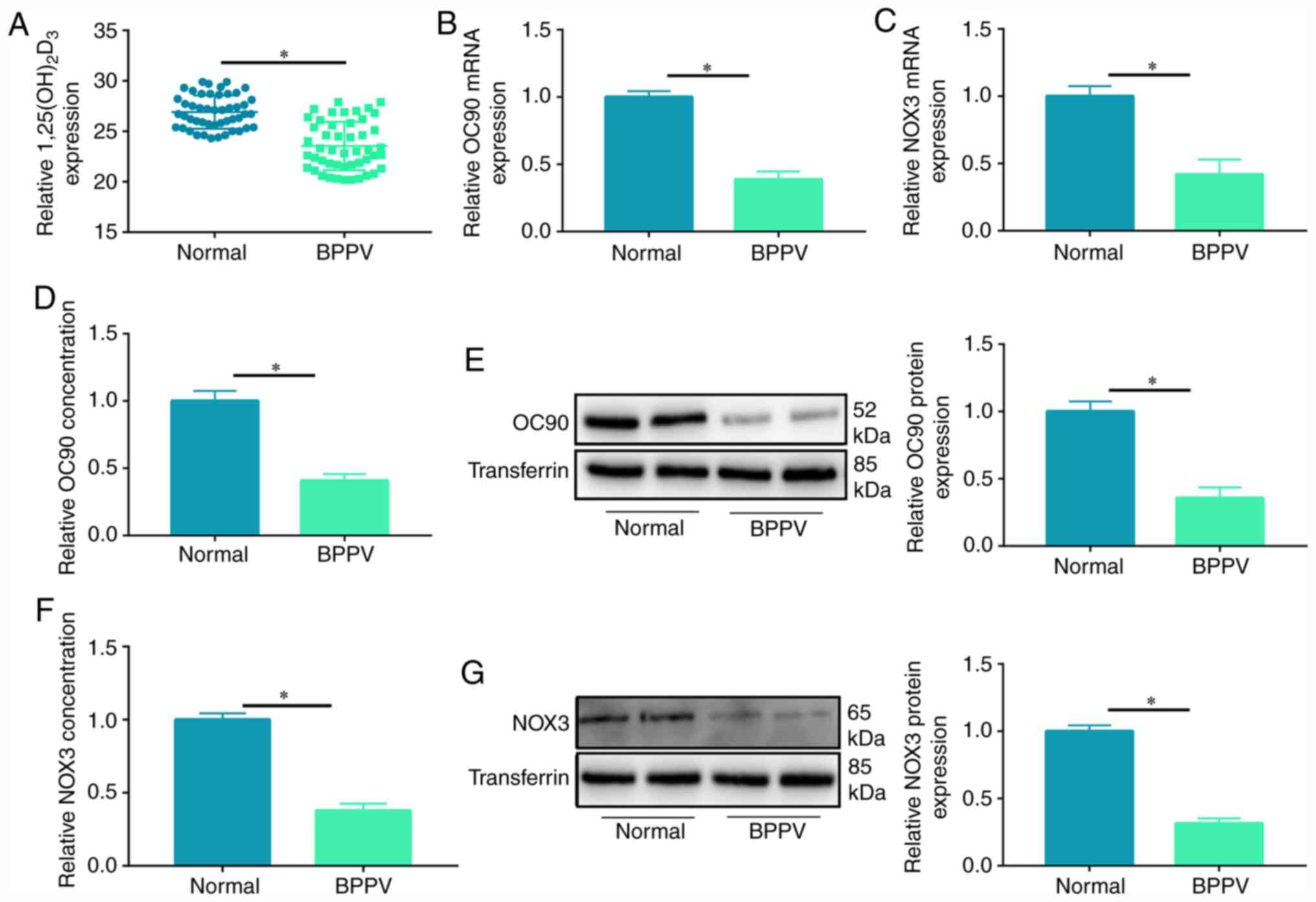
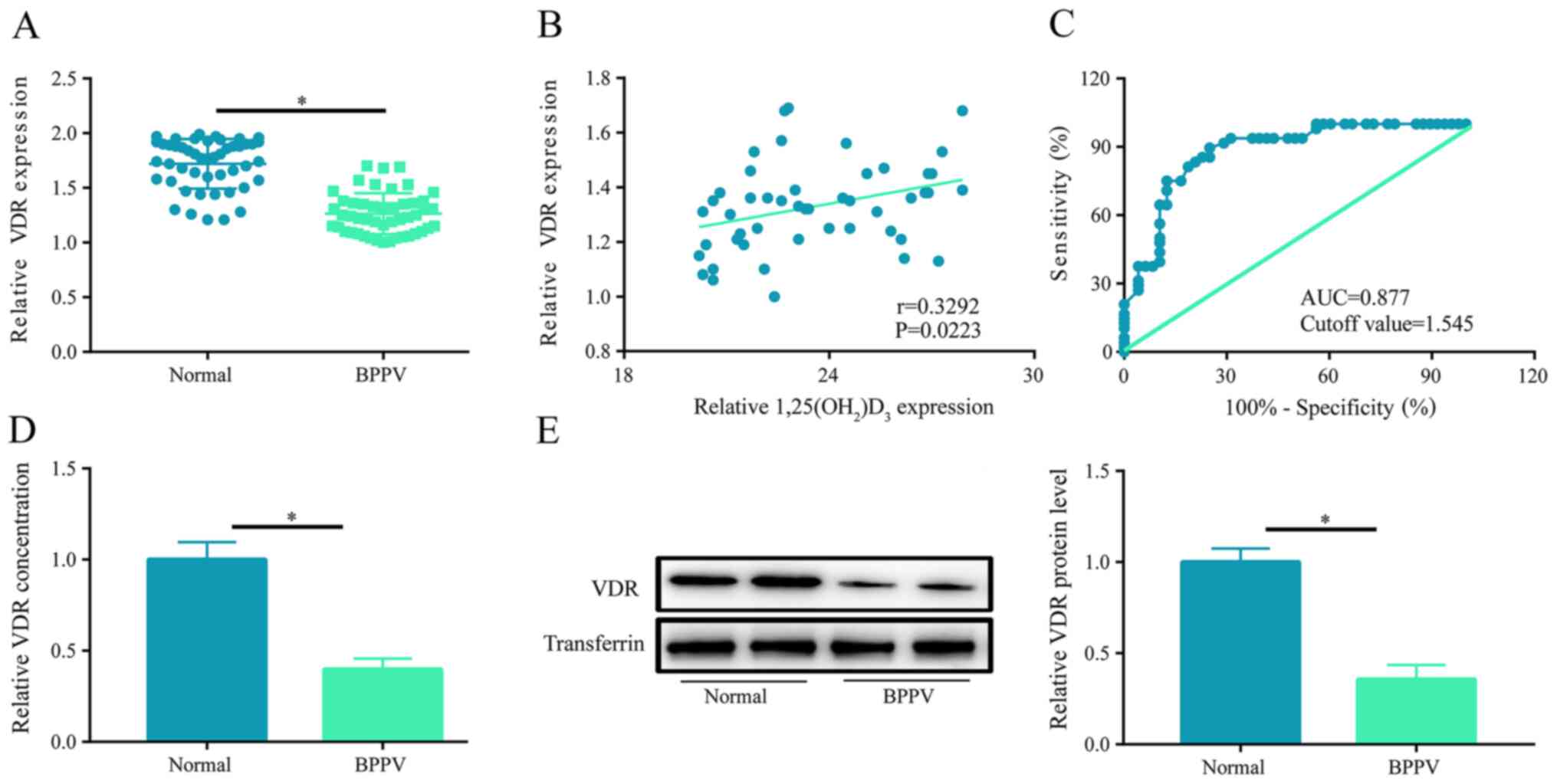
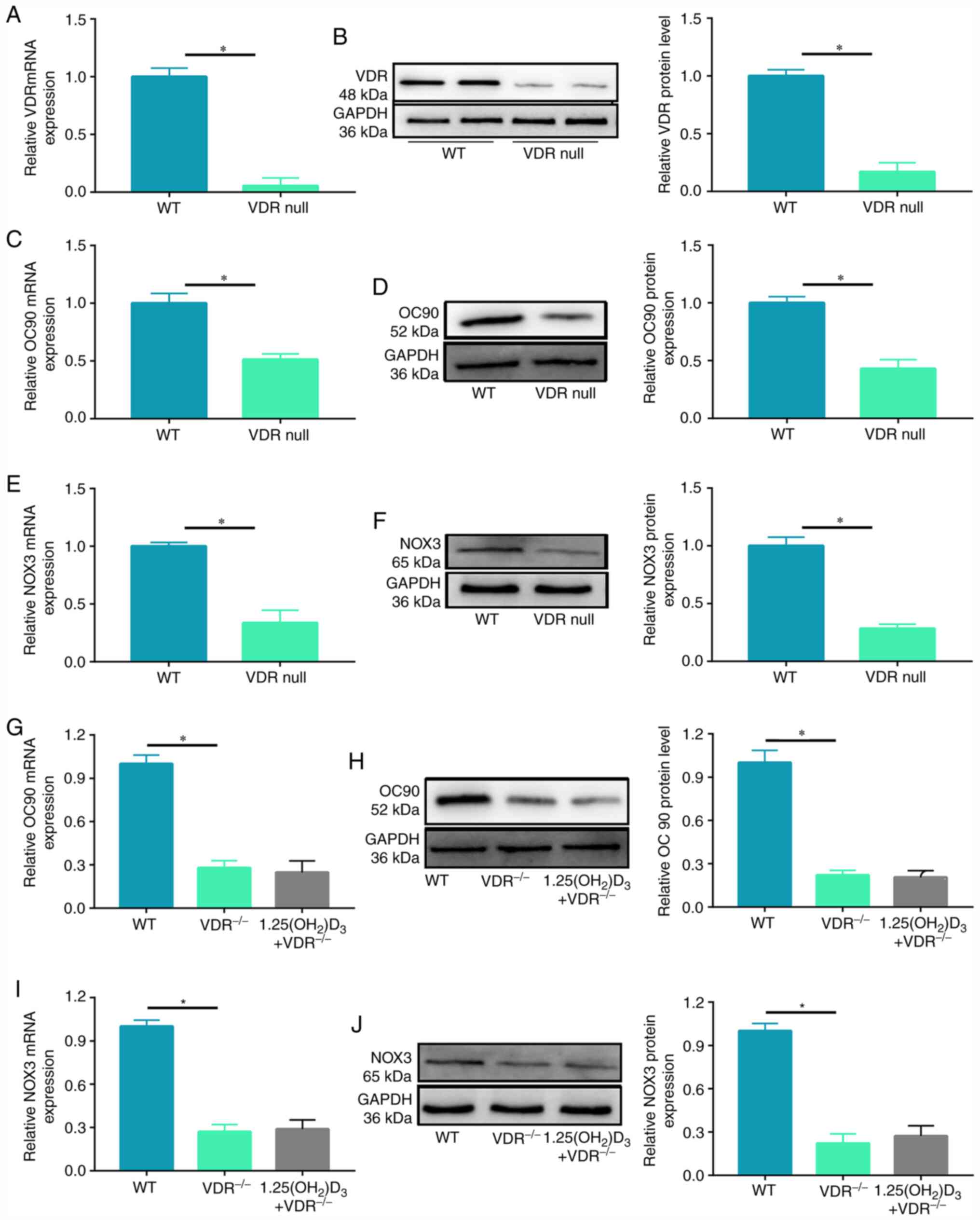
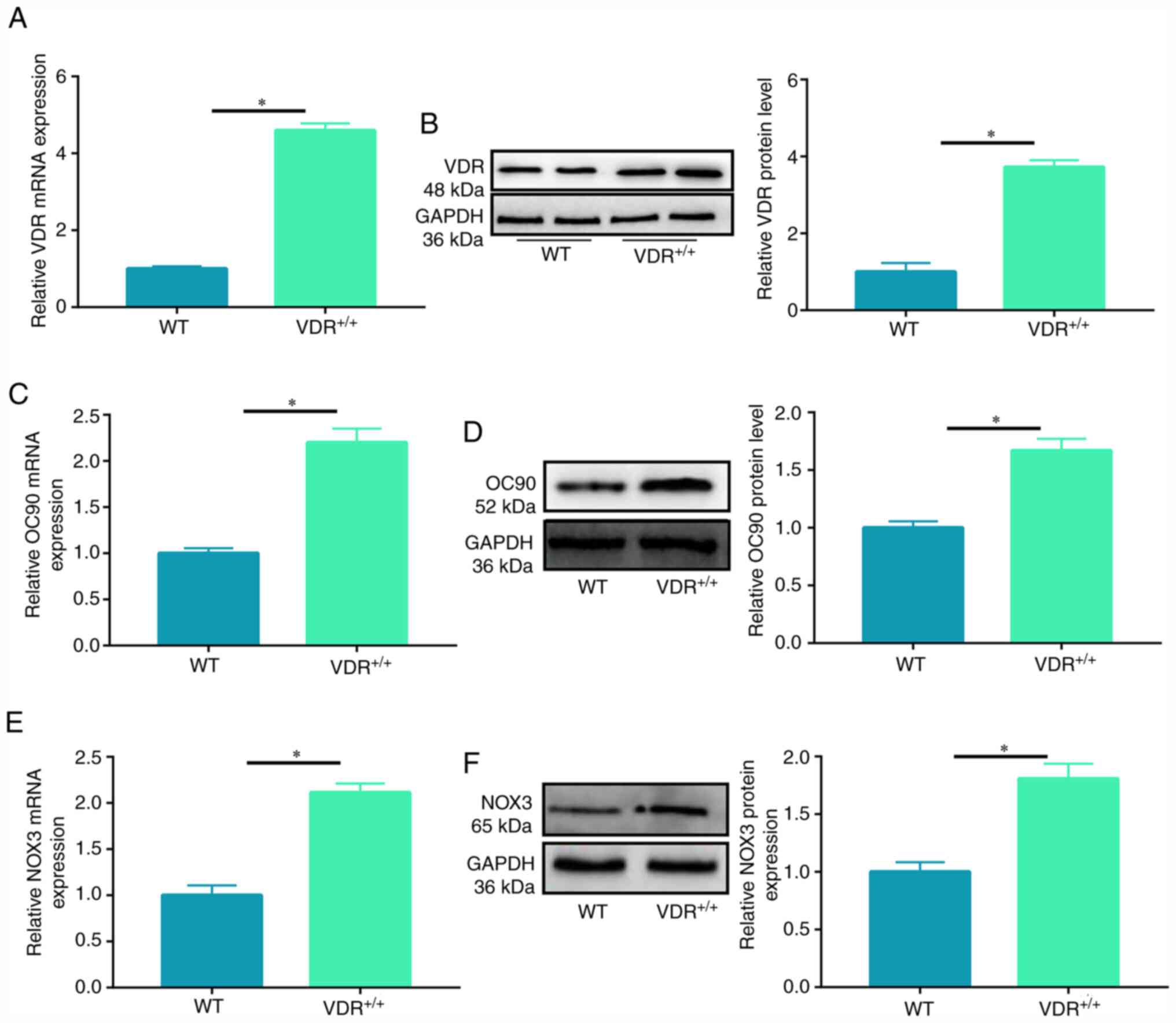
|
1
|
Froehling DA, Silverstein MD, Mohr DN,
Beatty CW, Offord KP and Ballard DJ: Benign positional vertigo:
Incidence and prognosis in a population-based study in Olmsted
County, Minnesota. Mayo Clin Proc. 66:596–601. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Imai T, Higashi-Shingai K, Takimoto Y,
Masumura C, Hattori K and Inohara H: New scoring system of an
interview for the diagnosis of benign paroxysmal positional
vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol. 136:283–288. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fife TD, Iverson DJ, Lempert T, Furman JM,
Baloh RW, Tusa RJ, Hain TC, Herdman S, Morrow MJ and Gronseth GS;
Quality Standards Subcommittee, American Academy of Neurology, :
Practice parameter: Therapies for benign paroxysmal positional
vertigo (an evidence-based review): Report of the quality standards
subcommittee of the American academy of neurology. Neurology.
70:2067–2074. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bhattacharyya N, Gubbels SP, Schwartz SR,
Edlow JA, El-Kashlan H, Fife T, Holmberg JM, Mahoney K,
Hollingsworth DB, Roberts R, et al: Clinical practice guideline:
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (Update). Otolaryngol Head
Neck Surg. 156 (3 Suppl):S1–S47. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ogun OA, Büki B, Cohn ES, Janky KL and
Lundberg YW: Menopause and benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.
Menopause. 21:886–889. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Imai T, Takeda N, Ikezono T, Shigeno K,
Asai M, Watanabe Y and Suzuki M; Committee for Standards in
Diagnosis of Japan Society for Equilibrium Research, :
Classification, diagnostic criteria and management of benign
paroxysmal positional vertigo. Auris Nasus Larynx. 44:1–6. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jeong SH, Kim JS, Shin JW, Kim S, Lee H,
Lee AY, Kim JM, Jo H, Song J and Ghim Y: Decreased serum vitamin D
in idiopathic benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Neurol.
260:832–838. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baloh RW, Honrubia V and Jacobson K:
Benign positional vertigo: Clinical and oculographic features in
240 cases. Neurology. 37:371–378. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lundberg YW, Xu Y, Thiessen KD and Kramer
KL: Mechanisms of otoconia and otolith development. Dev Dyn.
244:239–253. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu Y, Gu C, Han W, Lu X, Chen C and Fan Z:
Reduction of bone mineral density in native Chinese female
idiopathic benign paroxysmal positional vertigo patients. Am J
Otolaryngol. 39:31–33. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yoda S, Cureoglu S, Yildirim-Baylan M,
Morita N, Fukushima H, Harada T and Paparella MM: Association
between type 1 diabetes mellitus and deposits in the semicircular
canals. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 145:458–462. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu J and Zhang J: LncRNA TP73-AS1 is a
novel regulator in cervical cancer via miR-329-3p/ARF1 axis. J Cell
Biochem. 121:344–352. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Holick MF: Resurrection of vitamin D
deficiency and rickets. J Clin Invest. 116:2062–2072. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Christakos S, Dhawan P, Verstuyf A,
Verlinden L and Carmeliet G: Vitamin D: Metabolism, molecular
mechanism of action, and pleiotropic effects. Physiol Rev.
96:365–408. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Büki B, Ecker M, Jünger H and Lundberg YW:
Vitamin D deficiency and benign paroxysmal positioning vertigo. Med
Hypotheses. 80:201–204. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Talaat HS, Kabel AM, Khaliel LH, Abuhadied
G, El-Naga HA and Talaat AS: Reduction of recurrence rate of benign
paroxysmal positional vertigo by treatment of severe vitamin D
deficiency. Auris Nasus Larynx. 43:237–241. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Haussler MR, Whitfield GK, Haussler CA,
Hsieh JC, Thompson PD, Selznick SH, Dominguez CE and Jurutka PW:
The nuclear vitamin D receptor: Biological and molecular regulatory
properties revealed. J Bone Miner Res. 13:325–349. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Feldman D, Krishnan AV, Swami S,
Giovannucci E and Feldman BJ: The role of vitamin D in reducing
cancer risk and progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:342–357. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dovnik A and Dovnik NF: Vitamin D and
ovarian cancer: Systematic review of the literature with a focus on
molecular mechanisms. Cells. 9:3352020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of
Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery; Society of
Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Chinese Medical:
Association, . Guideline of diagnosis and treatment of benign
paroxysmal positional vertigo (2017). Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou
Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 52:173–177. 2017.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Code of practice for the care and use of
animals for experimental purposes in Australia. Med J Aust.
141:871–876. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jang YS, Hwang CH, Shin JY, Bae WY and Kim
LS: Age-related changes on the morphology of the otoconia.
Laryngoscope. 116:996–1001. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang X, Ling X, Shen B, Hong Y, Li K, Si L
and Kim JS: Diagnosis strategy and Yacovino maneuver for anterior
canal-benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Neurol.
266:1674–1684. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Thalmann R, Ignatova E, Kachar B, Ornitz
DM and Thalmann I: Development and maintenance of otoconia:
Biochemical considerations. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 942:162–178. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao X, Jones SM, Yamoah EN and Lundberg
YW: Otoconin-90 deletion leads to imbalance but normal hearing: A
comparison with other otoconia mutants. Neuroscience. 153:289–299.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Deans MR, Peterson JM and Wong GW:
Mammalian otolin: A multimeric glycoprotein specific to the inner
ear that interacts with otoconial matrix protein otoconin-90 and
Cerebellin-1. PLoS One. 5:e127652010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Parham K, Sacks D, Bixby C and Fall P:
Inner ear protein as a biomarker in circulation? Otolaryngol Head
Neck Surg. 151:1038–1040. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lundberg YW, Zhao X and Yamoah EN:
Assembly of the otoconia complex to the macular sensory epithelium
of the vestibule. Brain Res. 1091:47–57. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hughes I, Thalmann I, Thalmann R and
Ornitz DM: Mixing model systems: Using zebrafish and mouse inner
ear mutants and other organ systems to unravel the mystery of
otoconial development. Brain Res. 1091:58–74. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao X, Yang H, Yamoah EN and Lundberg YW:
Gene targeting reveals the role of Oc90 as the essential organizer
of the otoconial organic matrix. Dev Biol. 304:508–524. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim E, Hyrc KL, Speck J, Salles FT,
Lundberg YW, Goldberg MP, Kachar B, Warchol ME and Ornitz DM:
Missense mutations in otopetrin 1 affect subcellular localization
and inhibition of purinergic signaling in vestibular supporting
cells. Mol Cell Neurosci. 46:655–661. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim E, Hyrc KL, Speck J, Lundberg YW,
Salles FT, Kachar B, Goldberg MP, Warchol ME and Ornitz DM:
Regulation of cellular calcium in vestibular supporting cells by
otopetrin 1. J Neurophysiol. 104:3439–3450. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Paffenholz R, Bergstrom RA, Pasutto F,
Wabnitz P, Munroe RJ, Jagla W, Heinzmann U, Marquardt A, Bareiss A,
Laufs J, et al: Vestibular defects in head-tilt mice result from
mutations in Nox3, encoding an NADPH oxidase. Genes Dev.
18:486–491. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Prosser DE and Jones G: Enzymes involved
in the activation and inactivation of vitamin D. Trends Biochem
Sci. 29:664–673. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nagpal S, Na S and Rathnachalam R:
Noncalcemic actions of vitamin D receptor ligands. Endocr Rev.
26:662–687. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hendrickson WK, Flavin R, Kasperzyk JL,
Fiorentino M, Fang F, Lis R, Fiore C, Penney KL, Ma J, Kantoff PW,
et al: Vitamin D receptor protein expression in tumor tissue and
prostate cancer progression. J Clin Oncol. 29:2378–2385. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Berger U, McClelland RA, Wilson P, Greene
GL, Haussler MR, Pike JW, Colston K, Easton D and Coombes RC:
Immunocytochemical determination of estrogen receptor, progesterone
receptor, and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor in breast cancer
and relationship to prognosis. Cancer Res. 51:239–244.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wen Y, Da M, Zhang Y, Peng L, Yao J and
Duan Y: Alterations in vitamin D signaling pathway in gastric
cancer progression: A study of vitamin D receptor expression in
human normal, premalignant, and malignant gastric tissue. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:13176–13184. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Minasyan A, Keisala T, Zou J, Zhang Y,
Toppila E, Syvälä H, Lou YR, Kalueff AV, Pyykkö I and Tuohimaa P:
Vestibular dysfunction in vitamin D receptor mutant mice. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 114:161–166. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|