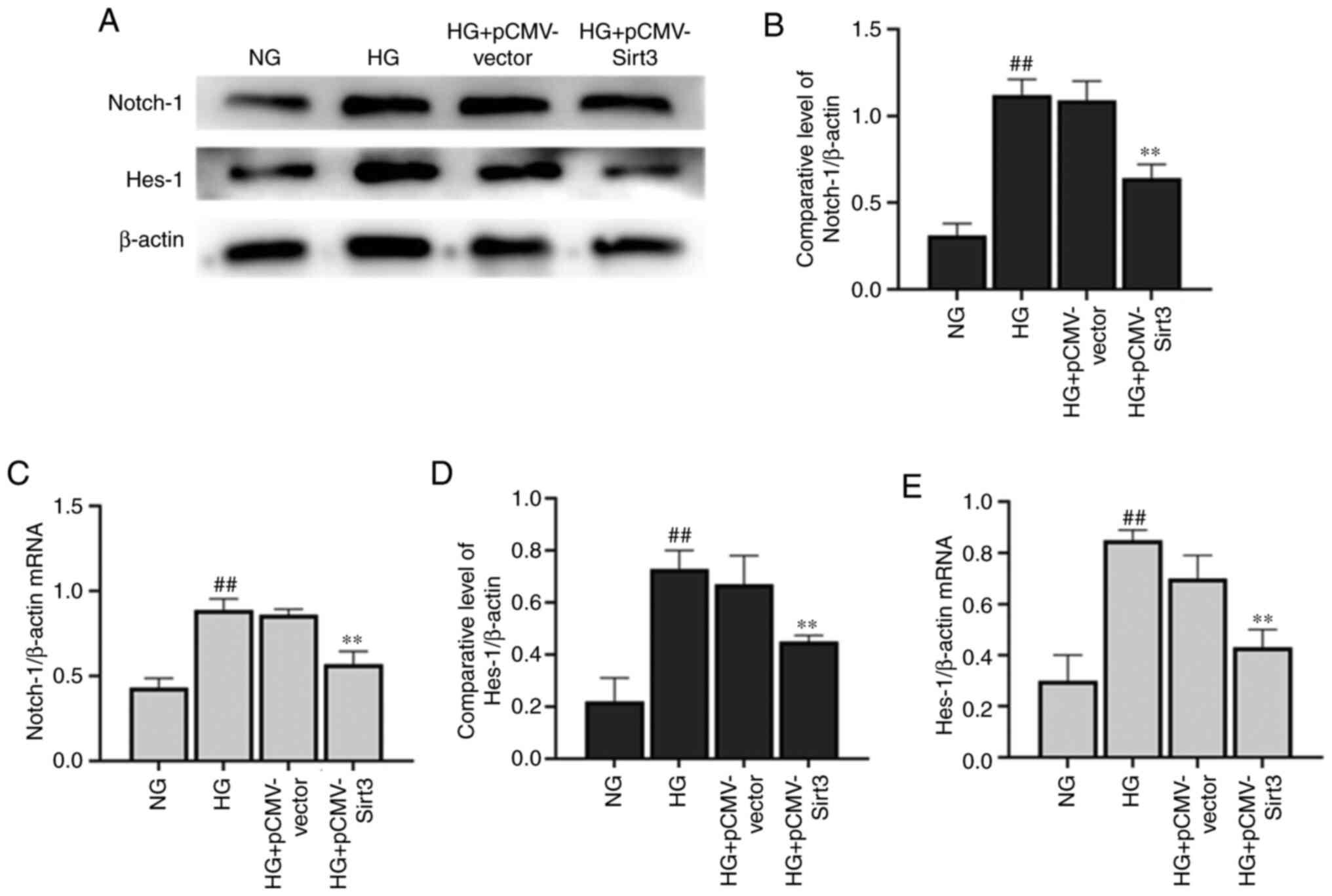
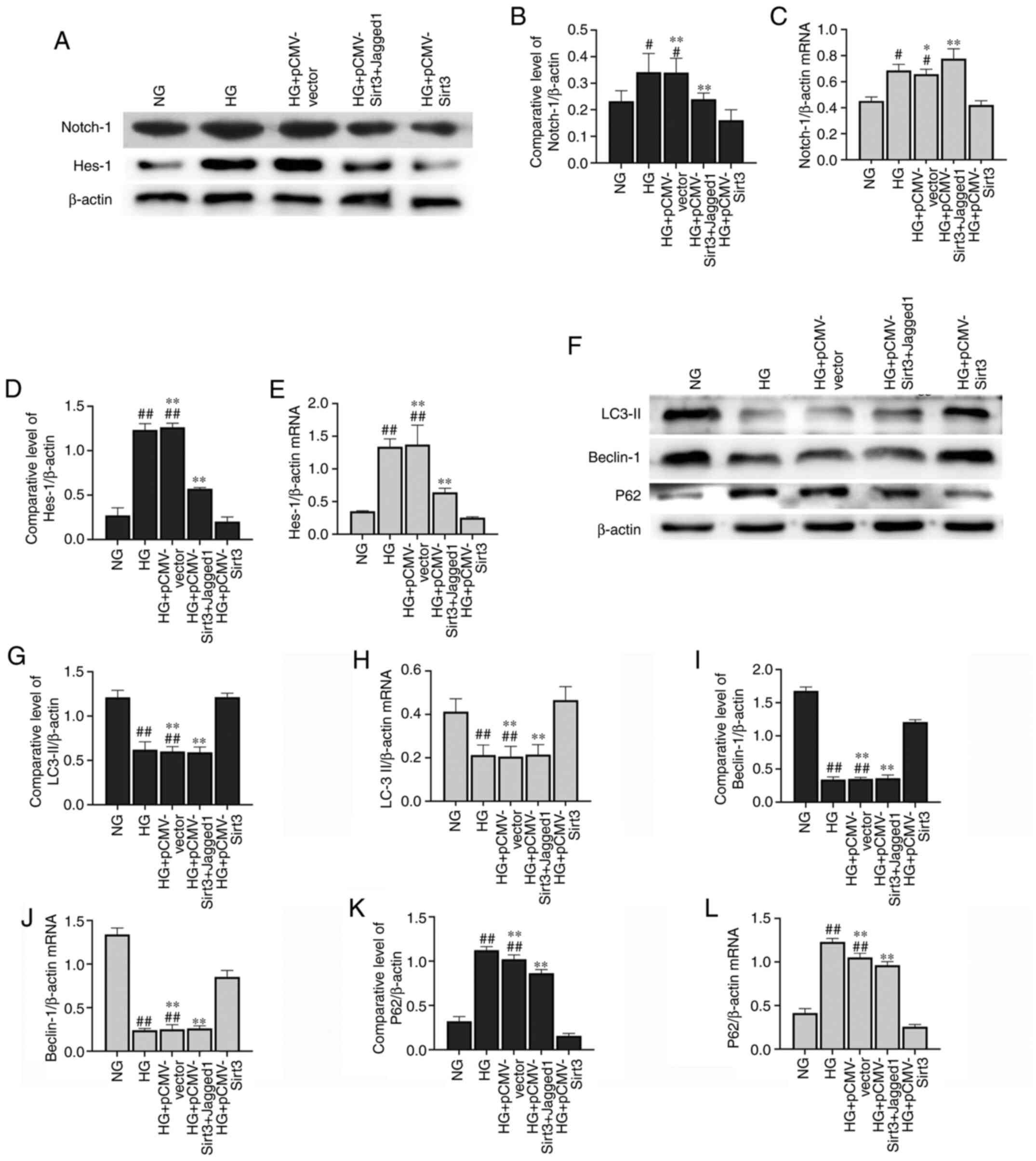
|
1
|
Warren AM, Knudsen ST and Cooper ME:
Diabetic nephropathy: An insight into molecular mechanisms and
emerging therapies. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 23:579–591. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gilbertson DT, Liu J, Xue JL, Louis TA,
Solid CA, Ebben JP and Collins AJ: Projecting the number of
patients with end-stage renal disease in the United States to the
year 2015. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:3736–3741. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tang C, Livingston MJ, Liu Z and Dong Z:
Autophagy in kidney homeostasis and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol.
16:489–508. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Small DM, Bennett NC, Coombes J, Johnson
DW and Gobe GC: Mitochondrial homeostasis is impeded by degradation
and autophagy in oxidative stress-induced renal cell injury.
Revista Española De Reumatismo Y Enfermedades Osteoarticulares.
11:67–73. 2013.
|
|
5
|
Kitada M, Ogura Y, Monno I and Koya D:
Regulating autophagy as a therapeutic target for diabetic
nephropathy. Curr Diab Rep. 17:532017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhu SY, Yao RQ, Li YX, Zhao PY, Ren C, Du
XH and Yao YM: Lysosomal quality control of cell fate: A novel
therapeutic target for human diseases. Cell Death Dis. 11:8172020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guo J, Zheng HJ, Zhang W, Lou W, Xia C,
Han XT, Huang WJ, Zhang F, Wang Y and Liu WJ: Accelerated kidney
aging in diabetes mellitus. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020:12340592020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee IH, Cao L, Mostoslavsky R, Lombard DB,
Liu J, Bruns NE, Tsokos M, Alt FW and Finkel T: A role for the
NAD-dependent deacetylase Sirt1 in the regulation of autophagy.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:3374–3379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li R, Xin T, Li D, Wang C, Zhu H and Zhou
H: Therapeutic effect of Sirtuin 3 on ameliorating nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease: The role of the ERK-CREB pathway and
Bnip3-mediated mitophagy. Redox Biol. 18:229–243. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang T, Liu J, Shen S, Tong Q, Ma X and
Lin L: SIRT3 promotes lipophagy and chaperon-mediated autophagy to
protect hepatocytes against lipotoxicity. Cell Death Differ.
27:329–344. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao W, Zhang L, Chen R, Lu H, Sui M, Zhu
Y and Zeng L: SIRT3 protects against acute kidney injury via
AMPK/mTOR-regulated autophagy. Front Physiol. 9:15262018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kitada M, Kume S, Takeda-Watanabe A,
Kanasaki K and Koya D: Sirtuins and renal diseases: Relationship
with aging and diabetic nephropathy. Clin Sci (Lond). 124:153–164.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yu W, Gao B, Li N, Wang J, Qiu C, Zhang G,
Liu M, Zhang R, Li C, Ji G and Zhang Y: Sirt3 deficiency
exacerbates diabetic cardiac dysfunction: Role of
Foxo3A-Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis
Dis. 1863:1973–1983. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen Y, Zhang F, Wang D, Li L, Si H, Wang
C, Liu J, Chen Y, Cheng J and Lu Y: Mesenchymal stem cells
attenuate diabetic lung fibrosis via adjusting Sirt3-mediated
stress responses in rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2020:80761052020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD and Lake RJ:
Notch signaling: Cell fate control and signal integration in
development. Science. 284:770–776. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yuri S, Nishikawa M and Yanagawa N, Jo OD
and Yanagawa N: Maintenance of mouse nephron progenitor cells in
aggregates with Gamma-secretase inhibitor. PLoS One.
10:e01292422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Y, Li Y, Yang Z, Wang Z, Chang J,
Zhang T, Chi Y, Han N and Zhao K: Pyridoxamine treatment of HK-2
human proximal tubular epithelial cells reduces oxidative stress
and the inhibition of autophagy induced by high glucose levels. Med
Sci Monit. 25:1480–1488. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jiao X, Li Y, Zhang T, Liu M and Chi Y:
Role of Sirtuin3 in high glucose-induced apoptosis in renal tubular
epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 480:387–393. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Z, Li Y, Wang Y, Zhao K, Chi Y and
Wang B: Pyrroloquinoline quinine protects HK-2cells against high
glucose-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis through Sirt3 and
PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
508:398–404. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mizushima N and Levine B: Autophagy in
human diseases. N Engl J Med. 383:1564–1576. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang P and Mizushima N: Autophagy and
human diseases. Cell Res. 24:69–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim KH and Lee MS: Autophagy-a key player
in cellular and body metabolism. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 10:322–337.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ding Y and Choi ME: Autophagy in diabetic
nephropathy. J Endocrinol. 224:R15–R30. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu WJ, Huang WF, Ye L, Chen RH, Yang C,
Wu HL, Pan QJ and Liu HF: The activity and role of autophagy in the
pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
22:3182–3189. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin F: Autophagy in renal tubular injury
and repair. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 220:229–237. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ng F and Tang BL: Sirtuins' modulation of
autophagy. J Cell Physiol. 228:2262–2270. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Peng Y, Yang C, Shi X, Li L, Dong H, Liu
C, Fang Z, Wang Z, Ming S, Liu M, et al: Sirt3 suppresses calcium
oxalate-induced renal tubular epithelial cell injury via
modification of FoxO3a-mediated autophagy. Cell Death Dis.
10:342019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang M, Deng YN, Zhang JY, Liu J, Li YB,
Su H and Qu QM: SIRT3 protects Rotenone-induced injury in SH-SY5Y
cells by promoting autophagy through the LKB1-AMPK-mTOR Pathway.
Aging Dis. 9:273–286. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang Y, Zhang X, Wang P, Shen Y, Yuan K,
Li M, Liang W and Que H: Sirt3 overexpression alleviates
hyperglycemia-induced vascular inflammation through regulating
redox balance, cell survival, and AMPK-mediated mitochondrial
homeostasis. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 39:341–349. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Surendran K, Boyle S, Barak H, Kim M,
Stomberski C, McCright B and Kopan R: The contribution of Notch1 to
nephron segmentation in the developing kidney is revealed in a
sensitized Notch2 background and can be augmented by reducing Mint
dosage. Dev Biol. 337:386–395. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vooijs M, Ong CT, Hadland B, Huppert S,
Liu Z, Korving J, van den Born M, Stappenbeck T, Wu Y, Clevers H
and Kopan R: Mapping the consequence of Notch1 proteolysis in vivo
with NIP-CRE. Development. 134:535–544. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zheng D, Tao M, Liang X, Li Y, Jin J and
He Q: p66Shc regulates podocyte autophagy in high glucose
environment through the Notch-PTEN-PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Histol
Histopathol. 35:405–415. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|