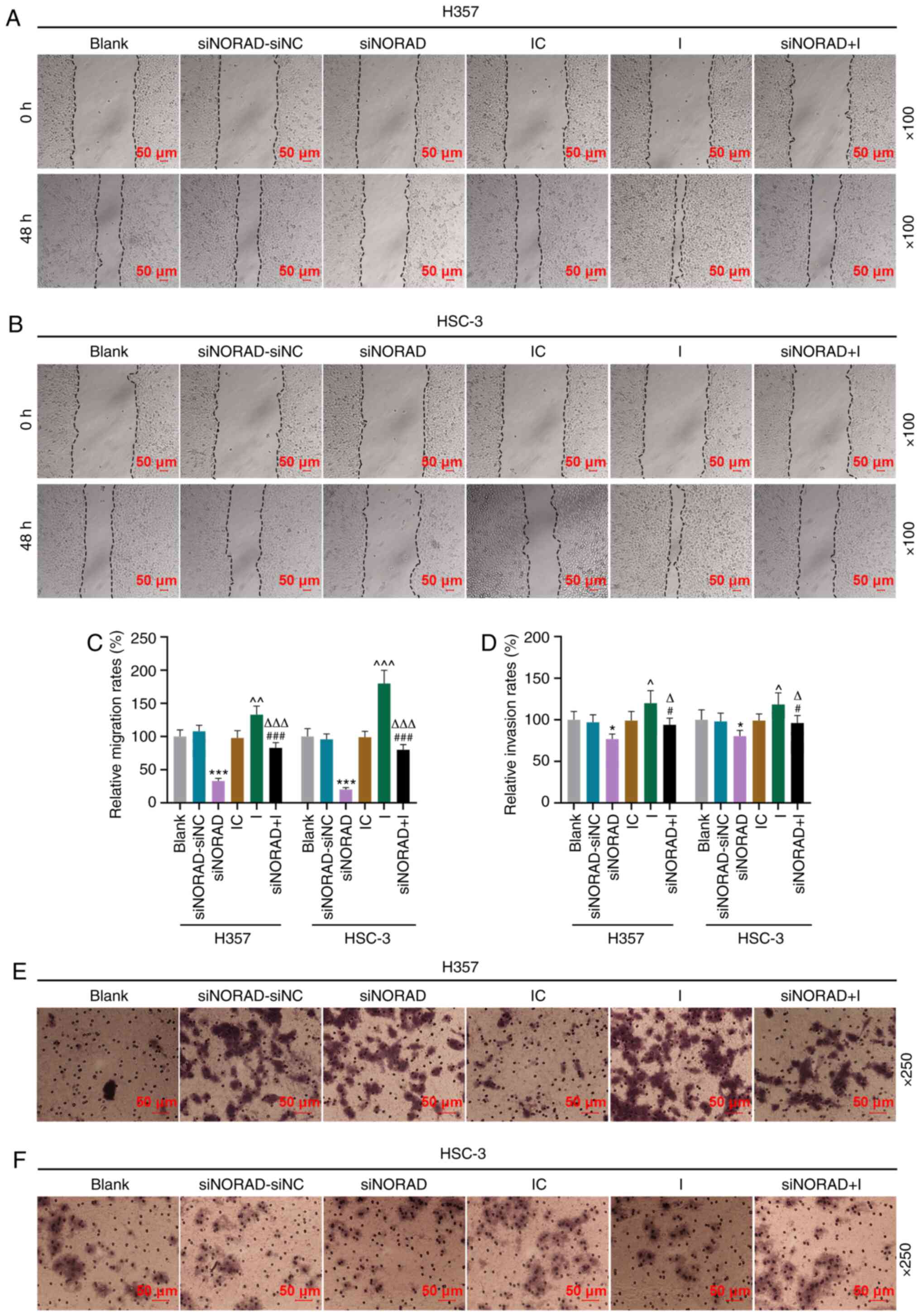
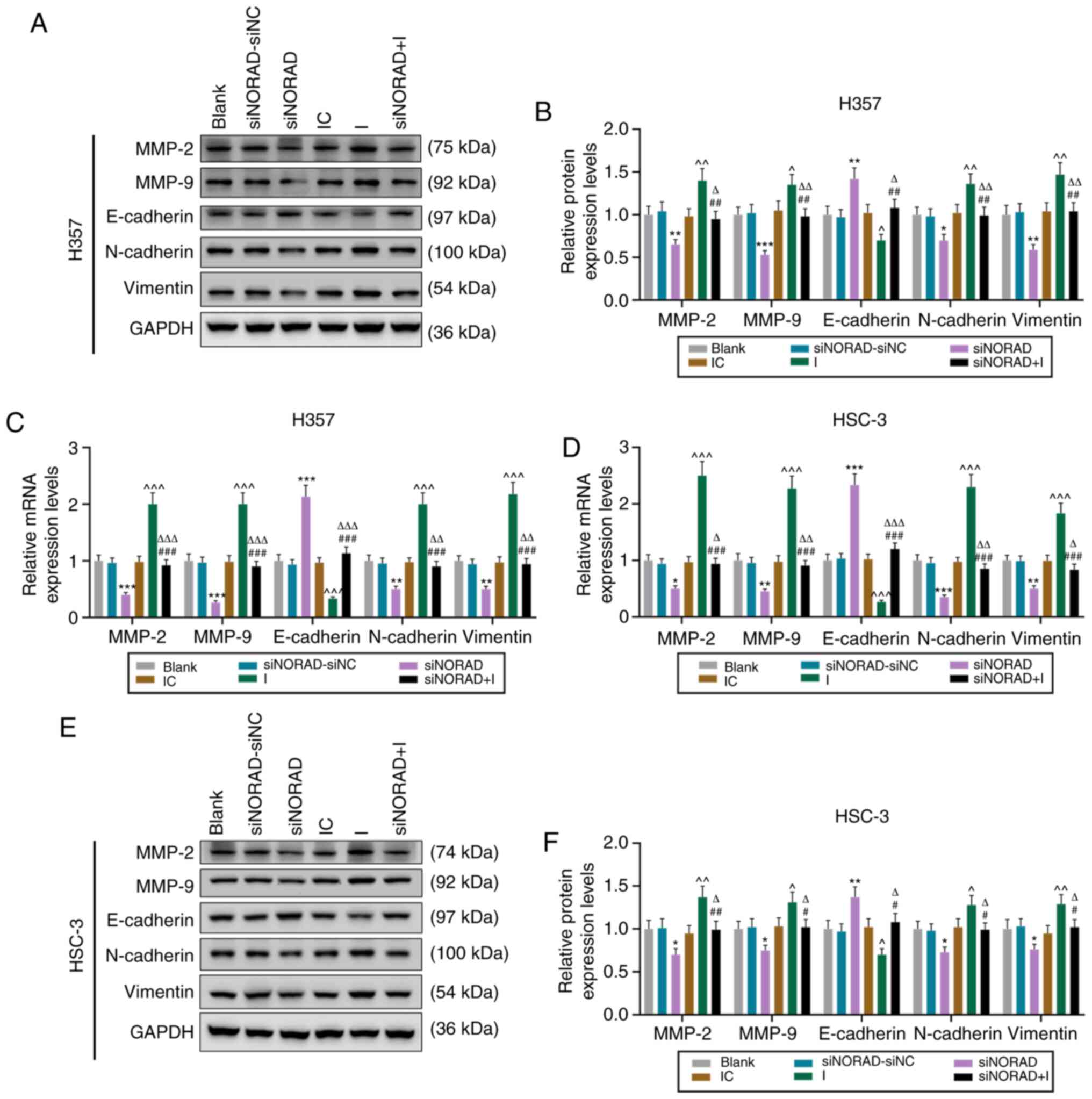
|
1
|
Svider PF, Blasco MA, Raza SN, Shkoukani
M, Sukari A, Yoo GH, Folbe AJ, Lin HS and Fribley AM: Head and Neck
Cancer. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 156:10–13. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mendez LC, Moraes FY, Poon I and Marta GN:
The management of head and neck tumors with high technology
radiation therapy. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 16:99–110. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Solomon B, Young RJ and Rischin D: Head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Genomics and emerging biomarkers
for immunomodulatory cancer treatments. Semin Cancer Biol.
52:228–240. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mermod M, Tolstonog G, Simon C and Monnier
Y: Extracapsular spread in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Oncol. 62:60–71. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chang JC: Cancer stem cells: Role in tumor
growth, recurrence, metastasis, and treatment resistance. Medicine
(Baltimore). 95 (Suppl 1):S20–S25. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nandy SB and Lakshmanaswamy R: Cancer Stem
Cells and Metastasis. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 151:137–176. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhou H and Xu R: Leukemia stem cells: The
root of chronic myeloid leukemia. Protein Cell. 6:403–412. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Leão R, Domingos C, Figueiredo A, Hamilton
R, Tabori U and Castelo-Branco P: Cancer Stem Cells in Prostate
Cancer: Implications for Targeted Therapy. Urol Int. 99:125–136.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Curtarelli RB, Gonçalves JM, Dos Santos
LGP, Savi MG, Nör JE, Mezzomo LAM and Rodríguez Cordeiro MM:
Expression of Cancer Stem Cell Biomarkers in Human Head and Neck
Carcinomas: A Systematic Review. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 14:769–784.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dawood S, Austin L and Cristofanilli M:
Cancer stem cells: Implications for cancer therapy. Oncology
(Williston Park). 28:1101–1107, 1110. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Peitzsch C, Nathansen J, Schniewind SI,
Schwarz F and Dubrovska A: Cancer Stem Cells in Head and Neck
Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Identification, Characterization and
Clinical Implications. Cancers (Basel). 11:E6162019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chen YC, Chen YW, Hsu HS, Tseng LM, Huang
PI, Lu KH, Chen DT, Tai LK, Yung MC, Chang SC, et al: Aldehyde
dehydrogenase 1 is a putative marker for cancer stem cells in head
and neck squamous cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 385:307–313.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Prince MEP, Zhou L, Moyer JS, Tao H, Lu L,
Owen J, Etigen M, Zheng F, Chang AE, Xia J, et al: Evaluation of
the immunogenicity of ALDH(high) human head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma cancer stem cells in vitro. Oral Oncol. 59:30–42. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ailles L and Prince M: Cancer stem cells
in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Methods Mol Biol.
568:175–193. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li J, Liang Y, Lv H, Meng H, Xiong G, Guan
X, Chen X, Bai Y and Wang K: miR-26a and miR-26b inhibit esophageal
squamous cancer cell proliferation through suppression of c-MYC
pathway. Gene. 625:1–9. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cabello P, Pineda B, Tormo E, Lluch A and
Eroles P: The Antitumor Effect of Metformin Is Mediated by miR-26a
in Breast Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 17:E12982016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Feng M, Xu D and Wang L: miR-26a inhibits
atherosclerosis progression by targeting TRPC3. Cell Biosci.
8:42018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin Y, Chen H, Hu Z, Mao Y, Xu X, Zhu Y,
Xu X, Wu J, Li S, Mao Q, et al: miR-26a inhibits proliferation and
motility in bladder cancer by targeting HMGA1. FEBS Lett.
587:2467–2473. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Deng M, Tang HL, Lu XH, Liu MY, Lu XM, Gu
YX, Liu JF and He ZM: miR-26a suppresses tumor growth and
metastasis by targeting FGF9 in gastric cancer. PLoS One.
8:e726622013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fukumoto I, Kikkawa N, Matsushita R, Kato
M, Kurozumi A, Nishikawa R, Goto Y, Koshizuka K, Hanazawa T,
Enokida H, et al: Tumor-suppressive microRNAs (miR-26a/b,
miR-29a/b/c and miR-218) concertedly suppressed
metastasis-promoting LOXL2 in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. J Hum Genet. 61:109–118. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang XM, Wang J, Liu ZL, Liu H, Cheng YF
and Wang T: LINC00657/miR-26a-5p/CKS2 ceRNA network promotes the
growth of esophageal cancer cells via the MDM2/p53/Bcl2/Bax
pathway. Biosci Rep. 40:BSR202005252020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cheng Y, Wen G, Sun Y, Shen Y, Zeng Y, Du
M, Zhu G, Wang G and Meng X: Osteopontin Promotes Colorectal Cancer
Cell Invasion and the Stem Cell-Like Properties through the
PI3K-AKT-GSK/3β-β/Catenin Pathway. Med Sci Monit. 25:3014–3025.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ghods AJ, Irvin D, Liu G, Yuan X,
Abdulkadir IR, Tunici P, Konda B, Wachsmann-Hogiu S, Black KL and
Yu JS: Spheres isolated from 9L gliosarcoma rat cell line possess
chemoresistant and aggressive cancer stem-like cells. Stem Cells.
25:1645–1653. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kuo SZ, Honda CO, Li WT, Honda TK, Kim E,
Altuna X, Abhold E, Wang-Rodriguez J and Ongkeko WM: Metformin
Results in Diametrically Opposed Effects by Targeting Non-Stem
Cancer Cells but Protecting Cancer Stem Cells in Head and Neck
Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 20:E1932019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang H and Guo H: Long non-coding RNA
NORAD induces cell proliferation and migration in prostate cancer.
J Int Med Res. 47:3898–3904. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu SY, Peng H, Zhu Q, Wu YX, Wu F, Han CR,
Yan B, Li Q and Xiang HG: Silencing the long noncoding RNA NORAD
inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation and invasion by the
RhoA/ROCK1 pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:3760–3770.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huo H, Tian J, Wang R, Li Y, Qu C and Wang
N: Long non-coding RNA NORAD upregulate SIP1 expression to promote
cell proliferation and invasion in cervical cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 106:1454–1460. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Toledo-Guzmán ME, Hernández MI,
Gómez-Gallegos ÁA and Ortiz-Sánchez E: ALDH as a Stem Cell Marker
in Solid Tumors. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 14:375–388. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sannigrahi MK, Sharma R, Panda NK and
Khullar M: Role of non-coding RNAs in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma: A narrative review. Oral Dis. 24:1417–1427. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zou AE, Zheng H, Saad MA, Rahimy M, Ku J,
Kuo SZ, Honda TK, Wang-Rodriguez J, Xuan Y, Korrapati A, et al: The
non-coding landscape of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 7:51211–51222. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vahabi M, Pulito C, Sacconi A, Donzelli S,
D'Andrea M, Manciocco V, Pellini R, Paci P, Sanguineti G, Strigari
L, et al: miR-96-5p targets PTEN expression affecting
radio-chemosensitivity of HNSCC cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
38:1412019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu C, Yu Z, Huang S, Zhao Q, Sun Z,
Fletcher C, Jiang Y and Zhang D: Combined identification of three
miRNAs in serum as effective diagnostic biomarkers for HNSCC.
EBioMedicine. 50:135–143. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tormo E, Adam-Artigues A, Ballester S,
Pineda B, Zazo S, González-Alonso P, Albanell J, Rovira A, Rojo F,
Lluch A, et al: The role of miR-26a and miR-30b in HER2+
breast cancer trastuzumab resistance and regulation of the CCNE2
gene. Sci Rep. 7:413092017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lafourcade CA, Fernández A, Ramírez JP,
Corvalán K, Carrasco MÁ, Iturriaga A, Bátiz LF, Luarte A and
Wyneken U: A Role for mir-26a in Stress: A Potential sEV Biomarker
and Modulator of Excitatory Neurotransmission. Cells. 9:E13642020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wei Z, Chang K, Fan C and Zhang Y:
miR-26a/miR-26b represses tongue squamous cell carcinoma
progression by targeting PAK1. Cancer Cell Int. 20:822020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Y, Wang P, Wu LL, Yan J, Pang XY and
Liu SJ: miR-26a-5p Inhibit Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation and
Invasion Through Mediated Wnt5a. OncoTargets Ther. 13:2537–2550.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tao W, Li Y, Zhu M, Li C and Li P: lncRNA
NORAD Promotes Proliferation And Inhibits Apoptosis Of Gastric
Cancer By Regulating miR-214/Akt/mTOR Axis. OncoTargets Ther.
12:8841–8851. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang Y and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer: Complexity and
opportunities. Front Med. 12:361–373. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
May CD, Sphyris N, Evans KW, Werden SJ,
Guo W and Mani SA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer
stem cells: A dangerously dynamic duo in breast cancer progression.
Breast Cancer Res. 13:2022011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhou P, Li B, Liu F, Zhang M, Wang Q, Liu
Y, Yao Y and Li D: The epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT)
and cancer stem cells: Implication for treatment resistance in
pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer. 16:522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Khan MI, Czarnecka AM, Lewicki S,
Helbrecht I, Brodaczewska K, Koch I, Zdanowski R, Król M and
Szczylik C: Comparative Gene Expression Profiling of Primary and
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Stem Cell-Like Cancer Cells. PLoS
One. 11:e01657182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shibue T and Weinberg RA: EMT, CSCs, and
drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications.
Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:611–629. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|