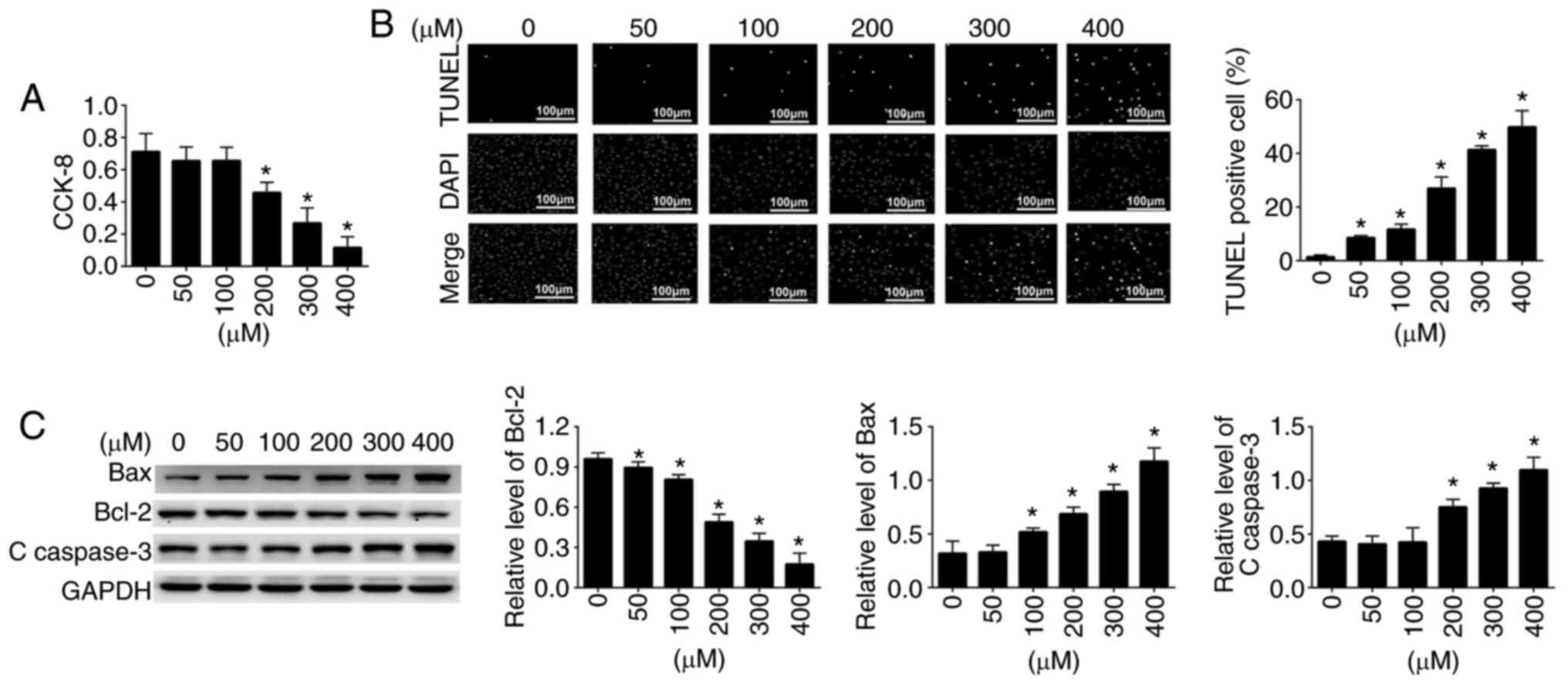
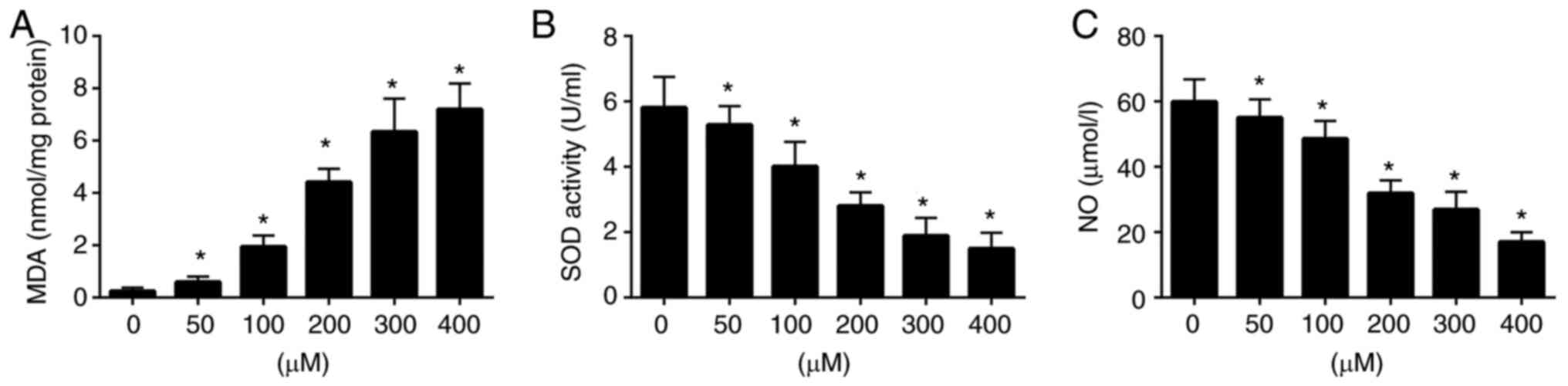
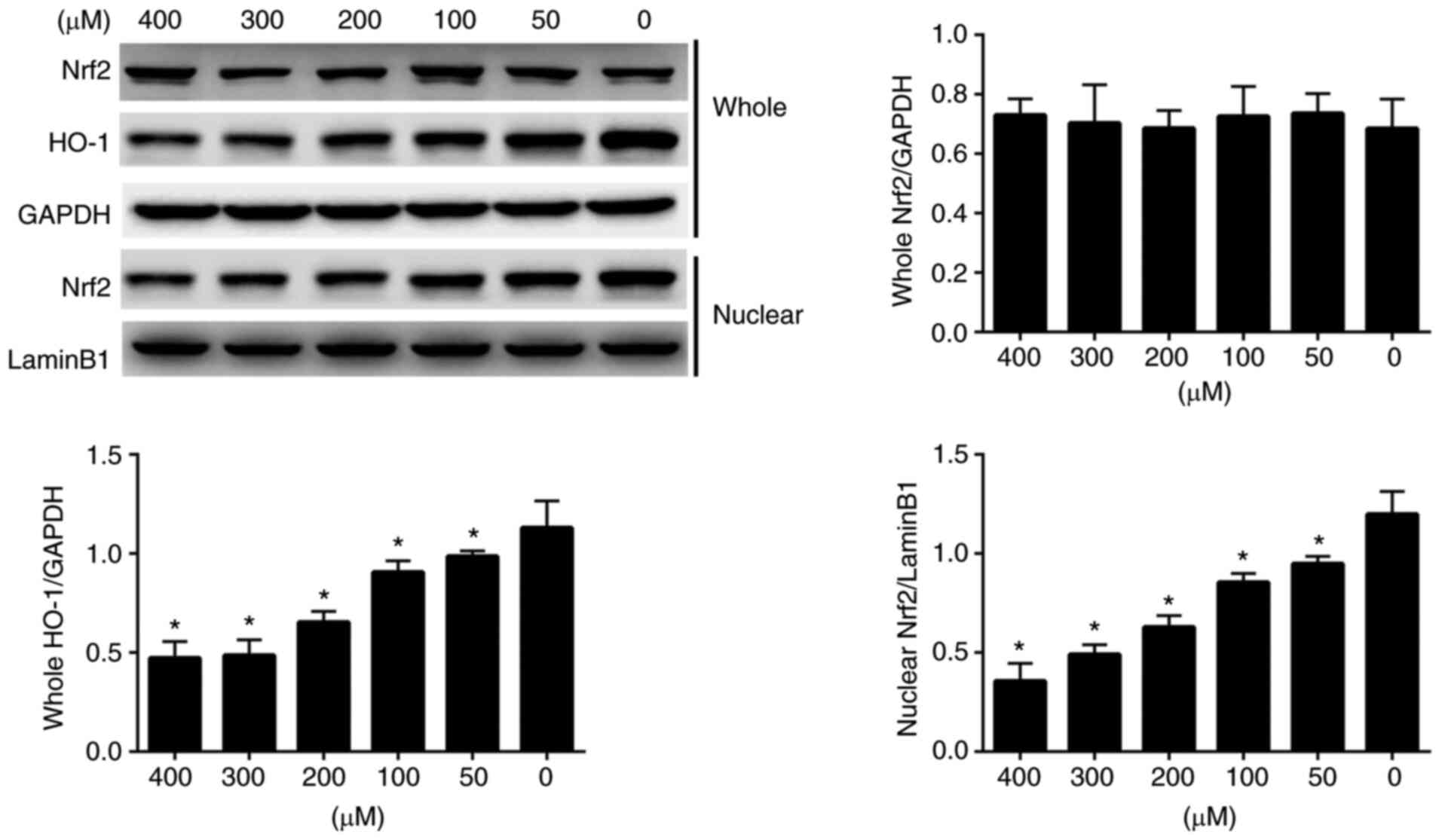
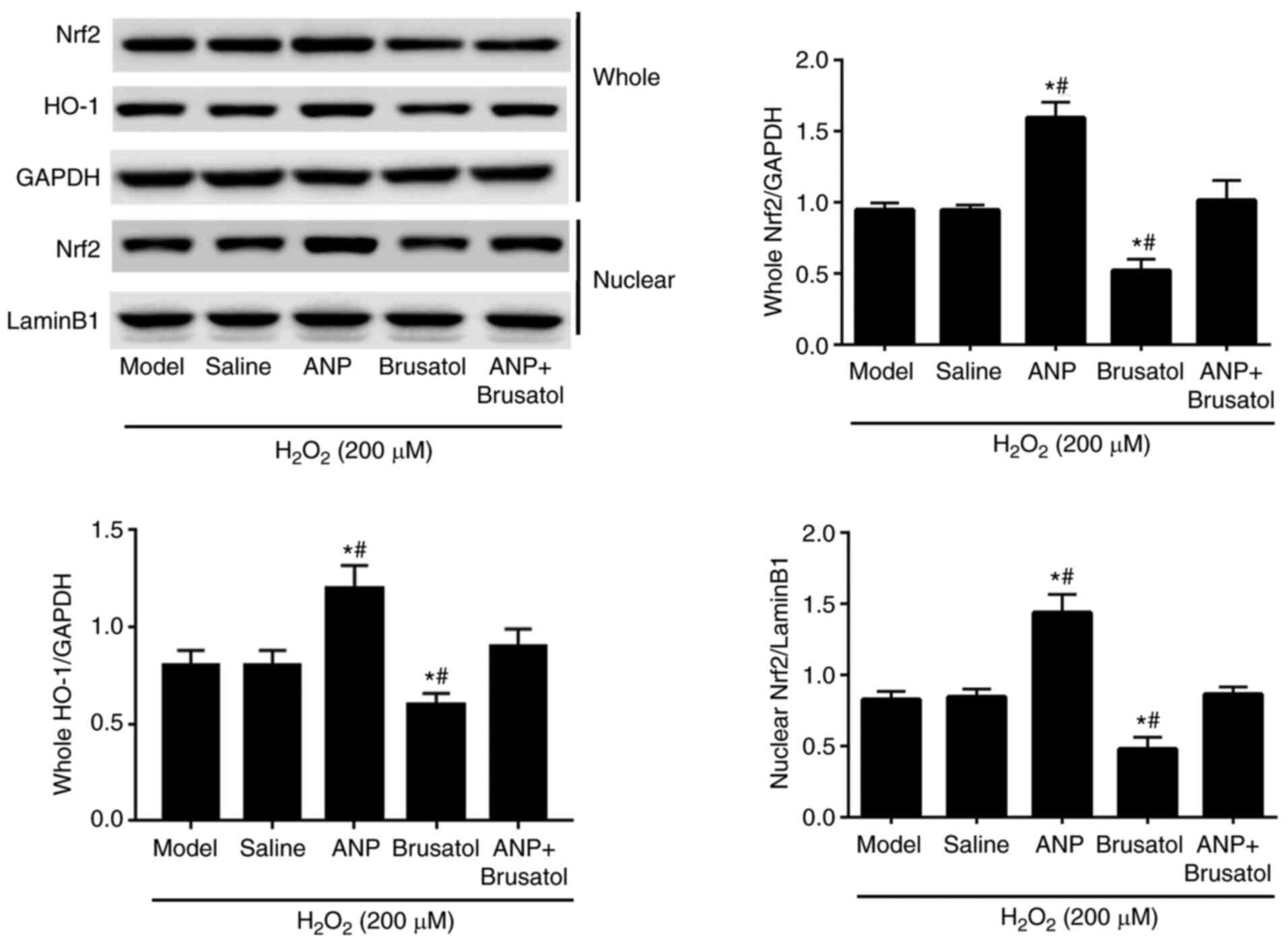
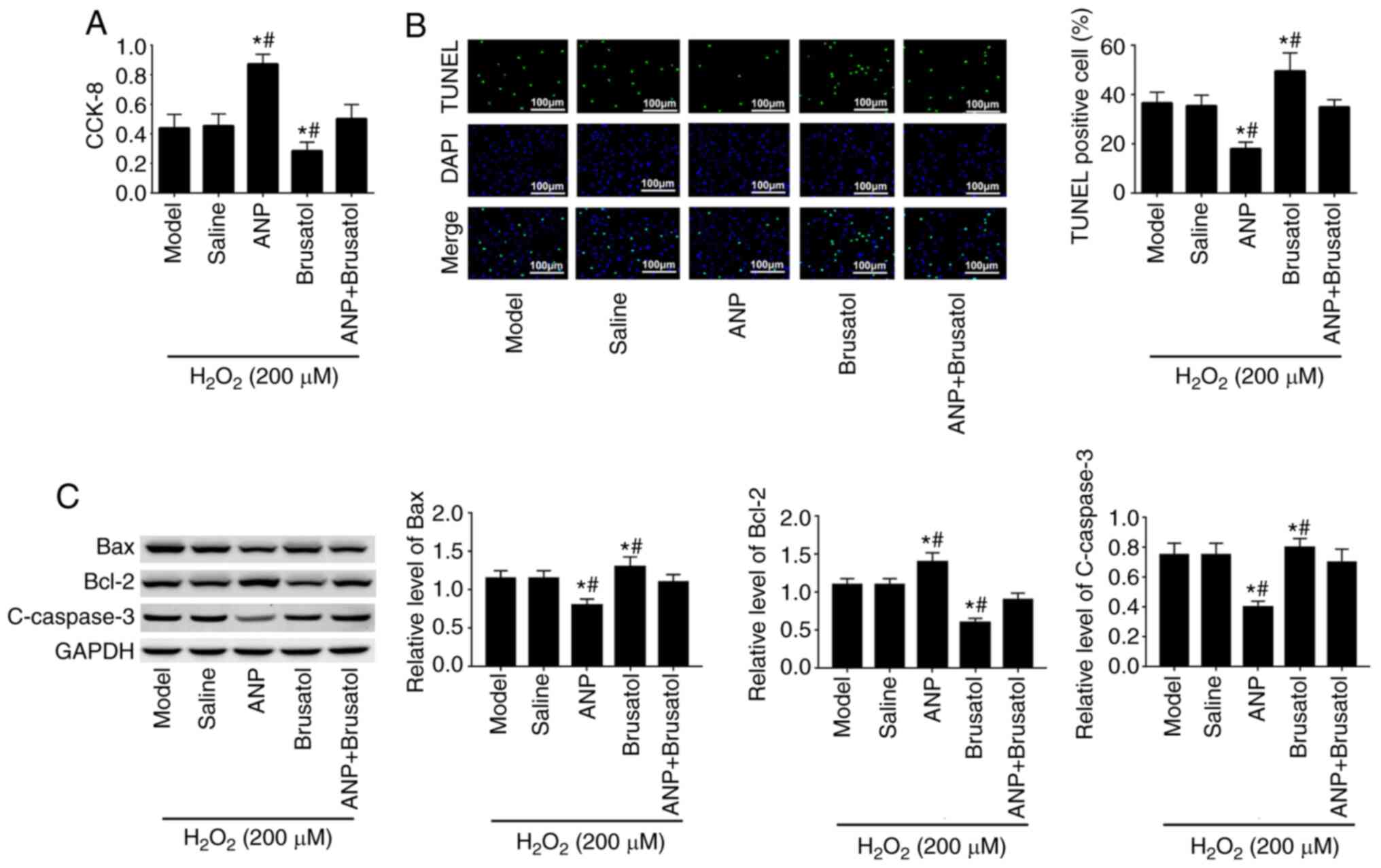
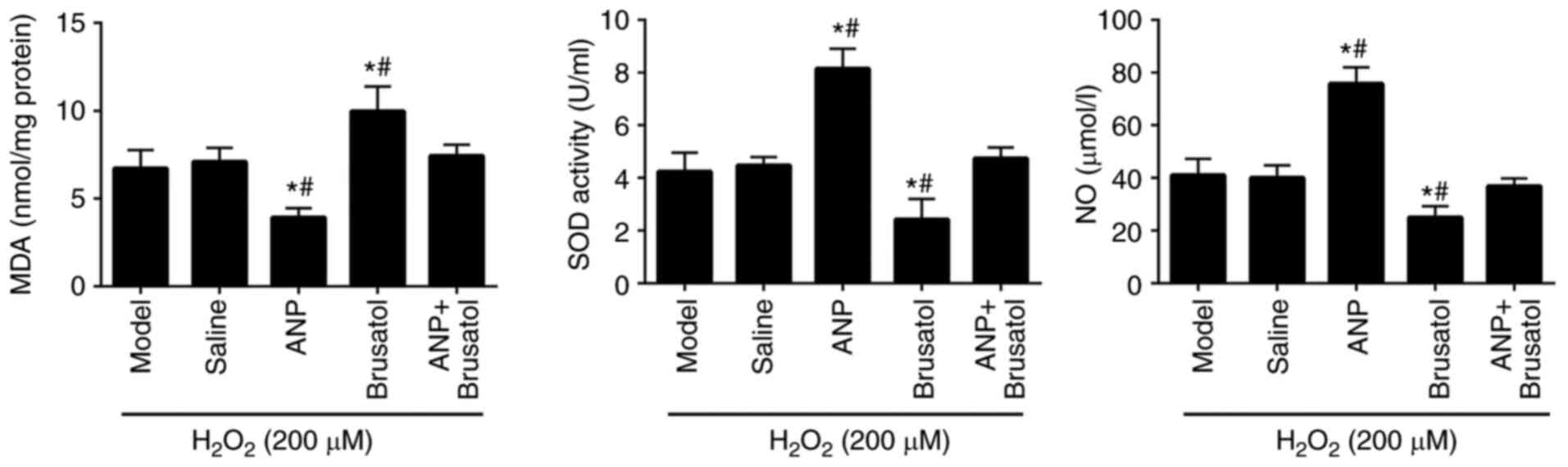
|
1
|
Hu RM, Levin ER, Pedram A and Frank HJL:
Atrial natriuretic peptide inhibits the production and secretion of
endothelin from cultured endothelial cells: Mediation through the C
receptor. J Biol Chem. 267:17384–9. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Smith S, Anderson S, Ballermann BJ and
Brenner BM: Role of atrial natriuretic peptide in adaptation of
sodium excretion with reduced renal mass. J Clin Invest.
77:1395–1398. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Baxter JD, Lewicki JA and Gardner DG:
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide. Nat Biotechnol. 6:529–546. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Abraham WT, Hensen J, Kim JK, Dürr J and
Schrier RW: Atrial natriuretic peptide and urinary cyclic guanosine
monophosphate in patients with chronic heart failure. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 2:1697–1703. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rahman SN, Kim GE, Mathew AS, Goldberg CA,
Allgren R, Schrier RW and Conger JD: Effects of atrial natriuretic
peptide in clinical acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 45:1731–1738.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bilzer M, Jaeschke H, Vollmar AM,
Paumgartner G and Gerbes AL: Prevention of Kupffer cell-induced
oxidant injury in rat liver by atrial natriuretic peptide. Am J
Physiol. 276:G1137–G1144. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bilzer M, Jaeschke H, Vollmar AM,
Paumgartner G and Gerbes AL: Reduction of Kupffer cell-induced
oxidant injury of the rat liver by atrial natriuretic peptide and
cyclo-GMP receptor proteins. J Hepatol. 28:471998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Fahn S and Cohen G: The oxidant stress
hypothesis in Parkinson's disease: Evidence supporting it. Ann
Neurol. 32:804–812. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jie B, Fan Y, Li D and Yi Z: Ghrelin
protects human lens epithelial cells against oxidative
stress-induced damage. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017:19104502017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Martinou JC and Youle RJ: Mitochondria in
apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Dev
Cell. 21:92–101. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR and
Newmeyer DD: The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria:
A primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science.
275:1132–1136. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shi L, Chen J, Yang J, Pan T, Zhang S and
Wang Z: miR-21 protected human glioblastoma U87MG cells from
chemotherapeutic drug temozolomide induced apoptosis by decreasing
Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-3 activity. Brain Res. 1352:255–264.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kensler TW, Wakabayashi N and Biswal S:
Cell Survival responses to environmental stresses via the
Keap1-Nrf2-ARE Pathway. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 47:89–116.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mukaigasa K, Nguyen LTP, Li L, Nakajima H,
Yamamoto M and Kobayashi M: Genetic evidence of an evolutionarily
conserved role for Nrf2 in the protection against oxidative stress.
Mol Cell Biol. 32:4455–4461. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Strom J: A critical role of Nrf2 in
protecting cardiomyocytes against oxidative stress and ischemic
injury. PhD dissertation, The University of Arizona, . 2014.
|
|
16
|
Buendia I, Michalska P, Navarro E, Gameiro
I and León R: Nrf2-ARE pathway: An emerging target against
oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative
diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 157:84–104. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yagishita Y, Fukutomi T, Sugawara A,
Kawamura H, Takahashi T, Pi J, Uruno A and Yamamoto M: Nrf2
protects pancreatic beta-cells from oxidative and nitrosative
stress in diabetic model mice. Diabetes. 63:605–618. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Loboda A, Damulewicz M, Pyza E, Jozkowicz
A and Dulak J: Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative
stress response and diseases: An evolutionarily conserved
mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:3221–3247. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jian Z, Li K, Liu L, Zhang Y, Zhou Z, Li C
and Gao T: Heme Oxygenase-1 protects human melanocytes from
H2O2-induced oxidative stress via the
Nrf2-ARE pathway. J Invest Dermatol. 131:1420–1427. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sahin K, Tuzcu M, Sahin N, Ali S and Kucuk
O: Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway may be the prime target for
chemoprevention of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by lycopene.
Food Chem Toxicol. 48:2670–2674. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Han Y, Li X, Yan M, Yang M, Wang S, Pan J,
Li L and Tan J: Oxidative damage induces apoptosis and promotes
calcification in disc cartilage endplate cell through
ROS/MAPK/NF-κB pathway: Implications for disc degeneration. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 516:1026–1032. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Giers MB, Munter BT, Eyster KJ, Ide GD,
Newcomb AGUS, Lehrman JN, Belykh E, Byvaltsev VA, Kelly BP, Preul
MC and Theodore N: Biomechanical and endplate effects on nutrient
transport in the intervertebral disc. World Neurosurg. 99:395–402.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ariga K, Yonenobu K, Nakase T, Hosono N,
Okuda S, Meng W, Tamura Y and Yoshikawa H: Mechanical
stress-induced apoptosis of endplate chondrocytes in organ-cultured
mouse intervertebral discs: An ex vivo study. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 28:1528–1533. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Otero M, Lago R, Lago F, Reino JJG and
Gualillo O: Signalling pathway involved in nitric oxide synthase
type II activation in chondrocytes: Synergistic effect of leptin
with interleukin-1. Arthritis Res Ther. 7:R581–R591. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang JX, Han YP, Bai C and Li Q: Notch1/3
and p53/p21 are a potential therapeutic target for APS-induced
apoptosis in non-small cell lung carcinoma cell lines. Int J Clin
Exp Med. 8:12539–12547. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang Z, Lin J, Tian N, Wu Y, Zhou Y, Wang
C, Wang Q, Jin H, Chen T, Nisar M, et al: Melatonin protects
vertebral endplate chondrocytes against apoptosis and calcification
via the Sirt1-autophagy pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 23:177–193. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou YF, Guo B, Ye MJ, Liao RF and Li SL:
Protective effect of rutin against
H2O2-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis
in human lens epithelial cells. Curr Eye Res. 41:933–942. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liang B, Wei W, Wang J, Zhang M, Xu R, Wu
F, Xiao H and Tang L: Protective effects of Semiaquilegia adoxoides
n-butanol extract against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative
stress in human lens epithelial cells. Pharm Biol. 54:1656–1663.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Salakou S, Kardamakis D, Tsamandas AC,
Zolota V, Apostolakis E, Tzelepi V, Papathanasopoulos P, Bonikos
DS, Papapetropoulos T, Petsas T and Dougenis D: Increased Bax/Bcl-2
ratio up-regulates caspase-3 and increases apoptosis in the thymus
of patients with myasthenia gravis. In Vivo. 21:123–132.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ghate NB, Hazra B, Sarkar R, Chaudhuri D
and Mandal N: Alteration of Bax/Bcl-2 ratio contributes to
Terminalia Belerica-induced apoptosis in human lung and breast
carcinoma. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 50:527–537. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen HM, Lai ZQ, Liao HJ, Xie JH, Xian YF,
Chen YL, Ip SP, Lin ZX and Su ZR: Synergistic antitumor effect of
brusatol combined with cisplatin on colorectal cancer cells. Int J
Mol Med. 41:1447–1454. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hart BA: Characterization of
cadmium-induced apoptosis in rat lung epithelial cells: Evidence
for the participation of oxidant stress. Toxicology. 133:43–58.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Olayanju A, Copple IM, Bryan HK, Edge GT,
Sison RL, Wong MW, Lai ZQ, Lin ZX, Dunn K, Sanderson CM, et al:
Brusatol provokes a rapid and transient inhibition of Nrf2
signaling and sensitizes mammalian cells to chemical
toxicity-implications for therapeutic targeting of Nrf2. Free Radic
Biol Med. 78:202–212. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
El-Beltagi HS and Mohamed HI: Reactive
oxygen species, lipid peroxidation and antioxidative defense
mechanism. Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca.
41:44–57. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zheng Y, Liu Y, Ge J, Wang X and Liu P:
Resveratrol protects human lens epithelial cells against
H2O2-induced oxidative stress by increasing
catalase, SOD-1, and HO-1 expression. Mol Vis. 16:1467–1474.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Velichkova M and Hasson T: Keap1 regulates
the oxidation-sensitive shuttling of Nrf2 into and out of the
nucleus via a Crm1-dependent nuclear export mechanism. Mol Cell
Biol. 25:4501–4513. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Camara NO and Soares MP: Heme oxygenase-1
(HO-1), a protective gene that prevents chronic graft dysfunction.
Free Radic Biol Med. 38:426–435. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Abraham NG and Kappas A: Heme oxygenase
and the cardiovascular-renal system. Free Radic Biol Med. 39:1–25.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ren D, Villeneuve NF, Jiang T, Wu T, Lau
A, Toppin HA and Zhang DD: Brusatol enhances the efficacy of
chemotherapy by inhibiting the Nrf2-mediated defense mechanism.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:1433–1438. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tang XQ, Feng JQ, Chen J, Chen PX, Zhi JL,
Cui Y, Guo RX and Yu HM: Protection of oxidative preconditioning
against apoptosis induced by H2O2 in PC12
cells: Mechanisms via MMP, ROS, and Bcl-2. Brain Res. 1057:57–64.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Buttke TM and Sandstrom P: Oxidative
stress as a mediator of apoptosis. Immunol Today. 15:7–10. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|