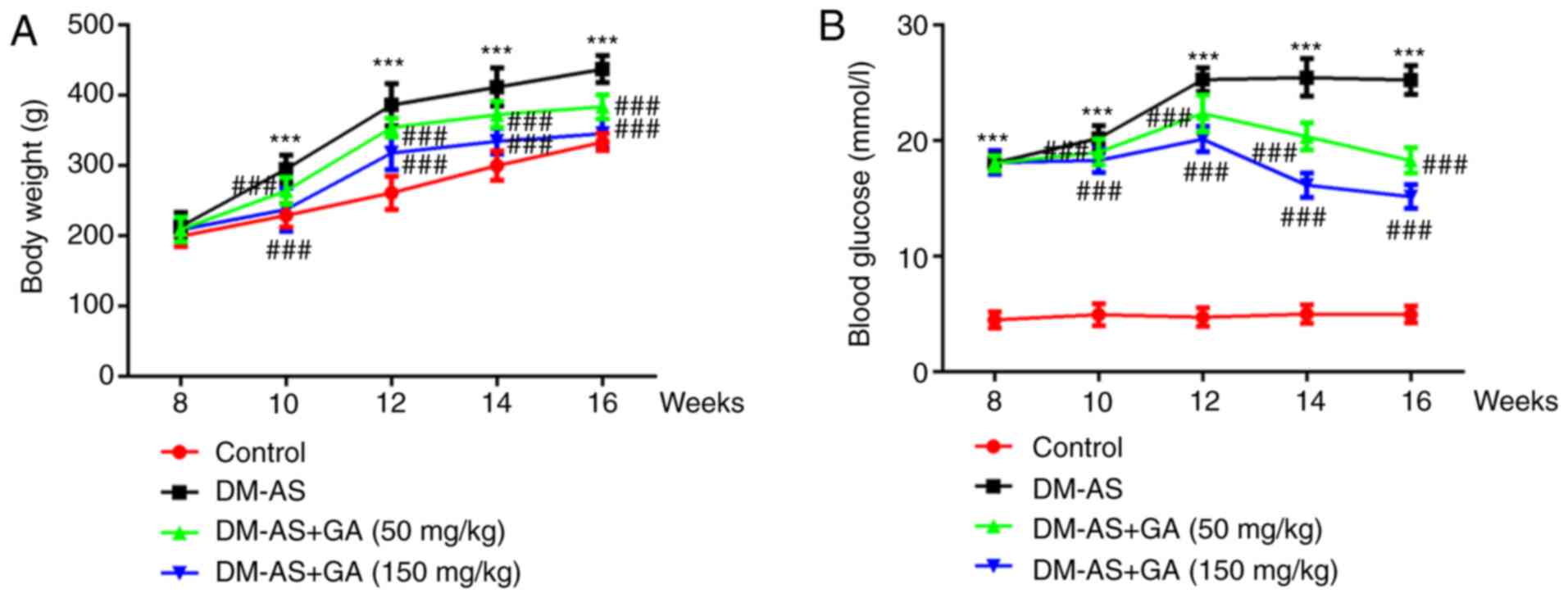
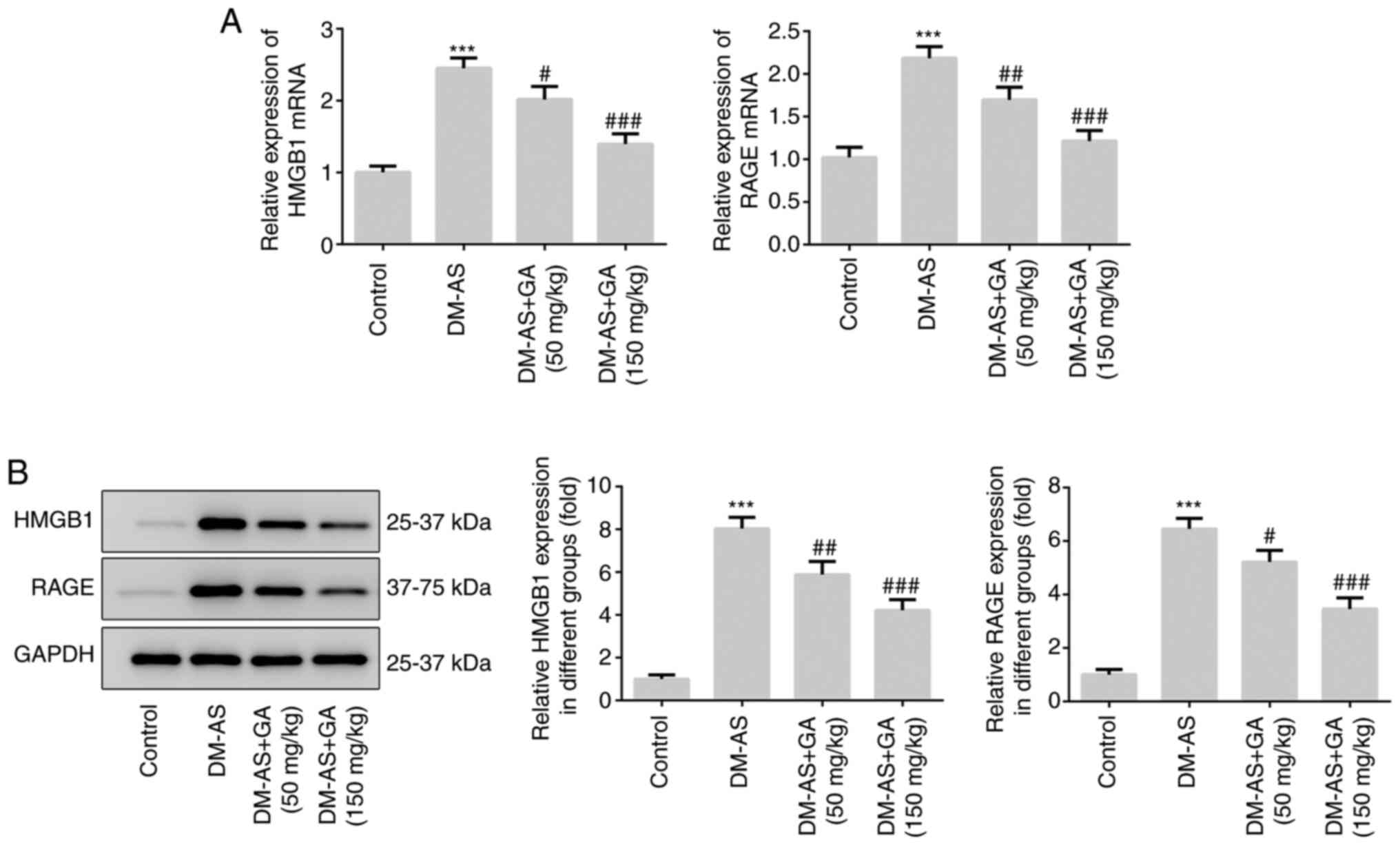
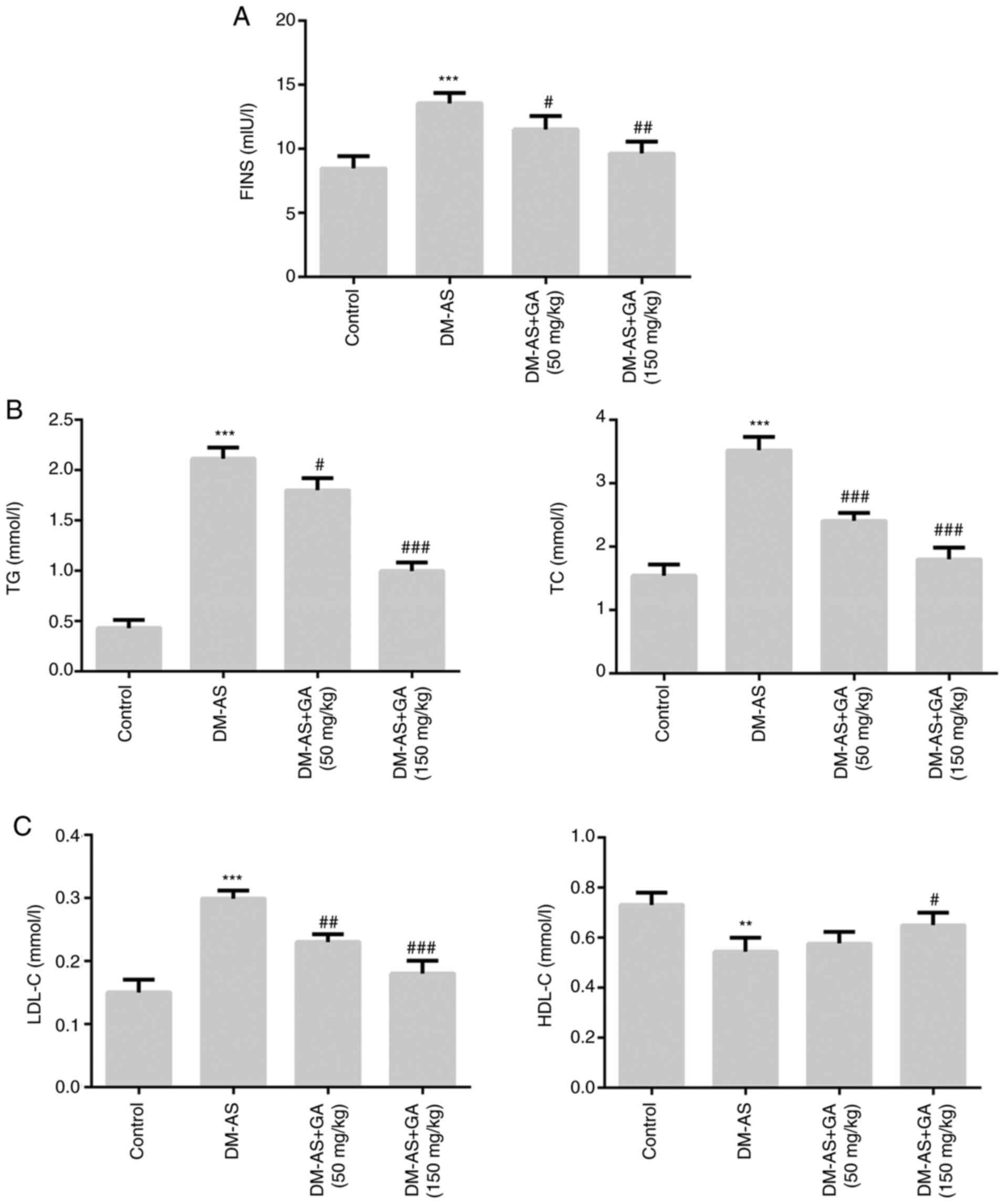
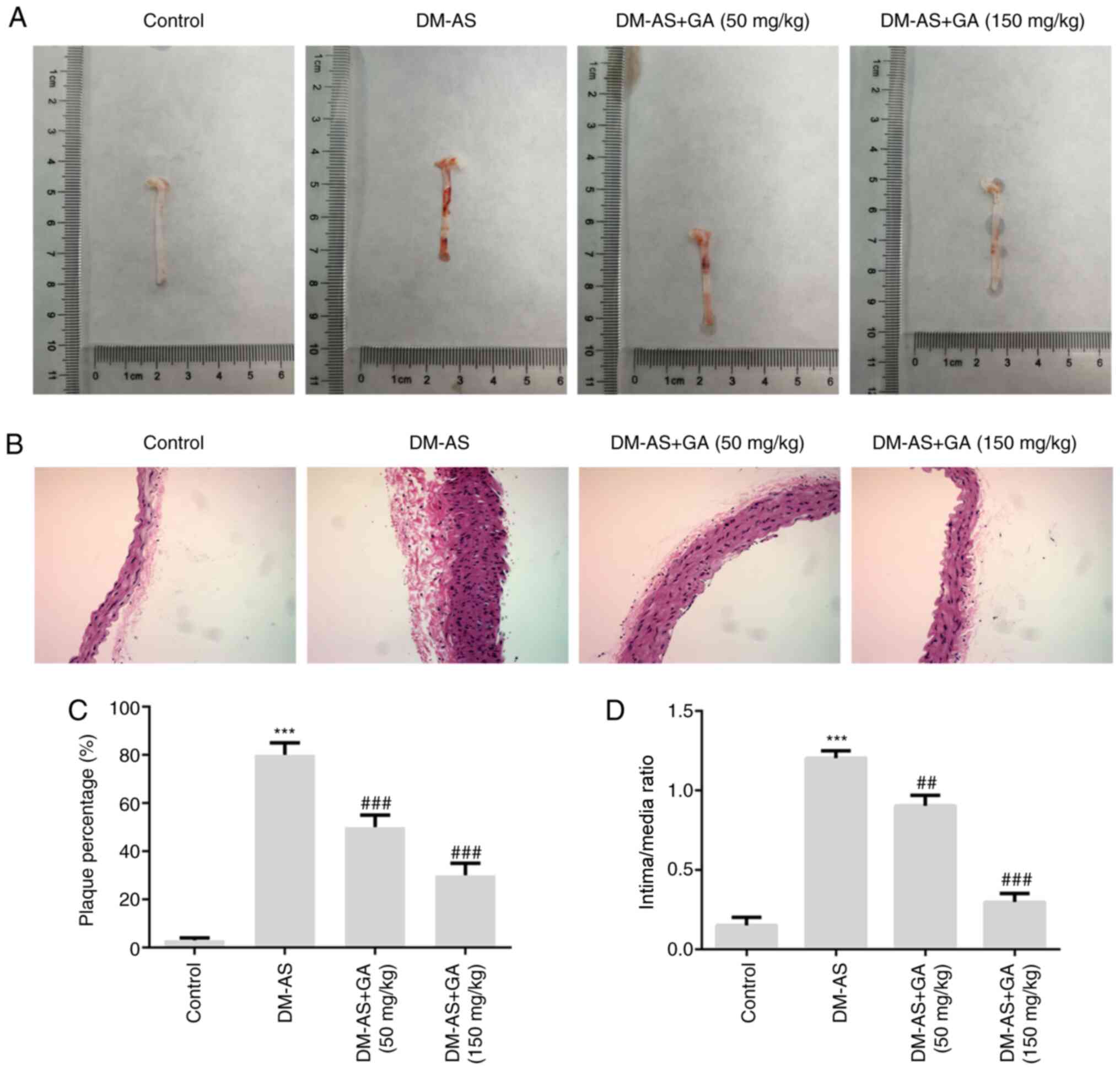
|
1
|
Guthrie RA and Guthrie DW: Pathophysiology
of diabetes mellitus. Crit Care Nurs Q. 27:113–125. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Unnikrishnan R, Anjana RM and Mohan V:
Diabetes mellitus and its complications in India. Nat Rev
Endocrinol. 12:357–370. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda
B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, Colagiuri S, Guariguata L, Motala AA,
Ogurtsova K, et al: Global and regional diabetes prevalence
estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from
the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas. (9(th)
edition). Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 157:1078432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Strain WD and Paldánius PM: Diabetes,
cardiovascular disease and the microcirculation. Cardiovasc
Diabetol. 17:572018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kannenkeril D, Bosch A, Harazny J, Karg M,
Jung S, Ott C and Schmieder RE: Early vascular parameters in the
micro- and macrocirculation in type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc
Diabetol. 17:1282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Di Pino A and DeFronzo RA: Insulin
resistance and atherosclerosis: Implications for
insulin-sensitizing agents. Endocr Rev. 40:1447–1467. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stabley JN and Towler DA: Arterial
calcification in diabetes mellitus: Preclinical models and
translational implications. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
37:205–217. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Poznyak A, Grechko AV, Poggio P,
Myasoedova VA, Alfieri V and Orekhov AN: The diabetes
mellitus-atherosclerosis connection: The role of lipid and glucose
metabolism and chronic inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 21:18352020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ioachimescu AG: Diabetes and
atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Endocrinol Metab Clin North
Am. 47:xiii–xiv. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhu Y, Xian X, Wang Z, Bi Y, Chen Q, Han
X, Tang D and Chen R: Research progress on the relationship between
atherosclerosis and inflammation. Biomolecules. 8:802018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Laakso M and Kuusisto J: Insulin
resistance and hyperglycaemia in cardiovascular disease
development. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 10:293–302. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yahagi K, Kolodgie FD, Lutter C, Mori H,
Romero ME, Finn AV and Virmani R: Pathology of human coronary and
carotid artery atherosclerosis and vascular calcification in
diabetes mellitus. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 37:191–204. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dryden M, Baguneid M, Eckmann C, Corman S,
Stephens J, Solem C, Li J, Charbonneau C, Baillon-Plot N and Haider
S: Pathophysiology and burden of infection in patients with
diabetes mellitus and peripheral vascular disease: Focus on skin
and soft-tissue infections. Clin Microbiol Infect. 21 (Suppl
2):S27–S32. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Malahfji M and Mahmarian JJ: Imaging to
stratify coronary artery disease risk in asymptomatic patients with
diabetes. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 14:266–272.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Andersson U and Tracey KJ: HMGB1 is a
therapeutic target for sterile inflammation and infection. Annu Rev
Immunol. 29:139–162. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Deng M, Scott MJ, Fan J and Billiar TR:
Location is the key to function: HMGB1 in sepsis and trauma-induced
inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 106:161–169. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang R, Wu W, Li W, Huang S, Li Z, Liu R,
Shan Z, Zhang C, Li W and Wang S: Activation of NLRP3 inflammasome
promotes foam cell formation in vascular smooth muscle cells and
atherogenesis Via HMGB1. J Am Heart Assoc. 7:e0085962018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang J, Zhang L, Zhang S, Yu Q, Xiong F,
Huang K, Wang CY and Yang P: HMGB1, an innate alarmin, plays a
critical role in chronic inflammation of adipose tissue in obesity.
Mol Cell Endocrinol. 454:103–111. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ding JW, Luo CY, Wang XA, Zhou T, Zheng
XX, Zhang ZQ, Yu B, Zhang J and Tong XH: Glycyrrhizin, a
high-mobility group box 1 inhibitor, improves lipid metabolism and
suppresses vascular inflammation in apolipoprotein e knockout mice.
J Vasc Res. 55:365–377. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hou S, Zhang T, Li Y, Guo F and Jin X:
Glycyrrhizic acid prevents diabetic nephropathy by activating
AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α Signaling in db/db Mice. J Diabetes Res.
2017:28659122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang H, Zhang R, Chen J, Shi M, Li W and
Zhang X: High Mobility Group Box1 inhibitor glycyrrhizic acid
attenuates kidney injury in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
Kidney Blood Press Res. 42:894–904. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li J, Liu X, Fang Q, Ding M and Li C:
Liraglutide attenuates atherosclerosis via inhibiting ER-induced
macrophage derived microvesicles production in T2DM rats. Diabetol
Metab Syndr. 9:942017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shah AD, Langenberg C, Rapsomaniki E,
Denaxas S, Pujades-Rodriguez M, Gale CP, Deanfield J, Smeeth L,
Timmis A and Hemingway H: Type 2 diabetes and incidence of
cardiovascular diseases: A cohort study in 1.9 million people.
Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 3:105–113. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Haas AV and McDonnell ME: Pathogenesis of
cardiovascular disease in diabetes. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am.
47:51–63. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Buszman PP, Bochenek A, Konkolewska M,
Trela B, Kiesz RS, Wilczyński M, Cisowski M, Krejca M,
Banasiewicz-Szkróbka I, Krol M, et al: Early and long-term outcomes
after surgical and percutaneous myocardial revascularization in
patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes and
unprotected left main disease. J Invasive Cardiol. 21:564–569.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou J, Zhe R, Guo X, Chen Y, Zou Y, Zhou
L and Wang Z: The Role of PPARδ Agosnist GW501516 in rats with
gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes.
13:2307–2316. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rani R, Dahiya S, Dhingra D, Dilbaghi N,
Kaushik A, Kim KH and Kumar S: Antidiabetic activity enhancement in
streptozotocin + nicotinamide-induced diabetic rats through
combinational polymeric nanoformulation. Int J Nanomedicine.
14:4383–4395. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Moroni F, Ammirati E, Norata GD, Magnoni M
and Camici PG: The role of monocytes and macrophages in human
atherosclerosis, plaque neoangiogenesis, and atherothrombosis.
Mediators Inflamm. 2019:74343762019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Palone F, Pasquali E, Giardullo P,
Stronati L, Vitali R and Mancuso M: Low dose of dipotassium
glycyrrhizate counteracts atherosclerosis progression in
apoe-/-female mice. J Vasc Res. 56:267–270. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Y, Le Y, Zhao W, Lin Y, Wu Y, Yu C,
Xiong J, Zou F, Dong H, Cai S and Zhao H: Short thymic stromal
lymphopoietin attenuates toluene diisocyanate-induced airway
inflammation and inhibits high mobility group box 1-receptor for
advanced glycation end products and long thymic stromal
lymphopoietin expression. Toxicol Sci. 157:276–290. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Brown MS and Goldstein JL: The SREBP
pathway: regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a
membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell. 89:331–340. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen J, Zhang J, Xu L, Xu C, Chen S, Yang
J and Jiang H: Inhibition of neointimal hyperplasia in the rat
carotid artery injury model by a HMGB1 inhibitor. Atherosclerosis.
224:332–339. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cybulsky MI, Cheong C and Robbins CS:
Macrophages and dendritic cells: Partners in atherogenesis. Circ
Res. 118:637–652. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|