|
1
|
Schultz G, Davidson J, Kirsner R,
Bornstein P and Herman I: Dynamic reciprocity in the wound
microenvironment. Wound Repair Regen. 19:134–148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Karppinen S, Heljasvaara R, Gullberg D,
Tasanen K and Pihlajaniemi T: Toward understanding scarless skin
wound healing and pathological scarring. F1000Res. 8:F10002019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brown BC, Moss TP, McGrouther DA and Bayat
A: Skin scar preconceptions must be challenged: Importance of
self-perception in skin scarring. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg.
63:1022–1029. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
van den Broek LJ, Limandjaja GC, Niessen
FB and Gibbs S: Human hypertrophic and keloid scar models:
Principles, limitations and future challenges from a tissue
engineering perspective. Exp Dermatol. 23:382–386. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yu J, Wang MY, Tai HC and Cheng NC: Cell
sheet composed of adipose-derived stem cells demonstrates enhanced
skin wound healing with reduced scar formation. Acta Biomater.
77:191–200. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu SC, Bamodu OA, Kuo KT, Fong IH, Lin
CC, Yeh CT and Chen SG: Adipose-derived stem cell induced-tissue
repair or wound healing is mediated by the concomitant upregulation
of miR-21 and miR-29b expression and activation of the AKT
signaling pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 705:1088952021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ni X, Shan X, Xu L, Yu W, Zhang M, Lei C,
Xu N, Lin J and Wang B: Adipose-derived stem cells combined with
platelet-rich plasma enhance wound healing in a rat model of
full-thickness skin defects. Stem Cell Res Ther. 12:2262021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cai Y, Li J, Jia C, He Y and Deng C:
Therapeutic applications of adipose cell-free derivatives: A
review. Stem Cell Res Ther. 11:3122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Basu J and Ludlow JW: Exosomes for repair,
regeneration and rejuvenation. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 16:489–506.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Merino-González C, Zuñiga FA, Escudero C,
Ormazabal V, Reyes C, Nova-Lamperti E, Salomón C and Aguayo C:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promote
angiogenesis: Potencial clinical application. Front Physiol.
7:242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Konala VB, Mamidi MK, Bhonde R, Das AK,
Pochampally R and Pal R: The current landscape of the mesenchymal
stromal cell secretome: A new paradigm for cell-free regeneration.
Cytotherapy. 18:13–24. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Casado-Díaz A, Quesada-Gómez JM and Dorado
G: Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSC)
in regenerative medicine: Applications in skin wound Healing. Front
Bioeng Biotechnol. 8:1462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rani S and Ritter T: The exosome - A
naturally secreted nanoparticle and its application to wound
healing. Advanced materials (Deerfield Beach Fla.). 28:5542–5552.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rani S, Ryan A, Griffin M and Ritter T:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: Toward
cell-free therapeutic applications. Molecular therapy : the journal
of the American Society of Gene Therapy. 23:812–823. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shabbir A, Cox A, Rodriguez-Menocal L,
Salgado M and Van Badiavas E: Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes induce
proliferation and migration of normal and chronic wound
fibroblasts, and enhance angiogenesis in vitro. Stem Cells Dev.
24:1635–1647. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Diegelmann R and Evans M: Wound healing:
an overview of acute, fibrotic and delayed healing. Front Biosci.
9:283–289. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yuan H, Guan J, Zhang J, Zhang R and Li M:
Exosomes secreted by human urine-derived stem cells accelerate skin
wound healing by promoting angiogenesis in rat. Cell Biol Int.
41:9332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu L, Wang J, Zhou X, Xiong Z, Zhao J, Yu
R, Huang F, Zhang H and Chen L: Exosomes derived from human adipose
mensenchymal stem cells accelerates cutaneous wound healing via
optimizing the characteristics of fibroblasts. Sci Rep.
6:329932016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li X, Liu L, Yang J, Yu Y, Chai J, Wang L,
Ma L and Yin H: Exosome derived from human umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cell mediates MiR-181c attenuating burn-induced
excessive inflammation. EBioMedicine. 8:72–82. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tafrihi M and Hasheminasab E: MiRNAs:
Biology, biogenesis, their Web-based tools, and databases.
MicroRNA. 8:4–27. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ha M and Kim VN: Regulation of microRNA
biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:509–524. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dietrich C, Singh M, Kumar N and Singh SR:
The emerging roles of microRNAs in stem cell aging. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 1056:11–26. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cheng J, Wang Y, Wang D and Wu Y:
Identification of collagen 1 as a post-transcriptional target of
miR-29b in skin fibroblasts: Therapeutic implication for scar
reduction. Am J Med Sci. 346:98–103. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Murali VP and Holmes CA: Mesenchymal
stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles for bone regeneration
therapy. Bone Rep. 14:1010932021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ichinohe N, Ishii M, Tanimizu N, Mizuguchi
T, Yoshioka Y, Ochiya T, Suzuki H and Mitaka T: Extracellular
vesicles containing miR-146a-5p secreted by bone marrow mesenchymal
cells activate hepatocytic progenitors in regenerating rat livers.
Stem Cell Res Ther. 12:3122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Du Y and Ning JZ: MiR-182 Promotes
ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury in rat by
targeting FoxO3. Urol Int. 105:687–696. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ouyang Z and Wei K: miRNA in cardiac
development and regeneration. Cell Regen (Lond).
10:142021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
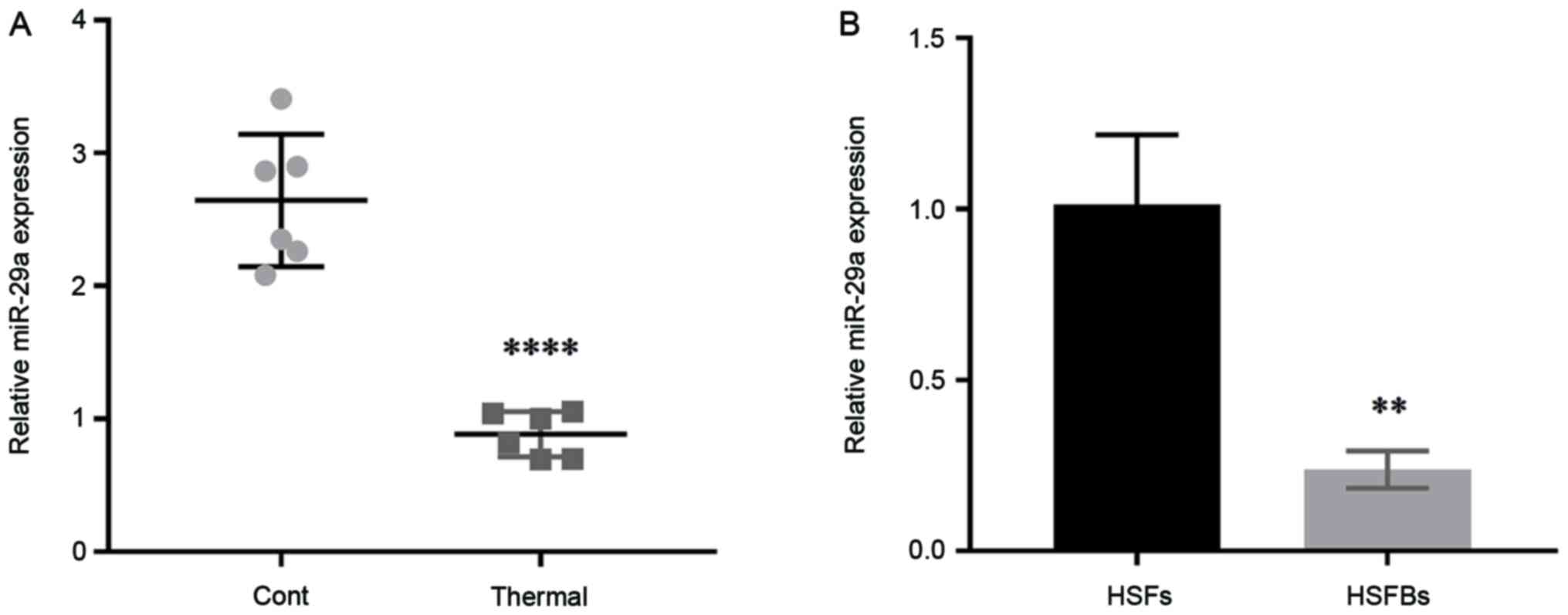
Zhou J, Zhang X, Liang P, Ren L, Zeng J,
Zhang M, Zhang P and Huang X: Protective role of microRNA-29a in
denatured dermis and skin fibroblast cells after thermal injury.
Biol Open. 5:211–219. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Guo L and Huang X, Liang P, Zhang P, Zhang
M, Ren L, Zeng J, Cui X and Huang X: Role of XIST/miR-29a/LIN28A
pathway in denatured dermis and human skin fibroblasts (HSFs) after
thermal injury. J Cell Biochem. 119:1463–1474. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zgheib C, Hodges M, Hu J, Beason DP,
Soslowsky LJ, Liechty KW and Xu J: Mechanisms of mesenchymal stem
cell correction of the impaired biomechanical properties of
diabetic skin: The role of miR-29a. Wound Repair Regen. 24:237–246.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Z, Feng C, Song K, Qi Z, Huang W and
Wang Y: lncRNA-H19/miR-29a axis affected the viability and
apoptosis of keloid fibroblasts through acting upon COL1A1
signaling. J Cell Biochem. 121:4364–4376. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang T, Wang X, Wang Z, Lou D, Fang QQ,
Hu YY, Zhao WY, Zhang LY, Wu LH and Tan WQ: Current potential
therapeutic strategies targeting the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway
to attenuate keloid and hypertrophic scar formation. Biomed
Pharmacother. 129:1102872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Guo J, Lin Q, Shao Y, Rong L and Zhang D:
miR-29b promotes skin wound healing and reduces excessive scar
formation by inhibition of the TGF-β1/Smad/CTGF signaling pathway.
Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 95:437–442. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu Y, Li Z, Wang Y, Li L, Wang D, Zhang
W, Liu L, Jiang H, Yang J and Cheng J: Overexpression of miR-29b
reduces collagen biosynthesis by inhibiting heat shock protein 47
during skin wound healing. Transl Res. 178:38–53.e6. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang SJ, Yun CJ, Liu J, Yao SY, Li Y,
Wang M, Wang C, Bai YY and Xue H: MicroRNA-29a attenuates
angiotensin-II induced-left ventricular remodeling by inhibiting
collagen, TGF-β and SMAD2/3 expression. J Geriatr Cardiol.
17:96–104. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ragni E, Perucca Orfei C, De Luca P,
Viganò M, Colombini A, Lugano G, Bollati V and de Girolamo L:
miR-22-5p and miR-29a-5p are reliable reference genes for analyzing
extracellular vesicle-associated miRNAs in adipose-derived
mesenchymal stem cells and are stable under inflammatory priming
mimicking osteoarthritis condition. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 15:743–754.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang X, Li Z, Cui Y, Cui X, Chen C and
Wang Z: Exosomes isolated from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
exert a protective effect on osteoarthritis via lncRNA
LYRM4-AS1-GRPR-miR-6515-5p. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:6443802021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bian W, Meng B, Li X, Wang S, Cao X, Liu
N, Yang M, Tang J, Wang Y and Yang X: OA-GL21, a novel bioactive
peptide from Odorrana andersonii, accelerated the healing of
skin wounds. Biosci Rep. Jun 21–2018.(Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1042/BSR20180215. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−ΔΔC(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bayat A, McGrouther DA and Ferguson MW:
Skin scarring. BMJ. 326:88–92. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
New SE, Alvarez-Gonzalez C, Vagaska B,
Gomez SG, Bulstrode NW, Madrigal A and Ferretti P: A matter of
identity - Phenotype and differentiation potential of human somatic
stem cells. Stem Cell Res (Amst). 15:1–13. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ren K: Exosomes in perspective: A
potential surrogate for stem cell therapy. Odontology. 107:271–284.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lopez-Verrilli MA, Caviedes A, Cabrera A,
Sandoval S, Wyneken U and Khoury M: Mesenchymal stem cell-derived
exosomes from different sources selectively promote neuritic
outgrowth. Neuroscience. 320:129–139. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Baglio SR, Rooijers K, Koppers-Lalic D,
Verweij FJ, Pérez Lanzón M, Zini N, Naaijkens B, Perut F, Niessen
HW, Baldini N, et al: Human bone marrow- and adipose-mesenchymal
stem cells secrete exosomes enriched in distinctive miRNA and tRNA
species. Stem Cell Res Ther. 6:1272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kang T, Jones TM, Naddell C, Bacanamwo M,
Calvert JW, Thompson WE, Bond VC, Chen YE and Liu D:
Adipose-derived stem cells induce angiogenesis via microvesicle
transport of miRNA-31. Stem Cells Transl Med. 5:440–450. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liang X, Zhang L, Wang S, Han Q and Zhao
RC: Exosomes secreted by mesenchymal stem cells promote endothelial
cell angiogenesis by transferring miR-125a. J Cell Sci.
129:2182–2189. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fang S, Xu C, Zhang Y, Xue C, Yang C, Bi
H, Qian X, Wu M, Ji K, Zhao Y, et al: Umbilical cord-derived
mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal MicroRNAs suppress
myofibroblast differentiation by inhibiting the transforming growth
factor-β/SMAD2 pathway during wound healing. Stem Cells Transl Med.
5:1425–1439. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Valluru M, Staton CA, Reed MW and Brown
NJ: Transforming growth factor-β and endoglin signaling orchestrate
wound healing. Front Physiol. 2:892011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Gras C, Ratuszny D, Hadamitzky C, Zhang H,
Blasczyk R and Figueiredo C: miR-145 contributes to hypertrophic
scarring of the skin by inducing myofibroblast activity. Mol Med.
21:296–304. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|