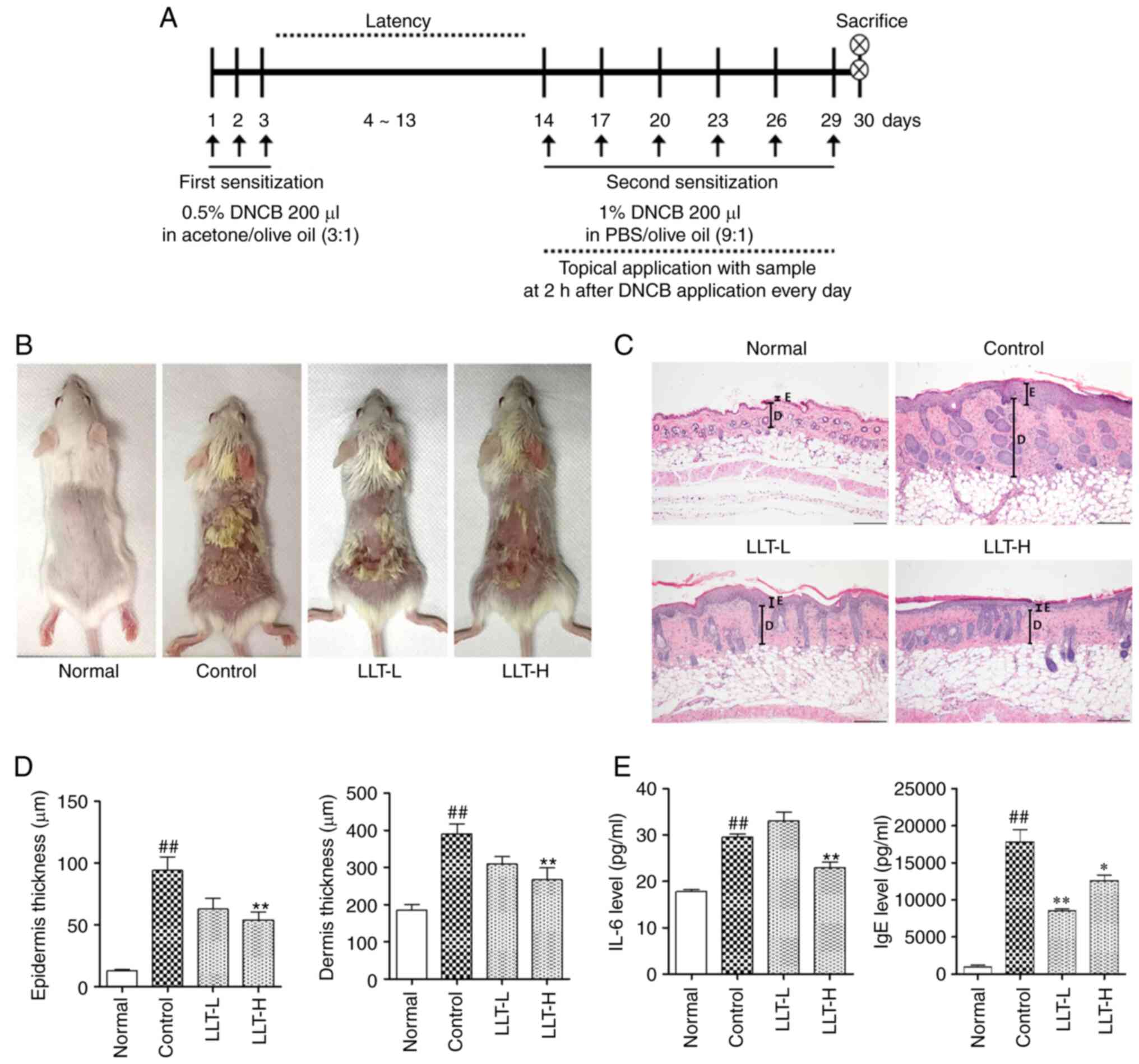
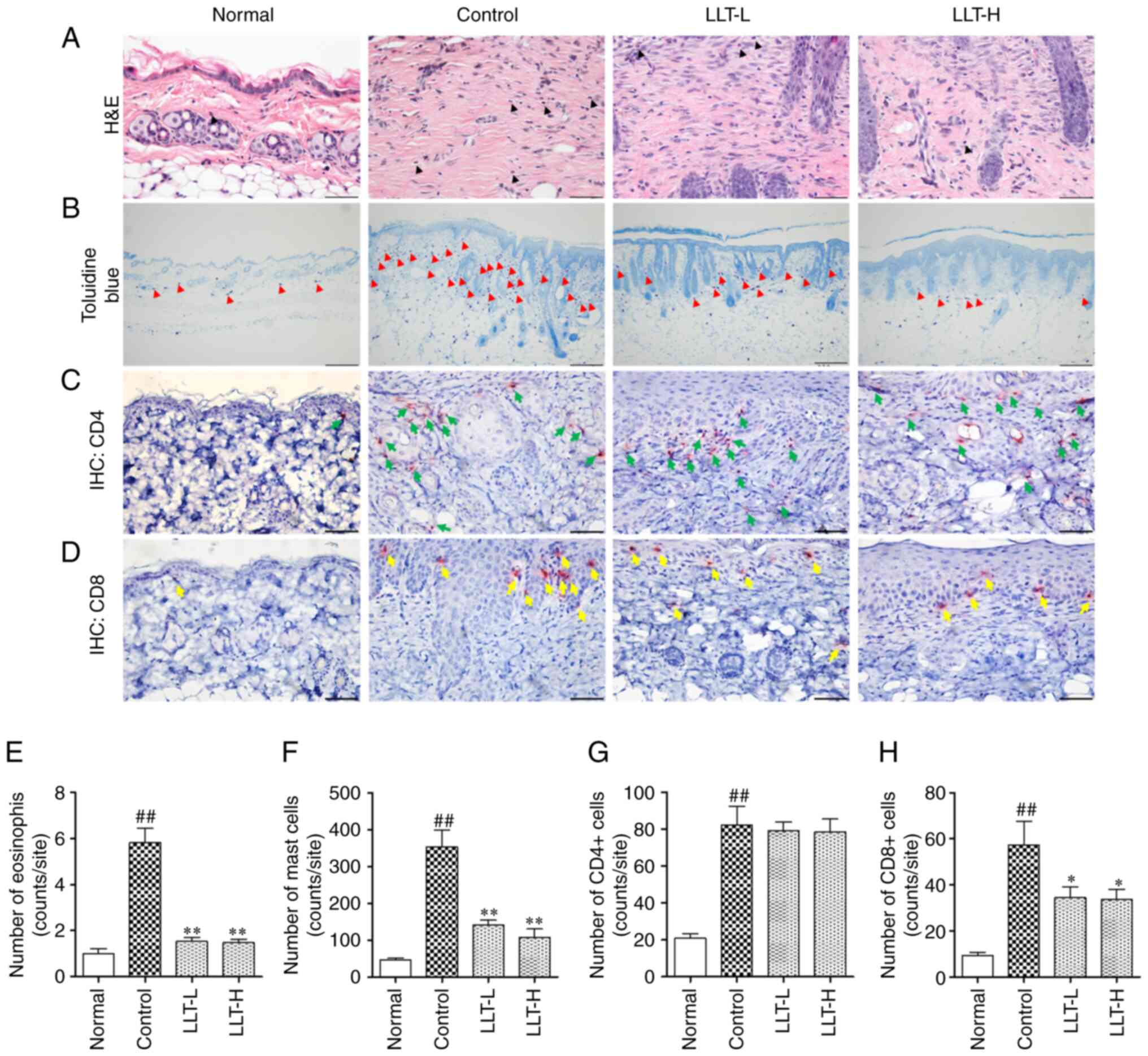
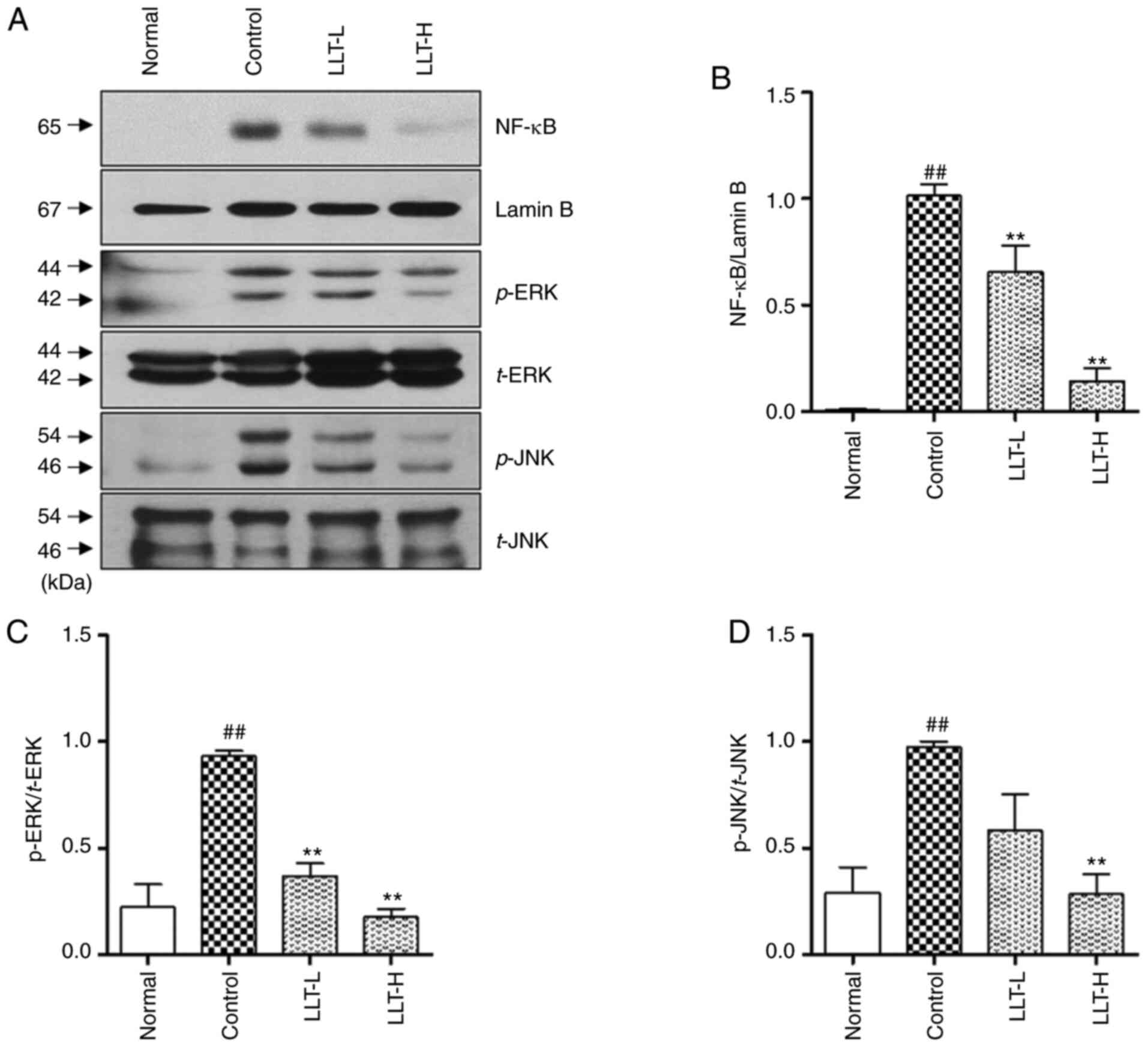
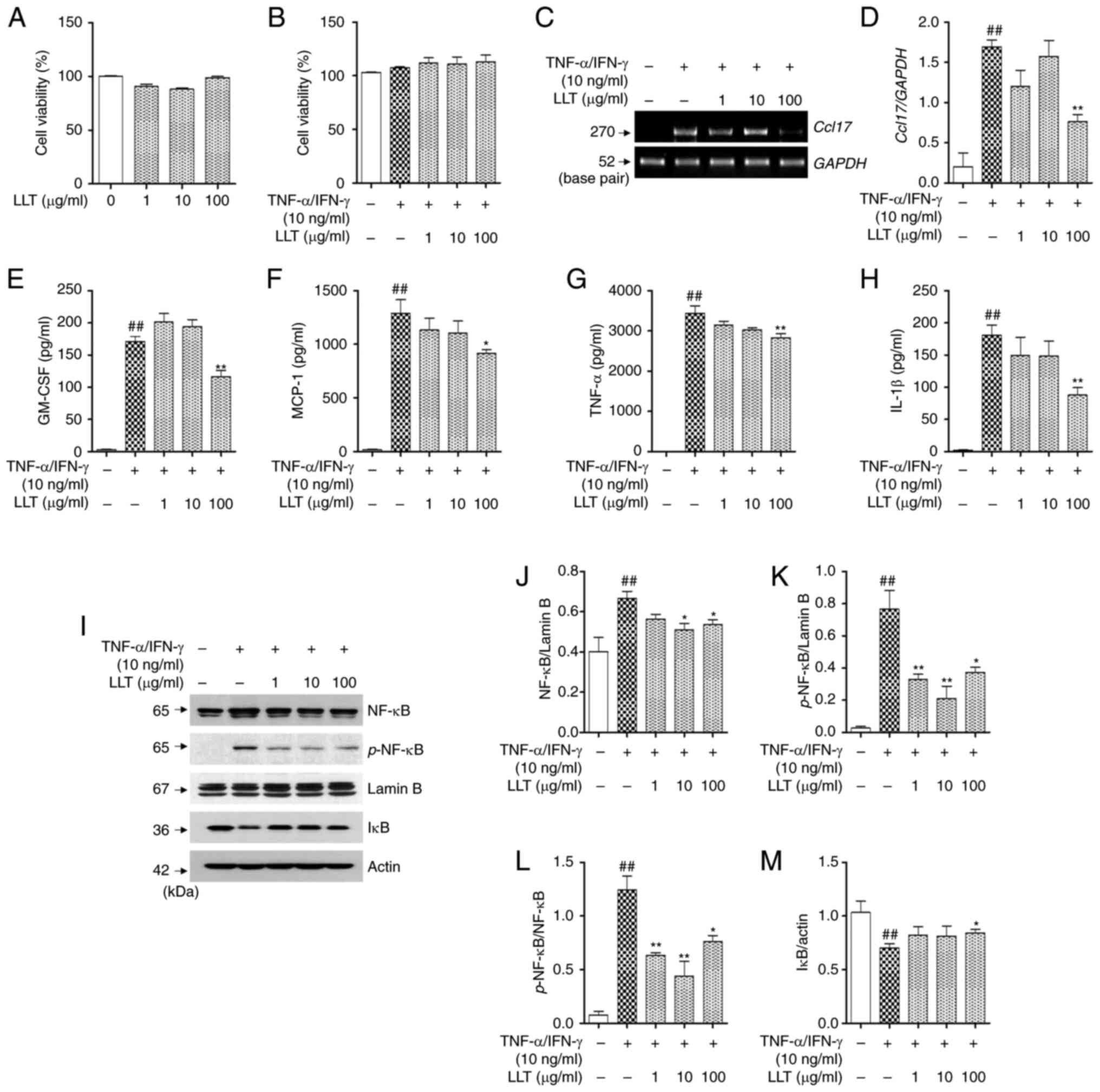
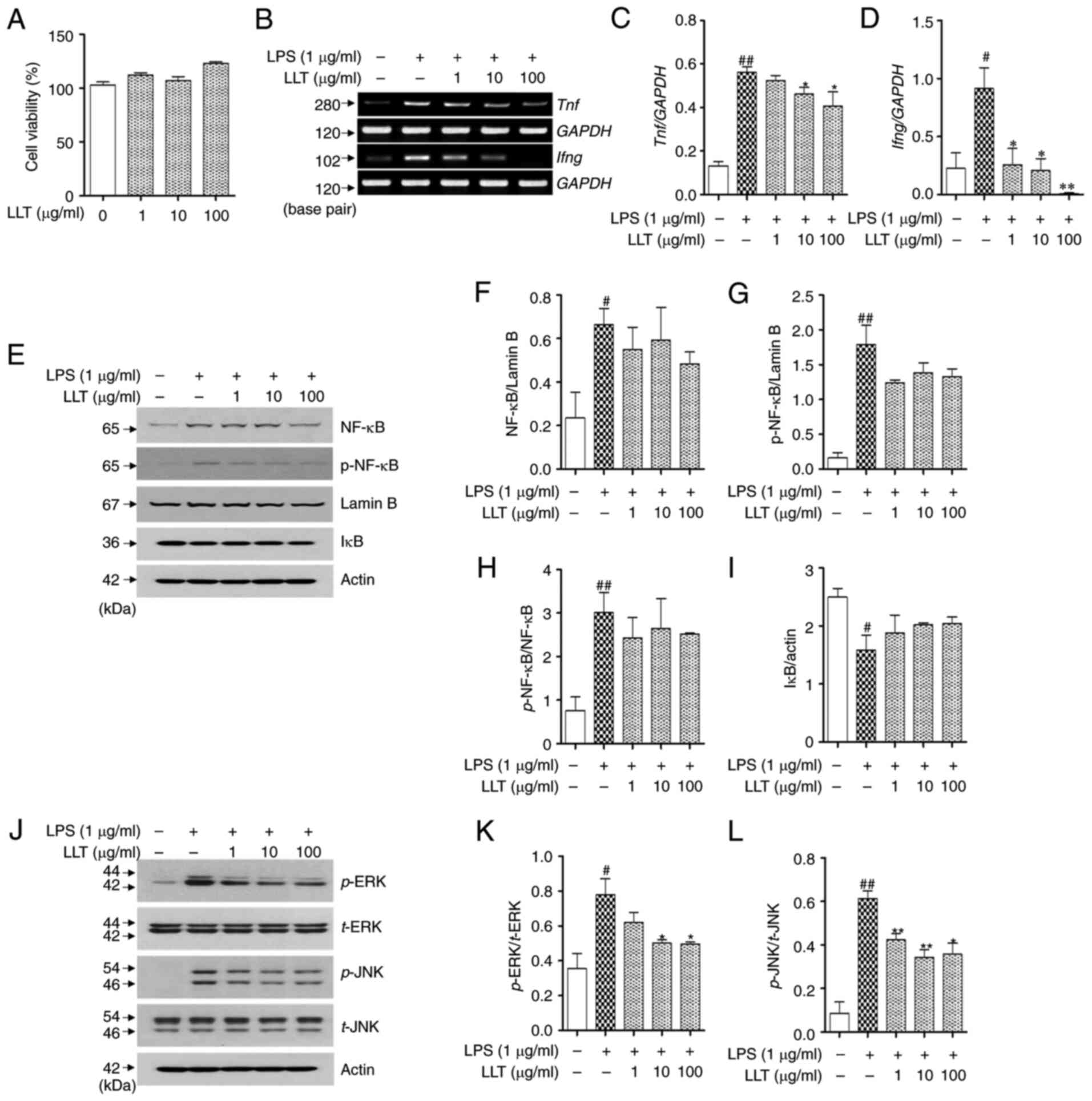
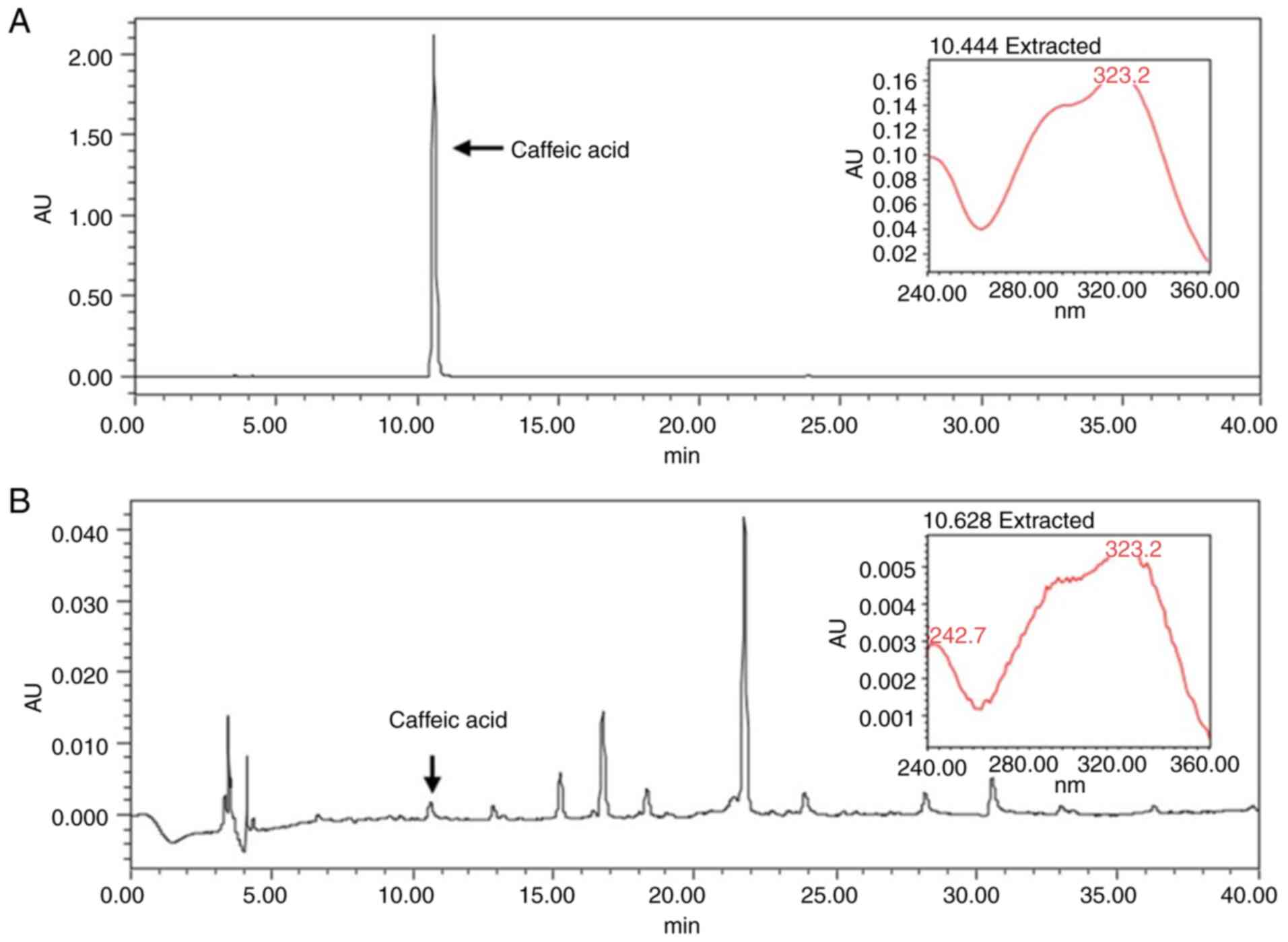
|
1
|
Choi JH, Kim HG, Jin SW, Han EH, Khanal T,
Do MT, Hwang YP, Choi JM, Chun SS, Chung YC, et al: Topical
application of Pleurotus eryngii extracts inhibits
2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice
by the regulation of Th1/Th2 balance. Food Chem Toxicol. 53:38–45.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Johansson SG, Hourihane JO, Bousquet J,
Bruijnzeel-Koomen C, Dreborg S, Haahtela T, Kowalski ML, Mygind N,
Ring J, van Cauwenberge P, et al: A revised nomenclature for
allergy. An EAACI position statement from the EAACI nomenclature
task force. Allergy. 56:813–824. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cookson W: The immunogenetics of asthma
and eczema: A new focus on the epithelium. Nat Rev Immunol.
4:978–988. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Denby KS and Beck LA: Update on systemic
therapies for atopic dermatitis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol.
12:421–426. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bieber T: Atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med.
358:1483–1494. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim JH, Kim MH, Yang G, Huh Y, Kim SH and
Yang WM: Effects of topical application of Astragalus membranaceus
on allergic dermatitis. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 35:151–156.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yuan XY, Ma HM, Li RZ, Wang RY, Liu W and
Guo JY: Topical application of aloperine improves
2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin
lesions in NC/Nga mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 658:263–269. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim EC, Lee HS, Kim SK, Choi MS, Lee S,
Han JB, An HJ, Um JY, Kim HM, Lee NY, et al: The bark of Betula
platyphylla var. Japonica inhibits the development of atopic
dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. J Ethnopharmacol.
116:270–278. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Watanabe H, Unger M, Tuvel B, Wang B and
Sauder DN: Contact hypersensitivity: The mechanism of immune
responses and T cell balance. J Interferon Cytokine Res.
22:407–412. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bieber T, Cork M and Reitamo S: Atopic
dermatitis: A candidate for disease-modifying strategy. Allergy.
67:969–975. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brandt EB and Sivaprasad U: Th2 cytokines
and atopic dermatitis. J Clin Cell Immunol. 2:1102011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tokura Y: Extrinsic and intrinsic types of
atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol Sci. 58:1–7. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu FT, Goodarzi H and Chen HY: IgE, mast
cells, and eosinophils in atopic dermatitis. Clin Rev Allergy
Immunol. 41:298–310. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Seitz CS, Lin Q, Deng H and Khavari PA:
Alterations in NF-kappaB function in transgenic epithelial tissue
demonstrate a growth inhibitory role for NF-kappaB. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 95:2307–2312. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Smahi A, Courtois G, Rabia SH, Doffinger
R, Bodemer C, Munnich A, Casanova JL and Israel A: The NF-kappaB
signalling pathway in human diseases: From incontinentia pigmenti
to ectodermal dysplasias and immune-deficiency syndromes. Hum Mol
Genet. 11:2371–2375. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kataoka Y: Thymus and activation-regulated
chemokine as a clinical biomarker in atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol.
41:221–229. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Emile JF, Fraitag S, Andry P, Leborgne M,
Lellouch-Tubiana A and Brousse N: Expression of GM-CSF receptor by
Langerhans' cell histiocytosis cells. Virchows Arch. 427:125–129.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rajagopalan LE, Burkholder JK, Turner J,
Culp J, Yang NS and Malter JS: Granulocyte-macrophage
colony-stimulating factor mRNA stabilization enhances transgenic
expression in normal cells and tissues. Blood. 86:2551–2558. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Breuhahn K, Mann A, Muller G, Wilhelmi A,
Schirmacher P, Enk A and Blessing M: Epidermal overexpression of
granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor induces both
keratinocyte proliferation and apoptosis. Cell Growth Differ.
11:111–121. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pastore S, Fanales-Belasio E, Albanesi C,
Chinni LM, Giannetti A and Girolomoni G: Granulocyte macrophage
colony-stimulating factor is overproduced by keratinocytes in
atopic dermatitis. Implications for sustained dendritic cell
activation in the skin. J Clin Invest. 99:3009–3017. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kaburagi Y, Shimada Y, Nagaoka T, Hasegawa
M, Takehara K and Sato S: Enhanced production of CC-chemokines
(RANTES, MCP-1, MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta, and eotaxin) in patients
with atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol Res. 293:350–355. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Klonowska J, Glen J, Nowicki RJ and
Trzeciak M: New cytokines in the pathogenesis of atopic
dermatitis-new therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci. 19:30862018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Leung DY: Atopic dermatitis: New insights
and opportunities for therapeutic intervention. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 105:860–876. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tan Q, Yang H, Liu E and Wang H: P38/ERK
MAPK signaling pathways are involved in the regulation of filaggrin
and involucrin by IL17. Mol Med Rep. 16:8863–8867. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cui HZ, Oh HC, Li X, Lee YJ, Cho KW, Kang
DG and Lee HS: Ethanol extract of Lycopus lucidus elicits
positive inotropic effect via activation of Ca2+ entry
and Ca2+ release in beating rabbit atria. J Med Food.
16:633–640. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jeong DW, Kim EY, Kim JH, Lee B, Hong S,
Park JH, Jung HS and Sohn Y: Lycopus lucidus Turcz Inhibits the
Osteoclastogenesis in RAW 264.7 Cells and Bone Loss in
Ovariectomized Rat Model. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2019:32317842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shin TY, Kim SH, Suk K, Ha JH, Kim I, Lee
MG, Jun CD, Kim SY, Lim JP, Eun JS, et al: Anti-allergic effects of
Lycopus lucidus on mast cell-mediated allergy model. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 209:255–262. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Woo ER and Piao MS: Antioxidative
constituents from Lycopus lucidus. Arch Pharm Res.
27:173–176. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee YJ, Kang DG, Kim JS and Lee HS:
Lycopus lucidus inhibits high glucose-induced vascular
inflammation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Vascul
Pharmacol. 48:38–46. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim KY, Oh TW, Ma JY and Park KI: Ethanol
extract of Lycopus lucidus Turcz. ex benth inhibits
metastasis by downregulation of Runx-2 in mouse colon cancer cells.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018:95132902018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ren Q, Ding L, Sun SS, Wang HY and Qu L:
Chemical identification and quality evaluation of Lycopus
lucidus Turcz by UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS and HPLC-MS/MS and hierarchical
clustering analysis. Biomed Chromatogr. 31:2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Slusarczyk S, Hajnos M, Skalicka-Woźniak K
and Matkowski A: Antioxidant activity of polyphenols from
Lycopus lucidus Turcz. Food Chem. 113:134–138. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kwon B, Hong SY, Kim EY, Kim JH, Kim M,
Park JH, Sohn Y and Jung HS: Effect of cone of pinus densiflora on
DNCB-induced allergic contact dermatitis-like skin lesion in Balb/c
Mice. Nutrients. 13:8392021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang EY, Chen AY and Zhu BT: Mechanism of
dinitrochlorobenzene-induced dermatitis in mice: Role of specific
antibodies in pathogenesis. PLoS One. 4:e77032009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Han MH, Yoon WK, Lee H, Han SB, Lee K,
Park SK, Yang KH, Kim HM and Kang JS: Topical application of
silymarin reduces chemical-induced irritant contact dermatitis in
BALB/c mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 7:1651–1658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Raschke WC, Baird S, Ralph P and Nakoinz
I: Functional macrophage cell lines transformed by Abelson leukemia
virus. Cell. 15:261–267. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bhardwaj M, Sali VK, Mani S and Vasanthi
HR: Neophytadiene from turbinaria ornata suppresses LPS-induced
inflammatory response in RAW 264.7 macrophages and sprague dawley
rats. Inflammation. 43:937–950. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee DH, Park JK, Choi J, Jang H and Seol
JW: Anti-inflammatory effects of natural flavonoid diosmetin in
IL-4 and LPS-induced macrophage activation and atopic dermatitis
model. Int Immunopharmacol. 89:1070462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee HN, Shin SA, Choo GS, Kim HJ, Park YS,
Kim BS, Kim SK, Cho SD, Nam JS, Choi CS, et al: Antiinflammatory
effect of quercetin and galangin in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7
macrophages and DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis animal models. Int J
Mol Med. 41:888–898. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Choi JK, Oh HM, Lee S, Kwon TK, Shin TY,
Rho MC and Kim SH: Salvia plebeia suppresses atopic dermatitis-like
skin lesions. Am J Chin Med. 42:967–985. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Proksch E, Folster-Holst R and Jensen JM:
Skin barrier function, epidermal proliferation and differentiation
in eczema. J Dermatol Sci. 43:159–169. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yarbrough KB, Neuhaus KJ and Simpson EL:
The effects of treatment on itch in atopic dermatitis. Dermatol
Ther. 26:110–119. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang Q, Gao S, Wu GZ, Yang N, Zu XP, Li
WC, Xie N, Zhang RR, Li CW, Hu ZL and Zhang WD: Total sesquiterpene
lactones isolated from Inula helenium L. attenuates 2,
4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions
in mice. Phytomedicine. 46:78–84. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kim JE, Kim JS, Cho DH and Park HJ:
Molecular mechanisms of cutaneous inflammatory disorder: Atopic
dermatitis. Int J Mol Sci. 17:12342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cesare AD, Meglio PD and Nestle FO: A role
for Th17 cells in the immunopathogenesis of atopic dermatitis? J
Invest Dermatol. 128:2569–2571. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Deo SS, Mistry KJ, Kakade AM and Niphadkar
PV: Role played by Th2 type cytokines in IgE mediated allergy and
asthma. Lung India. 27:66–71. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Stone KD, Prussin C and Metcalfe DD: IgE,
mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 125
(Suppl 2):S73–S80. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Metcalfe DD, Baram D and Mekori YA: Mast
cells. Physiol Rev. 77:1033–1079. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Inagaki N, Shiraishi N, Igeta K, Itoh T,
Chikumoto T, Nagao M, Kim JF and Nagai H: Inhibition of scratching
behavior associated with allergic dermatitis in mice by tacrolimus,
but not by dexamethasone. Eur J Pharmacol. 546:189–196. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Plager DA, Henke SA, Matsuwaki Y, Madaan
A, Squillace DL, Dierkhising RA and Kita H: Pimecrolimus reduces
eosinophil activation associated with calcium mobilization. Int
Arch Allergy Immunol. 149:119–126. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Fujii Y, Takeuchi H, Sakuma S, Sengoku T
and Takakura S: Characterization of a
2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced chronic dermatitis model in rats.
Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 22:240–247. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Galli SJ and Tsai M: IgE and mast cells in
allergic disease. Nat Med. 18:693–704. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sismanopoulos N, Delivanis DA,
Alysandratos KD, Angelidou A, Therianou A, Kalogeromitros D and
Theoharides TC: Mast cells in allergic and inflammatory diseases.
Curr Pharm Des. 18:2261–2277. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Won TJ, Kim B, Lee Y, Bang JS, Oh ES, Yoo
JS, Hyung KE, Yoon J, Hwang S, Park ES, et al: Therapeutic
potential of Lactobacillus plantarum CJLP133 for house-dust
mite-induced dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. Cell Immunol. 277:49–57.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ikoma A, Steinhoff M, Stander S,
Yosipovitch G and Schmelz M: The neurobiology of itch. Nat Rev
Neurosci. 7:535–547. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Paus R, Schmelz M, Biro T and Steinhoff M:
Frontiers in pruritus research: Scratching the brain for more
effective itch therapy. J Clin Invest. 116:1174–1186. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
James EA and Kwok WW: Autoreactive CD4(+)
T cells in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
128:100–101. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Murota H, El-latif MA, Tamura T, Amano T
and Katayama I: Olopatadine hydrochloride improves dermatitis score
and inhibits scratch behavior in NC/Nga mice. Int Arch Allergy
Immunol. 153:121–132. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yamanaka K and Mizutani H: The role of
cytokines/chemokines in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Curr
Probl Dermatol. 41:80–92. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Barcena J and Blanco E: Design of novel
vaccines based on virus-like particles or chimeric virions. Subcell
Biochem. 68:631–665. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Eisenbarth SC, Baumjohann D, Craft J,
Fazilleau N, Ma CS, Tangye SG, Vinuesa CG and Linterman MA:
CD4+ T cells that help B cells-a proposal for uniform
nomenclature. Trends Immunol. 42:658–669. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Mitchison NA: T-cell-B-cell cooperation.
Nat Rev Immunol. 4:308–312. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Gri G, Piconese S, Frossi B, Manfroi V,
Merluzzi S, Tripodo C, Viola A, Odom S, Rivera J, Colombo MP and
Pucillo CE: CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells
suppress mast cell degranulation and allergic responses through
OX40-OX40L interaction. Immunity. 29:771–781. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Fong TA and Mosmann TR: Alloreactive
murine CD8+ T cell clones secrete the Th1 pattern of
cytokines. J Immunol. 144:1744–1752. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yagi R, Nagai H, Iigo Y, Akimoto T, Arai T
and Kubo M: Development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in
STAT6-deficient NC/Nga mice. J Immunol. 168:2020–2027. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Tan HP, Lebeck LK and Nehlsen-Cannarella
SL: Regulatory role of cytokines in IgE-mediated allergy. J Leukoc
Biol. 52:115–118. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Barnes PJ and Karin M: Nuclear
factor-kappaB: A pivotal transcription factor in chronic
inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med. 336:1066–1071. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Finco TS and Baldwin AS: Mechanistic
aspects of NF-kappa B regulation: The emerging role of
phosphorylation and proteolysis. Immunity. 3:263–272. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Choi YY, Kim MH, Lee JY, Hong J, Kim SH
and Yang WM: Topical application of Kochia scoparia inhibits the
development of contact dermatitis in mice. J Ethnopharmacol.
154:380–385. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Arthur JS and Ley SC: Mitogen-activated
protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:679–692.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Hommes DW, Peppelenbosch MP and van
Deventer SJ: Mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinase signal
transduction pathways and novel anti-inflammatory targets. Gut.
52:144–151. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Jeon YD, Kee JY, Kim DS, Han YH, Kim SH,
Kim SJ, Um JY and Hong SH: Effects of Ixeris dentata water extract
and caffeic acid on allergic inflammation in vivo and in vitro. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 15:1962015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Venuprasad K, Elly C, Gao M,
Salek-Ardakani S, Harada Y, Luo JL, Yang C, Croft M, Inoue K, Karin
M and Liu YC: Convergence of Itch-induced ubiquitination with
MEKK1-JNK signaling in Th2 tolerance and airway inflammation. J
Clin Invest. 116:1117–1126. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Campbell JJ, Haraldsen G, Pan J, Rottman
J, Qin S, Ponath P, Andrew DP, Warnke R, Ruffing N, Kassam N, et
al: The chemokine receptor CCR4 in vascular recognition by
cutaneous but not intestinal memory T cells. Nature. 400:776–780.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Hijnen D, De Bruin-Weller M, Oosting B,
Lebre C, De Jong E, Bruijnzeel-Koomen C and Knol E: Serum thymus
and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC) and cutaneous T
cell-attracting chemokine (CTACK) levels in allergic diseases: TARC
and CTACK are disease-specific markers for atopic dermatitis. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 113:334–340. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Shimada Y, Takehara K and Sato S: Both Th2
and Th1 chemokines (TARC/CCL17, MDC/CCL22, and Mig/CXCL9) are
elevated in sera from patients with atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol
Sci. 34:201–208. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Cooper KD: Atopic dermatitis: Recent
trends in pathogenesis and therapy. J Invest Dermatol. 102:128–137.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Deshmane SL, Kremlev S, Amini S and Sawaya
BE: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): An overview. J
Interferon Cytokine Res. 29:313–326. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Homey B, Steinhoff M, Ruzicka T and Leung
DY: Cytokines and chemokines orchestrate atopic skin inflammation.
J Allergy Clin Immunol. 118:178–189. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Danso MO, van Drongelen V, Mulder A, van
Esch J, Scott H, van Smeden J, El Ghalbzouri A and Bouwstra JA:
TNF-α and Th2 cytokines induce atopic dermatitis-like features on
epidermal differentiation proteins and stratum corneum lipids in
human skin equivalents. J Invest Dermatol. 134:1941–1950. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Pacheco KA, Tarkowski M, Sterritt C, Negri
J, Rosenwasser LJ and Borish L: The influence of diesel exhaust
particles on mononuclear phagocytic cell-derived cytokines: IL-10,
TGF-beta and IL-1 beta. Clin Exp Immunol. 126:374–383. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Luna JD, Chan CC, Derevjanik NL, Mahlow J,
Chiu C, Peng B, Tobe T, Campochiaro PA and Vinores SA:
Blood-retinal barrier (BRB) breakdown in experimental autoimmune
uveoretinitis: Comparison with vascular endothelial growth factor,
tumor necrosis factor alpha, and interleukin-1beta-mediated
breakdown. J Neurosci Res. 49:268–280. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Murata T, Watahiki M, Tanaka Y, Miyase T
and Yoshizaki F: Hyaluronidase inhibitors from Takuran, Lycopus
lucidus. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 58:394–397. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Kunz B, Oranje AP, Labreze L, Stalder JF,
Ring J and Taieb A: Clinical validation and guidelines for the
SCORAD index: Consensus report of the European task force on atopic
dermatitis. Dermatology. 195:10–19. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Lee J, Jung E, Koh J, Kim YS and Park D:
Effect of rosmarinic acid on atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol.
35:768–771. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Gendrisch F, Esser PR, Schempp CM and
Wolfle U: Luteolin as a modulator of skin aging and inflammation.
Biofactors. 47:170–180. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Kang J, Lee S, Kim N, Dhakal H, Choi YA,
Kwon TK, Khang D and Kim SH: Hispidulin alleviates
2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene and house dust mite extract-induced atopic
dermatitis-like skin inflammation. Biomed Pharmacother.
137:1113592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|