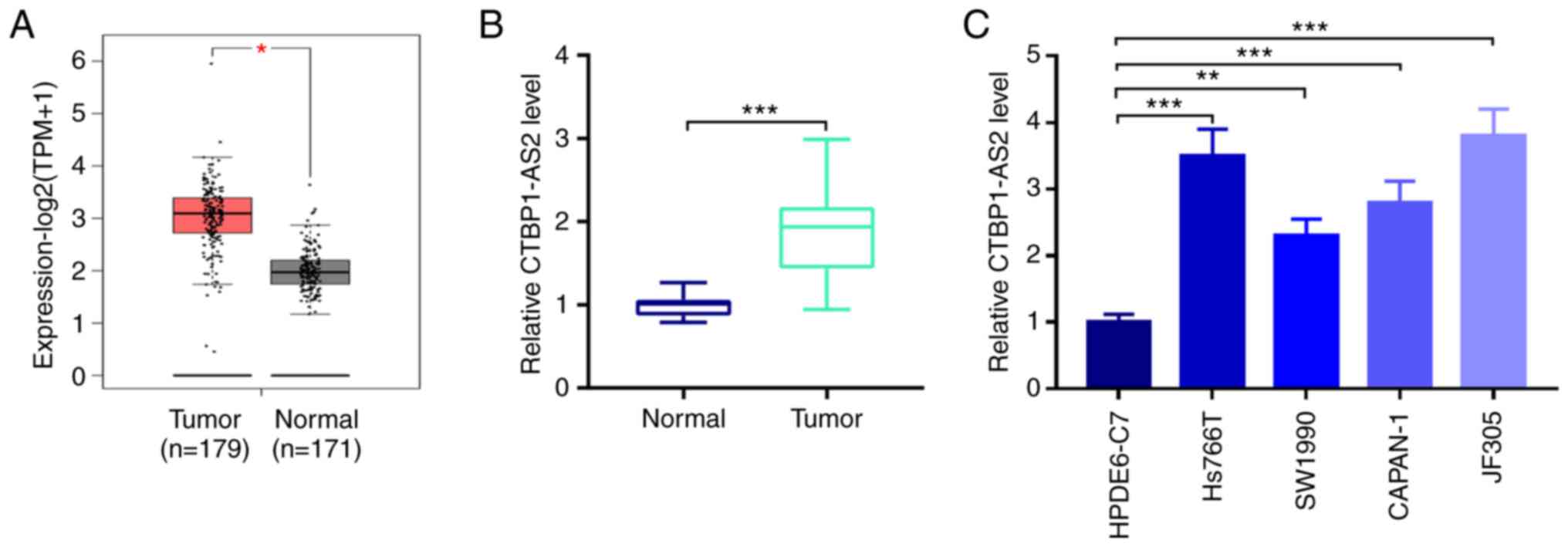
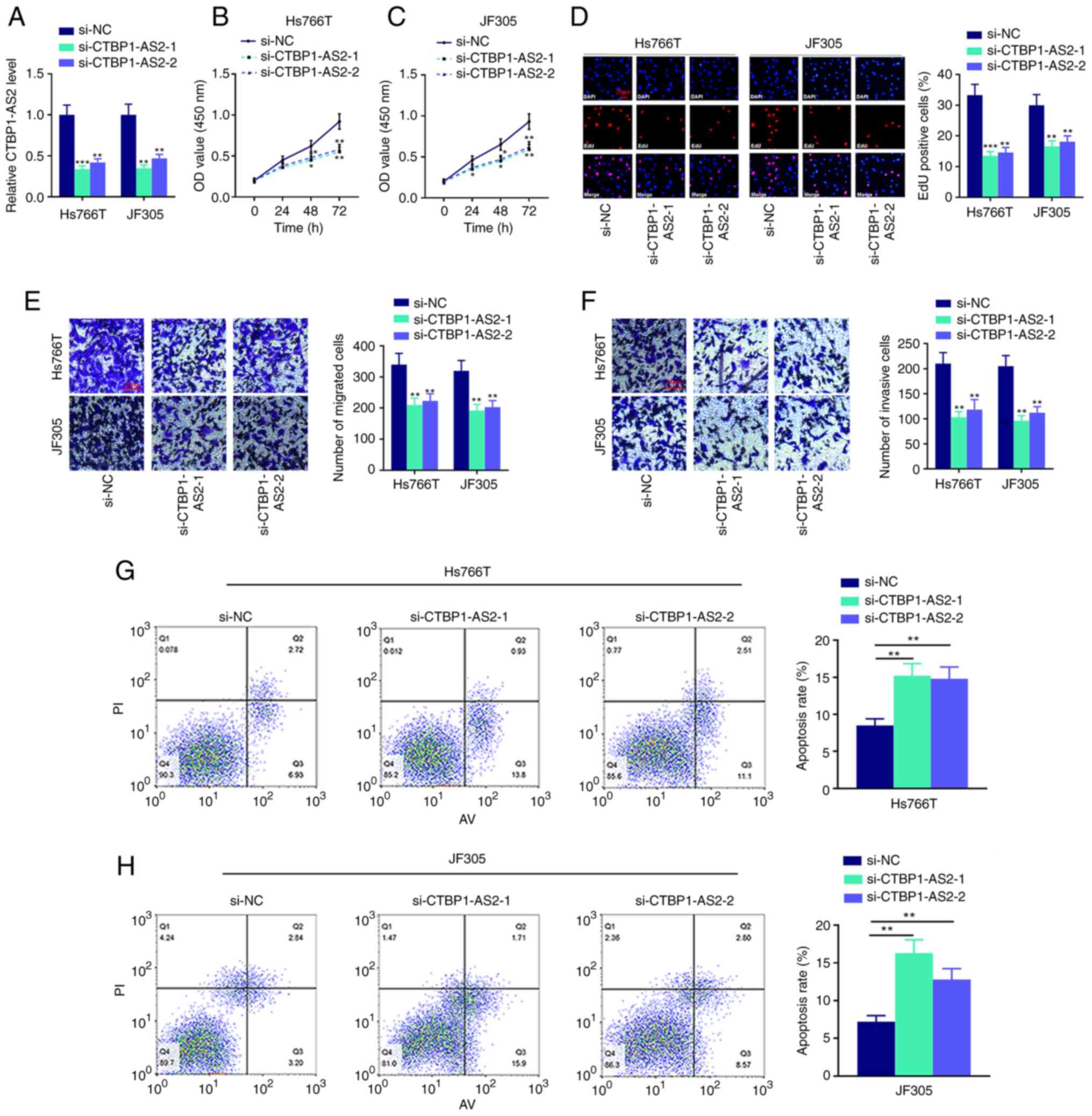
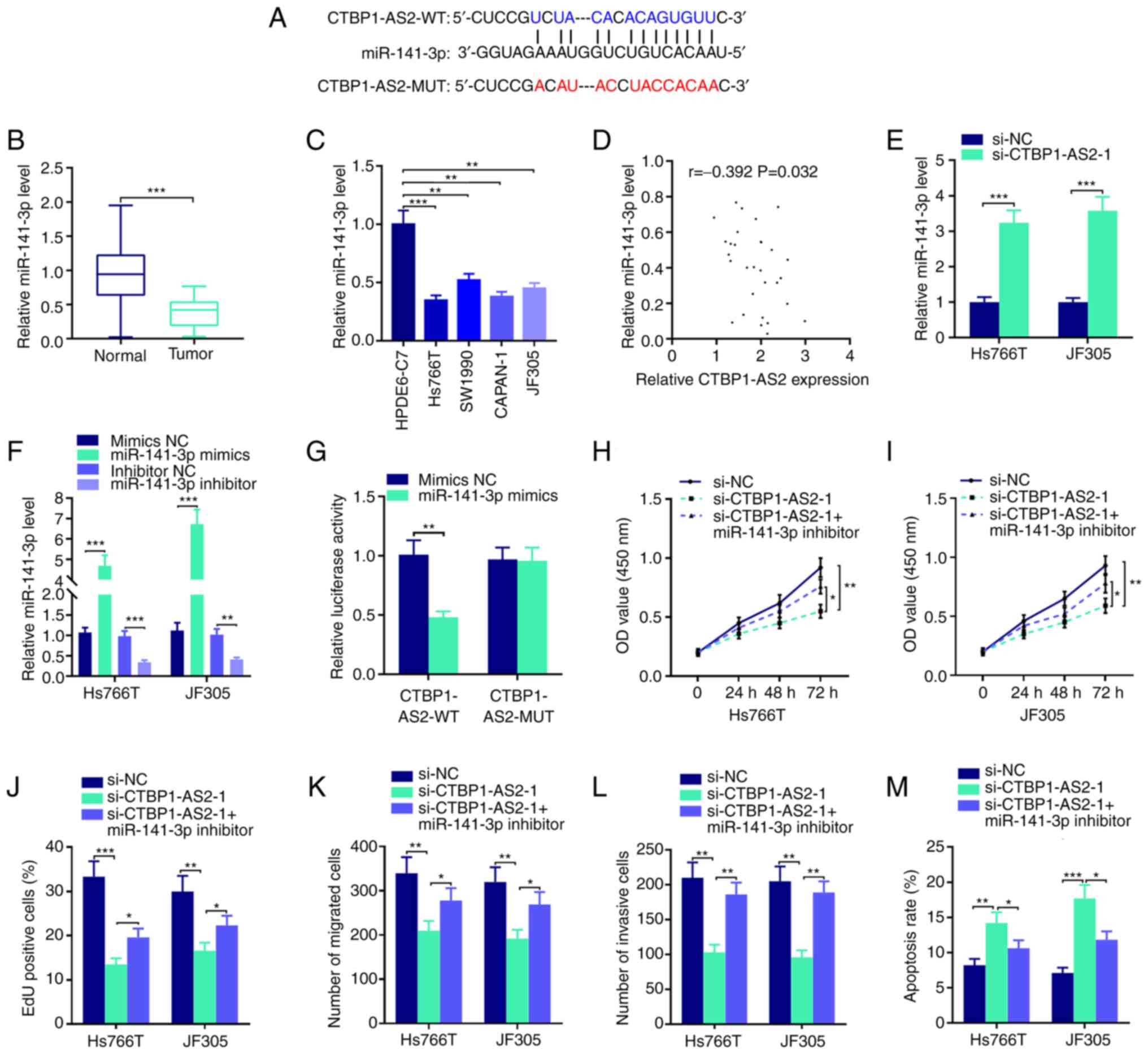
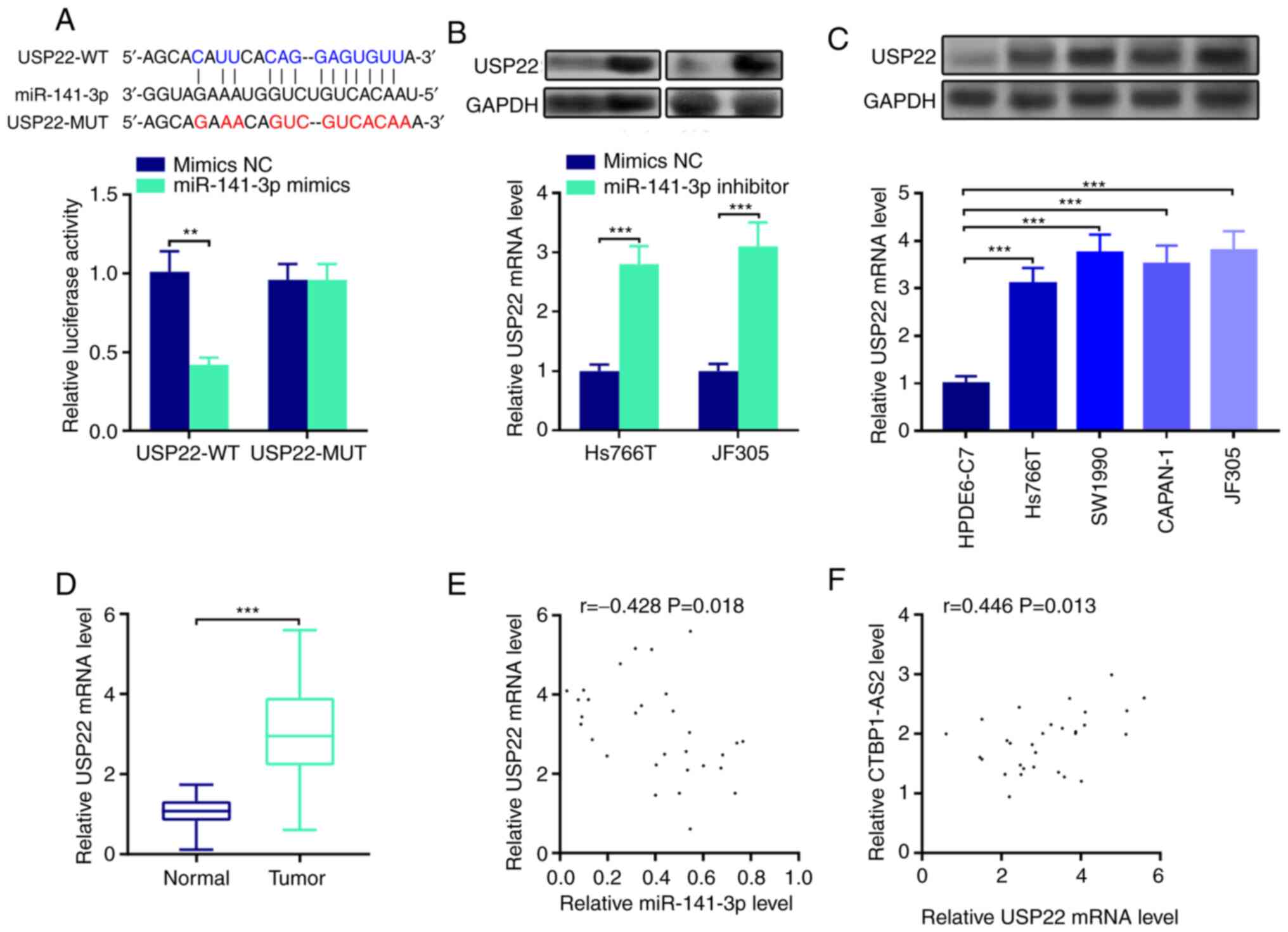
|
1
|
Grossberg AJ, Chu LC, Deig CR, Fishman EK,
Hwang WL, Maitra A, Marks DL, Mehta A, Nabavizadeh N, Simeone DM,
et al: Multidisciplinary standards of care and recent progress in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:375–403.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang P, Wang J, Tan H, Weng S, Cheng L,
Zhou Z and Wen S: Acid- and reduction-sensitive micelles for
improving the drug delivery efficacy for pancreatic cancer therapy.
Biomater Sci. 6:1262–1270. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sheng J, Wang L, Han Y, Chen W, Liu H,
Zhang M, Deng L and Liu YN: Dual roles of protein as a template and
a sulfur provider: A general approach to metal sulfides for
efficient photothermal therapy of cancer. Small. 14:Nov
17–2017.doi: 10.1002/smll.201702529. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Batista IA and Melo SA: Exosomes and the
future of immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
20:5672019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chan JJ and Tay Y: Noncoding RNA: RNA
regulatory networks in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 19:13102018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu T, Lei T, Li SQ, Mai EH, Ding FH and
Niu B: DNAH17-AS1 promotes pancreatic carcinoma by increasing PPME1
expression via inhibition of miR-432-5p. World J Gastroenterol.
26:1745–1757. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang H, Feng X, Zhang M, Liu A, Tian L,
Bo W, Wang H and Hu Y: Long non-coding RNA CASC2 upregulates PTEN
to suppress pancreatic carcinoma cell metastasis by downregulating
miR-21. Cancer Cell Int. 19:182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guo JQ, Yang ZJ, Wang S, Wu ZZ, Yin LL and
Wang DC: LncRNA SNHG16 functions as an oncogene by sponging
miR-200a-3p in pancreatic cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
24:72182020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang M and Zhao H: LncRNA CTBP1-AS2
promotes cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma by
regulating miR-623/Cyclin d1 axis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm.
35:765–770. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang QA, Yang Y and Liang X: LncRNA
CTBP1-AS2 sponges miR-216a to upregulate PTEN and suppress
endometrial cancer cell invasion and migration. J Ovarian Res.
13:372020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tang M, Xie X, Shi M, Xin W, Zheng G,
Zhang Y, Zhang Z and Lian X: Antileukemic effect of caffeic acid
3,4-dihydroxyphenetyl ester. Evidences for its mechanisms of
action. Phytomedicine. 80:1533832021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA
language? Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ning Z, Wang A, Liang J, Xie Y, Liu J, Yan
Q and Wang Z: USP22 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition via
the FAK pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
32:1451–1458. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mattiuzzi C and Lippi G: Cancer
statistics: A comparison between World Health Organization (WHO)
and global burden of disease (GBD). Eur J Public Health.
30:1026–1027. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Weng W, Zhang Z, Huang W, Xu X, Wu B, Ye
T, Shan Y, Shi K and Lin Z: Identification of a competing
endogenous RNA network associated with prognosis of pancreatic
adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 20:2312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang Y, Gao M, Li Y, Li M and Ma Q: LncRNA
CTBP1-AS2 facilitates gastric cancer progression via regulating the
miR-139-3p/MMP11 axis. Onco Targets Ther. 13:11537–11547. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang H, Li J, Shao W and Shen N: LncRNA
CTBP1-AS2 is upregulated in osteoarthritis and increases the
methylation of miR-130a gene to inhibit chondrocyte proliferation.
Clin Rheumatol. 39:3473–3478. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li Y, Zong J and Zhao C: lncRNA CTBP1-AS2
promotes proliferation and migration of glioma by modulating
miR-370-3p-Wnt7a-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Biochem Cell Biol. 98:661–668. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cui K and Zhu G: LncRNA CTBP1-AS2
regulates miR-216a/PTEN to suppress ovarian cancer cell
proliferation. J Ovarian Res. 13:842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang S, Shi F, Du Y, Wang Z, Feng Y, Song
J, Liu Y and Xiao M: Long non-coding RNA CTBP1-AS2 enhances
cervical cancer progression via up-regulation of ZNF217 through
sponging miR-3163. Cancer Cell Int. 20:3432020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang L: MiR-141-3p overexpression
suppresses the malignancy of osteosarcoma by targeting FUS to
degrade LDHB. Biosci Rep. 40:BSR201934042020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liang Z, Li X, Liu S, Li C, Wang X and
Xing J: MiR-141-3p inhibits cell proliferation, migration and
invasion by targeting TRAF5 in colorectal cancer. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 514:699–705. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun J and Zhang Y: LncRNA XIST enhanced
TGF-β2 expression by targeting miR-141-3p to promote pancreatic
cancer cells invasion. Biosci Rep. 39:BSR201903322019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao G, Wang B, Liu Y, Zhang JG, Deng SC,
Qin Q, Tian K, Li X, Zhu S, Niu Y, et al: MiRNA-141, downregulated
in pancreatic cancer, inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by
directly targeting MAP4K4. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:2569–2580. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Melo-Cardenas J, Zhang Y, Zhang DD and
Fang D: Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 22 functions and its
involvement in disease. Oncotarget. 7:44848–44856. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lim C, Xu JC, Chen TY, Xu JX, Chen WF, Hu
JW, Li QL and Zhang YQ: Ubiquitin-specific peptide 22 acts as an
oncogene in gastric cancer in a son of sevenless 1-dependent
manner. Cancer Cell Int. 20:452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou D, Liu P, Sun DW, Chen ZJ, Hu J, Peng
SM and Liu YL: USP22 down-regulation facilitates human
retinoblastoma cell aging and apoptosis via inhibiting TERT/P53
pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:2785–2792. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li J, Yuan S, Norgard RJ, Yan F, Yamazoe
T, Blanco A and Stanger BZ: Tumor Cell-Intrinsic USP22 suppresses
antitumor immunity in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Immunol Res.
8:282–291. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|