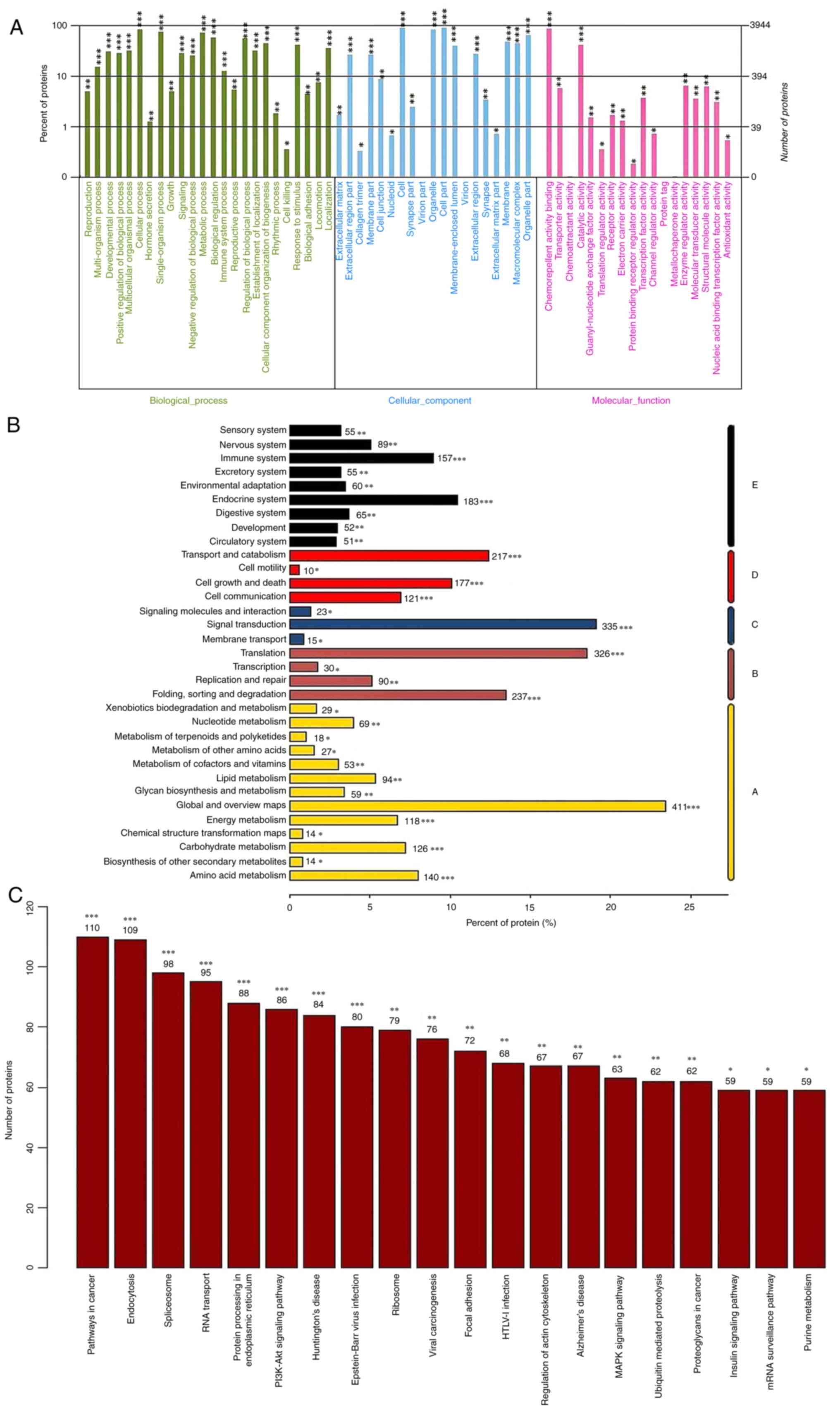
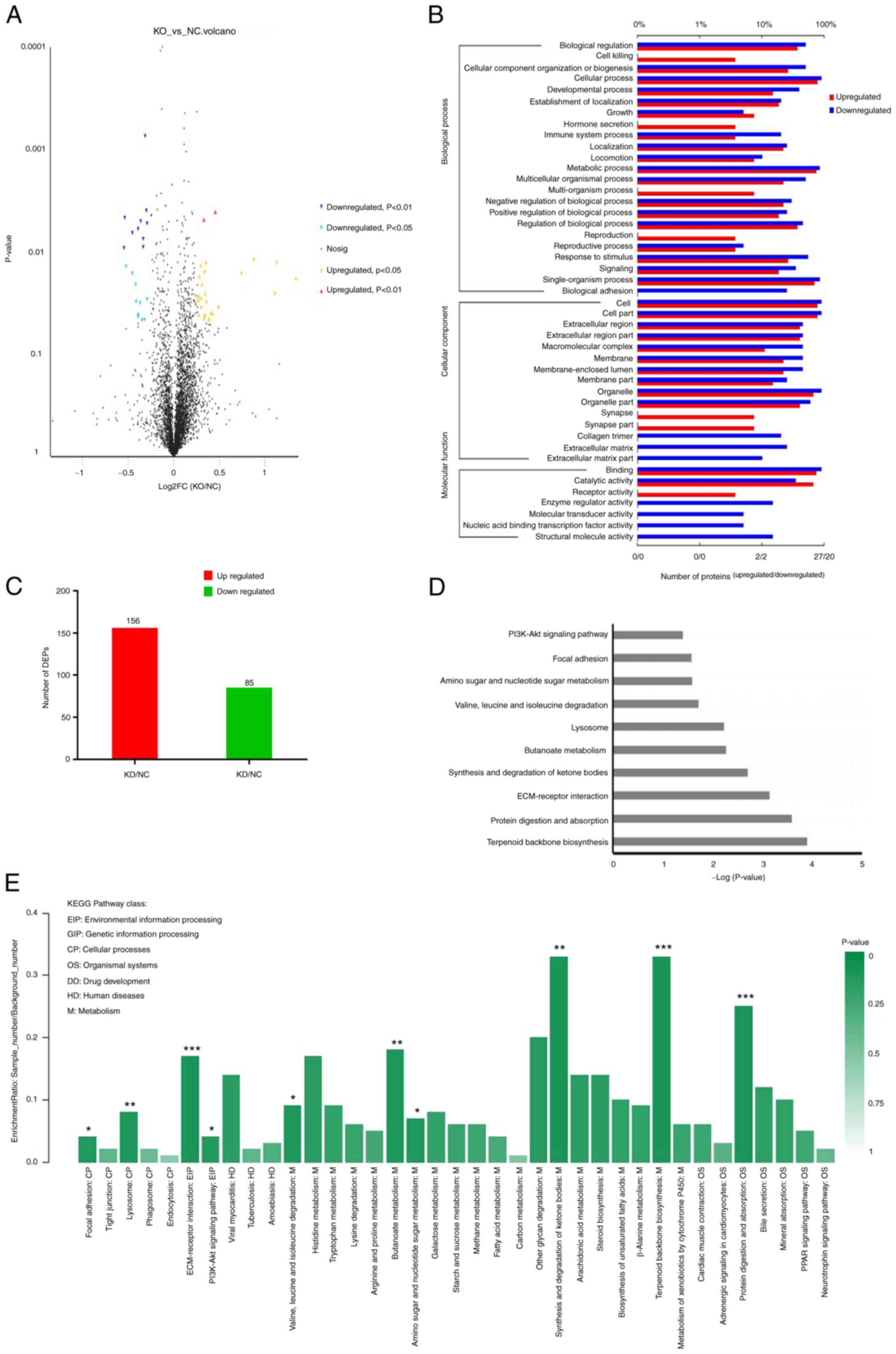
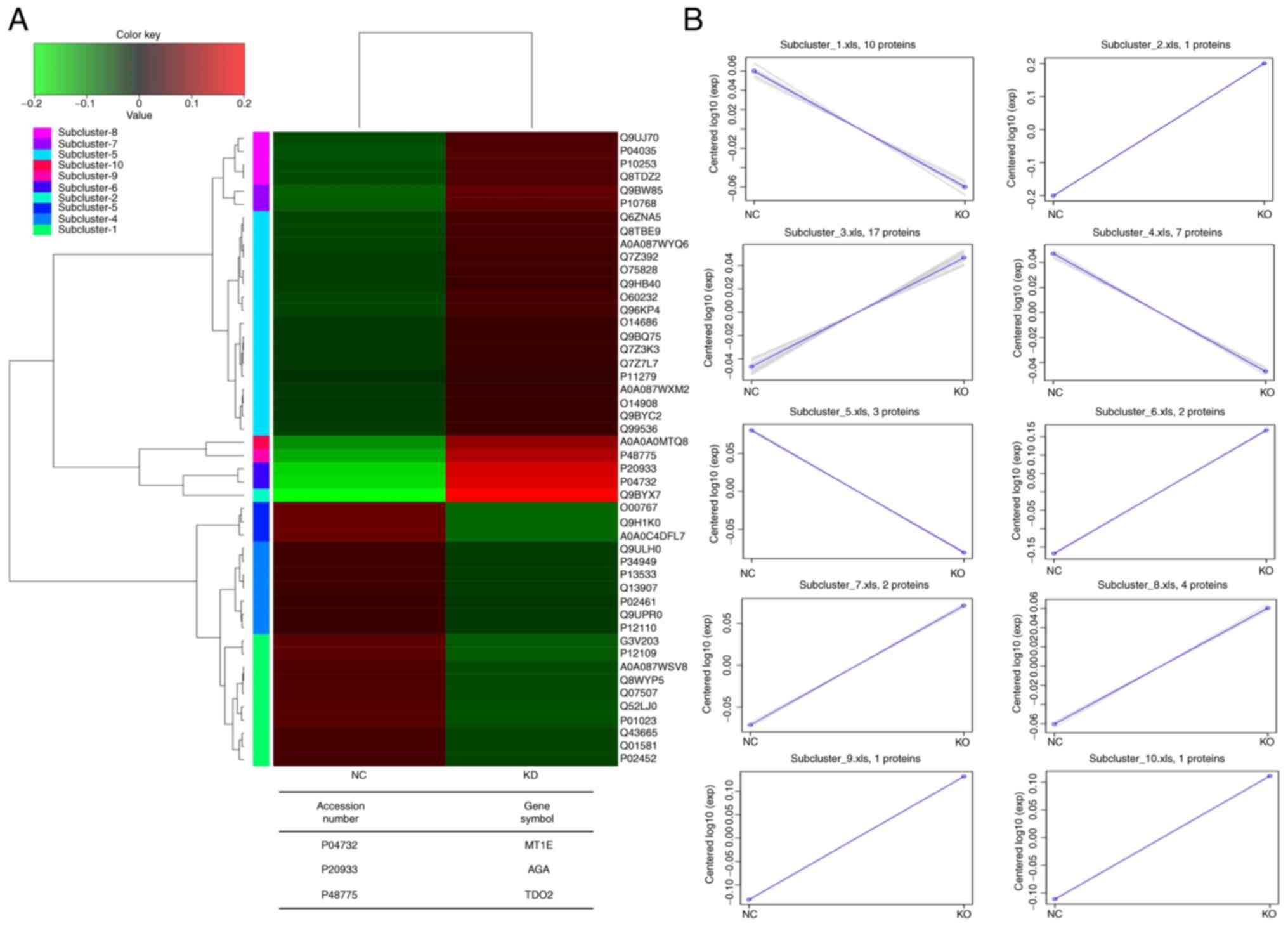
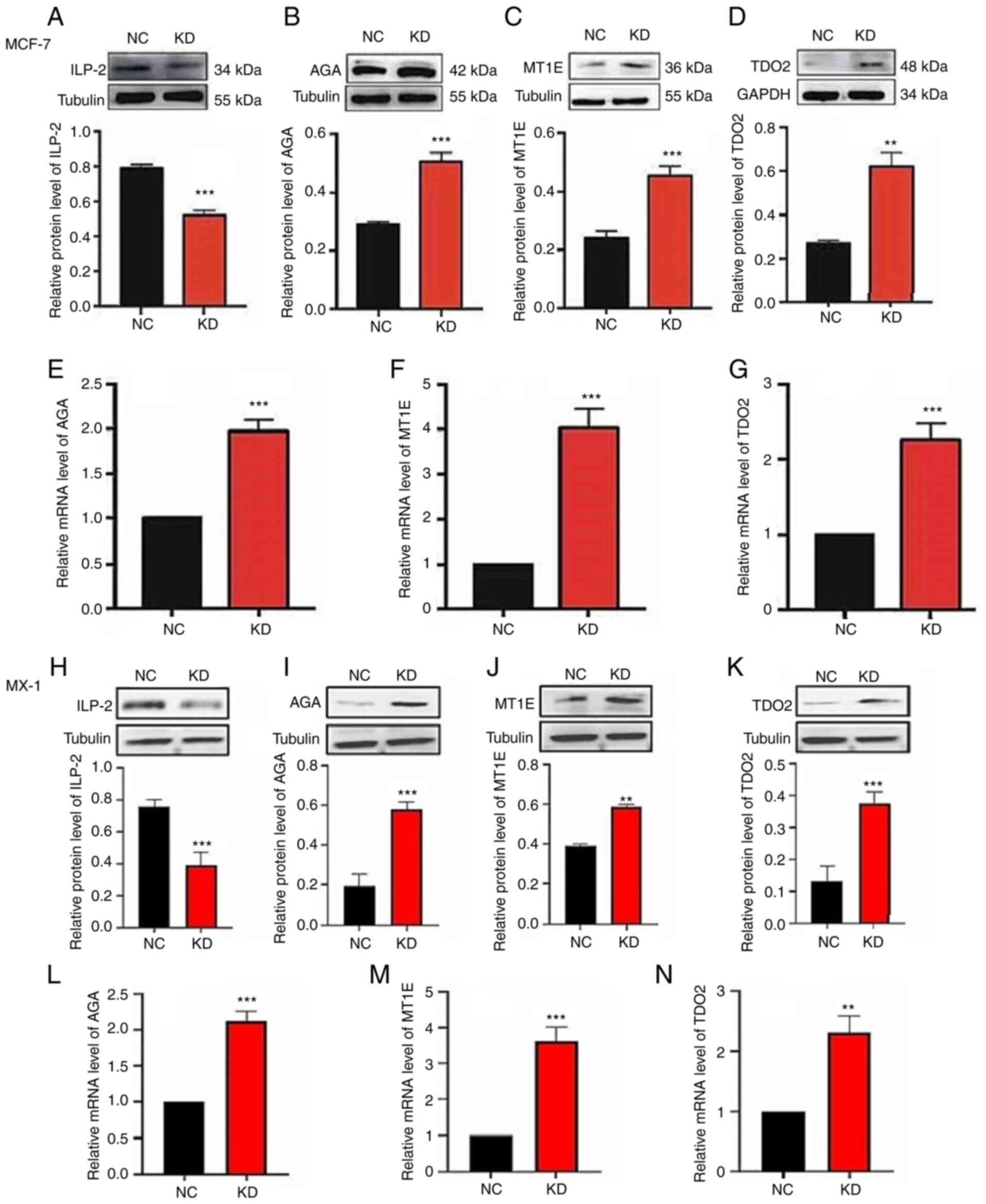
|
1
|
Kimball CC, Nichols CI and Vose JG: The
payer and patient cost burden of open breast conserving procedures
following percutaneous breast biopsy. Breast Cancer (Auckl).
12:11782234187777662018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Al-Darwish AA, Al-Naim AF, Al-Mulhim KS,
Al-Otaibi NK, Morsi MS and Aleem AM: Knowledge about cervical
cancer early warning signs and symptoms, risk factors and
vaccination among students at a medical school in Al-Ahsa, Kingdom
of Saudi Arabia. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:2529–2532. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thomas KH and Ramirez RA: Leptomeningeal
disease and the evolving role of molecular targeted therapy and
immunotherapy. Ochsner J. 17:362–378. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Costa RLB, Han HS and Gradishar WJ:
Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in triple-negative breast
cancer: A review. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 169:397–406. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Qing L and Qing W: Development of
epidermal growth factor receptor targeted therapy in pancreatic
cancer. Minerva Chir. 73:488–496. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu L, Zhou W, Zhu X, Xiang S, Wang S,
Peng Y, Lu B, Tang P, Chen Q, Wu M, et al: Inhibitor of apoptosis
protein-like protein-2: A novel growth accelerator for breast
cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 40:2047–2055. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xiang M, Zhou W, Gao D, Fang X and Liu Q:
Inhibitor of apoptosis protein-like protein-2 as a novel
serological biomarker for breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
13:16737–16750. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ouyang H, Wang Z, Chen X, Yu J, Li Z and
Nie Q: Proteomic analysis of chicken skeletal muscle during
embryonic development. Front Physiol. 8:2812017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Campos JM, Neves LX, de Paiva NC, de
Oliveira E Castro RA, Casé AH, Carneiro CM, Andrade MH and
Castro-Borges W: Understanding global changes of the liver proteome
during murine schistosomiasis using a label-free shotgun approach.
J Proteomics. 151:193–203. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu J, Liu Z, Chen L and Zhang H:
iTRAQ-based proteomic analysis reveals alterations in the liver
induced by restricted meal frequency in a pig model. Nutrition.
32:871–876. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Minjarez B, Calderón-González KG,
Rustarazo ML, Herrera-Aguirre ME, Labra-Barrios ML, Rincon-Limas
DE, Del Pino MM, Mena R and Luna-Arias JP: Identification of
proteins that are differentially expressed in brains with
Alzheimer's disease using iTRAQ labeling and tandem mass
spectrometry. J Proteomics. 139:103–121. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu YC, Ma WH, Ge YL, Xue ML, Zhang Z,
Zhang JY, Hou L and Mu RH: RNAi-mediated gene silencing of vascular
endothelial growth factor C suppresses growth and induces apoptosis
in mouse breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Lett.
12:3896–3904. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yan F, Wang X, Zhu M and Hu X:
RNAi-mediated downregulation of cyclin Y to attenuate human breast
cancer cell growth. Oncol Rep. 36:2793–2799. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang X, Li Y, Xu G, Liu M, Xue L, Liu L,
Hu S, Zhang Y, Nie Y, Liang S, et al: Mechanism study of peptide
GMBP1 and its receptor GRP78 in modulating gastric cancer MDR by
iTRAQ-based proteomic analysis. BMC Cancer. 15:3582015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu ZM, Zhu Q, Li HX, Geng Y, Shi JS and Xu
ZH: Vanillin promotes the germination of antrodia camphorata
arthroconidia through PKA and MAPK signaling pathways. Front
Microbiol. 8:20482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:(Database Issue). D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ju J, Zhu AJ and Yuan P: Progress in
targeted therapy for breast cancer. Chronic Dis Transl Med.
4:164–175. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jitariu AA, Raica M, Cîmpean AM and Suciu
SC: The role of PDGF-B/PDGFR-BETA axis in the normal development
and carcinogenesis of the breast. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
131:46–52. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zoi I, Karamouzis MV, Adamopoulos C and
Papavassiliou AG: RANKL signaling and ErbB receptors in breast
carcinogenesis. Trends Mol Med. 22:839–850. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jana S, Sengupta S, Biswas S, Chatterjee
A, Roy H and Bhattacharyya A: miR-216b suppresses breast cancer
growth and metastasis by targeting SDCBP. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 482:126–133. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Y, Zhou J, Wang Z, Wang P and Li S:
Upregulation of SOX2 activated LncRNA PVT1 expression promotes
breast cancer cell growth and invasion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
493:429–436. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Stricker TP, Brown CD, Bandlamudi C,
McNerney M, Kittler R, Montoya V, Peterson A, Grossman R and White
KP: Robust stratification of breast cancer subtypes using
differential patterns of transcript isoform expression. PLoS Genet.
13:e10065892017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shi Y, Yang F, Sun Z, Zhang W, Gu J and
Guan X: Differential microRNA expression is associated with
androgen receptor expression in breast cancer. Mol Med Rep.
15:29–36. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Finn RS, Dering J, Conklin D, Kalous O,
Cohen DJ, Desai AJ, Ginther C, Atefi M, Chen I, Fowst C, et al: PD
0332991, a selective cyclin D kinase 4/6 inhibitor, preferentially
inhibits proliferation of luminal estrogen receptor-positive human
breast cancer cell lines in vitro. Breast Cancer Res. 11:R772009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Stavik B, Skretting G, Olstad OK, Sletten
M, Dehli Vigeland M, Sandset PM and Iversen N: TFPI alpha and beta
regulate mRNAs and microRNAs involved in cancer biology and in the
immune system in breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 7:e47184. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vences-Catalán F, Duault C, Kuo CC,
Rajapaksa R, Levy R and Levy S: CD81 as a tumor target. Biochem Soc
Trans. 45:531–535. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gurel V, Sens DA, Somji S, Garrett SH,
Weiland T and Sens MA: Post-transcriptional regulation of
metallothionein isoform 1 and 2 expression in the human breast and
the MCF-10A cell line. Toxicol Sci. 85:906–915. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tai SK, Tan OJ, Chow VT, Jin R, Jones JL,
Tan PH, Jayasurya A and Bay BH: Differential expression of
metallothionein 1 and 2 isoforms in breast cancer lines with
different invasive potential: Identification of a novel nonsilent
metallothionein-1H mutant variant. Am J Pathol. 163:2009–2019.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Novikov O, Wang Z, Stanford EA, Parks AJ,
Ramirez-Cardenas A, Landesman E, Laklouk I, Sarita-Reyes C,
Gusenleitner D, Li A, et al: An Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated
amplification loop that enforces cell migration in
ER-/PR-/Her2-human breast cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol. 90:674–688.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
D'Amato NC, Rogers TJ, Gordon MA, Greene
LI, Cochrane DR, Spoelstra NS, Nemkov TG, D'Alessandro A, Hansen KC
and Richer JK: A TDO2-AhR signaling axis facilitates anoikis
resistance and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 75:4651–4664. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Saarela J, von Schantz C, Peltonen L and
Jalanko A: A novel aspartylglucosaminuria mutation affects
translocation of aspartylglucosaminidase. Hum Mutat. 24:350–351.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Saarela J, Oinonen C, Jalanko A, Rouvinen
J and Peltonen L: Autoproteolytic activation of human
aspartylglucosaminidase. Biochem J. 378:363–371. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|