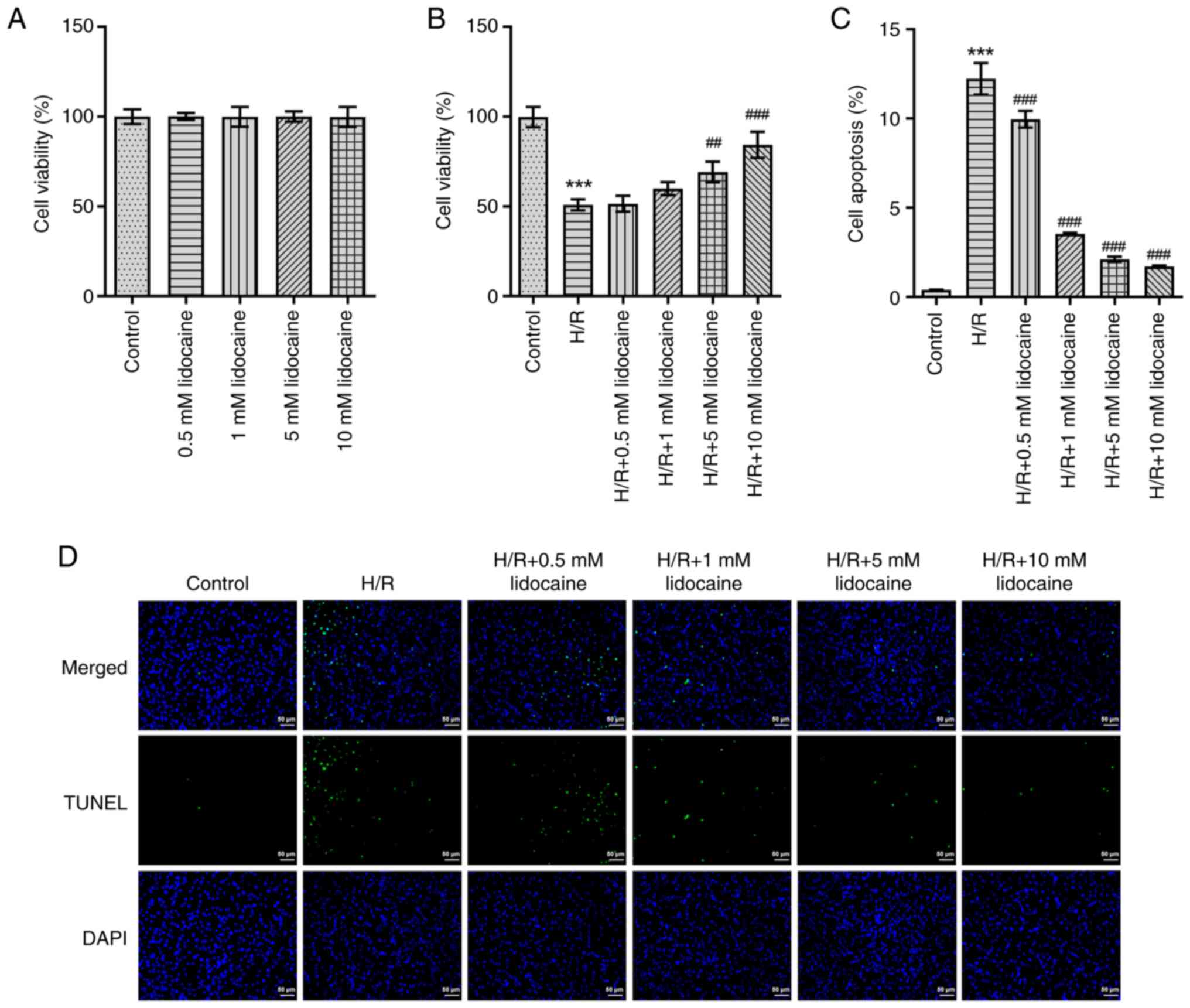
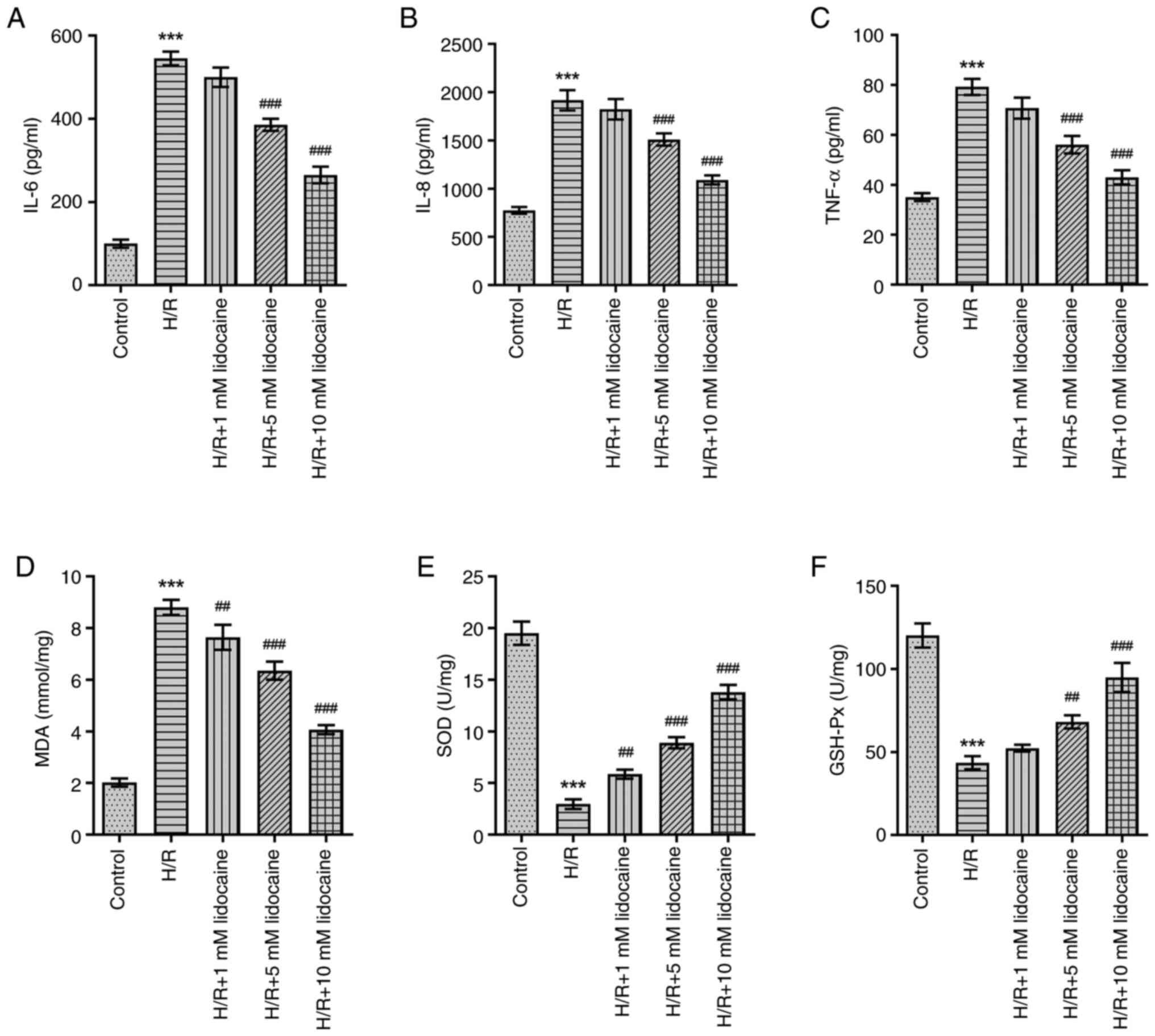
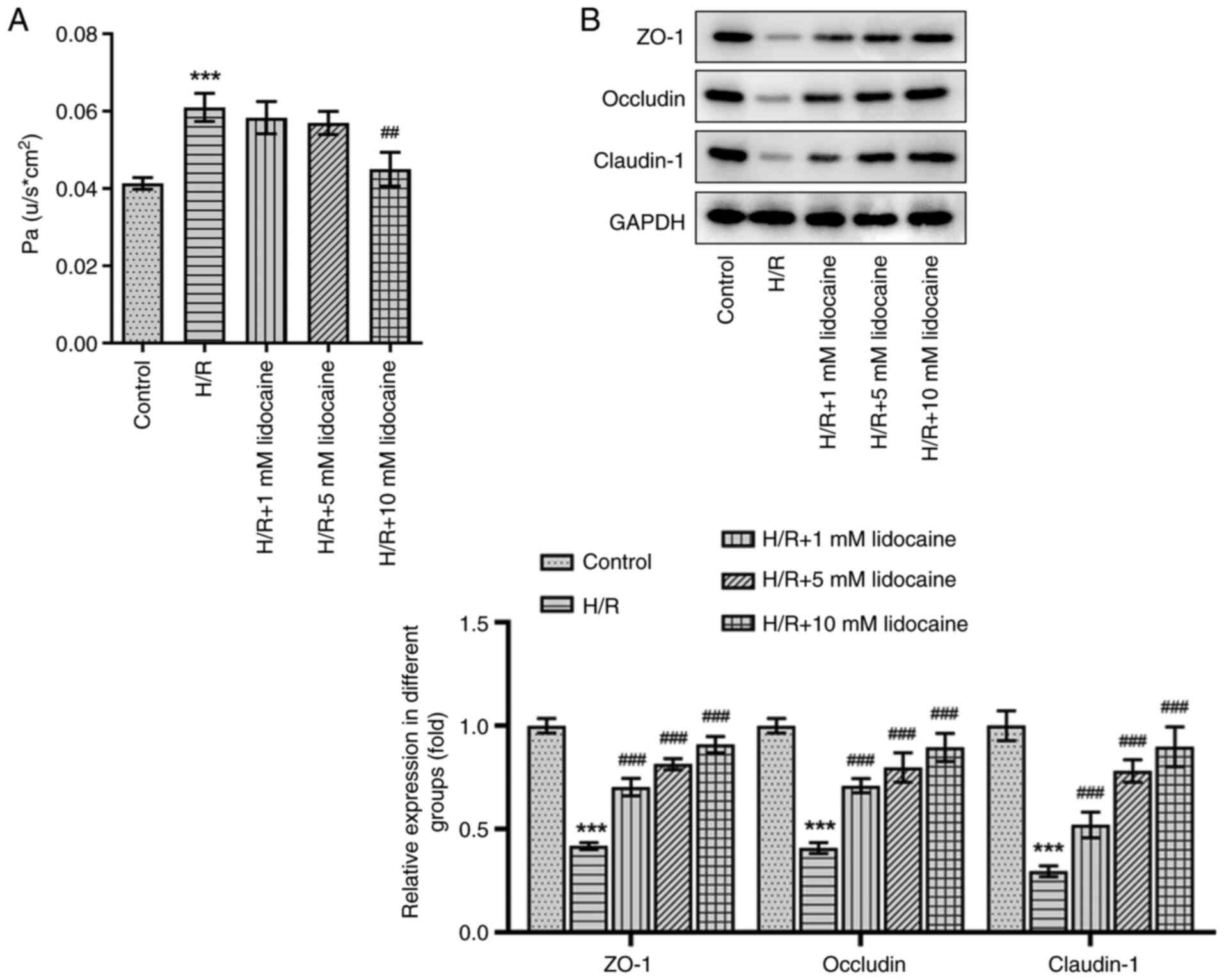
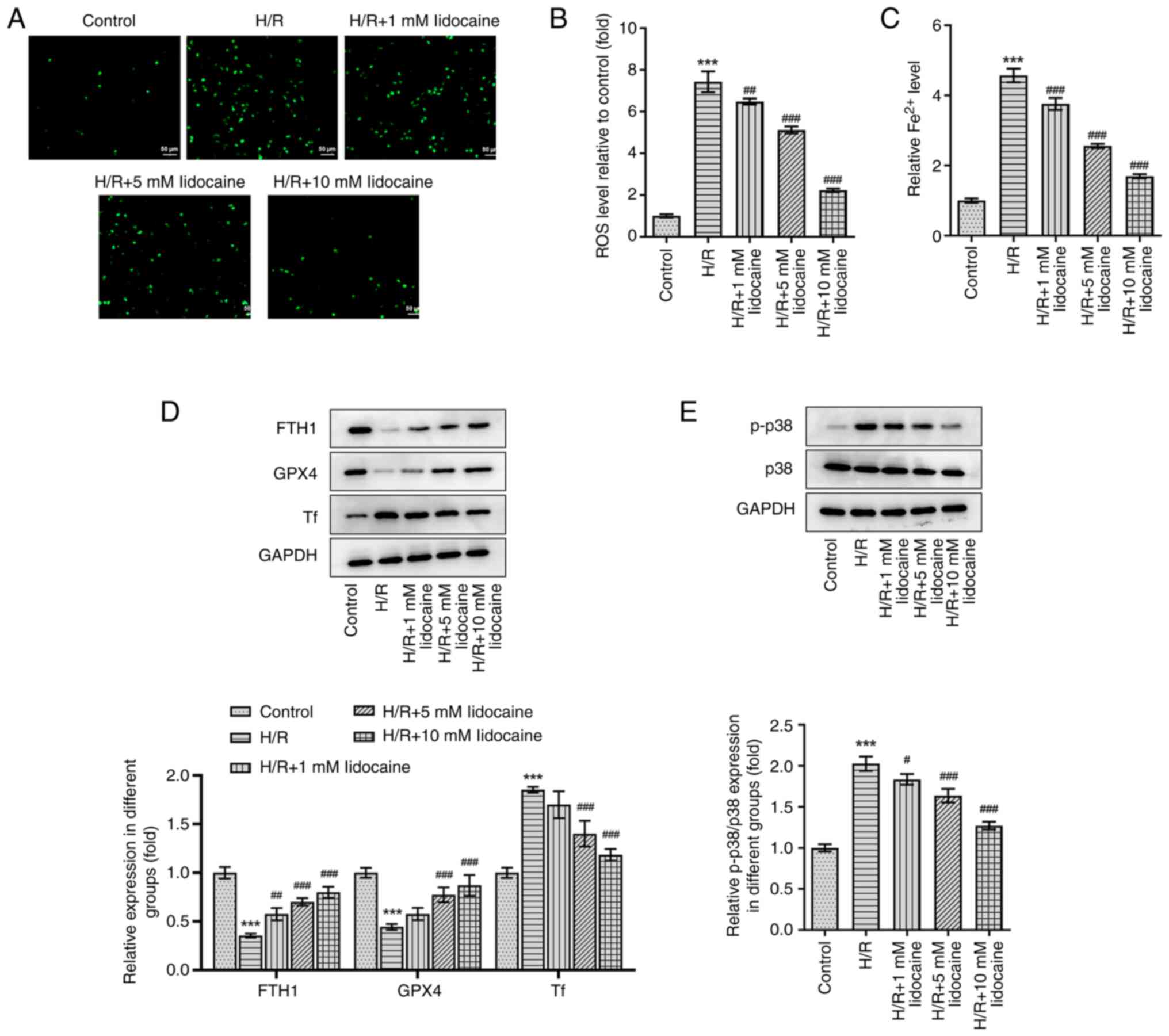
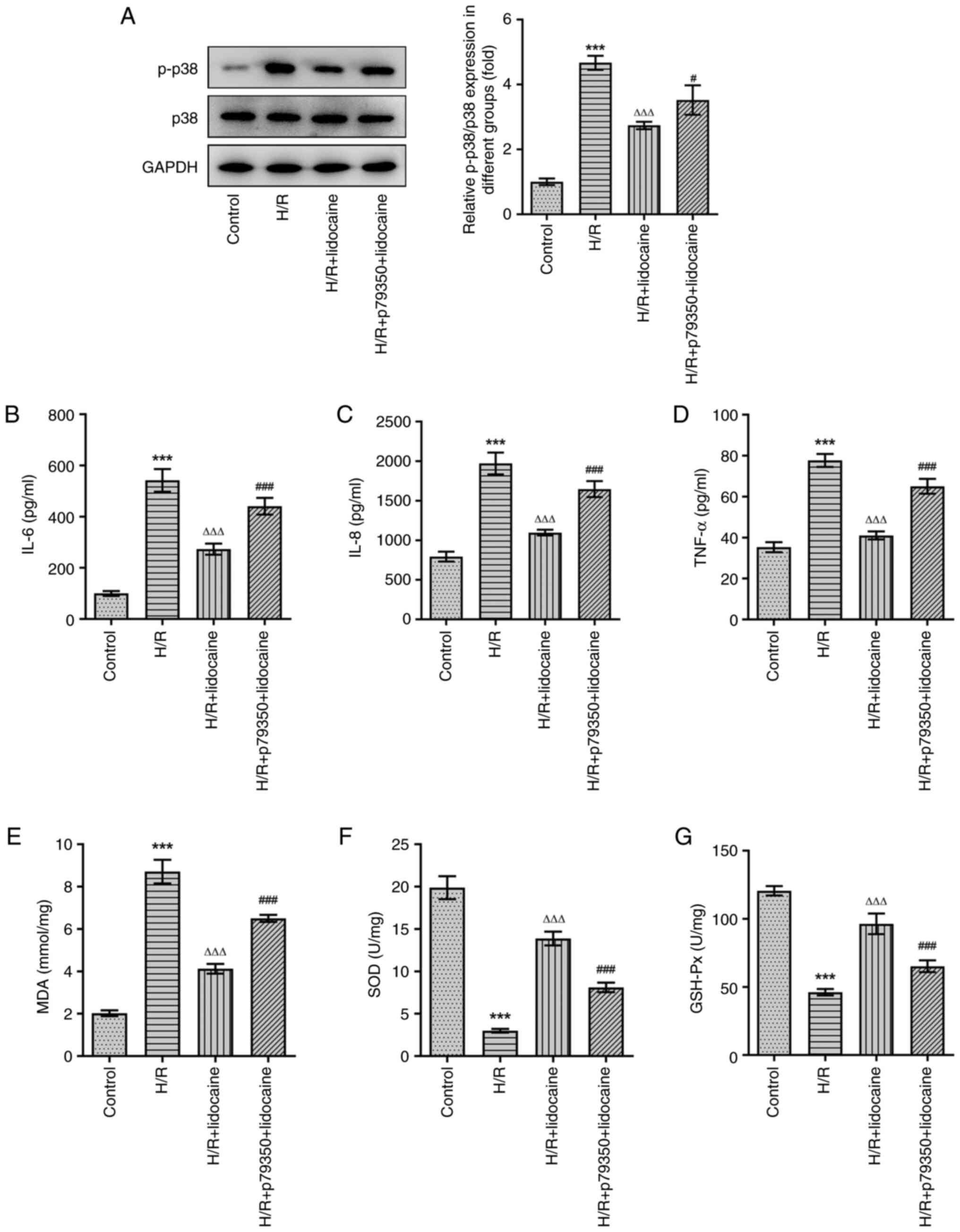
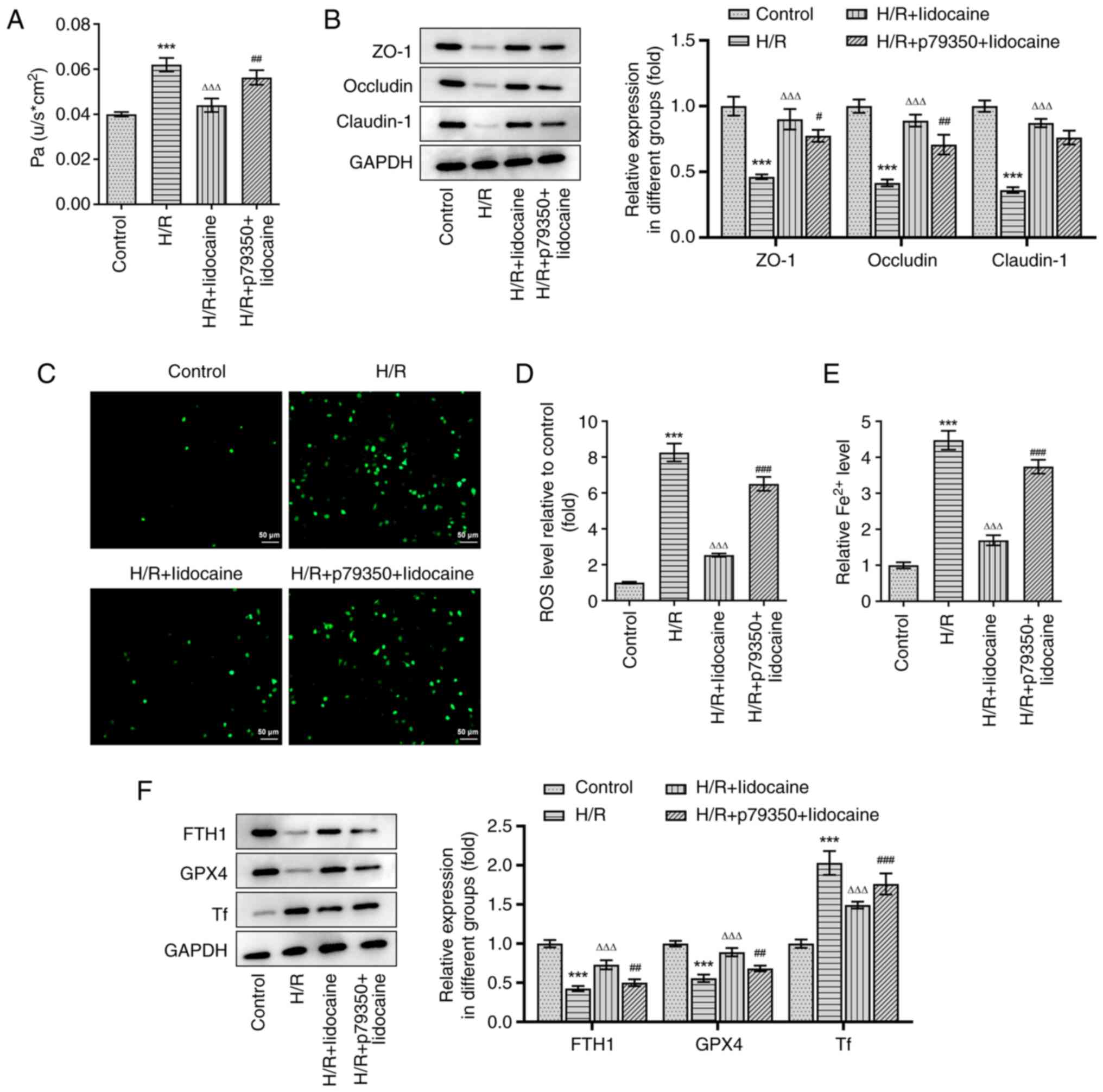
|
1
|
Sharma AK, Charles EJ, Zhao Y, Narahari
AK, Baderdinni PK, Good ME, Lorenz UM, Kron IL, Bayliss DA,
Ravichandran KS, et al: Pannexin-1 channels on endothelial cells
mediate vascular inflammation during lung ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 315:L301–L312. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Weyker PD, Webb CA, Kiamanesh D and Flynn
BC: Lung ischemia reperfusion injury: A bench-to-bedside review.
Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 17:28–43. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Diamond JM, Lee JC, Kawut SM, Shah RJ,
Localio AR, Bellamy SL, Lederer DJ, Cantu E, Kohl BA, Lama VN, et
al: Clinical risk factors for primary graft dysfunction after lung
transplantation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 187:527–534. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fei L, Jingyuan X, Fangte L, Huijun D, Liu
Y, Ren J, Jinyuan L and Linghui P: Preconditioning with rHMGB1
ameliorates lung ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting alveolar
macrophage pyroptosis via the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. J
Transl Med. 18:3012020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Laubach VE and Sharma AK: Mechanisms of
lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. Curr Opin Organ Transplant.
21:246–252. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cherobin AC and Tavares GT: Safety of
local anesthetics. An Bras Dermatol. 95:82–90. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Berk T and Silberstein SD: The use and
method of action of intravenous lidocaine and its metabolite in
headache disorders. Headache. 58:783–789. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lancaster RJ, Wren K, Hudson A, Leavitt K,
Albala M and Tischaefer D: Intravenous lidocaine for chronic
neuropathic pain a systematic review addressing nursing care. Pain
Manag Nurs. 21:194–200. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Canyon SJ and Dobson GP: Protection
against ventricular arrhythmias and cardiac death using adenosine
and lidocaine during regional ischemia in the in vivo rat. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 287:H1286–H1295. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen MY, Li CH, Huang ZQ, Liu JC, Zhou NX,
Huang XQ and Wang YS: Protective effects of lidocaine injected into
the hepatoduodenal ligament on warm inschemia-reperfusion injury to
the rat liver. Chin Med J (Engl). 117:275–279. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lei B, Cottrell JE and Kass IS:
Neuroprotective effect of low-dose lidocaine in a rat model of
transient focal cerebral ischemia. Anesthesiology. 95:445–451.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fang X, Wang H, Han D, Xie E, Yang X, Wei
J, Gu S, Gao F, Zhu N, Yin X, et al: Ferroptosis as a target for
protection against cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
116:2672–2680. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gao M, Monian P, Quadri N, Ramasamy R and
Jiang X: Glutaminolysis and transferrin regulate ferroptosis. Mol
Cell. 59:298–308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li N, Wang W, Zhou H, Wu Q, Duan M, Liu C,
Wu H, Deng W, Shen D and Tang Q: Ferritinophagy-mediated
ferroptosis is involved in sepsis-induced cardiac injury. Free
Radic Biol Med. 160:303–318. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun D, Li YC and Zhang XY: Lidocaine
promoted ferroptosis by targeting miR-382-5p /SLC7A11 axis in
ovarian and breast cancer. Front Pharmacol. 12:6812232021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yong HY, Koh MS and Moon A: The p38 MAPK
inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases and cancer.
Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 18:1893–1905. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee S, Rauch J and Kolch W: Targeting MAPK
signaling in cancer: Mechanisms of drug resistance and sensitivity.
Int J Mol Sci. 21:11022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sui XB, Kong N, Ye L, Han W, Zhou J, Zhang
Q, He C and Pan H: p38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of
apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents.
Cancer Lett. 344:174–179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang CH, Hao ZY, Zhou J, Zhang L, Sun Y
and Liang C: Rutae carpine alleviates renal ischemia reperfusion
injury in rats by suppressing the JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway
and interfering with the oxidative stress response. Mol Med Rep.
16:922–928. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
An ST, Wang X, Shi HR, Zhang X, Meng H, Li
W, Chen D and Ge J: Apelin protects against ischemia-reperfusion
injury in diabetic myocardium via in hibiting apoptosis and
oxidative stress through P38K and p38-MAPK signaling pathways.
Aging (Albany NY). 12:25120–25137. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Duarte S, Shen X-D, Fondevila C, Busuttil
RW and Coito AJ: Fibronectin-α4β1 interactions in hepatic cold
ischemia and reperfusion injury: Regulation of MMP-9 and MT1-MMP
via the p38 MAPK pathway. Am J Transplant. 12:2689–2699. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang R, Liao J, Yang MC, Deng J, Hu YX,
Li P and Li MT: Lidocaine mediates the progression of cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats via inhibiting the activation
of NF-kappaB p65 and p38 MAPK. Ann Transl Med. 8:5482020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen LJ, Ding YB, Ma PL, Jiang SH, Li KZ,
Li AZ, Li MC, Shi CX, Du J and Zhou HD: The protective effect of
lidocaine on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats
through NF-κB and p38 MAPK signaling pathway and excessive
inflammatory responses. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:2099–2108.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu SY, Li MH, Ko FC, Wu GC, Huang KL and
Chu SJ: Protective effect of hypercapnic acidosis in
ischemia-reperfusion lung injury is attributable to upregulation of
heme oxygenase-1. PLoS One. 8:e747422013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li M, Wang X, Lu S, He C, Wang C, Wang L,
Wang X, Ge P and Song D: Erastin triggers autophagic death of
breast cancer cells by increasing intracellular iron levels. Oncol
Lett. 20:572020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Beckers PAJ, Gielis JF, Van Schil PE and
Adriaensen D: Lung ischemia reperfusion injury: The therapeutic
role of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibition. Ann Transl Med.
5:1292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kalogeris T, Baines CP, Krenz M and
Korthuis RJ: Cell biology of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int Rev
Cell Mol Biol. 298:229–317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Saito M, Chen-Yoshikawa TF, Suetsugu K,
Okabe R, Takahagi A, Masuda S and Date H: Pirfenidone alleviates
lung ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model. J Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 158:289–296. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ebel D, Lipfert P, Frassdorf J, Preckel B,
Müllenheim J, Thämer V and Schlack W: Lidocaine reduces ischaemic
but not reperfusion injury in isolated rat heart. Br J Anaesth.
86:846–852. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lei B, Popp S, Capuano-Waters C, Cottrell
JE and Kass IS: Effects of delayed administration of low-dose
lidocaine on transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats.
Anesthesiology. 97:1534–1540. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lan XY and Xu YM: Protective role of
lidocaine against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury: An in
vitro study. Exp Ther Med. 23:422022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu LW, Xu YF, Zhou YC, Li S and Yao J:
Regionally infused lidocaine can dose-dependently protect the
ischemic spinal cord in rabbits and may be associated with the EAA
changes. Neurosci Lett. 725:1348892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Aldakkak M, Stowe DF, Lesnefsky EJ,
Heisner JS, Chen Q and Camara AKS: Modulation of mitochondrial
bioenergetics in isolated guinea pig beating heart by potassium and
lidocaine cardioplegia: Implications for cardioprotection. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 54:298–309. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kaczmarek DJ, Herzog C, Larmann J,
Gillmann HJ, Hildebrand R, Schmitz M, Westermann A, Harendza T,
Werdehausen R, Osthaus AW, et al: Lidocaine protects from
myocardial damage due to ischemia and reperfusion in mice by its
antiapoptotic effects. Anesthesiology. 110:1041–1049. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu Y, Zhang J, Zan J, Zhang F, Liu G and
Wu A: Lidocaine improves cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in
rats through cAMP/PKA signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 20:495–499.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chang YC, Hsu YC, Liu CL, Huang SY, Hu MC
and Cheng SP: Local anesthetics induce apoptosis in human thyroid
cancer cells through the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.
PLoS One. 9:e895632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhu J and Han S: Lidocaine inhibits
cervical cancer cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis by
modulating the lncRNA-MEG3/miR-421/BTG1 pathway. Am J Transl Res.
11:5404–5416. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen Z, Chen Y, Zhou J, Li Y, Gong C and
Wang X: Netrin-1 reduces lung ischemia-reperfusion injury by
increasing the proportion of regulatory T cells. J Int Med Res.
48:3000605209264152020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lan CC, Peng CK, Tang SE, Huang KL and Wu
CP: Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor attenuates ischemia-reperfusion
induced acute lung injury. PLoS One. 12:e01798222017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
De Perrot M, Liu M, Waddell TK and
Keshavjee S: Ischemia-reperfusion-induced lung injury. Am J Respir
Crit Care Med. 167:490–511. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
De Perrot M, Sekine Y, Fischer S, Waddell
TK, McRae K, Liu M, Wigle DA and Keshavjee S: Interleukin-8 release
during early reperfusion predicts graft function in human lung
transplantation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 165:211–215. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ng CS, Wan S, Arifi AA and Yim AP:
Inflammatory response to pulmonary ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Surg Today. 36:205–214. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang F, Wang F, Li F, Wang D, Li H, He X
and Zhang J: Methane attenuates lung ischemia-reperfusion injury
via regulating PI3K-AKT-NFκB signaling pathway. J Recept Signal
Transduct Res. 40:209–217. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jiang F, Zhang Y and Dusting GJ: NADPH
oxidase-mediated redox signaling: Roles in cellular stress
response, stress tolerance, and tissue repair. Pharmacol Rev.
63:218–242. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xu Y, Li X, Cheng Y, Yang M and Wang R:
Inhibition of ACSL4 attenuates ferroptotic damage after pulmonary
ischemia-reperfusion. FASEB J. 34:16262–16275. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Friedmann Angeli JP, Schneider M, Proneth
B, Tyurina YY, Tyurin VA, Hammond VJ, Herbach N, Aichler M, Walch
A, Eggenhofer E, et al: Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator
Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol.
16:1180–1191. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Matsushita M, Freigang S, Schneider C,
Conrad M, Bornkamm GW and Kopf M: T cell lipid peroxidation induces
ferroptosis and prevents immunity to infection. J Exp Med.
212:555–568. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mayr L, Grabherr F, Schwärzler J,
Reitmeier I, Sommer F, Gehmacher T, Niederreiter L, He GW, Ruder B,
Kunz KTR, et al: Dietary lipids fuel GPX4-restricted enteritis
resembling Crohn's disease. Nat Commun. 11:17752020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Muller T, Dewitz C, Schmitz J, Schröder
AS, Bräsen JH, Stockwell BR, Murphy JM, Kunzendorf U and Krautwald
S: Necroptosis and ferroptosis are alternative cell death pathways
that operate in acute kidney failure. Cell Mol Life Sci.
74:3631–3645. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li Y, Feng D, Wang Z, Zhao Y, Sun R, Tian
D, Liu D, Zhang F, Ning S, Yao J and Tian X: Ischemia-induced ACSL4
activation contributes to ferroptosis-mediated tissue injury in
intestinal ischemia/reperfusion. Cell Death Differ. 26:2284–2299.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yang ZH, Lu YJ, Gu KP, Xiang ZY and Huang
HM: Effect of ulinastatin on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
through JNK and P38 MAPK signaling pathways. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 23:8658–8664. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|