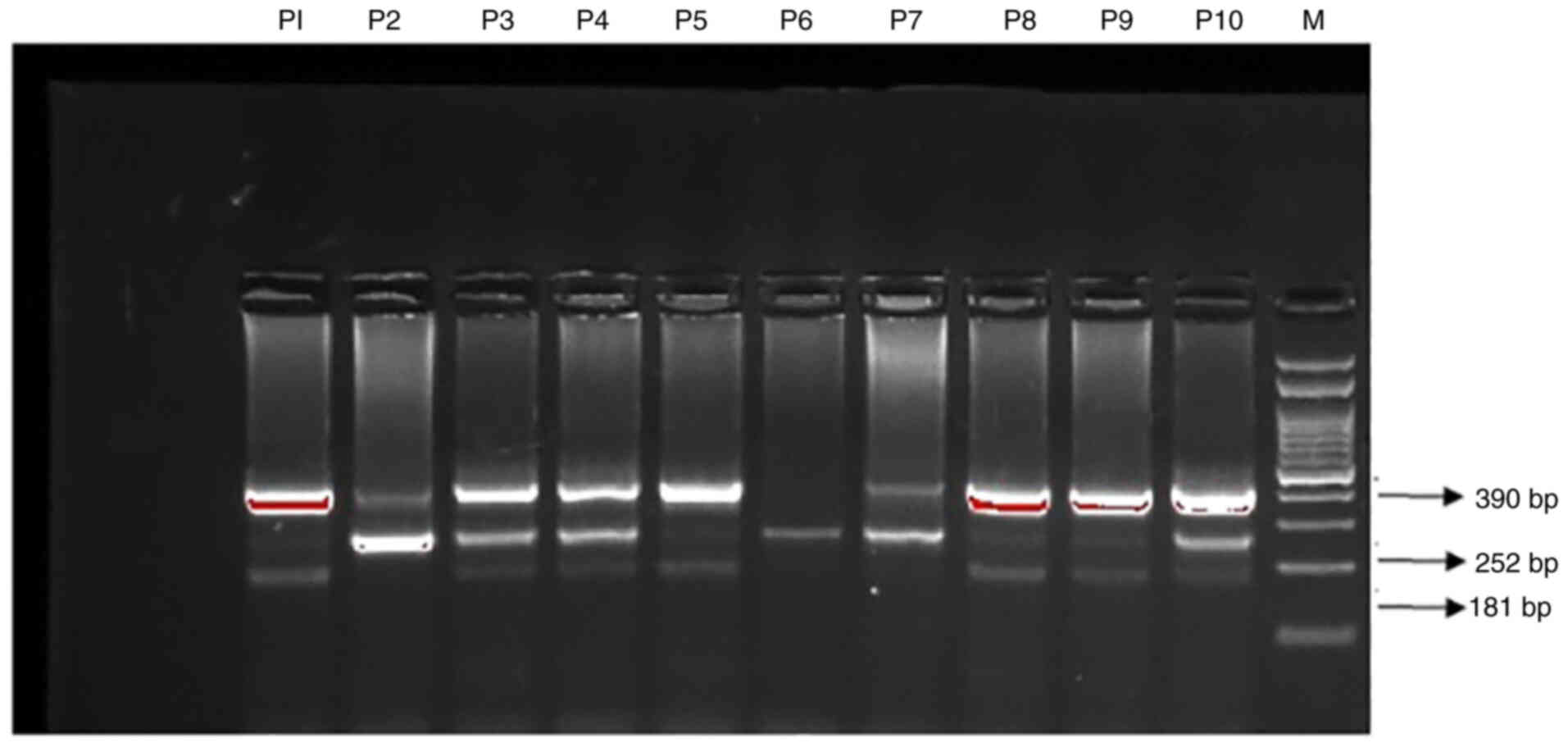
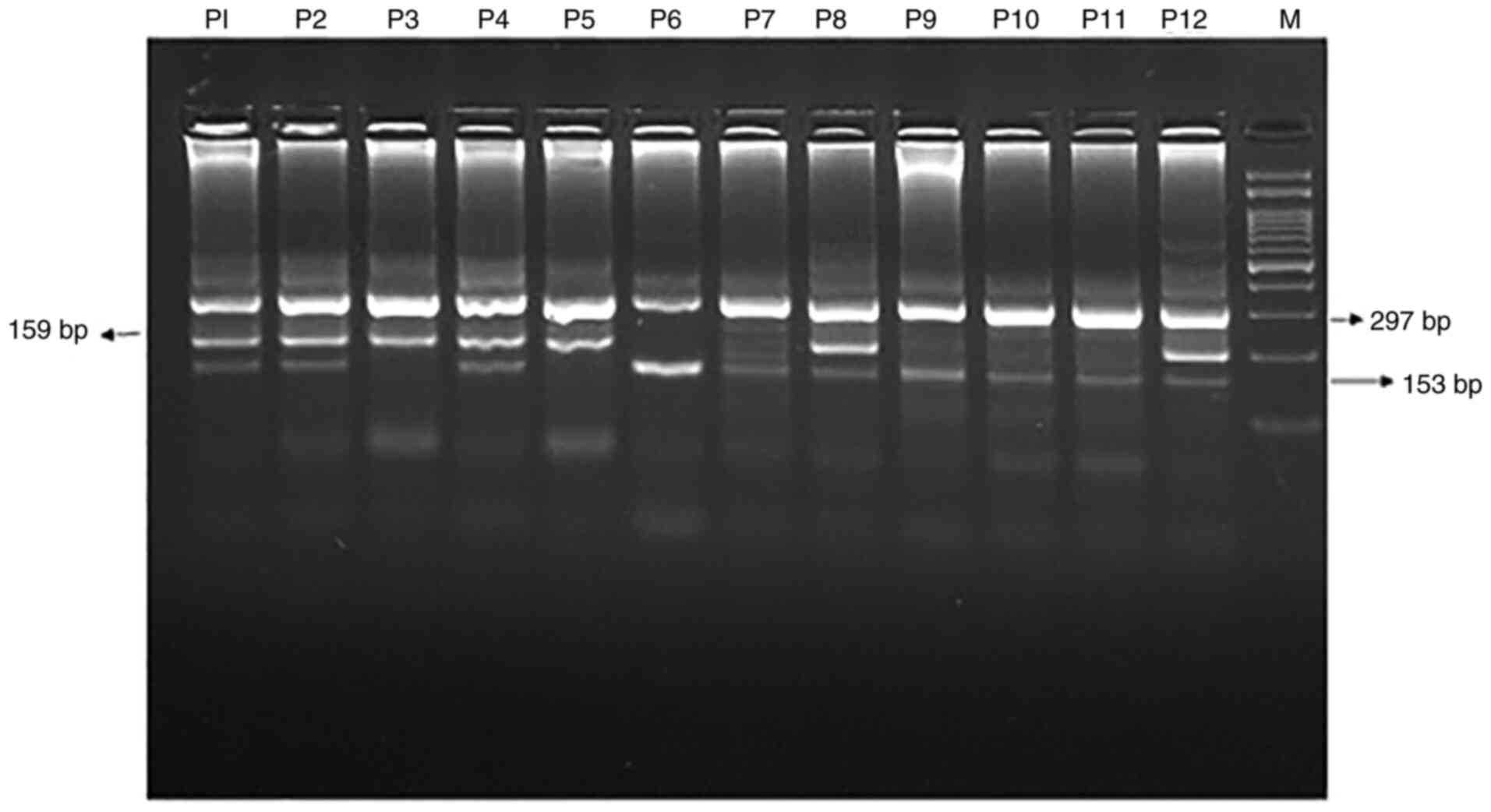
|
1
|
Al Mansour MA: The prevalence and risk
factors of type 2 diabetes mellitus (DMT2) in a semi-urban Saudi
population. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 17:72019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gaál Z and Balogh I: Monogenic forms of
diabetes mellitus. Exp Suppl. 111:385–416. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Moin ASM and Butler AE: Alterations in
beta cell identity in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep.
19:832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Forbes JM and Cooper ME: Mechanisms of
diabetic complications. Physiol Rev. 93:137–188. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sacks DB and McDonald JM: The pathogenesis
of type II diabetes mellitus. A polygenic disease. Am J Clin
Pathol. 105:149–156. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
De Backer I, Hussain SS, Bloom SR and
Gardiner JV: Insights into the role of neuronal glucokinase. Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 311:E42–E55. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Iynedjian PB: Molecular physiology of
mammalian glucokinase. Cell Mol Life Sci. 66:27–42. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Toulis KA, Nirantharakumar K, Pourzitaki
C, Barnett AH and Tahrani AA: Glucokinase activators for type 2
diabetes: Challenges and future developments. Drugs. 80:467–475.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Osbak KK, Colclough K, Saint-Martin C,
Beer NL, Bellanné-Chantelot C, Ellard S and Gloyn AL: Update on
mutations in glucokinase (GCK), which cause maturity-onset diabetes
of the young, permanent neonatal diabetes, and hyperinsulinemic
hypoglycemia. Hum Mutat. 30:1512–1526. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
FendLer W, Rizzo M, Borowiec M,
Malachowska B, Antosik K, Szadkowska A, Banach M, Urbanska-Kosinska
M, Szopa M, Malecki M and Mlynarski W: Less but better:
Cardioprotective lipid profile of patients with GCK-MODY despite
lower HDL cholesterol level. Acta Diabetol. 51:625–632. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Spyer G, Macleod KM, Shepherd M, Ellard S
and Hattersley AT: Pregnancy outcome in patients with raised blood
glucose due to a heterozygous glucokinase gene mutation. Diabet
Med. 26:14–18. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Njølstad PR, Søvik O, Cuesta-Muñoz A,
Bjørkhaug L, Massa O, Barbetti F, Undlien DE, Shiota C, Magnuson
MA, Molven A, et al: Neonatal diabetes mellitus due to complete
glucokinase deficiency. N Engl J Med. 344:1588–1592. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fu D, Cong X, Ma Y, Cai H, Cai M, Li D, Lv
M, Yuan X, Huang Y and Lv Z: Genetic polymorphism of glucokinase on
the risk of type 2 diabetes and impaired glucose regulation:
Evidence based on 298,468 subjects. PLoS One. 8:e557272013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Murad AS, Smith GD, Lewis SJ, Cox A,
Donovan JL, Neal DE, Hamdy FC and Martin RM: A polymorphism in the
glucokinase gene that raises plasma fasting glucose, rs1799884, is
associated with diabetes mellitus and prostate cancer: Findings
from a population-based, case-control study (the ProtecT study).
Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet. 1:175–183. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li C, Yang Y, Liu X, Li Z, Liu H and Tan
Q: Glucose metabolism-related gene polymorphisms as the risk
predictors of type 2 diabetes. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 12:972020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Muller YL, Piaggi P, Hoffman D, Huang K,
Gene B, Kobes S, Thearle MS, Knowler WC, Hanson RL, Baier LJ and
Bogardus C: Common genetic variation in the glucokinase gene (GCK)
is associated with type 2 diabetes and rates of carbohydrate
oxidation and energy expenditure. Diabetologia. 57:1382–1390. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Reiling E, van 't Riet E, Groenewoud MJ,
Welschen LM, van Hove EC, Nijpels G, Maassen JA, Dekker JM and 't
Hart LM: Combined effects of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in
GCK, GCKR, G6PC2 and MTNR1B on fasting plasma glucose and type 2
diabetes risk. Diabetologia. 52:1866–1870. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cauchi S, Nead KT, Choquet H, Horber F,
Potoczna N, Balkau B, Marre M, Charpentier G, Froguel P and Meyre
D: The genetic susceptibility to type 2 diabetes may be modulated
by obesity status: Implications for association studies. BMC Med
Genet. 9:452008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cauchi S, Ezzidi I, El Achhab Y, Mtiraoui
N, Chaieb L, Salah D, Nejjari C, Labrune Y, Yengo L, Beury D, et
al: European genetic variants associated with type 2 diabetes in
North African Arabs. Diabetes Metab. 38:316–323. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cirillo F, Catellani C, Lazzeroni P,
Sartori C and Street ME: The role of MicroRNAs in influencing body
growth and development. Horm Res Paediatr. 93:7–15. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tan W, Liu B, Qu S, Liang G, Luo W and
Gong C: MicroRNAs and cancer: Key paradigms in molecular therapy.
Oncol Lett. 15:2735–2742. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Raue R, Frank AC, Syed SN and Brüne B:
Therapeutic targeting of MicroRNAs in the tumor microenvironment.
Int J Mol Sci. 22:22102021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fridrichova I and Zmetakova I: MicroRNAs
contribute to breast cancer invasiveness. Cells. 8:13612019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ashrafizadeh M, Ang HL, Moghadam ER,
Mohammadi S, Zarrin V, Hushmandi K, Samarghandian S, Zarrabi A,
Najafi M, Mohammadinejad R and Kumar AP: MicroRNAs and their
influence on the ZEB family: Mechanistic aspects and therapeutic
applications in cancer therapy. Biomolecules. 10:10402020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mir R, Elfaki I, Khullar N, Waza AA, Jha
C, Mir MM, Nisa S, Mohammad B, Mir TA, Maqbool M, et al: Role of
selected miRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in
cardiovascular diseases, including coronary artery disease,
myocardial infarction and atherosclerosis. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis.
8:222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Elfaki I, Mir R, Duhier FMA, Alotaibi MA,
Alalawy AI, Barnawi J, Babakr AT, Mir MM, Altayeb F, Mirghani H and
Frah EAM: Clinical implications of MiR128, angiotensin I converting
enzyme and vascular endothelial growth factor gene abnormalities
and their association with T2D. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 43:1859–1875.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ibrahim AA, Ramadan A, Wahby AA, Hassan M,
Soliman HM and Abdel Hamid TA: Micro-RNA 196a2 expression and
miR-196a2 (rs11614913) polymorphism in T1DM: A pilot study. J
Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 32:1171–1179. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhuang GQ and Wang YX: A tiny RNA molecule
with a big impact on type 2 diabetes mellitus susceptibility.
Biomed Environ Sci. 30:855–861. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Blum A, Meerson A, Rohana H, Jabaly H,
Nahul N, Celesh D, Romanenko O and Tamir S: MicroRNA-423 may
regulate diabetic vasculopathy. Clin Exp Med. 19:469–477. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang W, Wang J, Chen Z, Chen J, Meng Y,
Chen L, Chang Y, Geng B, Sun L, Dou L, et al: NFE2 induces
miR-423-5p to promote gluconeogenesis and hyperglycemia by
repressing the hepatic FAM3A-ATP-Akt pathway. Diabetes.
66:1819–1832. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Delvaux N, da Costa VD, da Costa MM and
Lampe E: Comparison of four methods of genotyping IL28B
polymorphisms in chronic hepatitis C patients. J Virol Methods.
220:1–4. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jha CK, Mir R, Elfaki I, Khullar N, Rehman
S, Javid J, Banu S and Chahal SMS: Potential impact of MicroRNA-423
gene variability in coronary artery disease. Endocr Metab Immune
Disord Drug Targets. 19:67–74. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rahim A, Afzal M and Naveed AK: Genetic
polymorphism of miRNA-196a and its target gene annexin-A1
expression based on ethnicity in Pakistani female breast cancer
patients. Pak J Med Sci. 35:1598–1604. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hudish LI, Reusch JE and Sussel L: β Cell
dysfunction during progression of metabolic syndrome to type 2
diabetes. J Clin Invest. 129:4001–4008. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Matschinsky FM and Wilson DF: The central
role of glucokinase in glucose homeostasis: A perspective 50 years
after demonstrating the presence of the enzyme in islets of
langerhans. Front Physiol. 10:1482019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tam CH, Ho JS, Wang Y, Lee HM, Lam VK,
Germer S, Martin M, So WY, Ma RC, Chan JC and Ng MC: Common
polymorphisms in MTNR1B, G6PC2 and GCK are associated with
increased fasting plasma glucose and impaired beta-cell function in
Chinese subjects. PLoS One. 5:e114282010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Weedon MN, Clark VJ, Qian Y, Ben-Shlomo Y,
Timpson N, Ebrahim S, Lawlor DA, Pembrey ME, Ring S, Wilkin TJ, et
al: A common haplotype of the glucokinase gene alters fasting
glucose and birth weight: Association in six studies and
population-genetics analyses. Am J Hum Genet. 79:991–1001. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tremblay J and Hamet P: Biomarkers of
vascular complications in type 2 diabetes. Metabolism. 64 (3 Suppl
1):S28–S32. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Qi Q, Wu Y, Li H, Loos RJ, Hu FB, Sun L,
Lu L, Pan A, Liu C, Wu H, et al: Association of GCKR rs780094,
alone or in combination with GCK rs1799884, with type 2 diabetes
and related traits in a Han Chinese population. Diabetologia.
52:834–843. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
März W, Nauck M, Hoffmann MM, Nagel D,
Boehm BO, Koenig W, Rothenbacher D and Winkelmann BR: G(−30)A
polymorphism in the pancreatic promoter of the glucokinase gene
associated with angiographic coronary artery disease and type 2
diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 109:2844–2849. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ormazabal V, Nair S, Elfeky O, Aguayo C,
Salomon C and Zuñiga FA: Association between insulin resistance and
the development of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
17:1222018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Khan MS, Rahman B, Haq TU, Jalil F, Khan
BM, Maodaa SN, Al-Farraj SA, El-Serehy HA and Shah AA: Deciphering
the variants located in the MIR196A2, MIR146A, and MIR423 with
type-2 diabetes mellitus in Pakistani population. Genes (Basel).
12:6642021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hoffman AE, Zheng T, Yi C, Leaderer D,
Weidhaas J, Slack F, Zhang Y, Paranjape T and Zhu Y: microRNA
miR-196a-2 and breast cancer: A genetic and epigenetic association
study and functional analysis. Cancer Res. 69:5970–5977. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ghanbari M, Sedaghat S, de Looper HW,
Hofman A, Erkeland SJ, Franco OH and Dehghan A: The association of
common polymorphisms in miR-196a2 with waist to hip ratio and
miR-1908 with serum lipid and glucose. Obesity (Silver Spring).
23:495–503. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dastani Z, Hivert MF, Timpson N, Perry
JRB, Yuan X, Scott RA, Henneman P, Heid IM, Kizer JR, Lyytikäinen
LP, et al: Novel loci for adiponectin levels and their influence on
type 2 diabetes and metabolic traits: A multi-ethnic meta-analysis
of 45,891 individuals. PLoS Genet. 8:e10026072012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wondmkun YT: Obesity, insulin resistance,
and type 2 diabetes: Associations and therapeutic implications.
Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 13:3611–3616. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hu Z, Chen J, Tian T, Zhou X, Gu H, Xu L,
Zeng Y, Miao R, Jin G, Ma H, et al: Genetic variants of miRNA
sequences and non-small cell lung cancer survival. J Clin Invest.
118:2600–2608. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu CJ, Tsai MM, Hung PS, Kao SY, Liu TY,
Wu KJ, Chiou SH, Lin SC and Chang KW: miR-31 ablates expression of
the HIF regulatory factor FIH to activate the HIF pathway in head
and neck carcinoma. Cancer Res. 70:1635–1644. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fragoso JM, Ramírez-Bello J, Martínez-Ríos
MA, Peña-Duque MA, Posadas-Sánchez R, Delgadillo-Rodríguez H,
Jiménez-Morales M, Posadas-Romero C and Vargas-Alarcón G: miR-196a2
(rs11614913) polymorphism is associated with coronary artery
disease, but not with in-stent coronary restenosis. Inflamm Res.
68:215–221. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sung JH, Kim SH, Yang WI, Kim WJ, Moon JY,
Kim IJ, Cha DH, Cho SY, Kim JO, Kim KA, et al: miRNA polymorphisms
(miR-146a, miR-149, miR-196a2 and miR-499) are associated with the
risk of coronary artery disease. Mol Med Rep. 14:2328–2342. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Agiannitopoulos K, Samara P, Papadopoulou
M, Efthymiadou A, Papadopoulou E, Tsaousis GN, Mertzanos G, Babalis
D and Lamnissou K: miRNA polymorphisms and risk of premature
coronary artery disease. Hellenic J Cardiol. 62:278–284. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Buraczynska M, Zukowski P, Wacinski P,
Ksiazek K and Zaluska W: Polymorphism in microRNA-196a2 contributes
to the risk of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes patients.
J Diabetes Complications. 28:617–620. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yuan S, Carter P, Bruzelius M, Vithayathil
M, Kar S, Mason AM, Lin A, Burgess S and Larsson SC: Effects of
tumour necrosis factor on cardiovascular disease and cancer: A
two-sample Mendelian randomization study. EBioMedicine.
59:1029562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Tian J, An X and Niu L: Role of microRNAs
in cardiac development and disease. Exp Ther Med. 13:3–8. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Li XY, Chen K and Lv ZT: APRISMA-compliant
systematic review and meta-analysis determining the association of
miRNA polymorphisms and risk of congenital heart disease. Medicine
(Baltimore). 98:e176532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ding Y, Sun X and Shan PF: MicroRNAs and
cardiovascular disease in diabetes mellitus. Biomed Res Int.
2017:40803642017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Tijsen AJ, Creemers EE, Moerland PD, de
Windt LJ, van der Wal AC, Kok WE and Pinto YM: MiR423-5p as a
circulating biomarker for heart failure. Circ Res. 106:1035–1039.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Jin C, Li Z, Zheng X, Shen K, Chao J, Dong
Y, Huang Q, Yin Q, Deng Y and Zhu W: Development and validation of
T-ARMS-PCR to detect CYP2C19*17 allele. J Clin Lab Anal.
34:e230052020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|