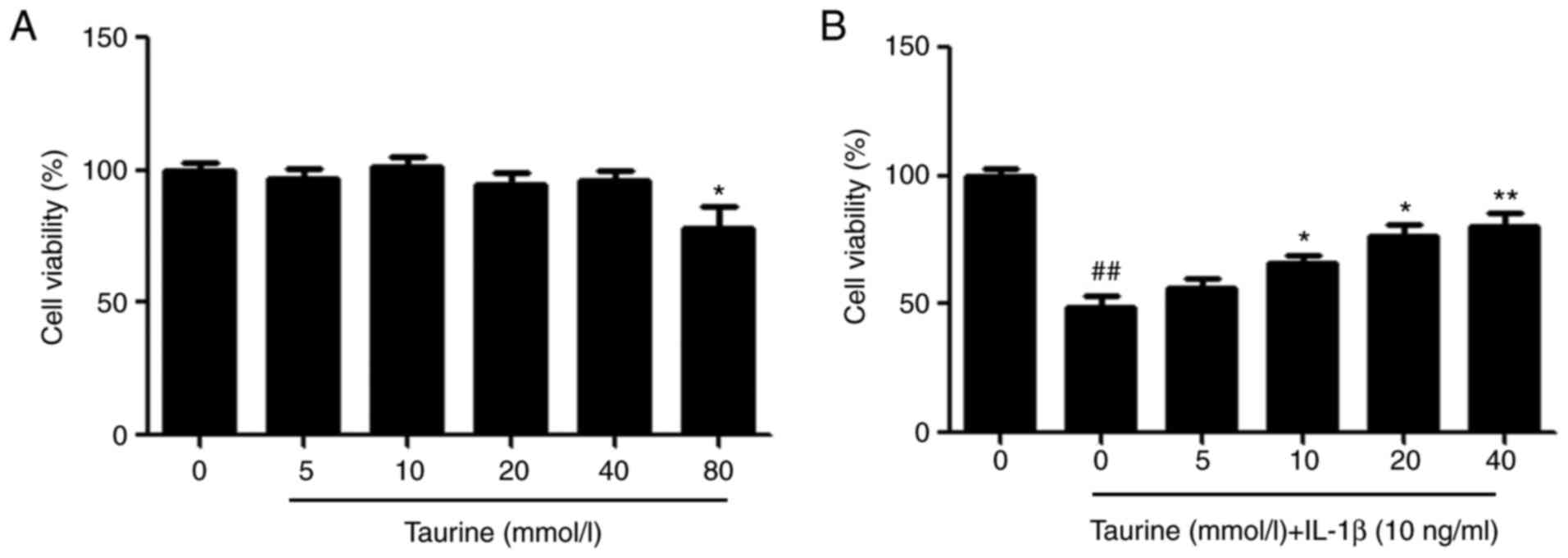
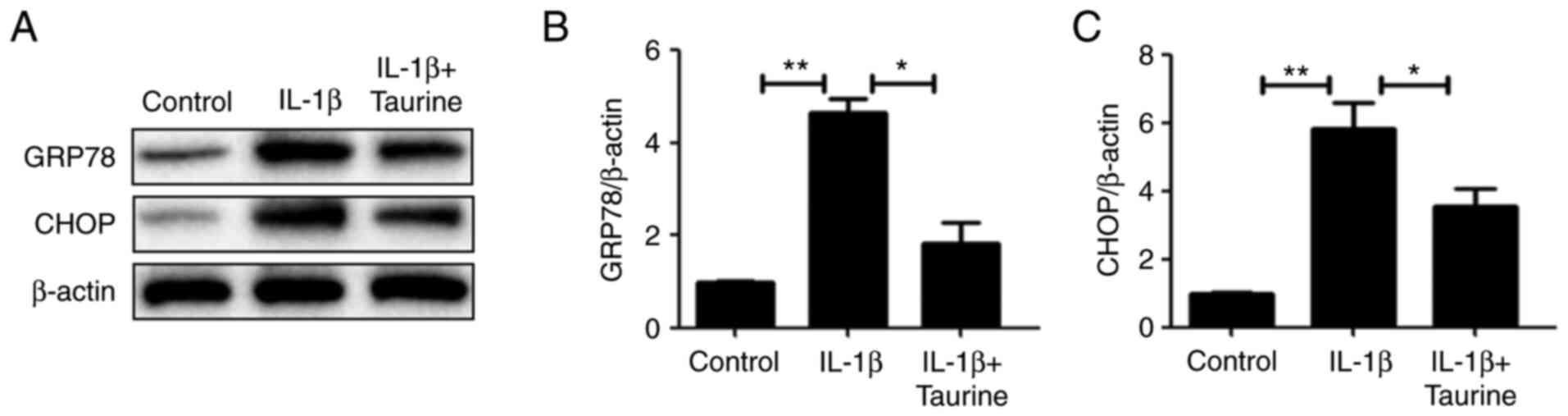
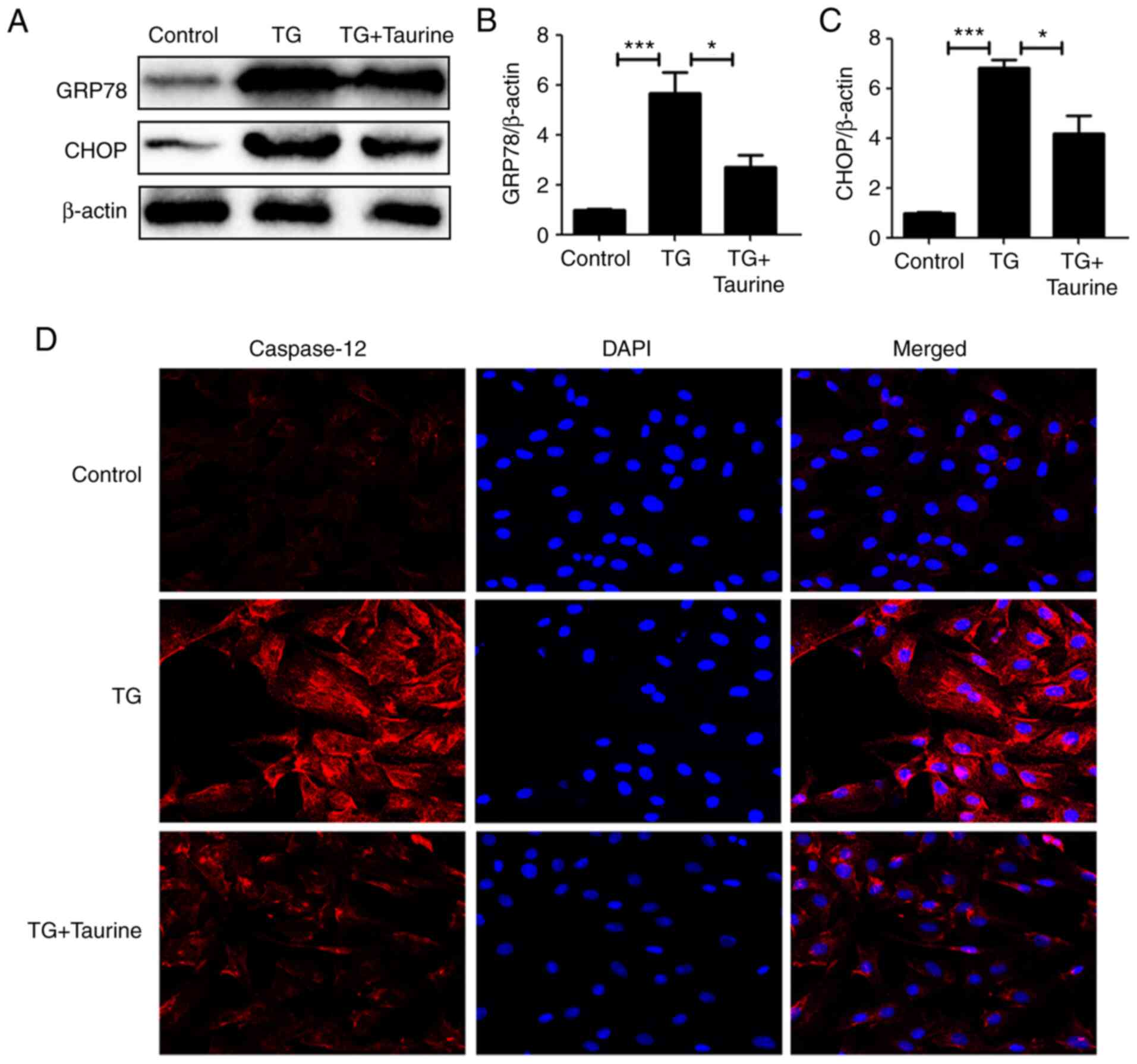
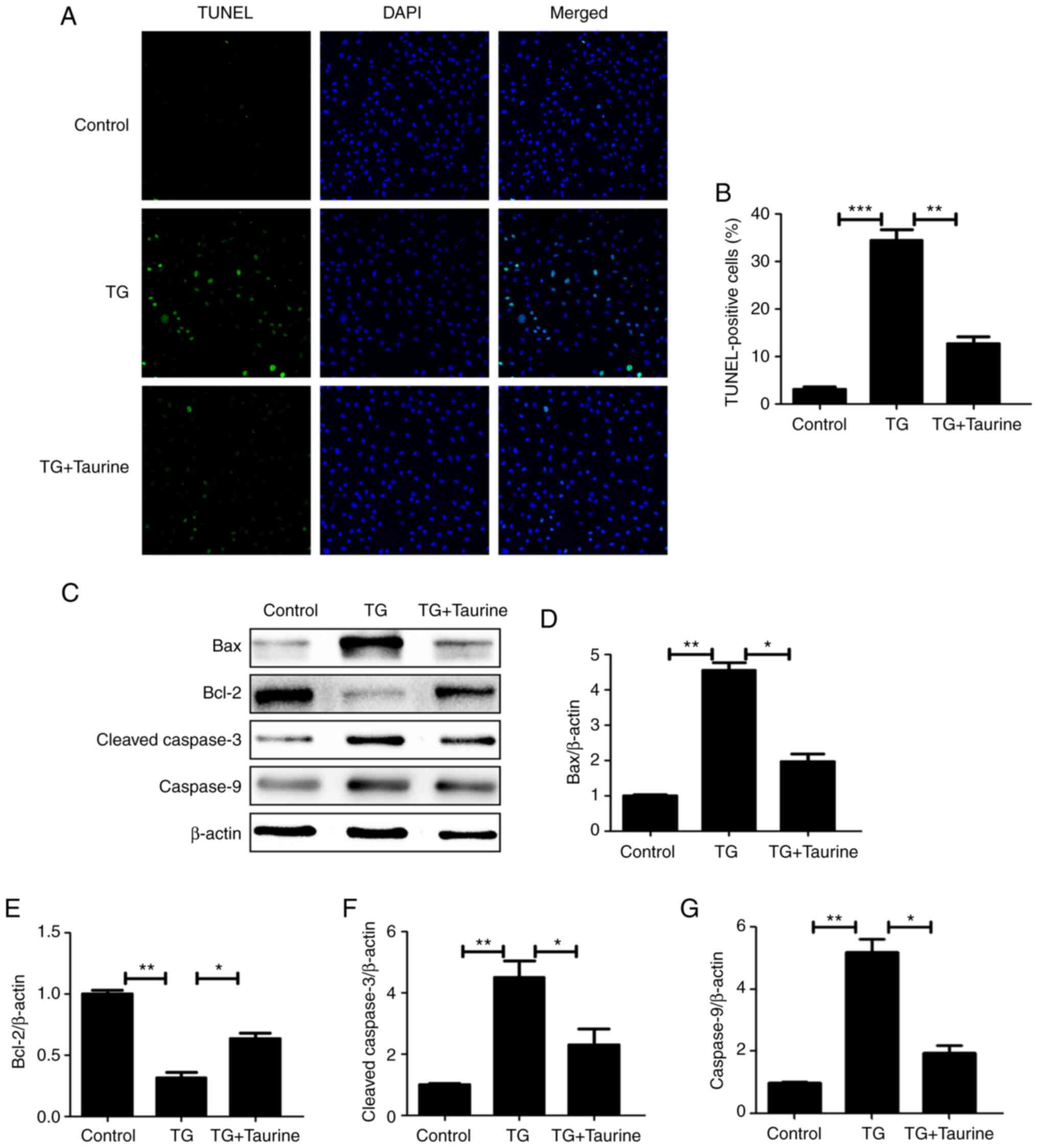
|
1
|
Wang F, Cai F, Shi R, Wang XH and Wu XT:
Aging and age related stresses: A senescence mechanism of
intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
24:398–408. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Simon J, McAuliffe M, Shamim F, Vuong N
and Tahaei A: Discogenic low back pain. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am.
25:305–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Petersen T, Laslett M and Juhl C: Clinical
classification in low back pain: Best-evidence diagnostic rules
based on systematic reviews. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 18:1882017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barrey CY and Le Huec JC; French Society
for Spine Surgery, : Chronic low back pain: Relevance of a new
classification based on the injury pattern. Orthop Traumatol Surg
Res. 105:339–346. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liang D, Hong D, Tang F, Wang Y, Li J, Li
L and Chen H: Upregulated lnc-HRK-2:1 prompts nucleus pulposus cell
senescence in intervertebral disc degeneration. Mol Med Rep.
22:5251–5261. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pattappa G, Li Z, Peroglio M, Wismer N,
Alini M and Grad S: Diversity of intervertebral disc cells:
Phenotype and function. J Anat. 221:480–496. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sakai D and Grad S: Advancing the cellular
and molecular therapy for intervertebral disc disease. Adv Drug
Deliv Rev. 84:159–171. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ding F, Shao ZW and Xiong LM: Cell death
in intervertebral disc degeneration. Apoptosis. 18:777–785. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu S, Liang T and Li S: Correlation
between polymorphism of TRAIL gene and condition of intervertebral
disc degeneration. Med Sci Monit. 21:2282–2287. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao Z, Zheng J, Ye Y, Zhao K and Wang R
and Wang R: MicroRNA-25-3p regulates human nucleus pulposus cell
proliferation and apoptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration by
targeting Bim. Mol Med Rep. 22:3621–3628. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tsingas M, Ottone OK, Haseeb A, Barve RA,
Shapiro IM, Lefebvre V and Risbud MV: Sox9 deletion causes severe
intervertebral disc degeneration characterized by apoptosis, matrix
remodeling, and compartment-specific transcriptomic changes. Matrix
Biol. 94:110–133. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Borrelli C and Buckley CT: Injectable
disc-derived ECM hydrogel functionalised with chondroitin sulfate
for intervertebral disc regeneration. Acta Biomater. 117:142–155.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ohnishi T, Novais EJ and Risbud MV:
Alterations in ECM signature underscore multiple sub-phenotypes of
intervertebral disc degeneration. Matrix Biol Plus. 6–7, 100036.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Le Maitre CL, Pockert A, Buttle DJ,
Freemont AJ and Hoyland JA: Matrix synthesis and degradation in
human intervertebral disc degeneration. Biochem Soc Trans.
35:652–655. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang WJ, Yu XH, Wang C, Yang W, He WS,
Zhang SJ, Yan YG and Zhang J: MMPs and ADAMTSs in intervertebral
disc degeneration. Clin Chim Acta. 448:238–246. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ding F and Li X: Apigenin mitigates
intervertebral disc degeneration through the amelioration of tumor
necrosis factor α (TNF-α) signaling pathway. Med Sci Monit.
26:e9245872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Roberts S, Caterson B, Menage J, Evans EH,
Jaffray DC and Eisenstein SM: Matrix metalloproteinases and
aggrecanase: Their role in disorders of the human intervertebral
disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 25:3005–3013. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pockert AJ, Richardson SM, Le Maitre CL,
Lyon M, Deakin JA, Buttle DJ, Freemont AJ and Hoyland JA: Modified
expression of the ADAMTS enzymes and tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinases 3 during human intervertebral disc degeneration.
Arthritis Rheum. 60:482–491. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yamori Y, Nara Y, Ikeda K and Mizushima S:
Is taurine a preventive nutritional factor of cardiovascular
diseases or just a biological marker of nutrition? Adv Exp Med
Biol. 403:623–629. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wallace DR and Dawson R Jr: Decreased
plasma taurine in aged rats. Gerontology. 36:19–27. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pacholczyk-Sienicka B, Radek M, Radek A
and Jankowski S: Characterization of metabolites determined by
means of 1H HR MAS NMR in intervertebral disc degeneration. MAGMA.
28:173–183. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Goodman CA, Horvath D, Stathis C, Mori T,
Croft K, Murphy RM and Hayes A: Taurine supplementation increases
skeletal muscle force production and protects muscle function
during and after high-frequency in vitro stimulation. J Appl
Physiol (1985). 107:144–154. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ghosh S, Chowdhury S, Das AK and Sil PC:
Taurine ameliorates oxidative stress induced inflammation and ER
stress mediated testicular damage in STZ-induced diabetic Wistar
rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 124:64–80. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rainesalo S, Keränen T, Palmio J, Peltola
J, Oja SS and Saransaari P: Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid amino
acids in epileptic patients. Neurochem Res. 29:319–324. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Engelborghs S, Marescau B and De Deyn PP:
Amino acids and biogenic amines in cerebrospinal fluid of patients
with Parkinson's disease. Neurochem Res. 28:1145–1150. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gao Z, Lin Y, Zhang P, Cheng Q, Ye L, Wu
F, Chen Y, Fu M, Cheng C and Gao Y: Sinomenine ameliorates
intervertebral disc degeneration via inhibition of apoptosis and
autophagy in vitro and in vivo. Am J Transl Res. 11:5956–5966.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu D, Gu Y, Wang W and Chen W: Astragalin
alleviates ischemia/reperfusion-induced brain injury via
suppression of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Med Rep.
22:4070–4078. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen J, Xuan J, Gu YT, Shi KS, Xie JJ,
Chen JX, Zheng ZM, Chen Y, Chen XB, Wu YS, et al: Celastrol reduces
IL-1β induced matrix catabolism, oxidative stress and inflammation
in human nucleus pulposus cells and attenuates rat intervertebral
disc degeneration in vivo. Biomed Pharmacother. 91:208–219. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pfaffl MW: A new mathematical model for
relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res.
29:e452001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Martirosyan NL, Patel AA, Carotenuto A,
Kalani MY, Belykh E, Walker CT, Preul MC and Theodore N: Genetic
alterations in intervertebral disc disease. Front Surg. 3:592016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yurube T, Takada T, Suzuki T, Kakutani K,
Maeno K, Doita M, Kurosaka M and Nishida K: Rat tail static
compression model mimics extracellular matrix metabolic imbalances
of matrix metalloproteinases, aggrecanases, and tissue inhibitors
of metalloproteinases in intervertebral disc degeneration.
Arthritis Res Ther. 14:R512012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ekşi MŞ, Özcan-Ekşi EE, Özmen BB, Turgut
VU, Huet SE, Dinç T, Kara M, Özgen S, Özek MM and Pamir MN: Lumbar
intervertebral disc degeneration, end-plates and paraspinal muscle
changes in children and adolescents with low-back pain. J Pediatr
Orthop B. 31:93–102. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Khan AN, Jacobsen HE, Khan J, Filippi CG,
Levine M, Lehman RA Jr, Riew KD, Lenke LG and Chahine NO:
Inflammatory biomarkers of low back pain and disc degeneration: A
review. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1410:68–84. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang B, Xu H, Wang J, Liu B and Sun G: A
narrative review of non-operative treatment, especially traditional
Chinese medicine therapy, for lumbar intervertebral disc
herniation. Biosci Trends. 11:406–417. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jacobs WC, van der Gaag NA, Kruyt MC,
Tuschel A, de Kleuver M, Peul WC, Verbout AJ and Oner FC: Total
disc replacement for chronic discogenic low back pain: A Cochrane
review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 38:24–36. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ogon I, Takashima H, Morita T, Oshigiri T,
Terashima Y, Yoshimoto M, Fukushi R, Fujimoto S, Emori M, Teramoto
A, et al: Relevance between schmorl's node and lumbar
intervertebral disc degeneration quantified with magnetic resonance
imaging T2 mapping in chronic low back pain. Asian Spine J.
14:621–628. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cherif H, Bisson DG, Mannarino M, Rabau O,
Ouellet JA and Haglund L: Senotherapeutic drugs for human
intervertebral disc degeneration and low back pain. Elife.
9:e546932020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang D, Chen Y, Cao S, Ren P, Shi H, Li H,
Xie L, Huang W, Shi B and Han J: Cyclic mechanical stretch
ameliorates the degeneration of nucleus pulposus cells through
promoting the ITGA2/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2021:66993262021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mobasheri A, Csaki C, Clutterbuck AL,
Rahmanzadeh M and Shakibaei M: Mesenchymal stem cells in connective
tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: Applications in
cartilage repair and osteoarthritis therapy. Histol Histopathol.
24:347–366. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhao CQ, Wang LM, Jiang LS and Dai LY: The
cell biology of intervertebral disc aging and degeneration. Ageing
Res Rev. 6:247–261. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xu H, Ji L, Yu C, Chen Q, Ge Q and Lu Y:
MiR-423-5p regulates cells apoptosis and extracellular matrix
degradation via nucleotide-binding, leucine-rich repeat containing
X1 (NLRX1) in interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β)-induced human nucleus
pulposus cells. Med Sci Monit. 26:e9224972020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Guo HT, Yang SD, Zhang F, Liu S, Yang DL,
Ma L, Wang H and Ding WY: 17β-Estradiol protects against
interleukin-1β-induced apoptosis in rat nucleus pulposus cells via
the mTOR/caspase-3 pathway. Mol Med Rep. 20:1523–1530.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Horiuchi K, Tohmonda T and Morioka H: The
unfolded protein response in skeletal development and homeostasis.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:2851–2869. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Uehara Y, Hirose J, Yamabe S, Okamoto N,
Okada T, Oyadomari S and Mizuta H: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced apoptosis contributes to articular cartilage
degeneration via C/EBP homologous protein. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 22:1007–1017. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shimizu A, Kaira K, Yasuda M, Asao T and
Ishikawa O: Clinical and pathological significance of ER stress
marker (BiP/GRP78 and PERK) expression in malignant melanoma.
Pathol Oncol Res. 23:111–116. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chern YJ, Wong JCT, Cheng GSW, Yu A, Yin
Y, Schaeffer DF, Kennecke HF, Morin G and Tai IT: The interaction
between SPARC and GRP78 interferes with ER stress signaling and
potentiates apoptosis via PERK/eIF2α and IRE1α/XBP-1 in colorectal
cancer. Cell Death Dis. 10:5042019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fu YF, Liu X, Gao M, Zhang YN and Liu J:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress induces autophagy and apoptosis while
inhibiting proliferation and drug resistance in multiple myeloma
through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Oncotarget.
8:61093–61106. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lee W, Kim DH, Boo JH, Kim YH, Park IS and
Mook-Jung I: ER stress-induced caspase-12 activation is inhibited
by PKC in neuronal cells. Apoptosis. 10:407–415. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yang Y, Zhang Y, Liu X, Zuo J, Wang K, Liu
W and Ge J: Exogenous taurine attenuates mitochondrial oxidative
stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress in rat cardiomyocytes. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 45:359–367. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yang YJ, Han YY, Chen K, Zhang Y, Liu X,
Li S, Wang KQ, Ge JB, Liu W and Zuo J: TonEBP modulates the
protective effect of taurine in ischemia-induced cytotoxicity in
cardiomyocytes. Cell Death Dis. 6:e20252015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nonaka H, Tsujino T, Watari Y, Emoto N and
Yokoyama M: Taurine prevents the decrease in expression and
secretion of extracellular superoxide dismutase induced by
homocysteine: Amelioration of homocysteine-induced endoplasmic
reticulum stress by taurine. Circulation. 104:1165–1170. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Li Z, Guo J, Bian Y and Zhang M:
Intermedin protects thapsigargin-induced endoplasmic reticulum
stress in cardiomyocytes by modulating protein kinase A and
sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Mol Med Rep.
23:1072021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Luo R, Song Y, Liao Z, Yin H, Zhan S, Wang
K, Li S, Li G, Ma L, Lu S, et al: Impaired calcium homeostasis via
advanced glycation end products promotes apoptosis through
endoplasmic reticulum stress in human nucleus pulposus cells and
exacerbates intervertebral disc degeneration in rats. FEBS J.
286:4356–4373. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Canová NK, Kmonícková E, Martínek J, Zídek
Z and Farghali H: Thapsigargin, a selective inhibitor of
sarco-endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPases, modulates
nitric oxide production and cell death of primary rat hepatocytes
in culture. Cell Biol Toxicol. 23:337–354. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mao HZ, Ehrhardt N, Bedoya C, Gomez JA,
DeZwaan-McCabe D, Mungrue IN, Kaufman RJ, Rutkowski DT and Péterfy
M: Lipase maturation factor 1 (lmf1) is induced by endoplasmic
reticulum stress through activating transcription factor 6α (Atf6α)
signaling. J Biol Chem. 289:24417–24427. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Finger F and Hoppe T: MicroRNAs meet
calcium: Joint venture in ER proteostasis. Sci Signal. 7:re112014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Groenendyk J, Peng Z, Dudek E, Fan X,
Mizianty MJ, Dufey E, Urra H, Sepulveda D, Rojas-Rivera D, Lim Y,
et al: Interplay between the oxidoreductase PDIA6 and microRNA-322
controls the response to disrupted endoplasmic reticulum calcium
homeostasis. Sci Signal. 7:ra542014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lama P, Zehra U, Balkovec C, Claireaux HA,
Flower L, Harding IJ, Dolan P and Adams MA: Significance of
cartilage endplate within herniated disc tissue. Eur Spine J.
23:1869–1877. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Novais EJ, Choi H, Madhu V, Suyama K, Anjo
SI, Manadas B, Shapiro IM, Salgado AJ and Risbud MV: Hypoxia and
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α regulate endoplasmic reticulum stress
in nucleus pulposus cells: Implications of endoplasmic reticulum
stress for extracellular matrix secretion. Am J Pathol.
191:487–502. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|