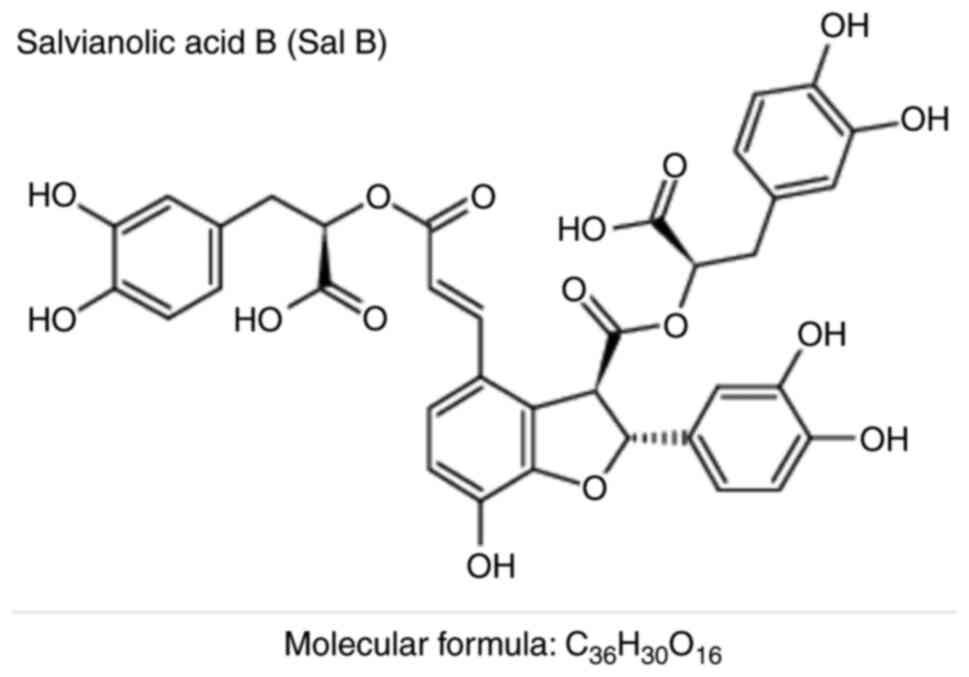
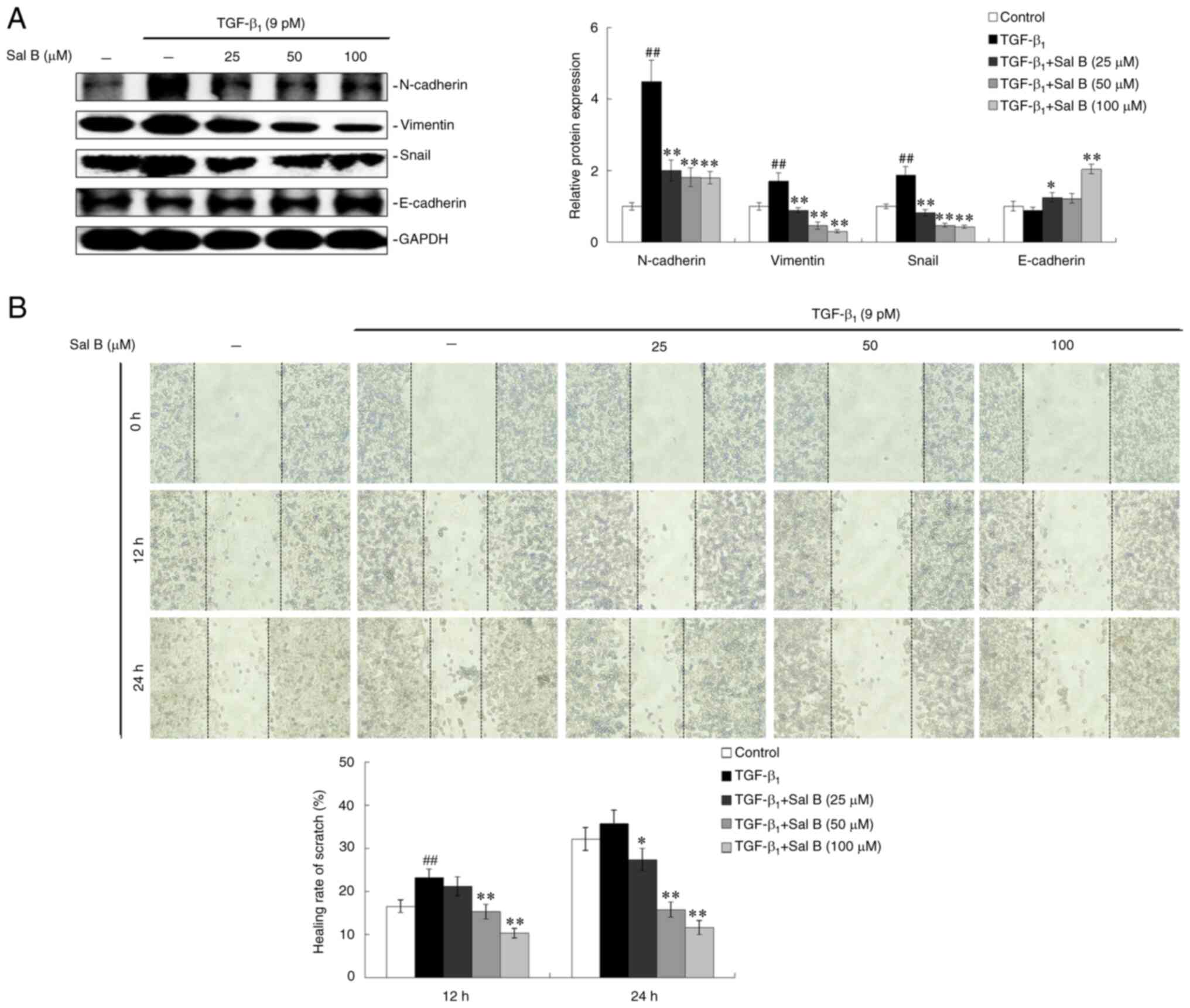
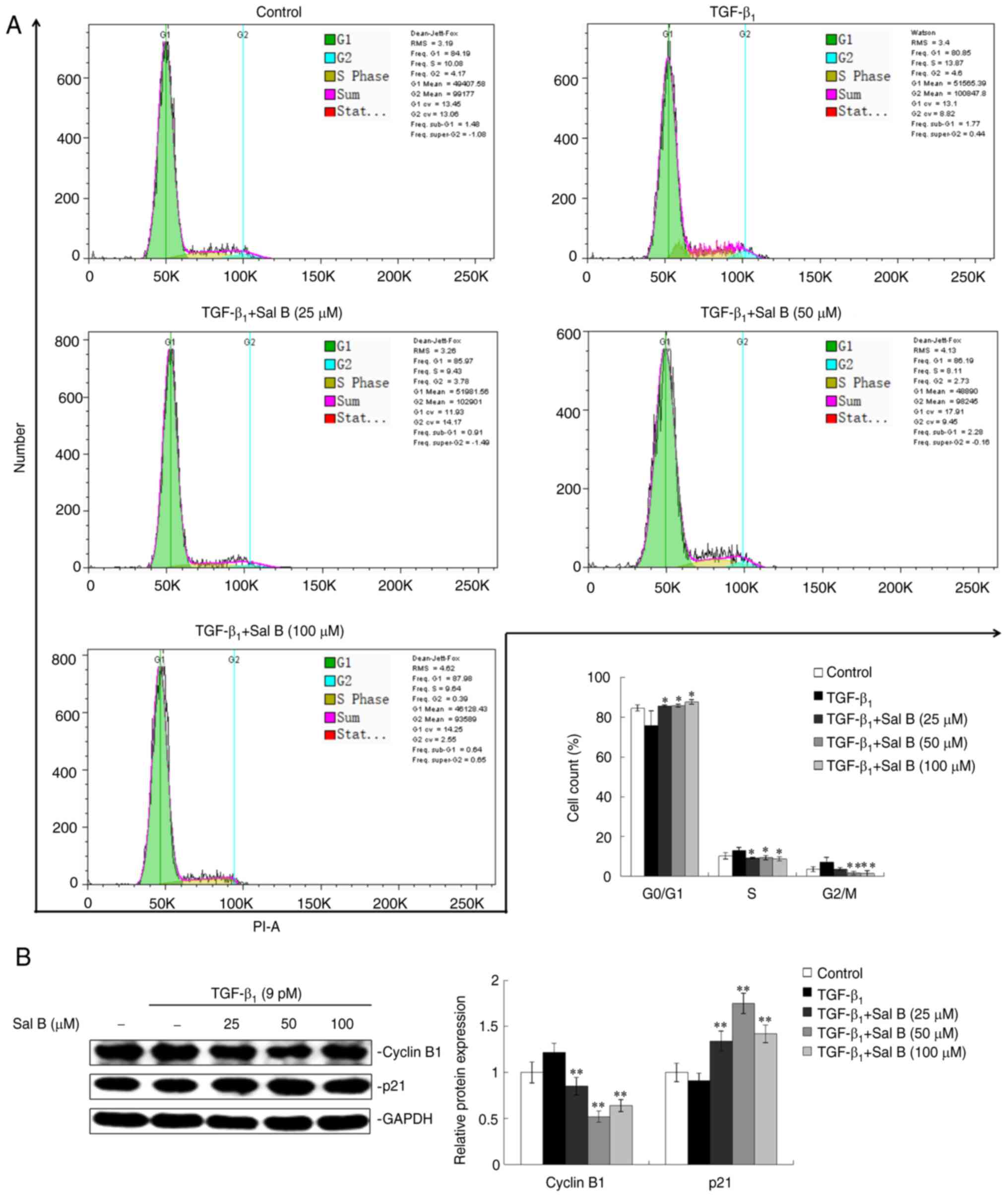
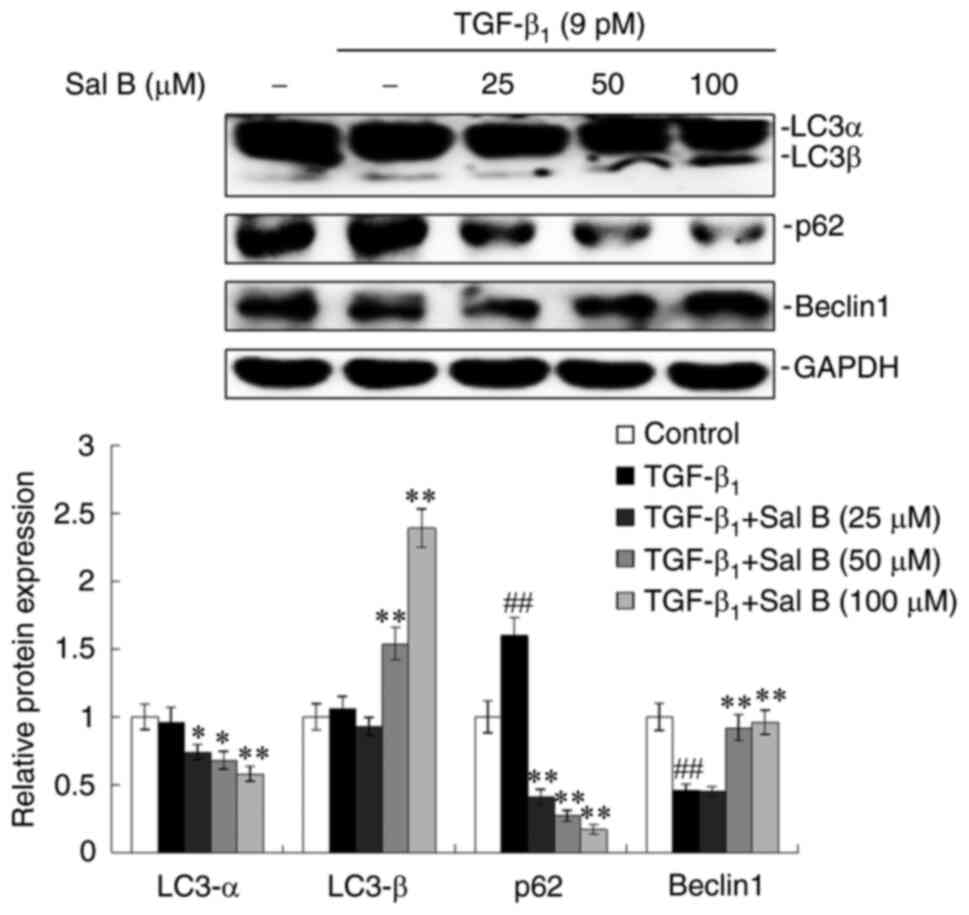
|
1
|
Bade BC and Dela Cruz CS: Lung cancer
2020: Epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin Chest Med.
41:1–24. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D and Boshoff C:
The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature.
553:446–454. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang LC, Chang YY, Lee IC, Kuo HC and Tsai
MY: Systematic review and meta-analysis of Chinese herbal medicine
as adjuvant treatment in advanced non-small cell lung cancer
patients. Complement Ther Med. 52:1024722020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen X, Guo J, Bao J, Lu J and Wang Y: The
anticancer properties of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge
(Danshen): A systematic review. Med Res Rev. 34:768–794. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hung YC, Pan TL and Hu WL: Roles of
reactive oxygen species in anticancer therapy with Salvia
miltiorrhiza Bunge. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:52932842016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gong L, Di C, Xia X, Wang J, Chen G, Shi
J, Chen P, Xu H and Zhang W: AKT/mTOR signaling pathway is involved
in salvianolic acid B-induced autophagy and apoptosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 49:2538–2548. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Katary MA, Abdelsayed R, Alhashim A,
Abdelhasib M and Elmarakby AA: Salvianolic acid B slows the
progression of breast cancer cell growth via enhancement of
apoptosis and reduction of oxidative stress, inflammation, and
angiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 20:56532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hao Y, Xie T, Korotcov A, Zhou Y, Pang X,
Shan L, Ji H, Sridhar R, Wang P, Califano J and Gu X: Salvianolic
acid B inhibits growth of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in
vitro and in vivo via cyclooxygenase-2 and apoptotic pathways. Int
J Cancer. 124:2200–2209. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen B, Huang C, Zhang Y, Tang X, Li S,
Wang Q and Lin Y: Salvia bowleyana Dunn root is a novel
source of salvianolic acid B and displays antitumor effects against
gastric cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 20:817–827. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jing Z, Fei W, Zhou J, Zhang L, Chen L,
Zhang X, Liang X, Xie J, Fang Y, Sui X, et al: Salvianolic acid B,
a novel autophagy inducer, exerts antitumor activity as a single
agent in colorectal cancer cells. Oncotarget. 7:61509–61519. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qin T, Rasul A, Sarfraz A, Sarfraz I,
Hussain G, Anwar H, Riaz A, Liu S, Wei W, Li J and Li X:
Salvianolic acid A & B: Potential cytotoxic polyphenols in
battle against cancer via targeting multiple signaling pathways.
Int J Biol Sci. 15:2256–2264. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tao L, Wang S, Zhao Y, Sheng X, Wang A,
Zheng S and Lu Y: Phenolcarboxylic acids from medicinal herbs exert
anticancer effects through disruption of COX-2 activity.
Phytomedicine. 21:1473–1482. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dongre A and Weinberg RA: New insights
into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
implications for cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:69–84. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jeong JH, Jang HJ, Kwak S, Sung GJ, Park
SH, Song JH, Kim H, Na Y and Choi KC: Novel TGF-β1 inhibitor
antagonizes TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
human A549 lung cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 120:977–987. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Eser PÖ and Jänne PA: TGFβ pathway
inhibition in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.
Pharmacol Ther. 184:112–130. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu Q, Chu H, Ma Y, Wu T, Qian F, Ren X,
Tu W, Zhou X, Jin L, Wu W and Wang J: Salvianolic acid B attenuates
experimental pulmonary fibrosis through inhibition of the TGF-β
signaling pathway. Sci Rep. 6:276102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu C, Chen W, Ding H, Li D, Wen G, Zhang
C, Lu W, Chen M and Yang Y: Salvianolic acid B exerts anti-liver
fibrosis effects via inhibition of MAPK-mediated phospho-Smad2/3 at
linker regions in vivo and in vitro. Life Sci. 239:1168812019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Boye A, Kan H, Wu C, Jiang Y, Yang X, He S
and Yang Y: MAPK inhibitors differently modulate TGF-β/Smad
signaling in HepG2 cells. Tumour Biol. 36:3643–3651. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hao Y, Baker D and Ten Dijke P:
TGF-β-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer
metastasis. Int J Mol Sci. 20:27672019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu X, Chen Y, Li Y, Petersen RB and Huang
K: Targeting mitosis exit: A brake for cancer cell proliferation.
Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1871:179–191. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mateen S, Raina K, Jain AK, Agarwal C,
Chan D and Agarwal R: Epigenetic modifications and p21-cyclin B1
nexus in anticancer effect of histone deacetylase inhibitors in
combination with silibinin on non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Epigenetics. 7:1161–1172. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu G, Pei F, Yang F, Li L, Amin AD, Liu
S, Buchan JR and Cho WC: Role of autophagy and apoptosis in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 18:3672017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim R, Emi M and Tanabe K: The role of
apoptosis in cancer cell survival and therapeutic outcome. Cancer
Biol Ther. 5:1429–1442. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mulder KM: Role of Ras and Mapks in
TGFbeta signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 11:23–35. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Derynck R and Zhang YE: Smad-dependent and
Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature.
425:577–584. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ooshima A, Park J and Kim SJ:
Phosphorylation status at Smad3 linker region modulates
transforming growth factor-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and cancer progression. Cancer Sci. 110:481–488. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou Y, Zheng J, Li Y, Xu DP, Li S, Chen
YM and Li HB: Natural polyphenols for prevention and treatment of
cancer. Nutrients. 8:5152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bi L, Chen J, Yuan X, Jiang Z and Chen W:
Salvianolic acid A positively regulates PTEN protein level and
inhibits growth of A549 lung cancer cells. Biomed Rep. 1:213–217.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tang XL, Yan L, Zhu L, Jiao DM, Chen J and
Chen QY: Salvianolic acid A reverses cisplatin resistance in lung
cancer A549 cells by targeting c-met and attenuating Akt/mTOR
pathway. J Pharmacol Sci. 135:1–7. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun Y, Zhu H, Wang J, Liu Z and Bi J:
Isolation and purification of salvianolic acid A and salvianolic
acid B from Salvia miltiorrhiza by high-speed
counter-current chromatography and comparison of their antioxidant
activity. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.
877:733–737. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xia H, Sun L, Lou H and Rahman MM:
Conversion of salvianolic acid B into salvianolic acid A in tissues
of radix salviae miltiorrhizae using high temperature, high
pressure and high humidity. Phytomedicine. 21:906–911. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Petty RD, Nicolson MC, Kerr KM,
Collie-Duguid E and Murray GI: Gene expression profiling in
non-small cell lung cancer: From molecular mechanisms to clinical
application. Clin Cancer Res. 10:3237–3248. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jeon HS and Jen J: TGF-beta signaling and
the role of inhibitory Smads in non-small cell lung cancer. J
Thorac Oncol. 5:417–419. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang J, Shao N, Ding X, Tan B, Song Q,
Wang N, Jia Y, Ling H and Cheng Y: Crosstalk between transforming
growth factor-β signaling pathway and long non-coding RNAs in
cancer. Cancer Lett. 370:296–301. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Schnittger A and De Veylder L: The dual
face of cyclin B1. Trends Plant Sci. 23:475–478. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mittal V: Epithelial mesenchymal
transition in aggressive lung cancers. Adv Exp Med Biol. 890:37–56.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Calles A, Sholl LM, Rodig SJ, Pelton AK,
Hornick JL, Butaney M, Lydon C, Dahlberg SE, Oxnard GR, Jackman DM
and Jänne PA: Immunohistochemical loss of LKB1 is a biomarker for
more aggressive biology in KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. Clin
Cancer Res. 21:2851–2860. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim C and Giaccone G: MEK inhibitors under
development for treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. Expert
Opin Investig Drugs. 27:17–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Murata M, Yoshida K, Yamaguchi T and
Matsuzaki K: Linker phosphorylation of Smad3 promotes
fibro-carcinogenesis in chronic viral hepatitis of hepatocellular
carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 20:15018–15027. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gong Y, Li D, Li L, Yang J, Ding H, Zhang
C, Wen G, Wu C, Fang Z, Hou S and Yang Y: Smad3 C-terminal
phosphorylation site mutation attenuates the hepatoprotective
effect of salvianolic acid B against hepatocarcinogenesis. Food
Chem Toxicol. 147:1119122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
He S, Liu X, Yang Y, Huang W, Xu S, Yang
S, Zhang X and Roberts MS: Mechanisms of transforming growth factor
beta(1)/Smad signalling mediated by mitogen-activated protein
kinase pathways in keloid fibroblasts. Br J Dermatol. 162:538–546.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Matsuzaki K, Kitano C, Murata M, Sekimoto
G, Yoshida K, Uemura Y, Seki T, Taketani S, Fujisawa J and Okazaki
K: Smad2 and Smad3 phosphorylated at both linker and COOH-terminal
regions transmit malignant TGF-beta signal in later stages of human
colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 69:5321–5330. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Dennler S, Itoh S, Vivien D, ten Dijke P,
Huet S and Gauthier JM: Direct binding of Smad3 and Smad4 to
critical TGF beta-inducible elements in the promoter of human
plasminogen activator inhibitor-type 1 gene. EMBO J. 17:3091–3100.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lin X, Lin BW, Chen XL, Zhang BL, Xiao XJ,
Shi JS, Lin JD and Chen X: PAI-1/PIAS3/Stat3/miR-34a forms a
positive feedback loop to promote EMT-mediated metastasis through
Stat3 signaling in non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 493:1464–1470. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kang J, Kim W, Kwon T, Youn H, Kim JS and
Youn B: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 enhances radioresistance
and aggressiveness of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncotarget.
7:23961–23974. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|