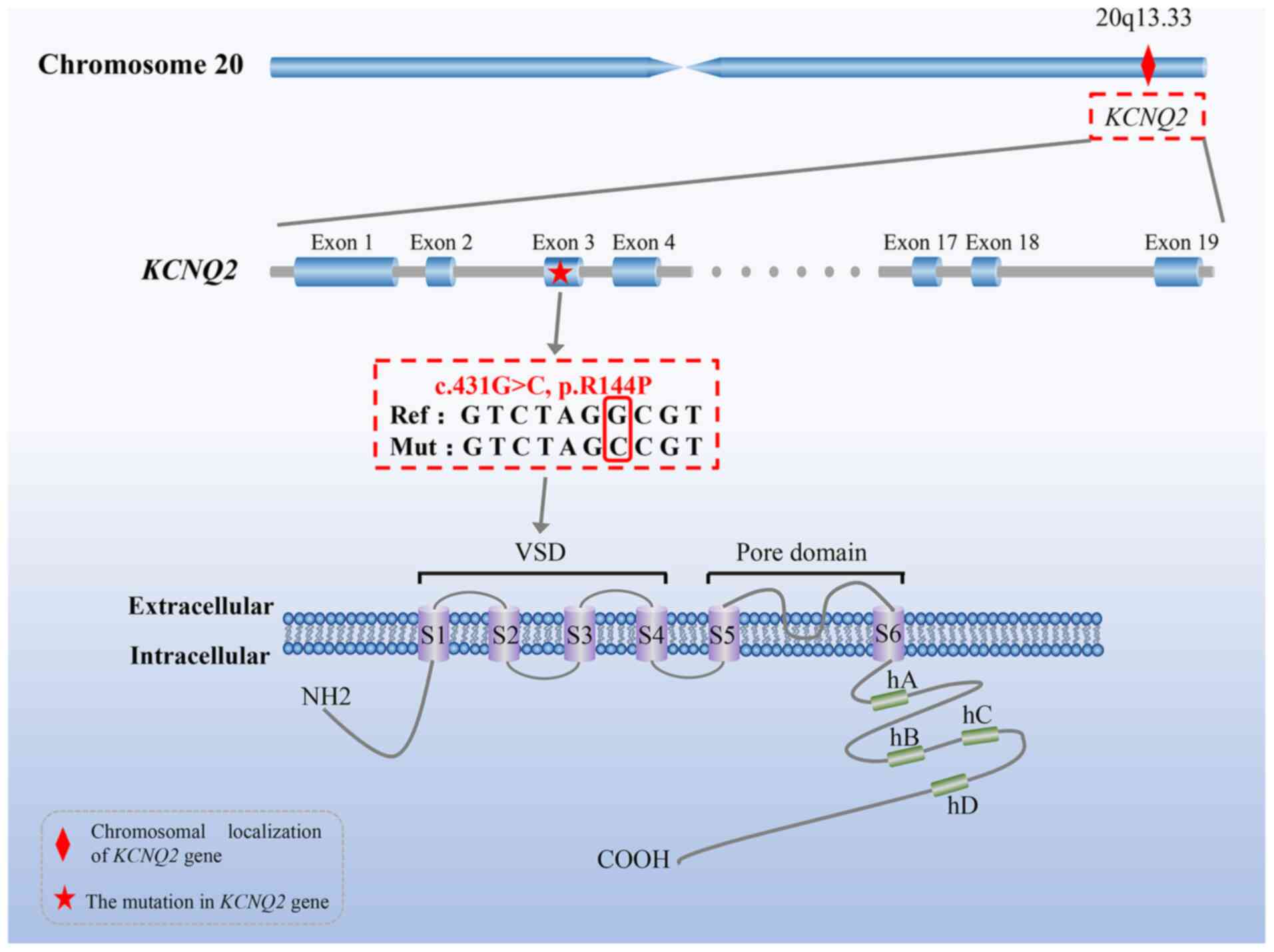
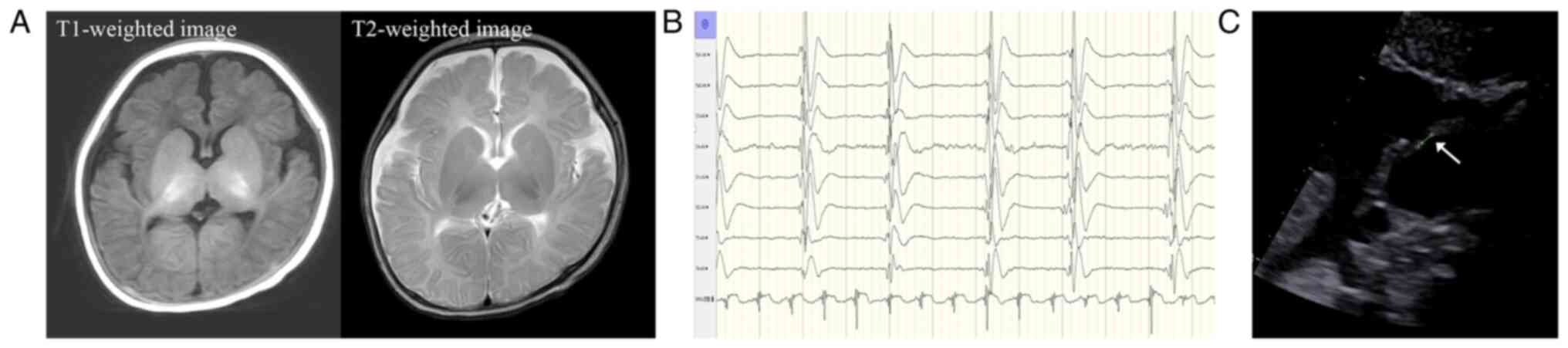
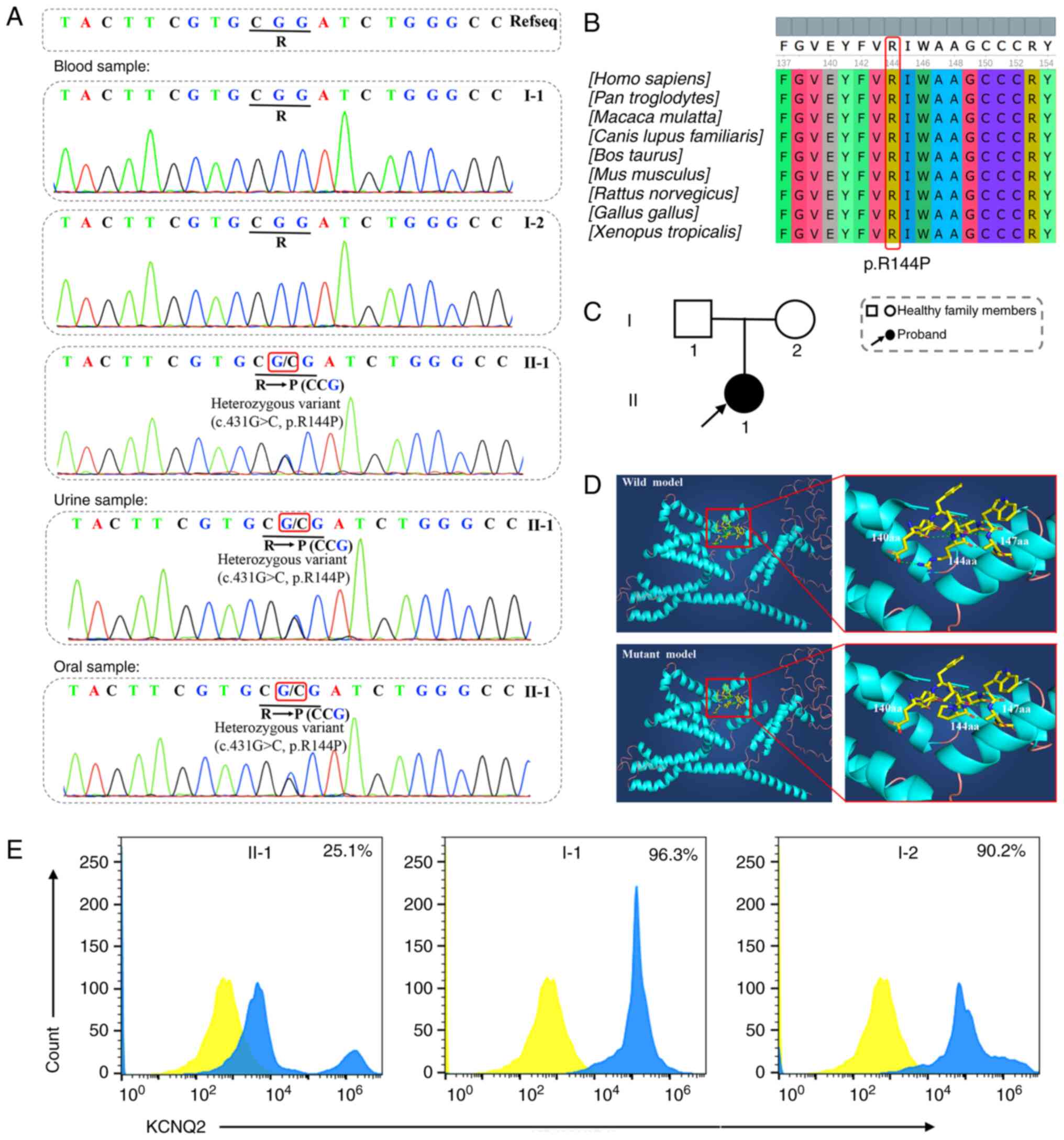
|
1
|
Nieh SE and Sherr EH: Epileptic
encephalopathies: New genes and new pathways. Neurotherapeutics.
11:796–806. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Alam S and Lux AL: Epilepsies in infancy.
Arch Dis Child. 97:985–992. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Galanopoulou AS and Moshé SL: The
epileptic hypothesis: Developmentally related arguments based on
animal models. Epilepsia. 50 (Suppl 7):S37–S42. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang JY, Zhou P, Wang J, Tang B, Su T, Liu
XR, Li BM, Meng H, Shi YW, Yi YH, et al: ARHGEF9 mutations in
epileptic encephalopathy/intellectual disability: Toward
understanding the mechanism underlying phenotypic variation.
Neurogenetics. 19:9–16. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jakimiec M, Paprocka J and Śmigiel R:
CDKL5 deficiency disorder-A complex epileptic encephalopathy. Brain
Sci. 10:1072020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gertler T, Bearden D, Bhattacharjee A and
Carvill G: KCNT1-related epilepsy. Adam MP, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA,
Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Gripp KW and Amemiya A:
GeneReviews® Seattle (WA): University of Washington;
Seattle: 1993–2022. 2018
|
|
7
|
Bonardi CM, Heyne HO, Fiannacca M,
Fitzgerald MP, Gardella E, Gunning B, Olofsson K, Lesca G, Verbeek
N, Stamberger H, et al: KCNT1-related epilepsies and epileptic
encephalopathies: Phenotypic and mutational spectrum. Brain.
144:3635–3650. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Talwar D and Hammer MF: SCN8A epilepsy,
developmental encephalopathy, and related disorders. Pediatr
Neurol. 122:76–83. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hammer MF, Wagnon JL, Mefford HC and
Meisler MH: SCN8A-related epilepsy with encephalopathy.
GeneReviews®. Adam MP, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE,
Bean LJH, Gripp KW and Amemiya A: University of Washington;
Seattle, Seattle, WA: 1993-2022. 2016
|
|
10
|
Reynolds C, King MD and Gorman KM: The
phenotypic spectrum of SCN2A-related epilepsy. Eur J Paediatr
Neurol. 24:117–122. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hedrich UBS, Lauxmann S and Lerche H:
SCN2A channelopathies: Mechanisms and models. Epilepsia. 60 (Suppl
3):S68–S76. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Agostinelli S, Traverso M, Accorsi P,
Beccaria F, Belcastro V, Capovilla G, Cappanera S, Coppola A, Dalla
Bernardina B, Darra F, et al: Early-onset absence epilepsy: SLC2A1
gene analysis and treatment evolution. Eur J Neurol. 20:856–859.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wild B and Nelson S: STXBP1-Related
developmental and epileptic encephalopathy. Pediatr Neurol Briefs.
33:62019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stamberger H, Nikanorova M, Willemsen MH,
Accorsi P, Angriman M, Baier H, Benkel-Herrenbrueck I, Benoit V,
Budetta M, Caliebe A, et al: STXBP1 encephalopathy: A
neurodevelopmental disorder including epilepsy. Neurology.
86:954–962. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Lian Y and Xie N: Early onset
epileptic encephalopathy with a novel GABRB3 mutation treated
effectively with clonazepam: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore).
96:e92732017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang Q, Li J, Zhao Y, Bao X, Wei L and
Wang J: Gene mutation analysis of 175 Chinese patients with
early-onset epileptic encephalopathy. Clin Genet. 91:717–724. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mastrangelo M and Leuzzi V: Genes of
early-onset epileptic encephalopathies: From genotype to phenotype.
Pediatr Neurol. 46:24–31. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Leppert M, Anderson VE, Quattlebaum T,
Stauffer D, O'Connell P, Nakamura Y, Lalouel JM and White R: Benign
familial neonatal convulsions linked to genetic markers on
chromosome 20. Nature. 337:647–648. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Biervert C, Schroeder BC, Kubisch C,
Berkovic SF, Propping P, Jentsch TJ and Steinlein OK: A potassium
channel mutation in neonatal human epilepsy. Science. 279:403–406.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang H, Pan Z, Shi W, Brown BS, Wymore RS,
Cohen IS, Dixon JE and MacKinnon D: KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 potassium
channel subunits: Molecular correlates of the M-channel. Science.
282:1890–1893. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Singh NA, Charlier C, Stauffer D, DuPont
BR, Leach RJ, Melis R, Ronen GM, Bjerre I, Quattlebaum T, Murphy
JV, et al: A novel potassium channel gene, KCNQ2, is mutated in an
inherited epilepsy of newborns. Nat Genet. 18:25–29. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jentsch TJ: Neuronal KCNQ potassium
channels: Physiology and role in disease. Nat Rev Neurosci.
1:21–30. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cooper EC and Jan LY: M-channels:
Neurological diseases, neuromodulation, and drug development. Arch
Neurol. 60:4962003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Goto A, Ishii A, Shibata M, Ihara Y,
Cooper EC and Hirose S: Characteristics of KCNQ2 variants causing
either benign neonatal epilepsy or developmental and epileptic
encephalopathy. Epilepsia. 60:1870–1880. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee IC, Yang JJ, Wong SH, Liou YM and Li
SY: Heteromeric Kv7.2 current changes caused by loss-of-function of
KCNQ2 mutations are correlated with long-term neurodevelopmental
outcomes. Sci Rep. 10:133752020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee IC, Chang TM, Liang JS and Li SY:
KCNQ2 mutations in childhood nonlesional epilepsy: Variable
phenotypes and a novel mutation in a case series. Mol Genet Genomic
Med. 7:e008162019. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Orhan G, Bock M, Schepers D, Ilina EI,
Reichel SN, Löffler H, Jezutkovic N, Weckhuysen S, Mandelstam S,
Suls A, et al: Dominant-negative effects of KCNQ2 mutations are
associated with epileptic encephalopathy. Ann Neurol. 75:382–394.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Maljevic S, Naros G, Yalçin Ö, Blazevic D,
Loeffler H, Cağlayan H, Steinlein OK and Lerche H: Temperature and
pharmacological rescue of a folding-defective, dominant-negative KV
7.2 mutation associated with neonatal seizures. Hum Mutat.
32:E2283–E2293. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Miceli F, Soldovieri MV, Ambrosino P,
Barrese V, Migliore M, Cilio MR and Taglialatela M:
Genotype-phenotype correlations in neonatal epilepsies caused by
mutations in the voltage sensor of K(v)7.2 potassium channel
subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:4386–4391. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang X, Pan G, Li WH, Zhang LM, Wu BB,
Wang HJ, Zhang P and Zhou SZ: Analysis of gene mutation of early
onset epileptic spasm with unknown reason. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi.
55:813–817. 2017.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zeng Q, Yang X, Zhang J, Liu A, Yang Z,
Liu X, Wu Y, Wu X, Wei L and Zhang Y: Genetic analysis of benign
familial epilepsies in the first year of life in a Chinese cohort.
J Hum Genet. 63:9–18. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang L, Chen X, Liu X, Dong X, Ye C, Deng
D, Lu Y, Lin Y and Zhou W: Clinical features and underlying genetic
causes in neonatal encephalopathy: A large cohort study. Clin
Genet. 98:365–373. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fang ZX, Zhang M, Xie LL, Jiang L, Hong
SQ, Li XJ, Hu Y and Chen J: KCNQ2 related early-onset epileptic
encephalopathies in Chinese children. J Neurol. 266:2224–2232.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang Y, Kong W, Gao Y, Liu X, Gao K, Xie
H, Wu Y, Zhang Y, Wang J, Gao F, et al: Gene mutation analysis in
253 Chinese children with unexplained epilepsy and
intellectual/developmental disabilities. PLoS One. 10:e01417822015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang H, Lu Y, Dong X, Lu G, Cheng G, Qian
Y, Ni Q, Zhang P, Yang L, Wu B and Zhou W: Optimized trio genome
sequencing (OTGS) as a first-tier genetic test in critically ill
infants: Practice in China. Hum Genet. 139:473–482. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fung CW, Kwong AK and Wong VC: Gene panel
analysis for nonsyndromic cryptogenic neonatal/infantile epileptic
encephalopathy. Epilepsia Open. 2:236–243. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou P, He N, Zhang JW, Lin ZJ, Wang J,
Yan LM, Meng H, Tang B, Li BM, Liu XR, et al: Novel mutations and
phenotypes of epilepsy-associated genes in epileptic
encephalopathies. Genes Brain Behav. 17:e124562018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu N, Schoch K, Luo X, Pena LDM, Bhavana
VH, Kukolich MK, Stringer S, Powis Z, Radtke K, Mroske C, et al:
Functional variants in TBX2 are associated with a syndromic
cardiovascular and skeletal developmental disorder. Hum Mol Genet.
27:2454–2465. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
He M, Tang BS, Li N, Mao X, Li J, Zhang
JG, Xiao JJ, Wang J, Jiang H, Shen L, et al: Using a combination of
whole-exome sequencing and homozygosity mapping to identify a novel
mutation of SCARB2. Clin Genet. 86:598–600. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tang B, Li H, Xia K, Jiang H, Pan Q, Shen
L, Long Z, Zhao G and Cai F: A novel mutation in KCNQ2 gene causes
benign familial neonatal convulsions in a Chinese family. J Neurol
Sci. 221:31–34. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhu T, Gong X, Bei F, Ma L, Chen Y, Zhang
Y, Wang X, Sun J, Wang J, Qiu G, et al: Application of
next-generation sequencing for genetic diagnosis in neonatal
intensive care units: Results of a multicenter study in China.
Front Genet. 11:5650782020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ambrosino P, Alaimo A, Bartollino S,
Manocchio L, De Maria M, Mosca I, Gomis-Perez C, Alberdi A, Scambia
G, Lesca G, et al: Epilepsy-causing mutations in Kv7.2 C-terminus
affect binding and functional modulation by calmodulin. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1852:1856–1866. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Miceli F, Soldovieri MV, Iannotti FA,
Barrese V, Ambrosino P, Martire M, Cilio MR and Taglialatela M: The
voltage-sensing domain of K(v)7.2 channels as a molecular target
for epilepsy-causing mutations and anticonvulsants. Front
Pharmacol. 2:22011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li P, Chen Z, Xu H, Sun H, Li H, Liu H,
Yang H, Gao Z, Jiang H and Li M: The gating charge pathway of an
epilepsy-associated potassium channel accommodates chemical
ligands. Cell Res. 23:1106–1118. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Miceli F, Vargas E, Bezanilla F and
Taglialatela M: Gating currents from Kv7 channels carrying neuronal
hyperexcitability mutations in the voltage-sensing domain. Biophys
J. 102:1372–1382. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Watanabe H, Nagata E, Kosakai A, Nakamura
M, Yokoyama M, Tanaka K and Sasai H: Disruption of the epilepsy
KCNQ2 gene results in neural hyperexcitability. J Neurochem.
75:28–33. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ackermann S, Quandt D, Hagenbuch N, Niesse
O, Christmann M, Knirsch W and Kretschmar O: Transcatheter atrial
septal defect closure in children with and without fluoroscopy: A
comparison. J Interv Cardiol. 2019:65986372019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
van der Linde D, Konings EE, Slager MA,
Witsenburg M, Helbing WA, Takkenberg JJ and Roos-Hesselink JW:
Birth prevalence of congenital heart disease worldwide: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol.
58:2241–2247. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Arvanitaki A, Giannakoulas G, Baumgartner
H and Lammers AE: Eisenmenger syndrome: Diagnosis, prognosis and
clinical management. Heart. 106:1638–1645. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Constantine A, Dimopoulos K and Opotowsky
AR: Congenital heart disease and pulmonary hypertension. Cardiol
Clin. 38:445–456. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Penaloza D and Arias-Stella J: The heart
and pulmonary circulation at high altitudes: Healthy highlanders
and chronic mountain sickness. Circulation. 115:1132–1146. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Mirrakhimov AE and Strohl KP:
High-altitude pulmonary hypertension: An update on disease
pathogenesis and management. Open Cardiovasc Med J. 10:19–27. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang N, Cheng W, Wang B, Liu Q and Zhou C:
Geomorphological regionalization theory system and division
methodology of China. J Geog Sci. 30:212–232. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|