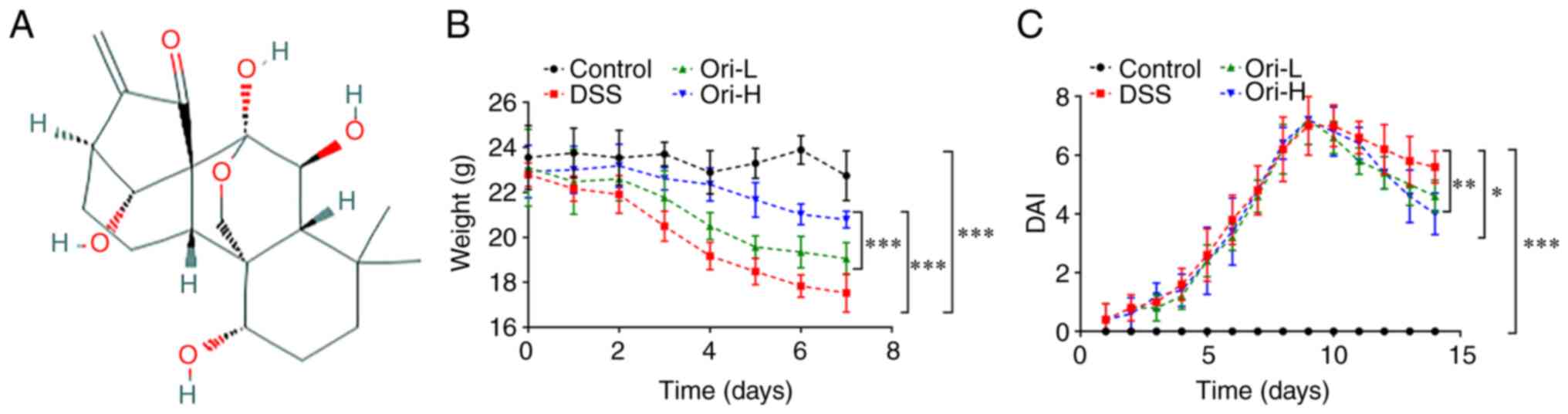
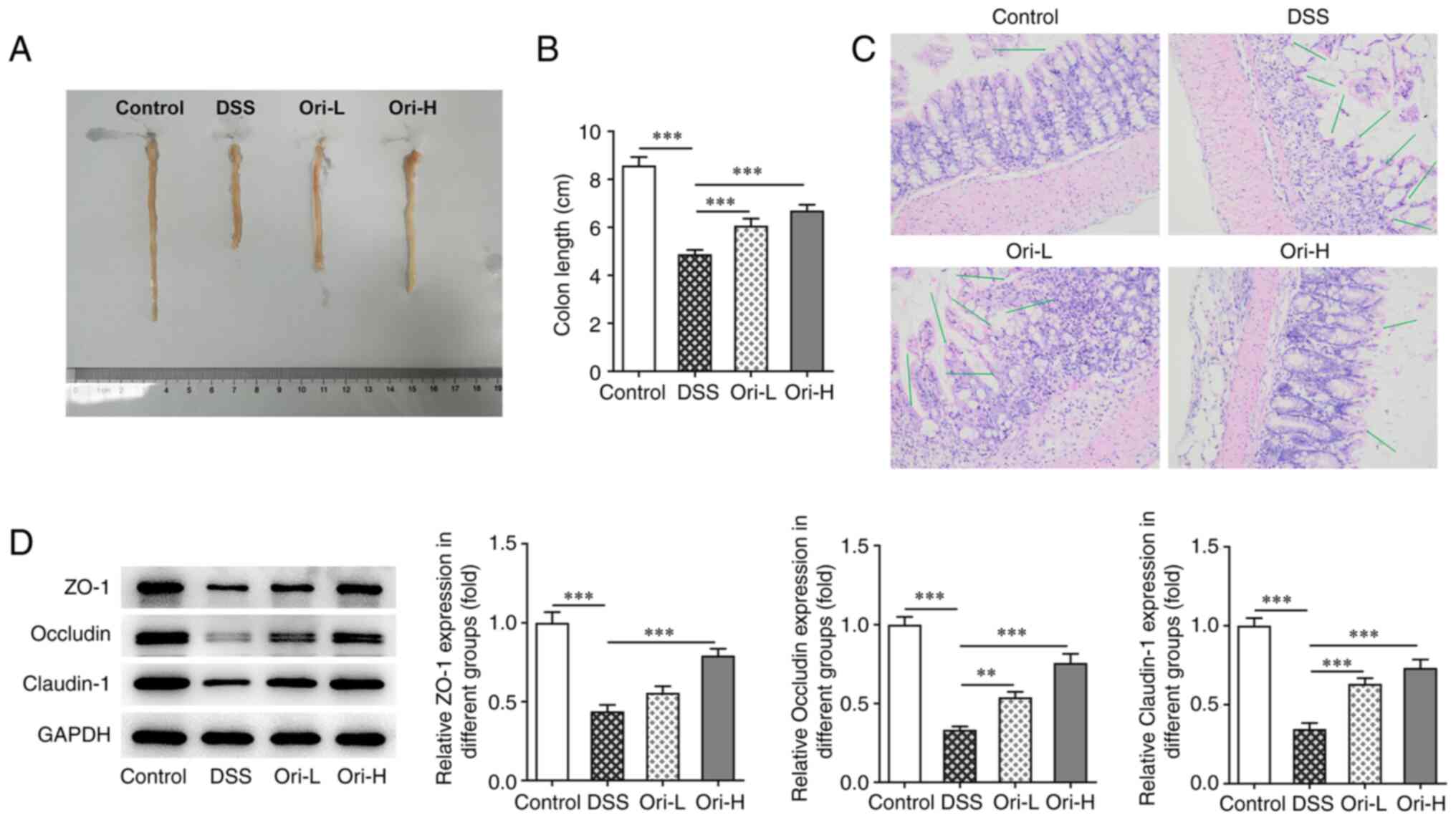
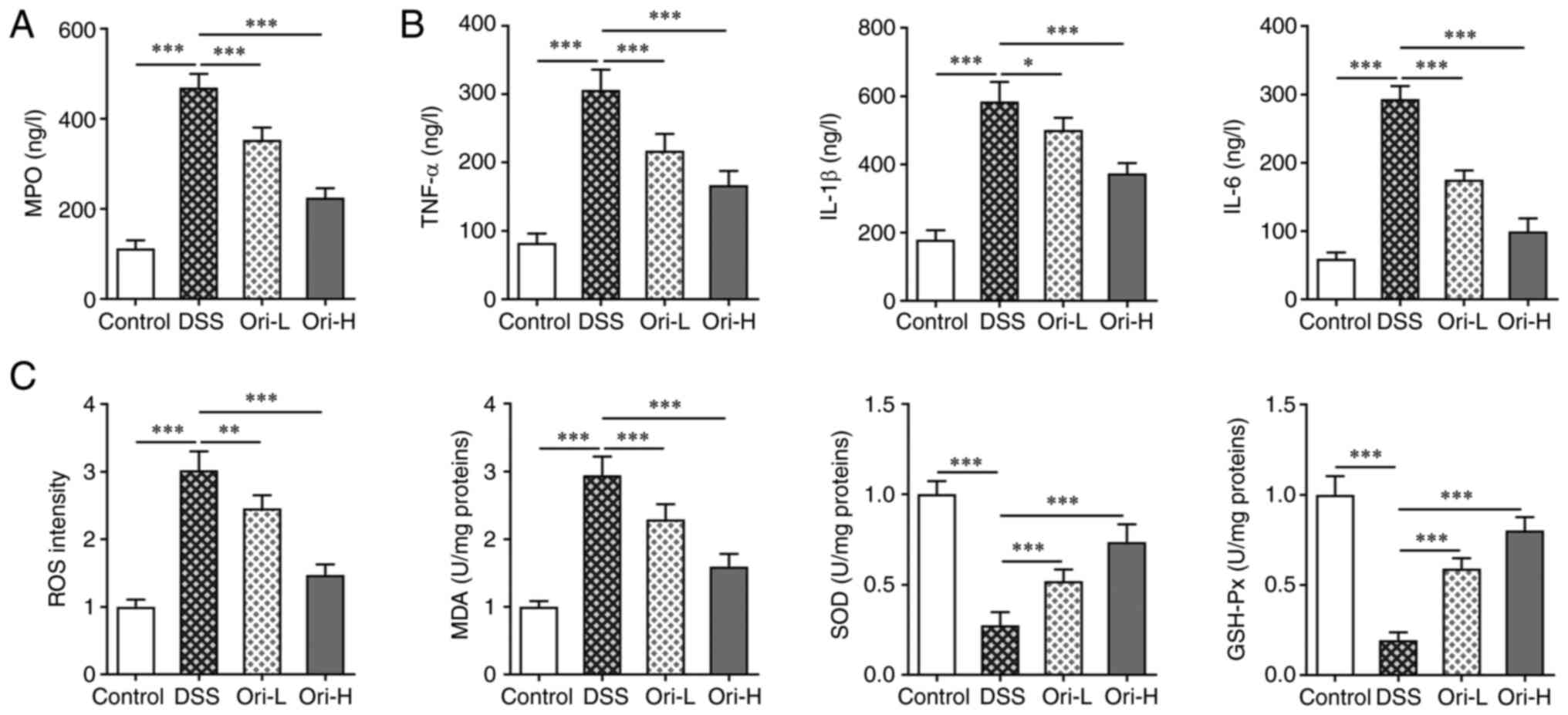
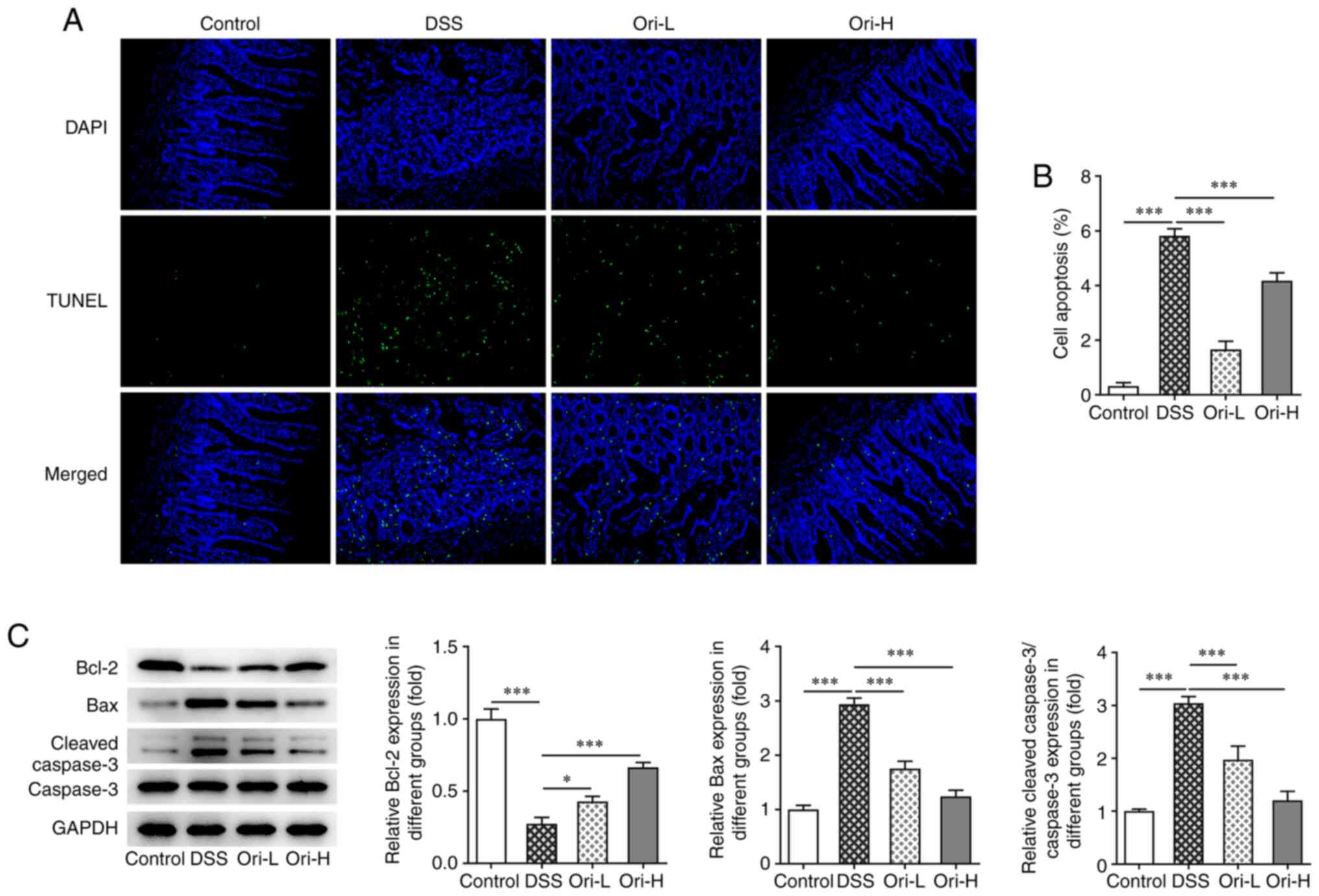
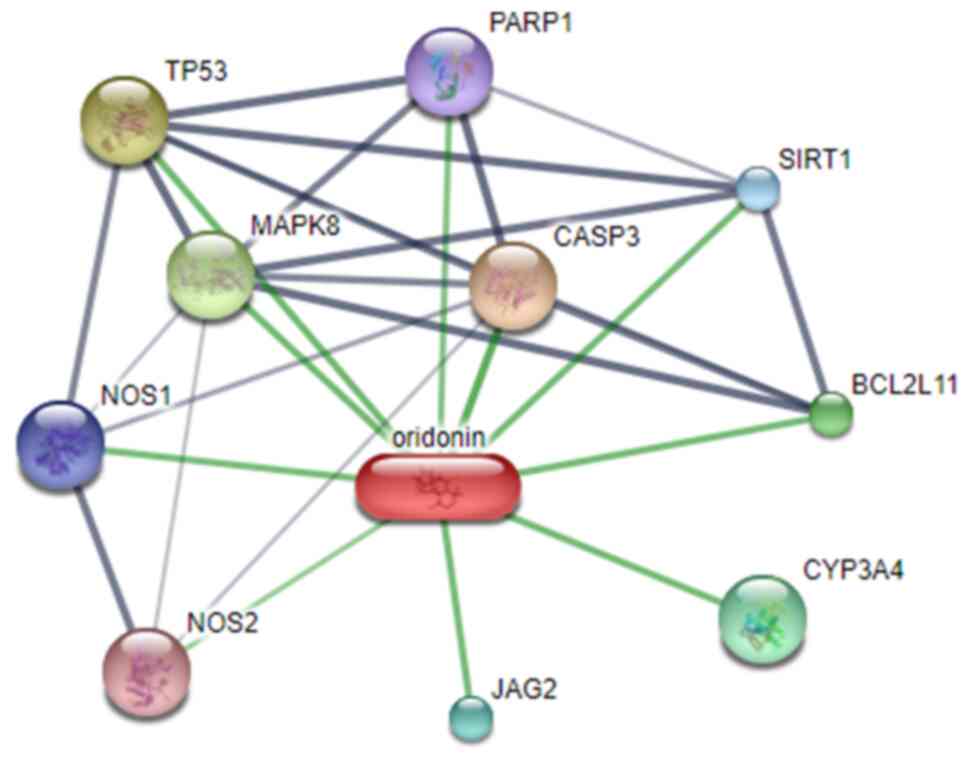
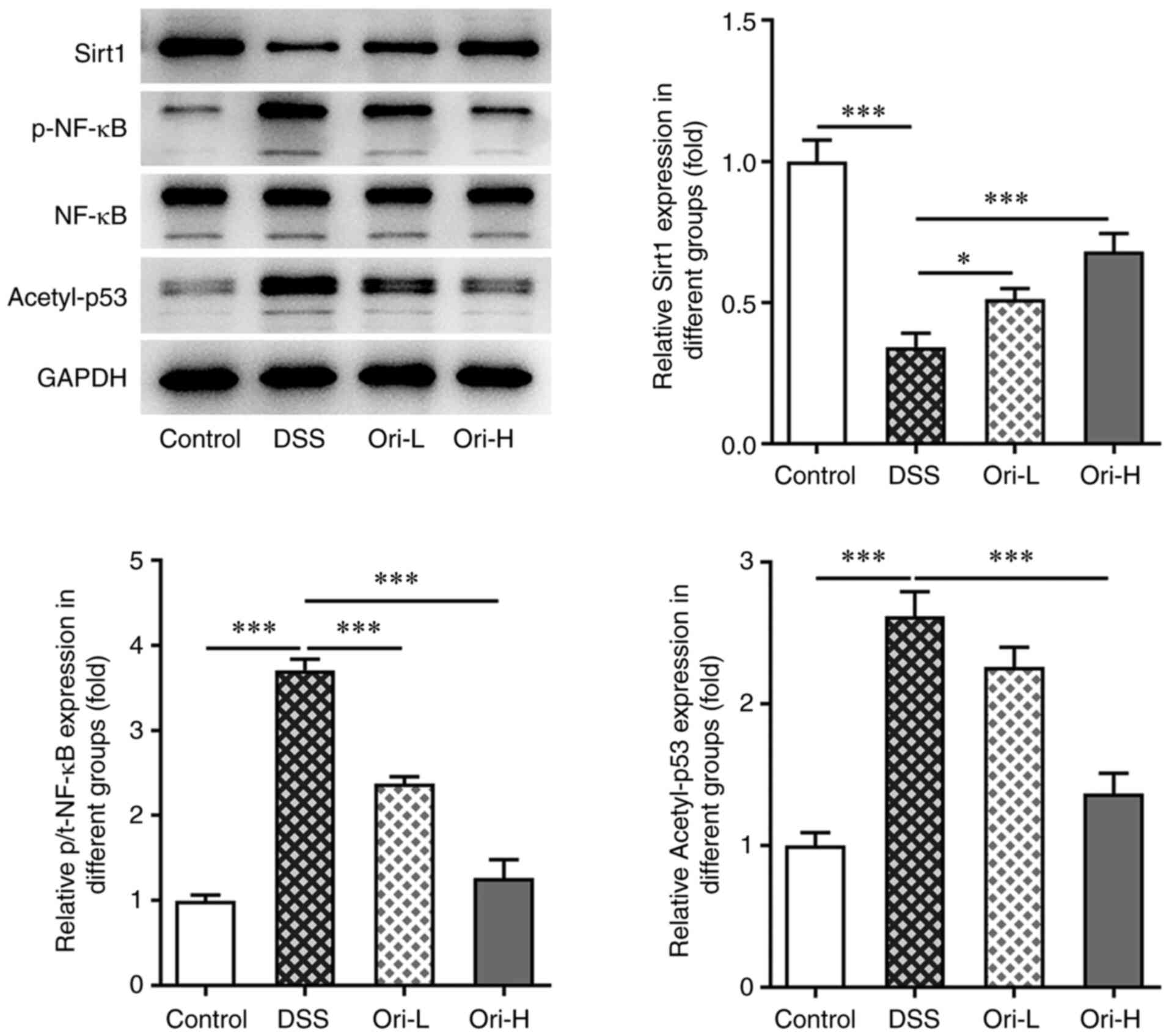
|
1
|
Huppertz-Hauss G, Hoivik ML,
Jelsness-Jorgensen LP, Opheim R, Henriksen M, Høie O, Hovde Ø,
Kempski-Monstad I, Solberg IC, Jahnsen J, et al: Fatigue in a
population-based cohort of patients with inflammatory bowel disease
20 years after diagnosis: The IBSEN study. Scand J Gastroenterol.
52:351–358. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Snider AJ, Bialkowska AB, Ghaleb AM, Yang
VW, Obeid LM and Hannun YA: Murine model for colitis-associated
cancer of the colon. Methods Mol Biol. 1438:245–254. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pandey A, Shen C and Man SM: Inflammasomes
in colitis and colorectal cancer: Mechanism of action and
therapies. Yale J Biol Med. 92:481–498. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Beamish LA, Osornio-Vargas AR and Wine E:
Air pollution: An environmental factor contributing to intestinal
disease. J Crohns Colitis. 5:279–286. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kucharzik T, Koletzko S, Kannengiesser K
and Dignass A: Ulcerative colitis-diagnostic and therapeutic
algorithms. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 117:564–574. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang J, Wong YK and Liao F: What has
traditional Chinese medicine delivered for modern medicine? Expert
Rev Mol Med. 20:e42018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yan YX, Shao MJ, Qi Q, Xu YS, Yang XQ, Zhu
FH, He SJ, He PL, Feng CL, Wu YW, et al: Artemisinin analogue SM934
ameliorates DSS-induced mouse ulcerative colitis via suppressing
neutrophils and macrophages. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 39:1633–1644.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen M, Ding Y and Tong Z: Efficacy and
safety of sophora flavescens (Kushen) based traditional Chinese
medicine in the treatment of ulcerative colitis: Clinical evidence
and potential mechanisms. Front Pharmacol. 11:6034762020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang S, Zhong Z, Wan J, Tan W, Wu G, Chen
M and Wang Y: Oridonin induces apoptosis inhibits migration and
invasion on highly-metastatic human breast cancer cells. Am J Chin
Med. 41:177–196. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zou BH, Tan YH, Deng WD, Zheng JH, Yang Q,
Ke MH, Ding ZB and Li XJ: Oridonin ameliorates inflammation-induced
bone loss in mice via suppressing DC-STAMP expression. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 42:744–754. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yan Y, Tan RZ, Liu P, Li JC, Zhong X, Liao
Y, Lin X, Wei C and Wang L: Oridonin alleviates IRI-induced kidney
injury by inhibiting inflammatory response of macrophages via
AKT-related pathways. Med Sci Monit. 26:e9211142020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shao YY, Guo Y, Feng XJ, Liu JJ, Chang ZP,
Deng GF, Xu D, Gao JP and Hou RG: Oridonin attenuates TNBS-induced
post-inflammatory irritable bowel syndrome via PXR/NF-κB signaling.
Inflammation. 44:645–658. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu QQ, Wang HL, Chen K, Wang SB, Xu Y, Ye
Q and Sun YW: Oridonin derivative ameliorates experimental colitis
by inhibiting activated T-cells and translocation of nuclear
factor-kappa B. J Dig Dis. 17:104–112. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ma Z, Hu C and Zhang Y: Therapeutic effect
of Rabdosia rubescens aqueous extract on chronic pharyngitis and
its safety. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 36:170–173.
2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ren MT, Gu ML, Zhou XX, Yu MS, Pan HH, Ji
F and Ding CY: Sirtuin 1 alleviates endoplasmic reticulum
stress-mediated apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells in
ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol. 25:5800–5813. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang K, Li YF, Lv Q, Li XM, Dai Y and Wei
ZF: Bergenin acting as an agonist of PPARgamma, ameliorates
experimental colitis in mice through improving expression of SIRT1,
and Therefore Inhibiting NF-κB-mediated macrophage activation.
Front Pharmacol. 8:9812017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pu Z, Liu Y, Li C, Xu M, Xie H and Zhao J:
Using network pharmacology for systematic understanding of
geniposide in ameliorating inflammatory responses in colitis
through suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome in macrophage by
AMPK/Sirt1 dependent signaling. Am J Chin Med. 48:1693–1713. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yan C, Yan H, Mao J, Liu Y, Xu L, Zhao H,
Shen J, Cao Y, Gao Y, Li K and Jin W: Neuroprotective effect of
oridonin on traumatic brain injury via inhibiting NLRP3
inflammasome in experimental mice. Front Neurosci. 14:5571702020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chaudhary G, Mahajan UB, Goyal SN, Ojha S,
Patil CR and Subramanya SB: Protective effect of Lagerstroemia
speciosa against dextran sulfate sodium induced ulcerative colitis
in C57BL/6 mice. Am J Transl Res. 9:1792–1800. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Szklarczyk D, Santos A, von Mering C,
Jensen LJ, Bork P and Kuhn M: STITCH 5: Augmenting protein-chemical
interaction networks with tissue and affinity data. Nucleic Acids
Res. 44(D1): D380–D384. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Oh SY, Cho KA, Kang JL, Kim KH and Woo SY:
Comparison of experimental mouse models of inflammatory bowel
disease. Int J Mol Med. 33:333–340. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang H, Lv H, Li H, Ci X and Peng L:
Oridonin protects LPS-induced acute lung injury by modulating
Nrf2-mediated oxidative stress and Nrf2-independent NLRP3 and NF-κB
pathways. Cell Commun Signal. 17:622019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang J, Zhang C, Guo C and Li X: Chitosan
ameliorates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis mice by enhancing
intestinal barrier function and improving microflora. Int J Mol
Sci. 20:57512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|