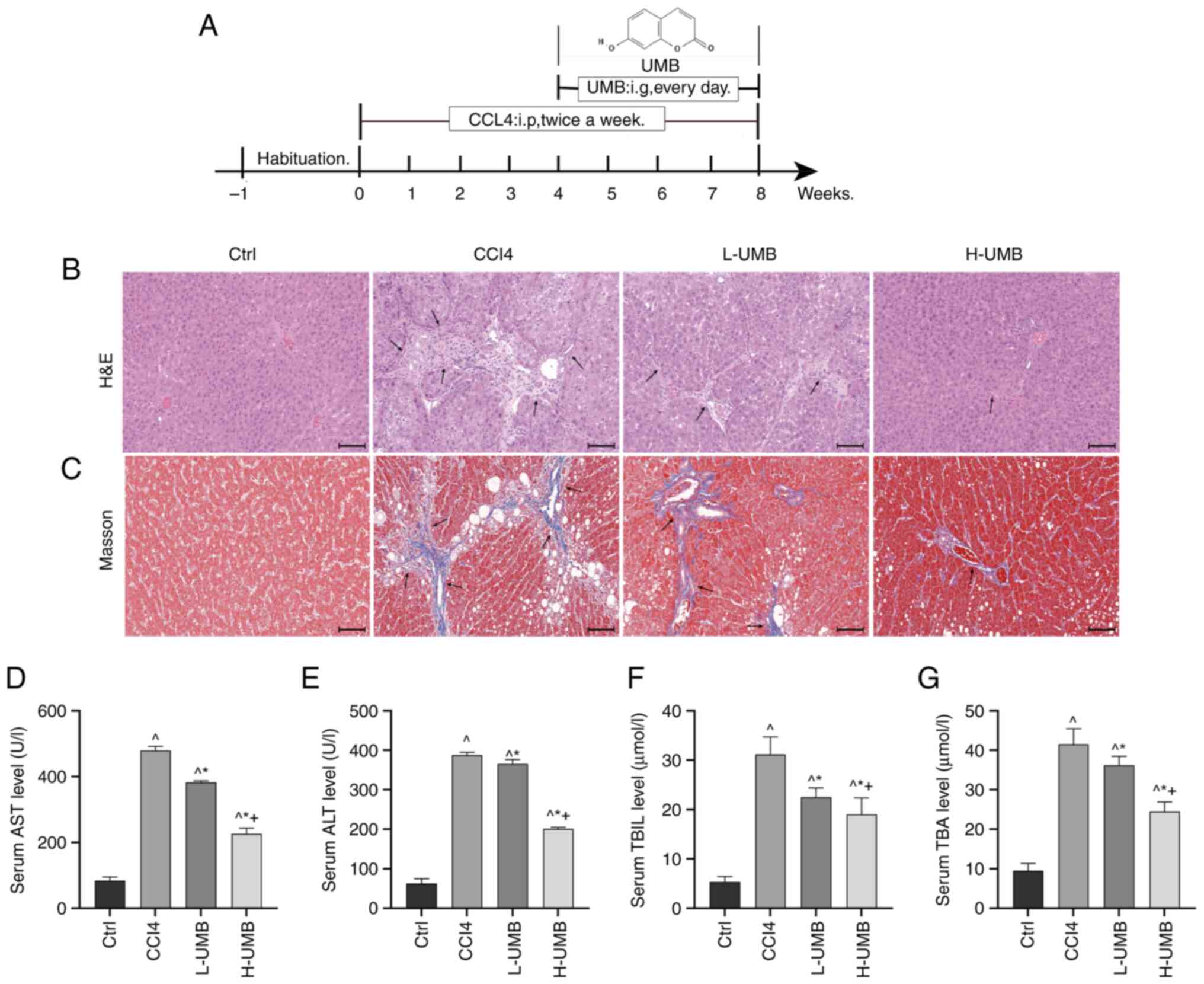
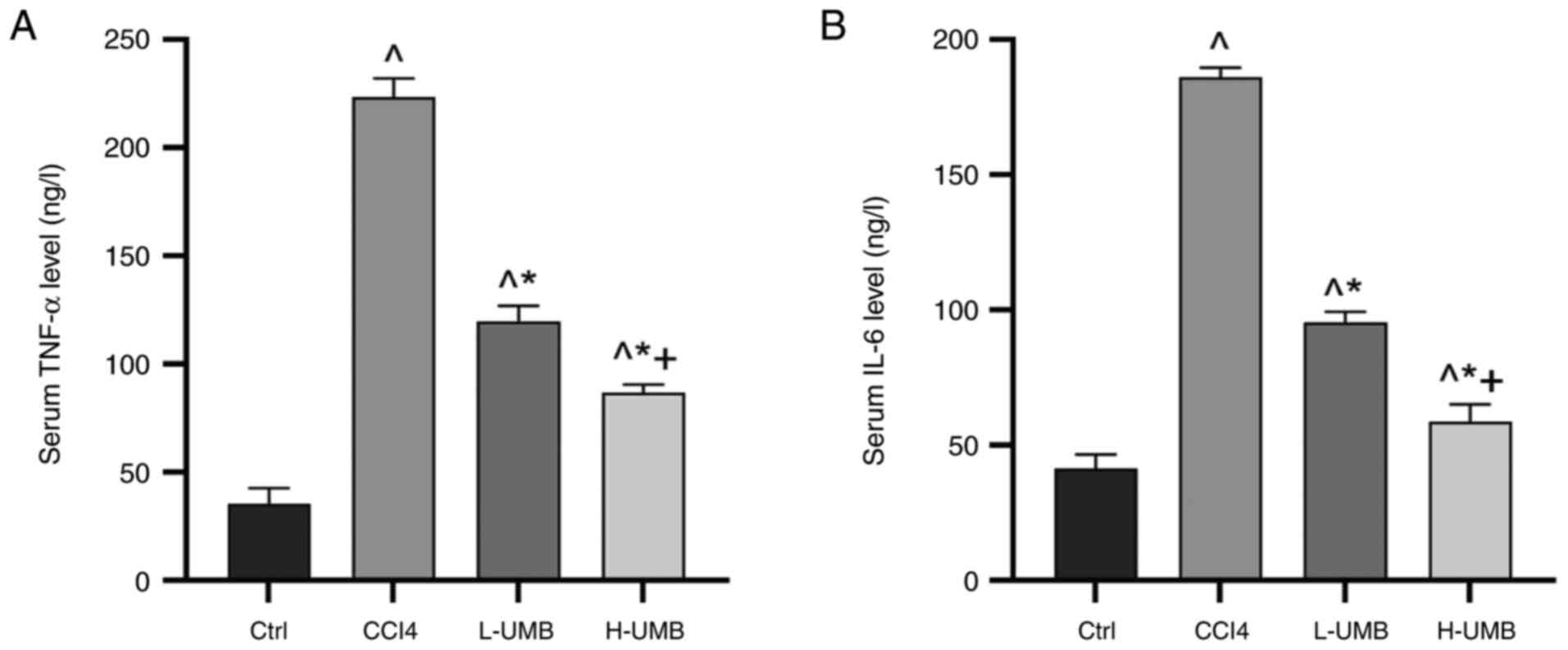
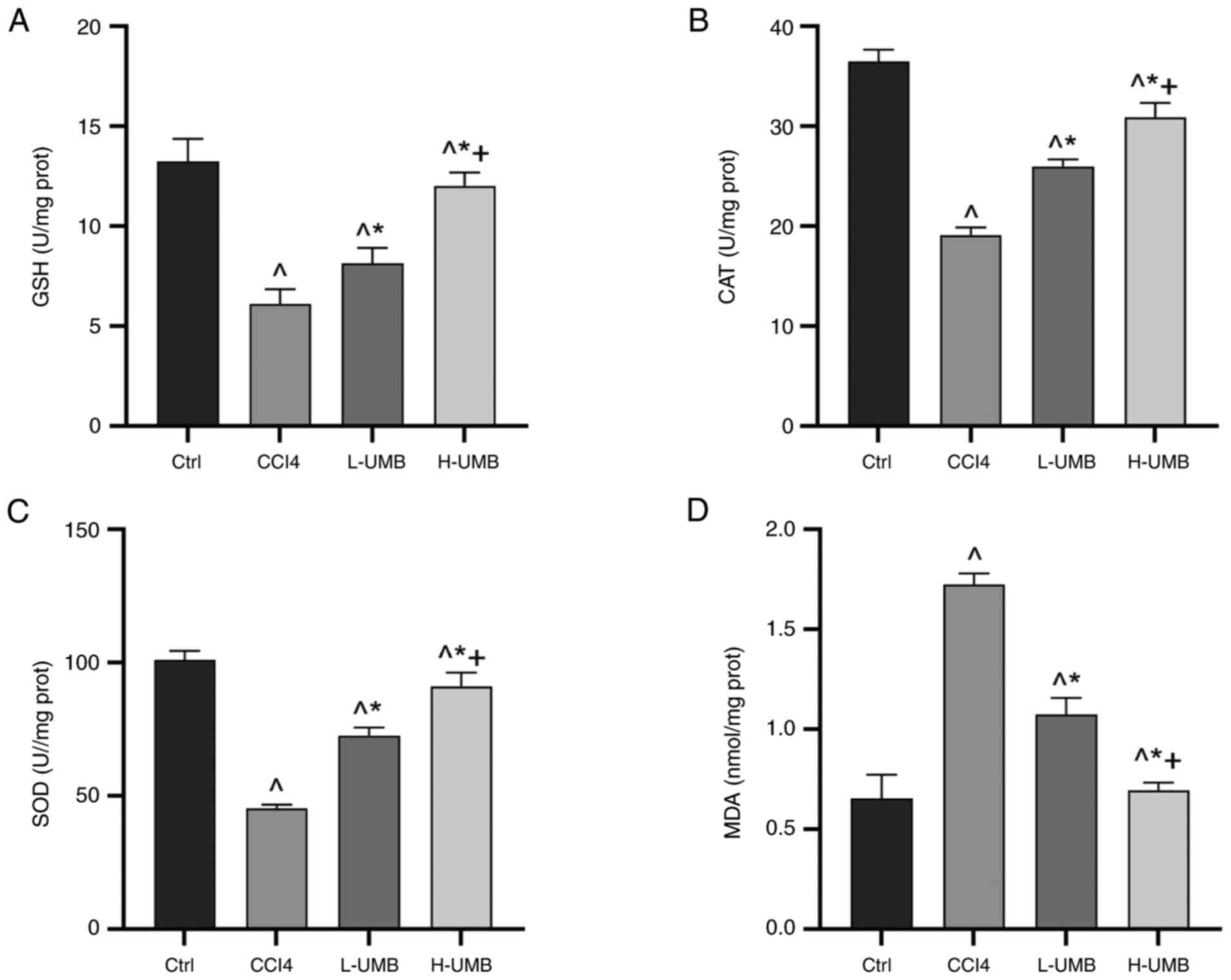
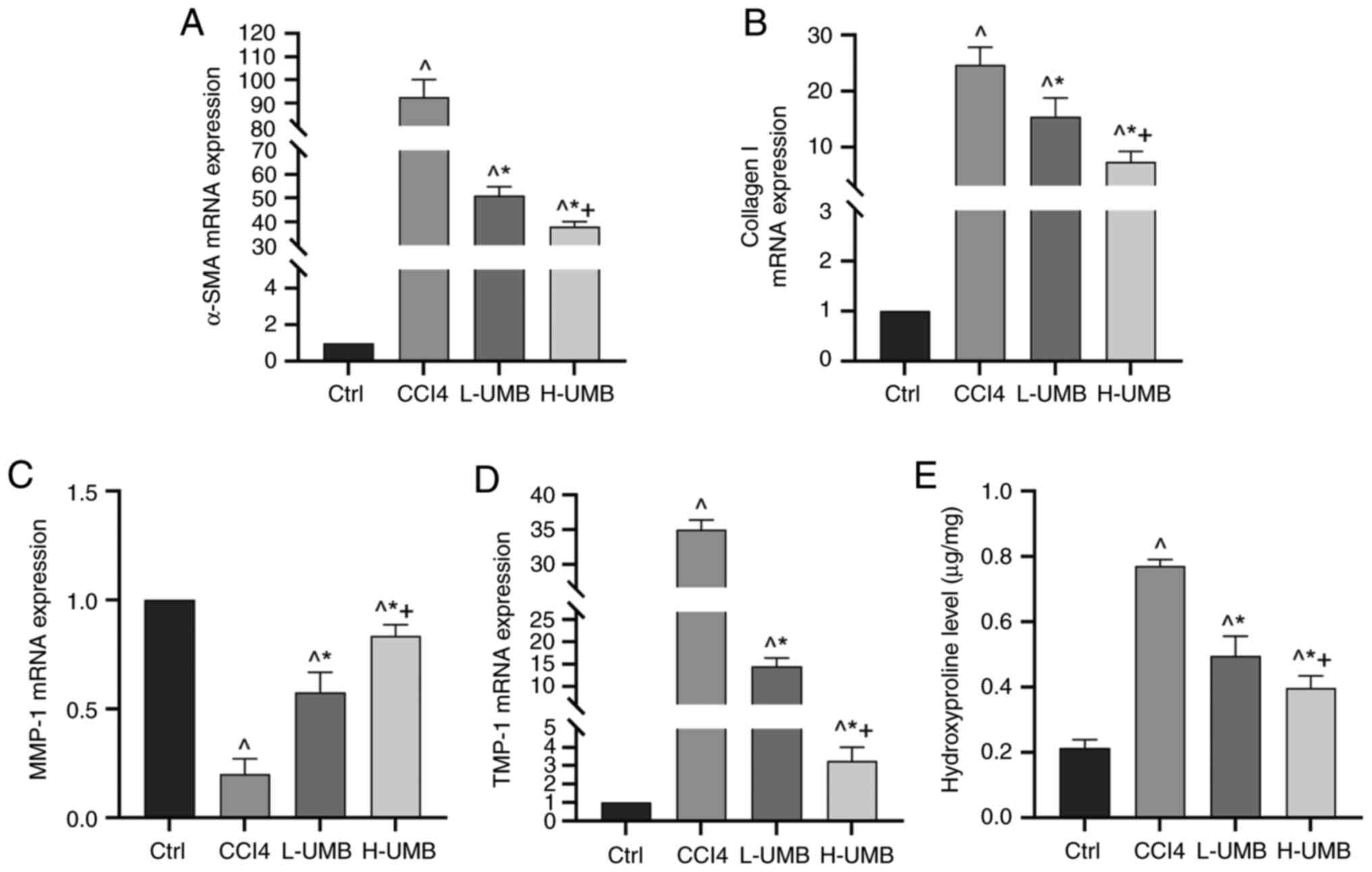
|
1
|
Pimpin L, Cortez-Pinto H, Negro F,
Corbould E, Lazarus JV, Webber L and Sheron N; EASL HEPAHEALTH
Steering Committee, : Burden of liver disease in Europe:
Epidemiology and analysis of risk factors to identify prevention
policies. J Hepatol. 69:718–735. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Caligiuri A, Gentilini A, Pastore M, Gitto
S and Marra F: Cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying liver
fibrosis regression. Cells. 10:27592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dawood RM, El-Meguid MA, Salum GM and El
Awady MK: Key players of hepatic fibrosis. J Interferon Cytokine
Res. 40:472–489. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Khanam A, Saleeb PG and Kottilil S:
Pathophysiology and treatment options for hepatic fibrosis: Can it
be completely cured? Cells. 10:10972021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Friedman SL: Hepatic fibrosis-overview.
Toxicology. 254:120–129. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ezhilarasan D, Sokal E and Najimi M:
Hepatic fibrosis: It is time to go with hepatic stellate
cell-specific therapeutic targets. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int.
17:192–197. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang Y, Deng X and Liang J: Modulation of
hepatic stellate cells and reversibility of hepatic fibrosis. Exp
Cell Res. 352:420–426. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang X, Zeng Y, Zhao L, Xu Q, Miao D and
Yu F: Targeting hepatic stellate cell death to reverse hepatic
fibrosis. Curr Drug Targets. 24:568–583. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Albanis E and Friedman SL: Hepatic
fibrosis. Pathogenesis and principles of therapy. Clin Liver Dis.
5:315–334. v–vi. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brenner DA, Waterboer T, Choi SK,
Lindquist JN, Stefanovic B, Burchardt E, Yamauchi M, Gillan A and
Rippe RA: New aspects of hepatic fibrosis. J Hepatol. 32 (1
Suppl):S32–S38. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gressner AM, Weiskirchen R, Breitkopf K
and Dooley S: Roles of TGF-beta in hepatic fibrosis. Front Biosci.
7:d793–d807. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hu HH, Chen DQ, Wang YN, Feng YL, Cao G,
Vaziri ND and Zhao YY: New insights into TGF-β/Smad signaling in
tissue fibrosis. Chem Biol Interact. 292:76–83. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu F, Liu C, Zhou D and Zhang L:
TGF-β/SMAD pathway and its regulation in hepatic fibrosis. J
Histochem Cytochem. 64:157–167. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Smith ME and Bauer-Wu S: Traditional
Chinese medicine for cancer-related symptoms. Semin Oncol Nurs.
28:64–74. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shan L, Liu Z, Ci L, Shuai C, Lv X and Li
J: Research progress on the anti-hepatic fibrosis action and
mechanism of natural products. Int Immunopharmacol. 75:1057652019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kornicka A, Balewski Ł, Lahutta M and
Kokoszka J: Umbelliferone and its synthetic derivatives as suitable
molecules for the development of agents with biological activities:
A review of their pharmacological and therapeutic potential.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 16:17322023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kassim NK, Rahmani M, Ismail A, Sukari MA,
Ee GC, Nasir NM and Awang K: Antioxidant activity-guided separation
of coumarins and lignan from Melicope glabra (Rutaceae). Food Chem.
139:87–92. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hassanein EHM, Hader HF, Elmansy RA,
Seleem HS, Elfiky M, Mohammedsaleh ZM, Ali FEM and Abd-Elhamid TH:
Umbelliferone alleviates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion-induced
oxidative stress injury via targeting Keap-1/Nrf-2/ARE and
TLR4/NF-κB-p65 signaling pathway. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int.
28:67863–67879. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu SM, Hu DH and Zhang JJ: Umbelliferone
exhibits anticancer activity via the induction of apoptosis and
cell cycle arrest in HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Med
Rep. 12:3869–3873. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vázquez JJ: Ground-glass hepatocytes:
light and electron microscopy. Characterization of the different
types. Histol Histopathol. 5:379–386. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Iezzoni JC: Diagnostic histochemistry in
hepatic pathology. Semin Diagn Pathol. 35:381–389. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sharma P: Value of liver function tests in
cirrhosis. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 12:948–964. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Farooqui N and Elhence A: Shalimar: A
current understanding of bile acids in chronic liver disease. J
Clin Exp Hepatol. 12:155–173. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Koyama Y and Brenner DA: Liver
inflammation and fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 127:55–64. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Finkel T: Oxidant signals and oxidative
stress. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 15:247–254. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sánchez-Valle V, Chávez-Tapia NC, Uribe M
and Méndez-Sánchez N: Role of oxidative stress and molecular
changes in liver fibrosis: A review. Curr Med Chem. 19:4850–4860.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Foyer CH and Noctor G: Redox homeostasis
and antioxidant signaling: A metabolic interface between stress
perception and physiological responses. Plant Cell. 17:1866–1875.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tsikas D: Assessment of lipid peroxidation
by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological
samples: Analytical and biological challenges. Anal Biochem.
524:13–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li Y, Fan W, Link F, Wang S and Dooley S:
Transforming growth factor β latency: A mechanism of cytokine
storage and signalling regulation in liver homeostasis and disease.
JHEP Rep. 4:1003972022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Naim A, Pan Q and Baig MS: Matrix
metalloproteinases (MMPs) in liver diseases. J Clin Exp Hepatol.
7:367–372. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dewidar B, Meyer C, Dooley S and
Meindl-Beinker AN: TGF-β in hepatic stellate cell activation and
liver fibrogenesis-updated 2019. Cells. 8:14192019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dhar D, Baglieri J, Kisseleva T and
Brenner DA: Mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its role in liver
cancer. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 245:96–108. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tsuchida T and Friedman SL: Mechanisms of
hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
14:397–411. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang M, Serna-Salas S, Damba T, Borghesan
M, Demaria M and Moshage H: Hepatic stellate cell senescence in
liver fibrosis: Characteristics, mechanisms and perspectives. Mech
Ageing Dev. 199:1115722021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mahmoud AM, Hozayen WG, Hasan IH, Shaban E
and Bin-Jumah M: Umbelliferone ameliorates CCl4-induced liver
fibrosis in rats by upregulating PPARγ and attenuating oxidative
stress, inflammation, and TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling. Inflammation.
42:1103–1116. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sim MO, Lee HI, Ham JR, Seo KI, Kim MJ and
Lee MK: Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of umbelliferone
in chronic alcohol-fed rats. Nutr Res Pract. 9:364–369. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang M and Zhang ST: Cells in fibrosis
and fibrotic diseases. Front Immunol. 11:11422020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Schuppan D, Ashfaq-Khan M, Yang AT and Kim
YO: Liver fibrosis: Direct antifibrotic agents and targeted
therapies. Matrix Biol. 68–69. 435–451. 2018.
|
|
40
|
Cui N, Hu M and Khalil RA: Biochemical and
biological attributes of matrix metalloproteinases. Prog Mol Biol
Transl Sci. 147:1–73. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Arakaki PA, Marques MR and Santos MC:
MMP-1 polymorphism and its relationship to pathological processes.
J Biosci. 34:313–320. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Iredale JP: Tissue inhibitors of
metalloproteinases in liver fibrosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
29:43–54. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gorrini C, Harris IS and Mak TW:
Modulation of oxidative stress as an anticancer strategy. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 12:931–947. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li S, Tan HY, Wang N, Zhang ZJ, Lao L,
Wong CW and Feng Y: The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants
in liver diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 16:26087–26124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Baghy K, Iozzo RV and Kovalszky I:
Decorin-TGFβ axis in hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. J Histochem
Cytochem. 60:262–268. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Meng XM, Nikolic-Paterson DJ and Lan HY:
TGF-β: the master regulator of fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol.
12:325–338. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang K, Fang S, Liu Q, Gao J, Wang X, Zhu
H, Zhu Z, Ji F, Wu J, Ma Y, et al: TGF-β1/p65/MAT2A pathway
regulates liver fibrogenesis via intracellular SAM. EBioMedicine.
42:458–469. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Filali-Mouncef Y, Hunter C, Roccio F,
Zagjou S, Dupont N, Primard C, Proikas-Cezann T and Reggiori F: The
ménage à trois of autophagy, lipid droplets and liver disease.
Autophagy. 18:50–72. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
De Oliveira da Silva B, Ramos LF and
Moraes KCM: Molecular interplays in hepatic stellate cells:
Apoptosis, senescence, and phenotype reversion as cellular
connections that modulate liver fibrosis. Cell Biol Int.
41:946–959. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tacke F and Weiskirchen R: Update on
hepatic stellate cells: Pathogenic role in liver fibrosis and novel
isolation techniques. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 6:67–80.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Weiskirchen R and Tacke F: Cellular and
molecular functions of hepatic stellate cells in inflammatory
responses and liver immunology. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 3:344–363.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|