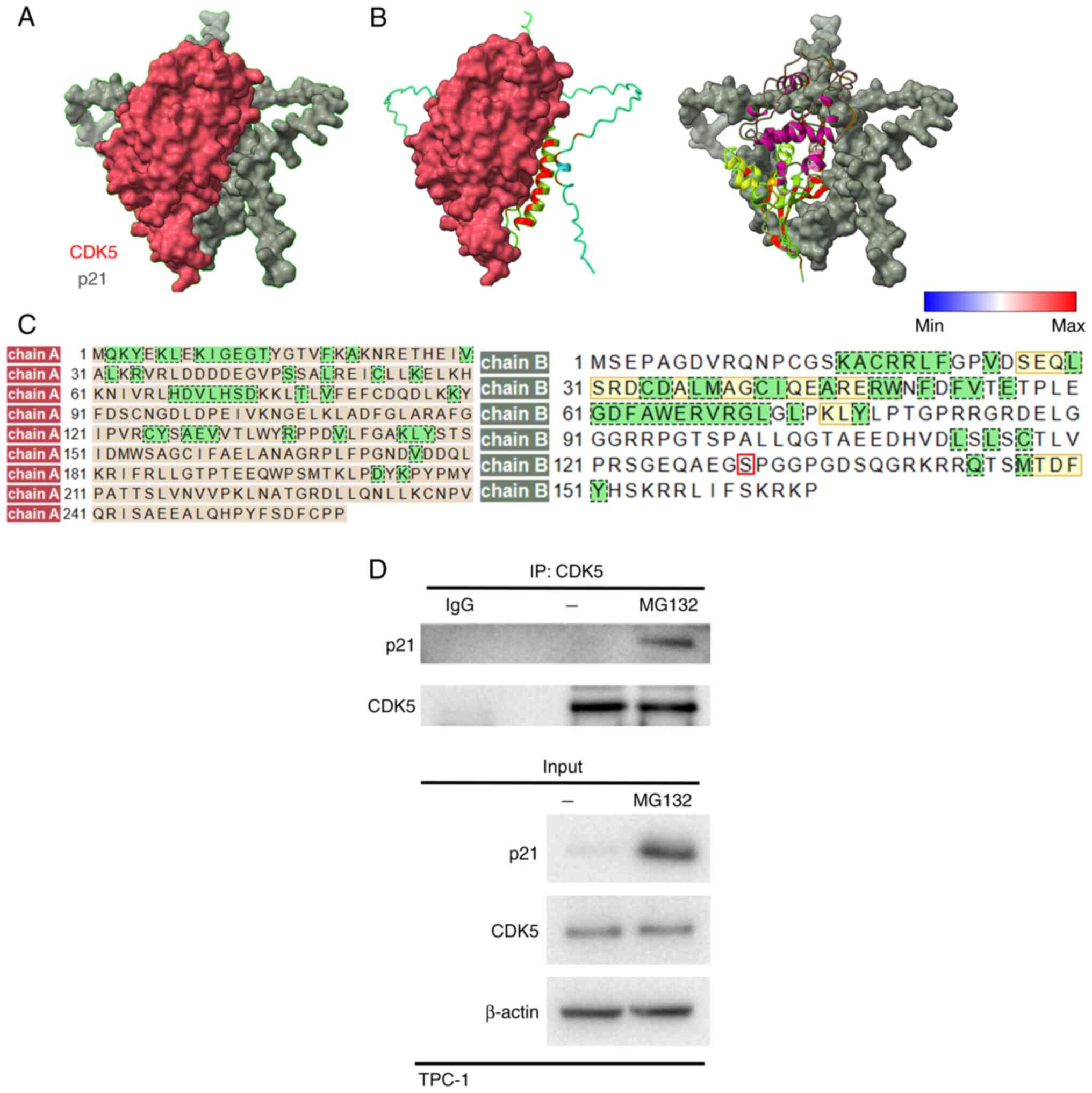
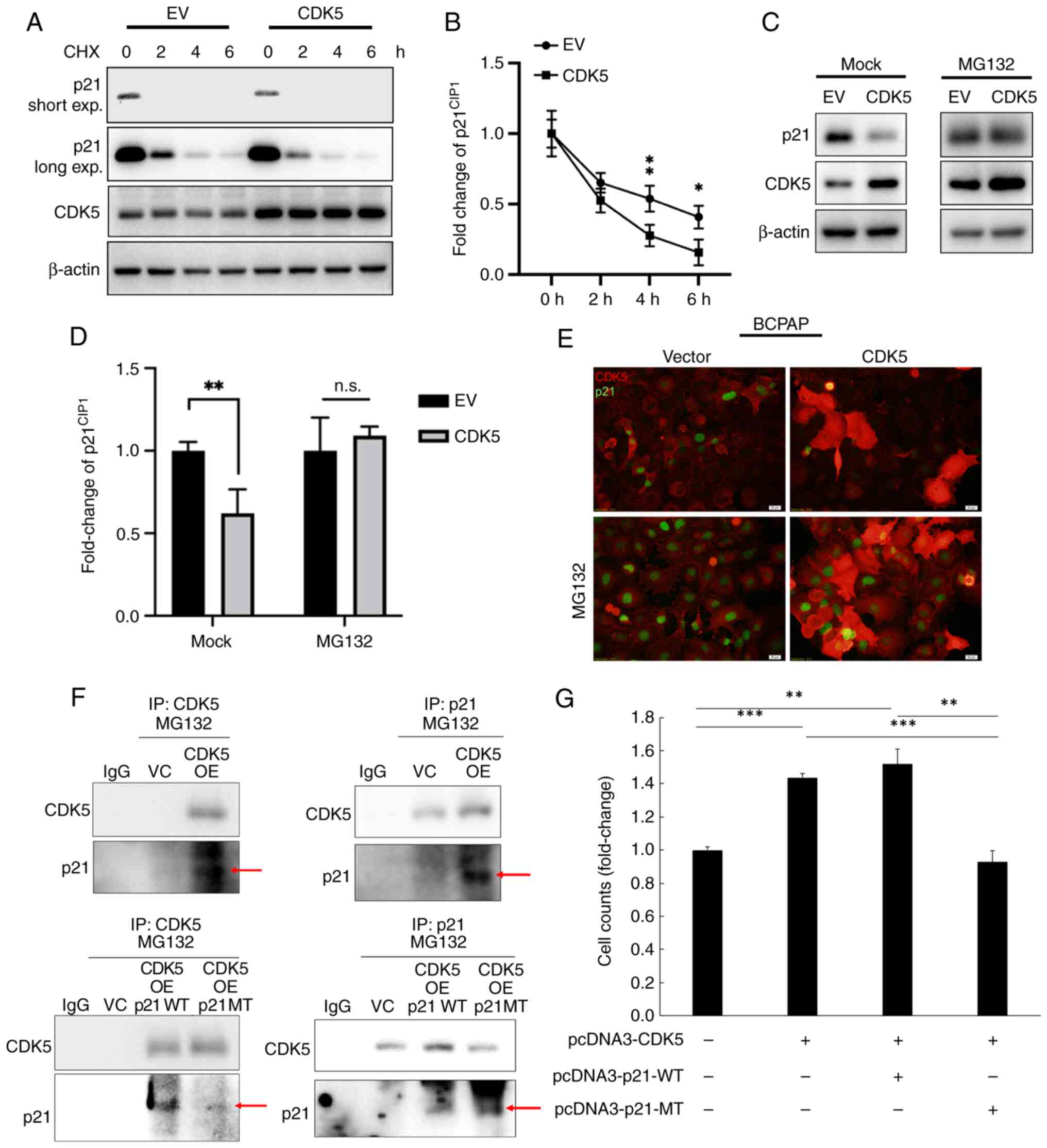
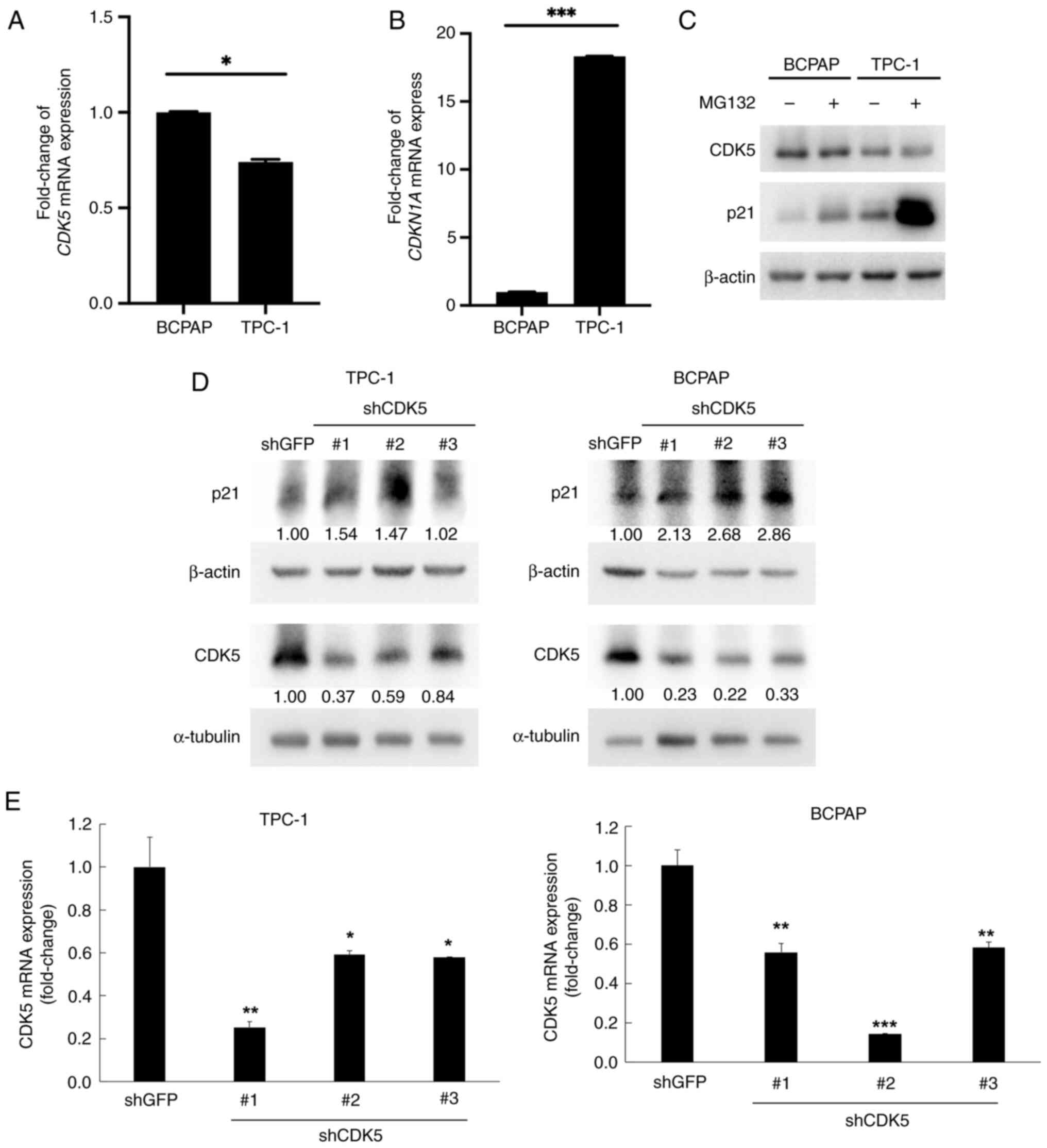
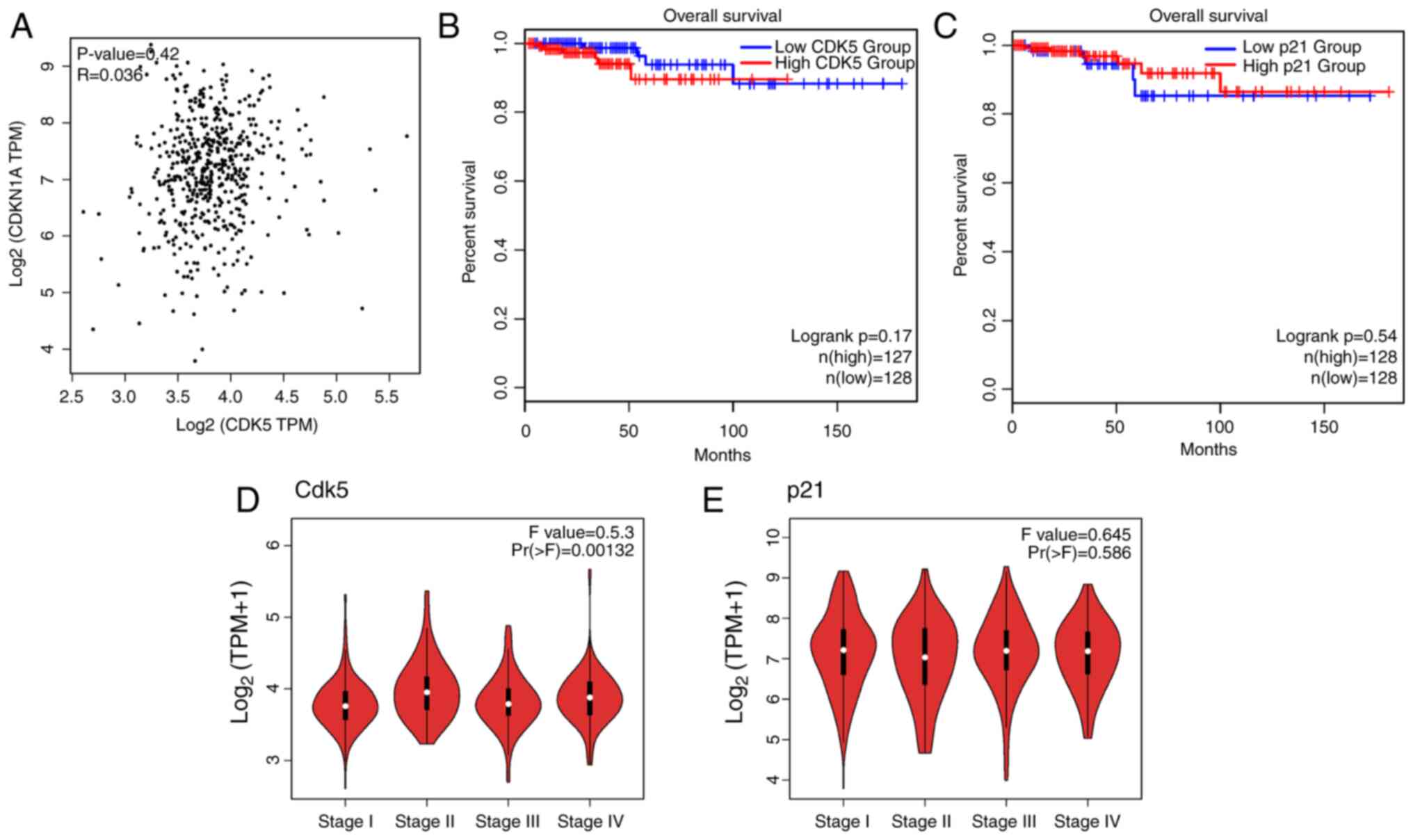
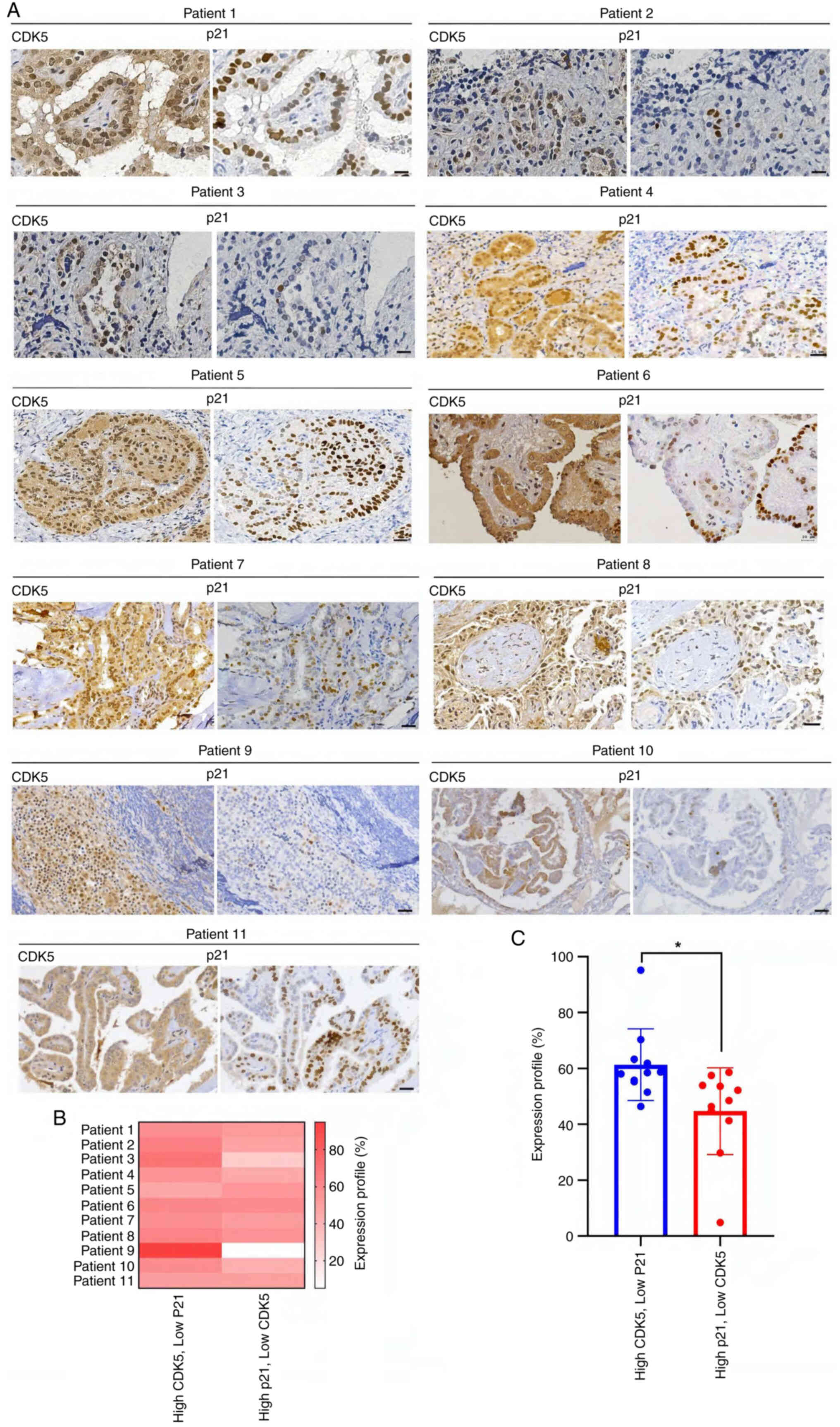
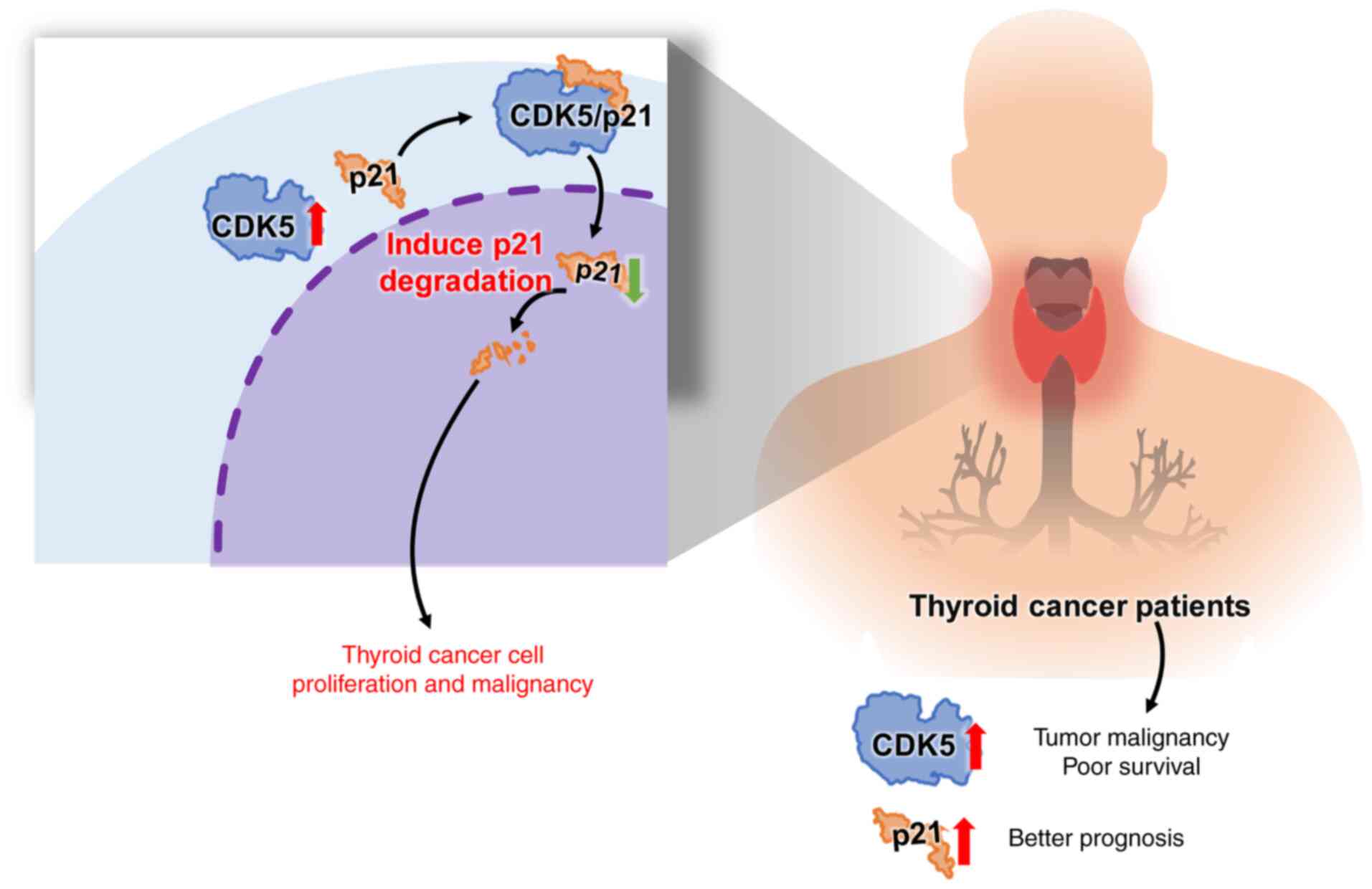
|
1
|
Oner M, Lin E, Chen MC, Hsu FN, Shazzad
Hossain Prince GM, Chiu KY, Teng CJ, Yang TY, Wang HY, Yue CH, et
al: Future aspects of CDK5 in prostate cancer: From pathogenesis to
therapeutic implications. Int J Mol Sci. 20:38812019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Oner M, Chen MC, Cheng PT, Li YH, Cheng
YC, Celik A, Soong SW, Hsu LW, Lin DY, Hossain Prince GMS, et al:
Impact of metformin on neocortical development during pregnancy:
Involvement of ERK and p35/CDK5 pathways. Chemosphere.
358:1421242024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Oner M, Chen MC, Cheng PT and Lin H:
Metformin inhibits nerve growth factor-induced sympathetic neuron
differentiation through p35/CDK5 inhibition. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 326:C1648–C1658. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Oner M, Cheng PT, Wang HY, Chen MC and Lin
H: Metformin alters dendrite development and synaptic plasticity in
rat cortical neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 710:1498742024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Oner M, Lin E, Chiu KY, Chen MC, Prince
GMSH, Lai CH, Hsieh JT, Wang HY and Lin HO: p35/CDK5 regulates
bladder cancer proliferation and migration and promotes higher
tumor grade and poor survival rate in patients with bladder cancer.
Anticancer Res. 44:543–553. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yue CH, Oner M, Chiu CY, Chen MC, Teng CL,
Wang HY, Hsieh JT, Lai CH and Lin H: RET Regulates human medullary
thyroid cancer cell proliferation through CDK5 and STAT3
activation. Biomolecules. 11:8602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen MC, Chen KC, Chang GC, Lin H, Wu CC,
Kao WH, Teng CJ, Hsu SL and Yang TY: RAGE acts as an oncogenic role
and promotes the metastasis of human lung cancer. Cell Death Dis.
11:2652020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen MC, Huang CY, Hsu SL, Lin E, Ku CT,
Lin H and Chen CM: Retinoic acid induces apoptosis of prostate
cancer DU145 cells through cdk5 overactivation. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2012:5807362012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hsu FN, Chen MC, Lin KC, Peng YT, Li PC,
Lin E, Chiang MC, Hsieh JT and Lin H: Cyclin-dependent kinase 5
modulates STAT3 and androgen receptor activation through
phosphorylation of Ser727 on STAT3 in prostate cancer
cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 305:E975–E986. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kuo HS, Hsu FN, Chiang MC, You SC, Chen
MC, Lo MJ and Lin H: The role of Cdk5 in retinoic acid-induced
apoptosis of cervical cancer cell line. Chin J Physiol. 52:23–30.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lin E, Chen MC, Huang CY, Hsu SL, Huang
WJ, Lin MS, Wu JC and Lin H: All-trans retinoic acid induces DU145
cell cycle arrest through Cdk5 activation. Cell Physiol Biochem.
33:1620–1630. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin H, Chen MC, Chiu CY, Song YM and Lin
SY: Cdk5 regulates STAT3 activation and cell proliferation in
medullary thyroid carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 282:2776–2784.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin H, Chen MC and Ku CT: Cyclin-dependent
kinase 5 regulates steroidogenic acute regulatory protein and
androgen production in mouse Leydig cells. Endocrinology.
150:396–403. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Prince G, Yang TY, Lin H and Chen MC:
Mechanistic insight of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 in modulating lung
cancer growth. Chin J Physiol. 62:231–240. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Teng CJ, Cheng PT, Cheng YC, Tsai JR, Chen
MC and Lin H: Dinaciclib inhibits the growth of acute myeloid
leukemia cells through either cell cycle-related or ERK1/STAT3/MYC
pathways. Toxicol In Vitro. 96:1057682024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Karimian A, Ahmadi Y and Yousefi B:
Multiple functions of p21 in cell cycle, apoptosis and
transcriptional regulation after DNA damage. DNA Repair (Amst).
42:63–71. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Foy R, Crozier L, Pareri AU, Valverde JM,
Park BH, Ly T and Saurin AT: Oncogenic signals prime cancer cells
for toxic cell overgrowth during a G1 cell cycle arrest. Mol Cell.
83:4047–4061.e6. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dimri GP, Nakanishi M, Desprez PY, Smith
JR and Campisi J: Inhibition of E2F activity by the
cyclin-dependent protein kinase inhibitor p21 in cells expressing
or lacking a functional retinoblastoma protein. Mol Cell Biol.
16:2987–2997. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nakanishi M, Kaneko Y, Matsushime H and
Ikeda K: Direct interaction of p21 cyclin-dependent kinase
inhibitor with the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 263:35–40. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hauge S, Macurek L and Syljuåsen RG: p21
limits S phase DNA damage caused by the Wee1 inhibitor MK1775. Cell
Cycle. 18:834–847. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pisonero-Vaquero S, Soldati C, Cesana M,
Ballabio A and Medina DL: TFEB modulates p21/WAF1/CIP1 during the
DNA damage response. Cells. 9:11862020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang PH, Chen MC, Peng YT, Kao WH, Chang
CH, Wang YC, Lai CH, Hsieh JT, Wang JH, Lee YT, et al: Cdk5
directly targets nuclear p21CIP1 and promotes cancer cell growth.
Cancer Res. 76:6888–6900. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Y, Zhang YJ, Zhao HY, Zhai QL, Zhang
Y and Shen YF: The impact of R213 mutation on p53-mediated p21
activity. Biochimie. 99:215–218. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen DW, Lang BHH, McLeod DSA, Newbold K
and Haymart MR: Thyroid cancer. Lancet. 401:1531–1544. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sinha RA and Yen PM: Metabolic messengers:
Thyroid hormones. Nat Metab. 6:639–650. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Basolo F, Macerola E, Poma AM and
Torregrossa L: The 5th edition of WHO classification of tumors of
endocrine organs: changes in the diagnosis of follicular-derived
thyroid carcinoma. Endocrine. 80:470–476. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Modica R, Benevento E and Colao A:
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and cancer: New perspectives
on an old relationship. J Endocrinol Invest. 46:667–677. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ijaz K and Yin F: Papillary thyroid
carcinoma with squamous dedifferentiation: A potential diagnostic
pitfall. Anticancer Res. 43:255–258. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ohashi R: Solid variant of papillary
thyroid carcinoma: An under-recognized entity. Endocr J.
67:241–248. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kang SY, Ahn HR, Youn HJ and Jung SH:
Prognosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma in relation to
preoperative subclinical hypothyroidism. Ann R Coll Surg Engl.
103:367–373. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee JS, Lee JS, Yun HJ, Kim SM, Chang H,
Lee YS, Chang HS and Park CS: Aggressive subtypes of papillary
thyroid carcinoma smaller than 1 cm. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
108:1370–1375. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mao J, Zhang Q, Zhang H, Zheng K, Wang R
and Wang G: Risk factors for lymph node metastasis in papillary
thyroid carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 11:2652020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu J, Deng Y, Liu T, Zhou J, Jia X, Xiao
T, Zhou S, Li J, Guo Y, Wang Y, et al: Lymph node metastasis
prediction of papillary thyroid carcinoma based on transfer
learning radiomics. Nat Commun. 11:48072020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang D, Zhu XL and Jiang J: Papillary
thyroid carcinoma with breast and bone metastasis. Ear Nose Throat
J. 102:259–262. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Daniels GH: Follicular thyroid carcinoma:
A perspective. Thyroid. 28:1229–1242. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pelizzo MR, Mazza EI, Mian C and Merante
Boschin I: Medullary thyroid carcinoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther.
23:943–957. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yang J and Barletta JA: Anaplastic thyroid
carcinoma. Semin Diagn Pathol. 37:248–256. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tjokorda Gde Dalem Pemayun, . Current
diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules. Acta Med Indones.
48:247–257. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Roman BR, Randolph GW and Kamani D:
Conventional thyroidectomy in the treatment of primary thyroid
cancer. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 48:125–141. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fullmer T, Cabanillas ME and Zafereo M:
Novel therapeutics in radioactive iodine-resistant thyroid cancer.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 12:7207232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Brierley JD: Update on external beam
radiation therapy in thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
96:2289–2295. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Salvatore D, Santoro M and Schlumberger M:
The importance of the RET gene in thyroid cancer and therapeutic
implications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 17:296–306. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Dong X, Akuetteh PDP, Song J, Ni C, Jin C,
Li H, Jiang W, Si Y, Zhang X, Zhang Q and Huang G: Major vault
protein (MVP) associated with BRAF V600E mutation is an
immune microenvironment-related biomarker promoting the progression
of papillary thyroid cancer via MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:6883702022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nikiforov YE and Nikiforova MN: Molecular
genetics and diagnosis of thyroid cancer. Nat Rev Endocrinol.
7:569–580. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nozhat Z and Hedayati M: PI3K/AKT Pathway
and its mediators in thyroid carcinomas. Mol Diagn Ther. 20:13–26.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chou CK, Chi SY, Hung YY, Yang YC, Fu HC,
Wang JH, Chen CC and Kang HY: Clinical impact of androgen
receptor-suppressing miR-146b expression in papillary thyroid
cancer aggressiveness. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 108:2852–2861.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cheng PT, Cheng YC, Oner M, Li YH, Chen
MC, Wu JH, Chang TC, Celik A, Liu FL, Wang HY, et al: Antrodia
salmonea extract inhibits cell proliferation through regulating
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in prostate cancer cell lines. Chin
J Physiol. 65:209–214. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chen CY, Li YH, Liao WL, Oner M, Cheng YC,
Liu FL, Cheng PT, Celik A, Wu JH, Lai CH, et al: Antrodia salmonea
extracts regulate p53-AR signaling and apoptosis in human prostate
cancer LNCaP cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2022:70331272022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Abramson J, Adler J, Dunger J, Evans R,
Green T, Pritzel A, Ronneberger O, Willmore L, Ballard AJ, Bambrick
J, et al: Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular
interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature. 630:493–500. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lee YK, Rovira A, Carroll PV and Simo R:
Management of aggressive variants of papillary thyroid cancer. Curr
Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 32:125–133. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Qu N, Chen D, Ma B, Zhang L, Wang Q, Wang
Y, Wang H, Ni Z, Wang W, Liao T, et al: Integrated proteogenomic
and metabolomic characterization of papillary thyroid cancer with
different recurrence risks. Nat Commun. 15:31752024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Coca-Pelaz A, Shah JP, Hernandez-Prera JC,
Ghossein RA, Rodrigo JP, Hartl DM, Olsen KD, Shaha AR, Zafereo M,
Suarez C, et al: Papillary thyroid cancer-aggressive variants and
impact on management: A narrative review. Adv Ther. 37:3112–3128.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Filetti S, Durante C, Hartl D, Leboulleux
S, Locati LD, Newbold K, Papotti MG and Berruti A; ESMO Guidelines
Committee. Electronic address, : simpleclinicalguidelines@esmo.org:
Thyroid cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis,
treatment and follow-up†. Ann Oncol. 30:1856–1883. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gunabushanam G: Perfluorobutane-enhanced
US helps differentiate benign lymph nodes from papillary thyroid
cancer metastases. Radiology. 307:e2305812023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Schonfeld SJ, Morton LM, Berrington de
Gonzalez A, Curtis RE and Kitahara CM: Risk of second primary
papillary thyroid cancer among adult cancer survivors in the United
States, 2000–2015. Cancer Epidemiol. 64:1016642020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Gao GB, Sun Y, Fang RD, Wang Y, Wang Y and
He QY: Post-translational modifications of CDK5 and their
biological roles in cancer. Mol Biomed. 2:222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Jin X, Yang C, Fan P, Xiao J, Zhang W,
Zhan S, Liu T, Wang D and Wu H: CDK5/FBW7-dependent ubiquitination
and degradation of EZH2 inhibits pancreatic cancer cell migration
and invasion. J Biol Chem. 292:6269–6280. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Mandl MM, Zhang S, Ulrich M, Schmoeckel E,
Mayr D, Vollmar AM and Liebl J: Inhibition of Cdk5 induces cell
death of tumor-initiating cells. Br J Cancer. 116:912–922. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Liu C, Zhai X, Zhao B, Wang Y and Xu Z:
Cyclin I-like (CCNI2) is a cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5)
activator and is involved in cell cycle regulation. Sci Rep.
7:409792017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhang J, Li H and Herrup K: Cdk5 nuclear
localization is p27-dependent in nerve cells: Implications for cell
cycle suppression and caspase-3 activation. J Biol Chem.
285:14052–14061. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Bautista L, Knippler CM and Ringel MD:
p21-activated kinases in thyroid cancer. Endocrinology.
161:bqaa1052020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Lu Z and Hunter T: Ubiquitylation and
proteasomal degradation of the p21(Cip1), p27(Kip1) and p57(Kip2)
CDK inhibitors. Cell Cycle. 9:2342–2352. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Takasugi T, Minegishi S, Asada A, Saito T,
Kawahara H and Hisanaga S: Two degradation pathways of the p35 Cdk5
(cyclin-dependent kinase) activation subunit, dependent and
independent of ubiquitination. J Biol Chem. 291:4649–4657. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhang S, Lu Z, Mao W, Ahmed AA, Yang H,
Zhou J, Jennings N, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Lopez-Berestein G, Miranda
R, et al: CDK5 regulates paclitaxel sensitivity in ovarian cancer
cells by modulating AKT activation, p21Cip1- and p27Kip1-mediated
G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. PLoS One. 10:e01318332015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Havens CG and Walter JC: Mechanism of
CRL4(Cdt2), a PCNA-dependent E3 ubiquitin ligase. Genes Dev.
25:1568–1582. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Jumper J, Evans R, Pritzel A, Green T,
Figurnov M, Ronneberger O, Tunyasuvunakool K, Bates R, Žídek A,
Potapenko A, et al: Highly accurate protein structure prediction
with AlphaFold. Nature. 596:583–589. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Harper JW, Elledge SJ, Keyomarsi K,
Dynlacht B, Tsai LH, Zhang P, Dobrowolski S, Bai C, Connell-Crowley
L, Swindell E, et al: Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases by
p21. Mol Biol Cell. 6:387–400. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Malumbres M: Cyclin-dependent kinases.
Genome Biol. 15:1222014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Hirai H, Kawanishi N and Iwasawa Y: Recent
advances in the development of selective small molecule inhibitors
for cyclin-dependent kinases. Curr Top Med Chem. 5:167–179. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ardelt MA, Fröhlich T, Martini E, Müller
M, Kanitz V, Atzberger C, Cantonati P, Meßner M, Posselt L, Lehr T,
et al: Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 5: A strategy to
improve sorafenib response in hepatocellular carcinoma therapy.
Hepatology. 69:376–393. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lenjisa JL, Tadesse S, Khair NZ,
Kumarasiri M, Yu M, Albrecht H, Milne R and Wang S: CDK5 in
oncology: Recent advances and future prospects. Future Med Chem.
9:1939–1962. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Pozo K and Bibb JA: The emerging role of
Cdk5 in cancer. Trends Cancer. 2:606–618. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhang M, Zhang L, Hei R, Li X, Cai H, Wu
X, Zheng Q and Cai C: CDK inhibitors in cancer therapy, an overview
of recent development. Am J Cancer Res. 11:1913–1935.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|