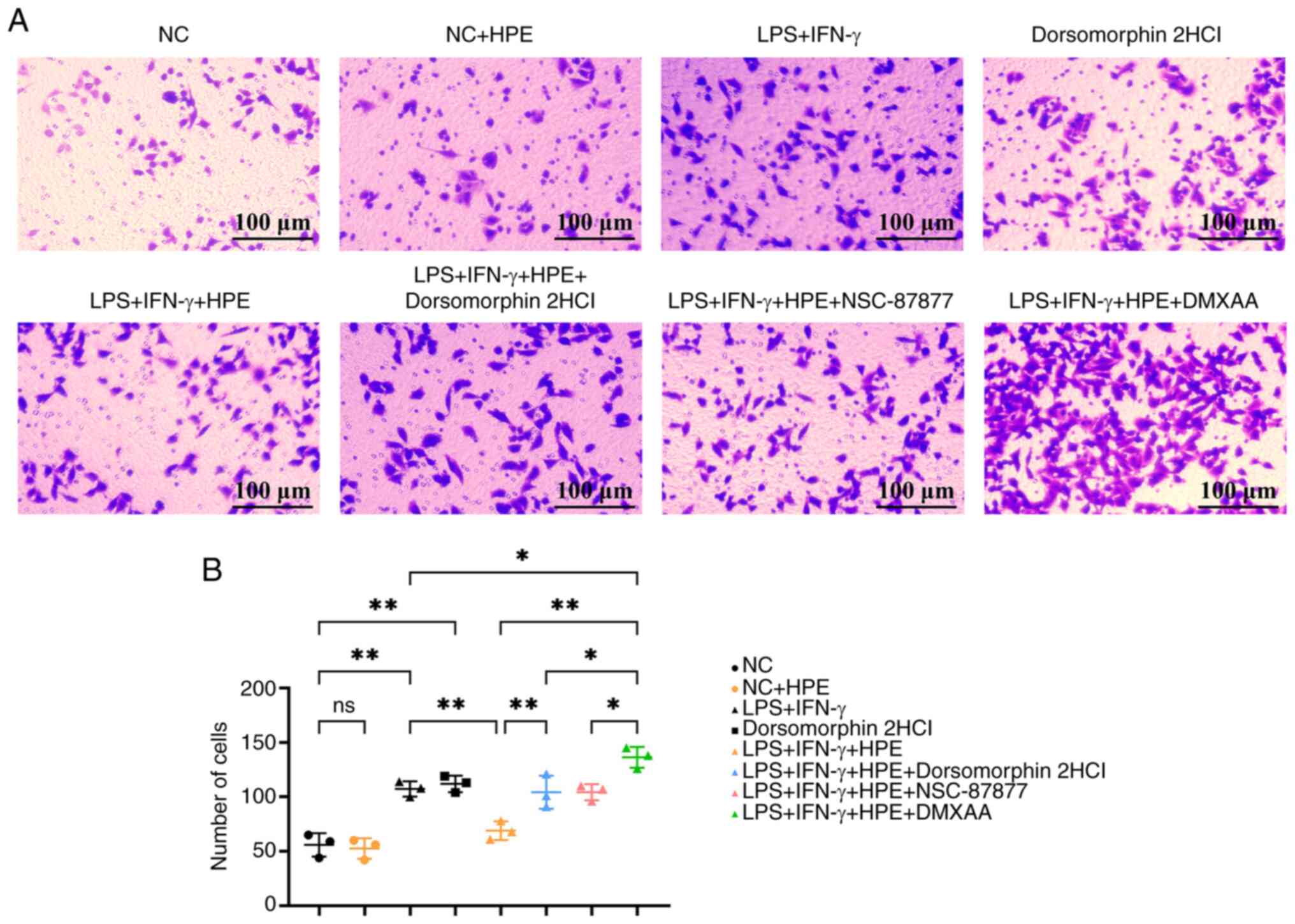
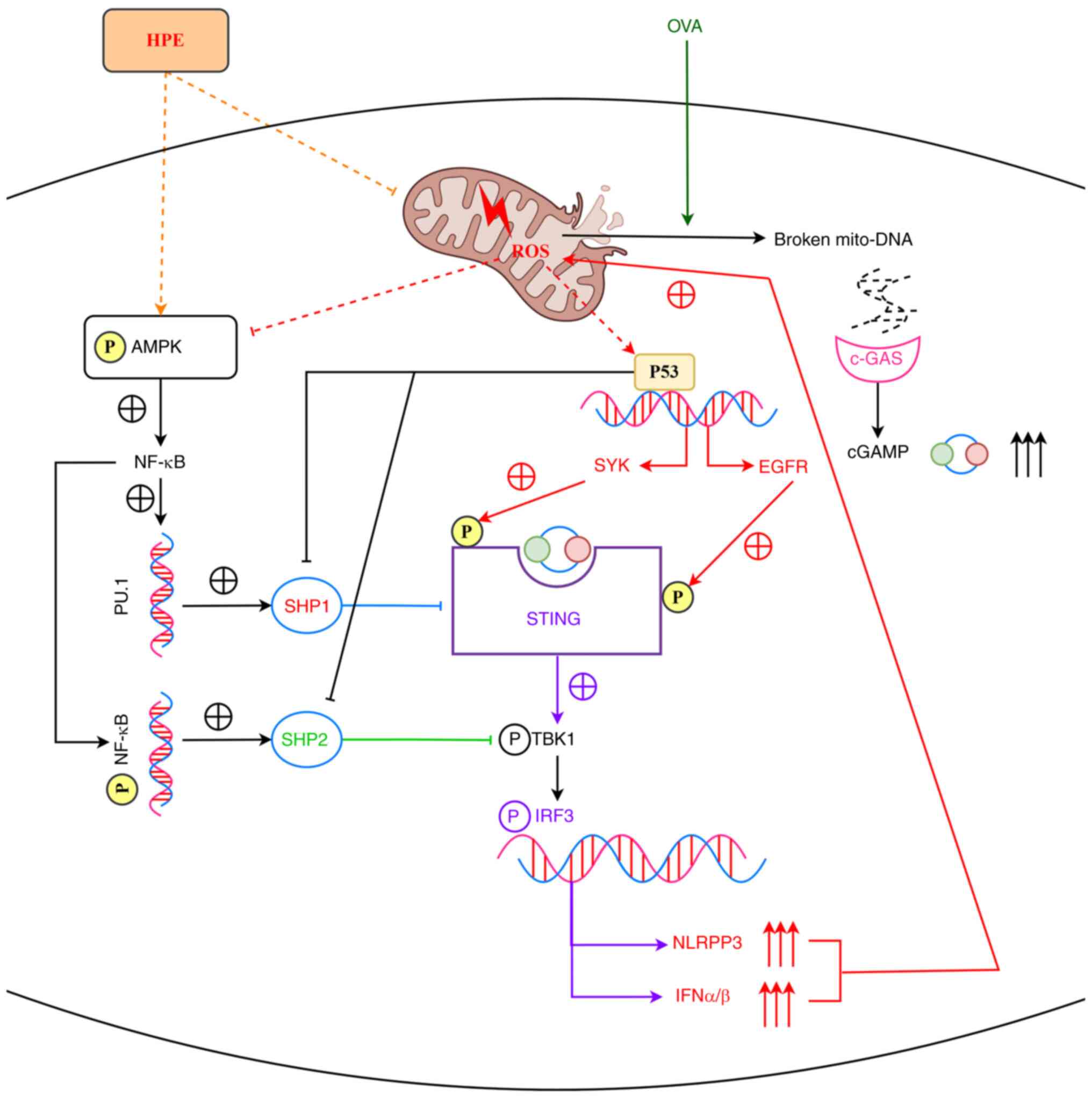
|
1
|
Siddiqui ZA, Walker A, Pirwani MM, Tahiri
M and Syed I: Allergic rhinitis: Diagnosis and management. Br J
Hosp Med (Lond). 83:1–9. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schuler Iv CF and Montejo JM: Allergic
rhinitis in children and adolescents. Pediatr Clin North Am.
66:981–993. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pyun BJ, Lee JY, Kim YJ, Ji KY, Jung DH,
Park KS, Jo K, Choi S, Jung MA, Kim YH and Kim T: Gardenia
jasminoides Attenuates Allergic Rhinitis-induced inflammation by
inhibiting periostin production. Pharmaceuticals (Basel).
14:9862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bjermer L, Westman M, Holmström M and
Wickman MC: The complex pathophysiology of allergic rhinitis:
Scientific rationale for the development of an alternative
treatment option. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 15:242019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
De D, Chakraborty PD and Bhattacharyya D:
Regulation of trypsin activity by peptide fraction of an aqueous
extract of human placenta used as wound healer. J Cell Physiol.
226:2033–2040. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee JO, Jang Y, Park AY, Lee JM, Jeong K,
Jeon SH, Jin H, Im M, Kim JW and Kim BJ: Human Placenta Extract
(HPH) suppresses inflammatory responses in TNF-α/IFN-γ-Stimulated
HaCaT cells and a DNCB atopic dermatitis (AD)-like mouse model. J
Microbiol Biotechnol. 34:1969–1980. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hackethal J, Weihs AM, Karner L, Metzger
M, Dungel P, Hennerbichler S, Redl H and Teuschl-Woller AH: Novel
human Placenta-based extract for vascularization strategies in
tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 27:616–632. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gwam C, Ohanele C, Hamby J, Chughtai N,
Mufti Z and Ma X: Human placental extract: A potential therapeutic
in treating osteoarthritis. Ann Transl Med. 11:3222023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Samiei F, Jamshidzadeh A, Noorafshan A and
Ghaderi A: Human placental extract ameliorates structural lung
changes iinduced by amiodarone in rats. Iran J Pharm Res. 15 (Suppl
1):S75–S82. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee YK, Chung HH and Kang SB: Efficacy and
safety of human placenta extract in alleviating climacteric
symptoms: Prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled
trial. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 35:1096–1101. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang W, Lu J, Wang Y, Sun P, Gao T, Xu N,
Zhang Y and Xie W: Canagliflozin attenuates lipotoxicity in
cardiomyocytes by inhibiting inflammation and ferroptosis through
activating AMPK pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 24:8582023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang J, Sun Y, Tang K, Xu H, Xiao J and
Li Y: RGC32 promotes the progression of ccRCC by activating the
NF-κB/SHP2/EGFR signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY). May
27–2024.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
13
|
Wang D, Paz-Priel I and Friedman AD:
NF-kappa B p50 regulates C/EBP alpha expression and inflammatory
cytokine-induced neutrophil production. J Immunol. 182:5757–5762.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bi L, Yu Z, Wu J, Yu K, Hong G, Lu Z and
Gao S: Honokiol inhibits constitutive and inducible STAT3 signaling
via PU.1-Induced SHP1 expression in acute myeloid leukemia cells.
Tohoku J Exp Med. 237:163–172. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li BL, Zhao DY, Du PL, Wang XT, Yang Q and
Cai YR: Luteolin alleviates ulcerative colitis through SHP-1/STAT3
pathway. Inflamm Res. 70:705–717. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun Z, Liu Q, Lv Z, Li J, Xu X, Sun H,
Wang M, Sun K, Shi T, Liu Z, et al: Targeting macrophagic SHP2 for
ameliorating osteoarthritis via TLR signaling. Acta Pharm Sin B.
12:3073–3084. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang B, Zeng M, Zhang Q, Wang R, Jia J,
Cao B, Liu M, Guo P, Zhang Y, Zheng X and Feng W: Ephedrae Herba
polysaccharides inhibit the inflammation of ovalbumin induced
asthma by regulating Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg cell immune imbalance.
Mol Immunol. 152:14–26. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nur Husna SM, Md Shukri N, Tuan Sharif SE,
Tan HTT, Mohd Ashari NS and Wong KK: IL-4/IL-13 axis in allergic
rhinitis: Elevated serum cytokines levels and inverse association
with tight junction molecules expression. Front Mol Biosci.
9:8197722022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shao YY, Zhou YM, Hu M, Li JZ, Chen CJ,
Wang YJ, Shi XY, Wang WJ and Zhang TT: The Anti-allergic rhinitis
effect of traditional Chinese medicine of Shenqi by regulating mast
cell degranulation and Th1/Th2 cytokine balance. Molecules.
22:5042017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Murray PJ and Wynn TA: Protective and
pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat Rev Immunol.
11:723–737. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hirano M, Ogita-Nakanishi H, Miyachi W,
Hannya N, Yamamoto-Kimoto Y, Sakurai K, Miyoshi-Higashino M,
Tashiro-Yamaji J, Kato R, Ijiri Y, et al: Essential role of
macrophages in the initiation of allergic rhinitis in mice
sensitized intranasally once with cedar pollen: Regulation of class
switching of immunoglobulin in B cells by controlling interleukin-4
production in T cells of submandibular lymph nodes. Microbiol
Immunol. 56:392–405. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Saradna A, Do DC, Kumar S, Fu QL and Gao
P: Macrophage polarization and allergic asthma. Transl Res.
191:1–14. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Qu J, Sun Y, Liang N, Li C, Huang Q, Wang
M, Wang D and Zhou B: Histopathological characteristics and
inflammatory cell infiltration in sinonasal inverted papilloma. Am
J Rhinol Allergy. 39:21–31. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang H, Ren Y, Liang H and Liu X, Nan J,
Zhao H and Liu X: Mechanism of TCONS_00147848 regulating apoptosis
of nasal mucosa cells and alleviating allergic rhinitis through
FOSL2-mediated JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway. Sci Rep. 11:159912021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Geng B, Dilley M and Anterasian C:
Biologic therapies for allergic rhinitis and nasal polyposis. Curr
Allergy Asthma Rep. 21:362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou Y, Que KT, Zhang Z, Yi ZJ, Zhao PX,
You Y, Gong JP and Liu ZJ: Iron overloaded polarizes macrophage to
proinflammation phenotype through ROS/acetyl-p53 pathway. Cancer
Med. 7:4012–4022. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang C, Sharma N, Veleeparambil M, Kessler
PM, Willard B and Sen GC: STING-Mediated interferon induction by
herpes simplex Virus 1 requires the protein tyrosine kinase syk.
mBio. 12:e03228212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Meng L, Hao D, Liu Y, Yu P, Luo J, Li C,
Jiang T, Yu J, Zhang Q, Liu S and Shi L: LRRC8A drives NADPH
oxidase-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation in
allergic rhinitis. J Transl Med. 22:10342024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Drazdauskaitė G, Layhadi JA and Shamji MH:
Mechanisms of allergen immunotherapy in allergic rhinitis. Curr
Allergy Asthma Rep. 21:22020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wen X, Tang L, Zhong R, Liu L, Chen L and
Zhang H: Role of mitophagy in regulating intestinal oxidative
damage. Antioxidants (Basel). 12:4802023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jiménez-Loygorri JI, Villarejo-Zori B,
Viedma-Poyatos Á, Zapata-Muñoz J, Benítez-Fernández R, Frutos-Lisón
MD, Tomás-Barberán FA, Espín JC, Area-Gómez E, Gomez-Duran A and
Boya P: Mitophagy curtails cytosolic mtDNA-dependent activation of
cGAS/STING inflammation during aging. Nat Commun. 15:8302024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ho TLF, Lee MY, Goh HC, Ng GYN, Lee JJH,
Kannan S, Lim YT, Zhao T, Lim EKH, Phua CZJ, et al: Domain-specific
p53 mutants activate EGFR by distinct mechanisms exposing
tissue-independent therapeutic vulnerabilities. Nat Commun.
14:17262023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zajkowicz A, Gdowicz-Kłosok A, Krześniak
M, Janus P, Łasut B and Rusin M: The Alzheimer's disease-associated
TREM2 gene is regulated by p53 tumor suppressor protein. Neuroscie
Lett. 681:62–67. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yum S, Li M, Fang Y and Chen ZJ: TBK1
recruitment to STING activates both IRF3 and NF-κB that mediate
immune defense against tumors and viral infections. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 118:e21002251182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tanaka Y and Chen ZJ: STING specifies IRF3
phosphorylation by TBK1 in the cytosolic DNA signaling pathway. Sci
Signal. 5:ra202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Duan N, Zhang Y, Tan S, Sun J, Ye M, Gao
H, Pu K, Wu M, Wang Q and Zhai Q: Therapeutic targeting of
STING-TBK1-IRF3 signalling ameliorates chronic stress induced
depression-like behaviours by modulating neuroinflammation and
microglia phagocytosis. Neurobiol Dis. 169:1057392022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wu T, He J, Yan S, Li J, Chen K, Zhang D,
Cheng M, Xiang Z and Fang Y: Human placental extract suppresses
mast cell activation and induces mast cell apoptosis. Allergy
Asthma Clin Immunol. 19:982023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jang SY, Park JW, Bu Y, Kang JO and Kim J:
Protective effects of hominis placenta hydrolysates on radiation
enteropathy in mice. Nat Prod Res. 25:1988–1992. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu C, Wang X, Qin W, Tu J, Li C, Zhao W,
Ma L, Liu B, Qiu H and Yuan X: Combining radiation and the ATR
inhibitor berzosertib activates STING signaling and enhances
immunotherapy via inhibiting SHP1 function in colorectal cancer.
Cancer Commun (Lond). 43:435–454. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ding H and Wu R: The Role of SHP2 in
advancing COPD: Insights into oxidative stress, endoplasmic
reticulum stress, and pyroptosis. Altern Ther Health Med. Apr
18–2024.(Epub ahead of print).
|