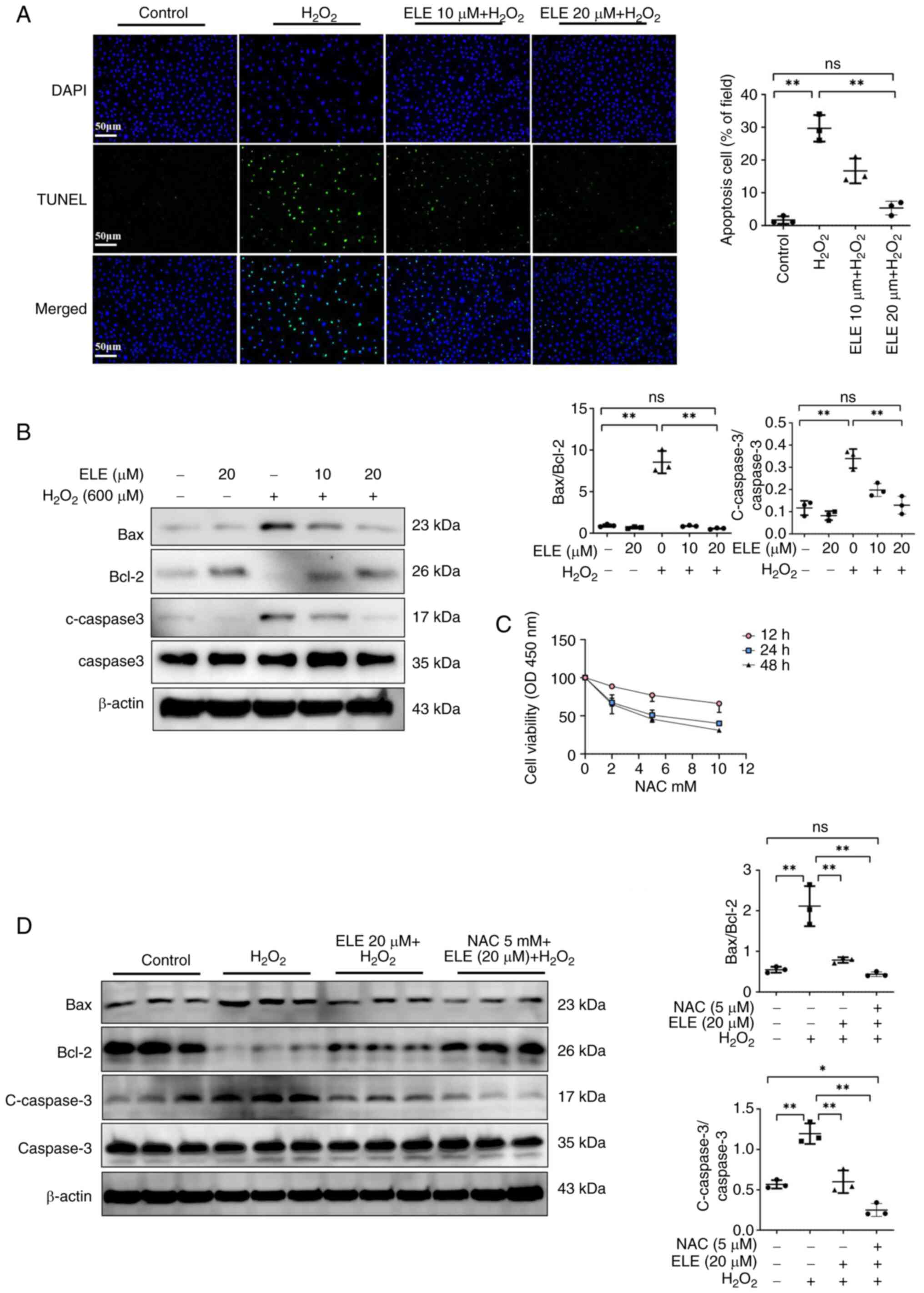
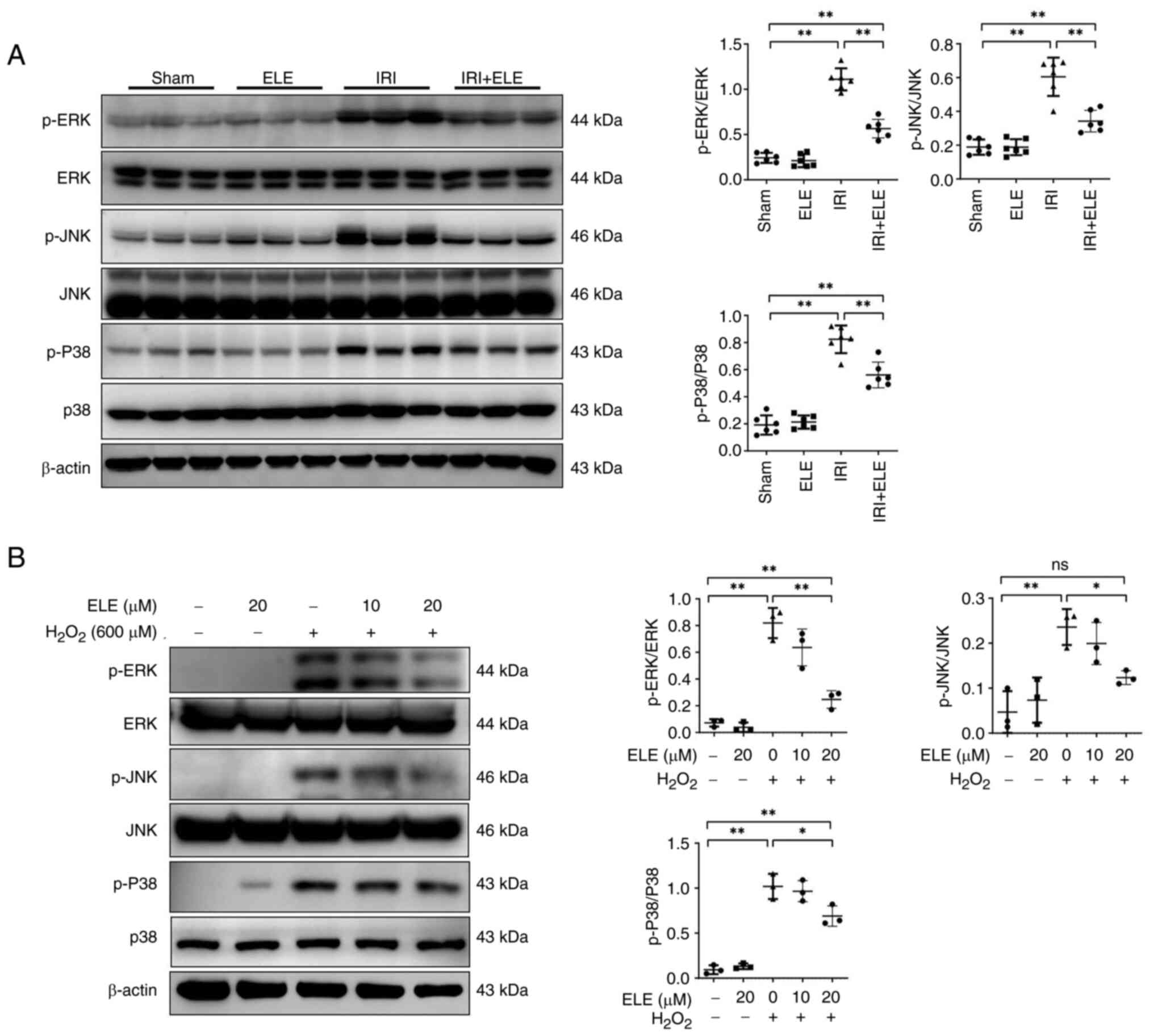
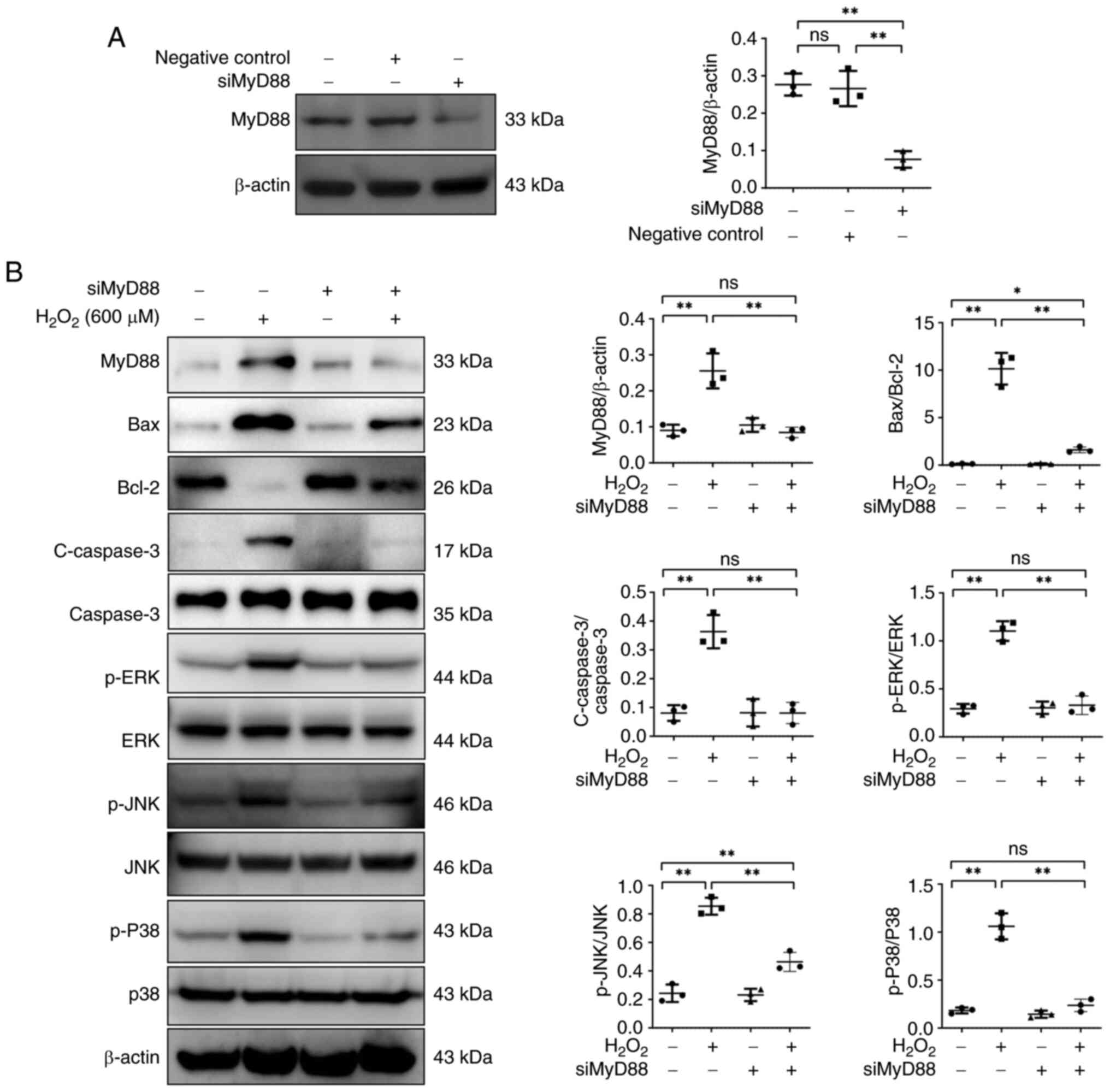
|
1
|
Waikar SS, Liu KD and Chertow GM:
Diagnosis, epidemiology and outcomes of acute kidney injury. Clin J
Am Soc Nephrol. 3:844–861. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Boratyńska M, Kamińska D and Mazanowska O:
Pathophysiology of ischemia-reperfusion injury in renal
transplantation. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 58:1–8. 2004.(In
Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dong Y, Zhang Q, Wen J, Chen T, He L, Wang
Y, Yin J, Wu R, Xue R, Li S, et al: Ischemic duration and frequency
determines AKI-to-CKD progression monitored by dynamic changes of
tubular biomarkers in IRI mice. Front Physiol. 10:1532019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Forbes JM, Hewitson TD, Becker GJ and
Jones CL: Ischemic acute renal failure: Long-term histology of cell
and matrix changes in the rat. Kidney Int. 57:2375–2385. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sanz AB, Sanchez-Niño MD, Ramos AM and
Ortiz A: Regulated cell death pathways in kidney disease. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 19:281–299. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Phaniendra A, Jestadi DB and Periyasamy L:
Free radicals: Properties, sources, targets, and their implication
in various diseases. Indian J Clin Biochem. 30:11–26. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim J, Seok YM, Jung KJ and Park KM:
Reactive oxygen species/oxidative stress contributes to progression
of kidney fibrosis following transient ischemic injury in mice. Am
J Physiol Renal Physiol. 297:F461–F470. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bonventre JV and Yang L: Cellular
pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. J Clin Invest.
121:4210–4221. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao L, Hao Y, Tang S, Han X, Li R and
Zhou X: Energy metabolic reprogramming regulates programmed cell
death of renal tubular epithelial cells and might serve as a new
therapeutic target for acute kidney injury. Front Cell Dev Biol.
11:12762172023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gong S, Xiong H, Lei Y, Huang S, Ouyang Y,
Cao C and Wang Y: Usp9× contributes to the development of
sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by promoting inflammation and
apoptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells via activation of the
TLR4/nf-κb pathway. Ren Fail. 46:23610892024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Devarajan P: Update on mechanisms of
ischemic acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 17:1503–1520. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang B, Lan S, Dieudé M, Sabo-Vatasescu
JP, Karakeussian-Rimbaud A, Turgeon J, Qi S, Gunaratnam L, Patey N
and Hébert MJ: Caspase-3 is a pivotal regulator of microvascular
rarefaction and renal fibrosis after ischemia-reperfusion injury. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 29:1900–1916. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang Q, Qian L and Zhang S: Ginsenoside
Rh1 alleviates HK-2 apoptosis by inhibiting ROS and the JNK/p53
pathways. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020:34010672020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu L, Zhang R, Lin S, Lin M and Wang J:
Silencing CDK6-AS1 inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory damage in HK-2
cells. Open Med (Wars). 16:1256–1264. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bai Z, Yao C, Zhu J, Xie Y, Ye XY, Bai R
and Xie T: Anti-tumor drug discovery based on natural product
β-Elemene: Anti-tumor mechanisms and structural modification.
Molecules. 26:14492021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhu T, Xu Y, Dong B, Zhang J, Wei Z, Xu Y
and Yao Y: β-elemene inhibits proliferation of human glioblastoma
cells through the activation of glia maturation factor β and
induces sensitization to cisplatin. Oncol Rep. 26:405–413.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu X, Li Z, Zhang Y, Xu M, Che Y, Tian X,
Wang R, Zou K and Zou L: β-elemene inhibits radiation and
hypoxia-induced macrophages infiltration via Prx-1/NF-κB/HIF-1α
signaling pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 12:4203–4211. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cai SZ, Xiong QW, Zhao L, Ji YT, Luo ZX
and Ma ZR: β-elemene triggers ROS-dependent apoptosis in
glioblastoma cells through suppressing STAT3 signaling pathway.
Pathol Oncol Res. 27:5942992021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun W, Choi HS, Kim CS, Bae EH, Ma SK and
Kim SW: Maslinic acid attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute
kidney injury by suppressing inflammation and apoptosis through
inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol.
13:8074522022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wei Q and Dong Z: Mouse model of ischemic
acute kidney injury: Technical notes and tricks. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 303:F1487–F1494. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Basile DP, Bonventre JV, Mehta R, Nangaku
M, Unwin R, Rosner MH, Kellum JA and Ronco C; ADQI XIII Work Group,
: ADQI XIII work group. Progression after AKI: Understanding
maladaptive repair processes to predict and identify therapeutic
treatments. J Am Soc Nephrol. 27:687–697. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun W, Kim DH, Byon CH, Choi HI, Park JS,
Bae EH, Ma SK and Kim SW: β-Elemene attenuates renal fibrosis in
the unilateral ureteral obstruction model by inhibition of STAT3
and Smad3 signaling via suppressing MyD88 expression. Int J Mol
Sci. 23:55532022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tak PP and Firestein GS: NF-kappaB: A key
role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest. 107:7–11. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Havasi A and Borkan SC: Apoptosis and
acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 80:29–40. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Meng F, Chen Q, Gu S, Cui R, Ma Q, Cao R
and Zhao M: Inhibition of Circ-Snrk ameliorates apoptosis and
inflammation in acute kidney injury by regulating the MAPK pathway.
Ren Fail. 44:672–681. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kyriakis JM and Avruch J: Mammalian MAPK
signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation:
A 10-year update. Physiol Rev. 92:689–737. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kwon O, Hong SM, Sutton TA and Temm CJ:
Preservation of peritubular capillary endothelial integrity and
increasing pericytes may be critical to recovery from postischemic
acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 295:F351–F359.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zheng Q, Xing J, Li X, Tang X and Zhang D:
PRDM16 suppresses ferroptosis to protect against sepsis-associated
acute kidney injury by targeting the NRF2/GPX4 axis. Redox Biol.
78:1034172024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li X, Yuan F, Xiong Y, Tang Y, Li Z, Ai J,
Miao J, Ye W, Zhou S, Wu Q, et al: FAM3A plays a key role in
protecting against tubular cell pyroptosis and acute kidney injury.
Redox Biol. 74:1032252024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Linkermann A, Chen G, Dong G, Kunzendorf
U, Krautwald S and Dong Z: Regulated cell death in AKI. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 25:2689–2701. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fang Y, Kang Y, Zou H, Cheng X, Xie T, Shi
L and Zhang H: β-elemene attenuates macrophage activation and
proinflammatory factor production via crosstalk with Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway. Fitoterapia. 124:92–102. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao Q, Chen L, Zhang X, Yang H, Li Y and
Li P: β-elemene promotes microglial M2-like polarization against
ischemic stroke via AKT/mTOR signaling axis-mediated autophagy.
Chin Med. 19:862024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang G, Xue C and Zeng Y: β-elemene
alleviates airway stenosis via the ILK/Akt pathway modulated by
MIR143HG sponging miR-1275. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 26:282021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhai B, Wu Q, Wang W, Zhang M, Han X, Li
Q, Chen P, Chen X, Huang X, Li G, et al: Preparation,
characterization, pharmacokinetics and anticancer effects of
PEGylated β-elemene liposomes. Cancer Biol Med. 17:60–75. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gan D, He W, Yin H and Gou X: β-elemene
enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in bladder cancer cells
through the ROS-AMPK signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 19:291–300.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee RX, Li QQ and Reed E: β-elemene
effectively suppresses the growth and survival of both
platinum-sensitive and -resistant ovarian tumor cells. Anticancer
Res. 32:3103–3113. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhou Y, Takano T, Wang Y, Li X, Wang R,
Wakatsuki Y, Nakajima-Adachi H, Tanokura M, Miyakawa T and
Hachimura S: Intestinal regulatory T cell induction by β-elemene
alleviates the formation of fat tissue-related inflammation.
iScience. 24:1018832021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Eltzschig HK and Collard CD: Vascular
ischaemia and reperfusion injury. Br Med Bull. 70:71–86. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ramesh G and Reeves WB: Inflammatory
cytokines in acute renal failure. Kidney Int Suppl. 91:S56–S61.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Delneste Y, Beauvillain C and Jeannin P:
Innate immunity: Structure and function of TLRs. Med Sci (Paris).
23:67–73. 2007.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen J, Hartono JR, John R, Bennett M,
Zhou XJ, Wang Y, Wu Q, Winterberg PD, Nagami GT and Lu CY: Early
interleukin 6 production by leukocytes during ischemic acute kidney
injury is regulated by TLR4. Kidney Int. 80:504–515. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wu H, Chen G, Wyburn KR, Yin J, Bertolino
P, Eris JM, Alexander SI, Sharland AF and Chadban SJ: TLR4
activation mediates kidney ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Clin
Invest. 117:2847–2859. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang LM, Liu JH, Xue CB, Li MQ, Xing S,
Zhang X, He WT, Jiang FC, Lu X and Zhou P: Pharmacological
inhibition of MyD88 homodimerization counteracts renal ischemia
reperfusion-induced progressive renal injury in vivo and in vitro.
Sci Rep. 6:269542016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Basnakian AG, Kaushal GP and Shah SV:
Apoptotic pathways of oxidative damage to renal tubular epithelial
cells. Antioxid Redox Signal. 4:915–924. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kaushal GP, Basnakian AG and Shah SV:
Apoptotic pathways in ischemic acute renal failure. Kidney Int.
66:500–506. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang H and Sun SC: NF-κB in inflammation
and renal diseases. Cell Biosci. 5:632015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Oberbauer R, Schwarz C, Regele HM,
Hansmann C, Meyer TW and Mayer G: Regulation of renal tubular cell
apoptosis and proliferation after ischemic injury to a solitary
kidney. J Lab Clin Med. 138:343–351. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zou G, Zhou Z, Xi X, Huang R and Hu H:
Pioglitazone ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via
inhibition of NF-κB activation and inflammation in rats. Front
Physiol. 12:7073442021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sun W, Byon CH, Kim DH, Choi HI, Park JS,
Joo SY, Kim IJ, Jung I, Bae EH, Ma SK and Kim SW: Renoprotective
effects of maslinic acid on experimental renal fibrosis in
unilateral ureteral obstruction model via targeting MyD88. Front
Pharmacol. 12:7085752021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li X, Huang R, Liu K, Li M, Luo H, Cui L,
Huang L and Luo L: Fucoxanthin attenuates LPS-induced acute lung
injury via inhibition of the TLR4/MyD88 signaling axis. Aging
(Albany NY). 13:2655–2667. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Cargnello M and Roux PP: Activation and
function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated
protein kinases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 75:50–83. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cuarental L, Sucunza-Sáenz D, Valiño-Rivas
L, Fernandez-Fernandez B, Sanz AB, Ortiz A, Vaquero JJ and
Sanchez-Niño MD: MAP3K kinases and kidney injury. Nefrologia (Engl
Ed). 39:568–580. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chu W, Li M, Li F, Hu R, Chen Z, Lin J and
Feng H: Immediate splenectomy down-regulates the MAPK-NF-κB
signaling pathway in rat brain after severe traumatic brain injury.
J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 74:1446–1453. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Guo X, Jiang H, Chen J, Zhang BF, Hu Q,
Yang S, Yang J and Zhang J: RP105 ameliorates hypoxia/reoxygenation
injury in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells by suppressing
TLR4/MAPKs/NF-κB signaling. Int J Mol Med. 42:505–513.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|