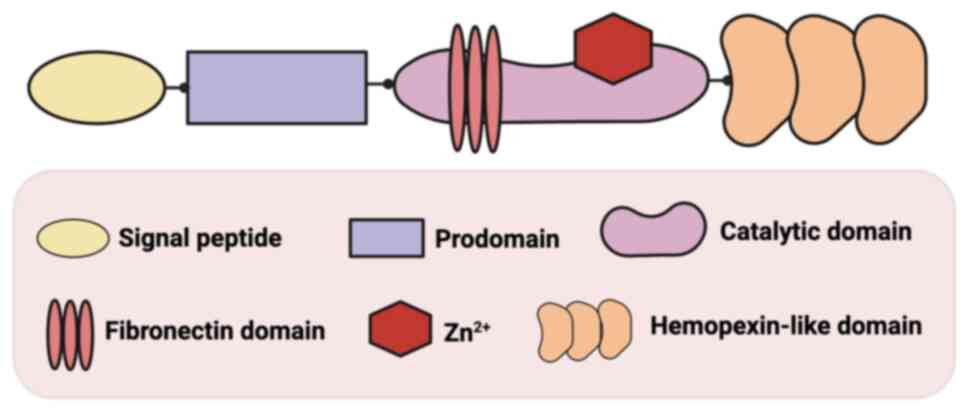
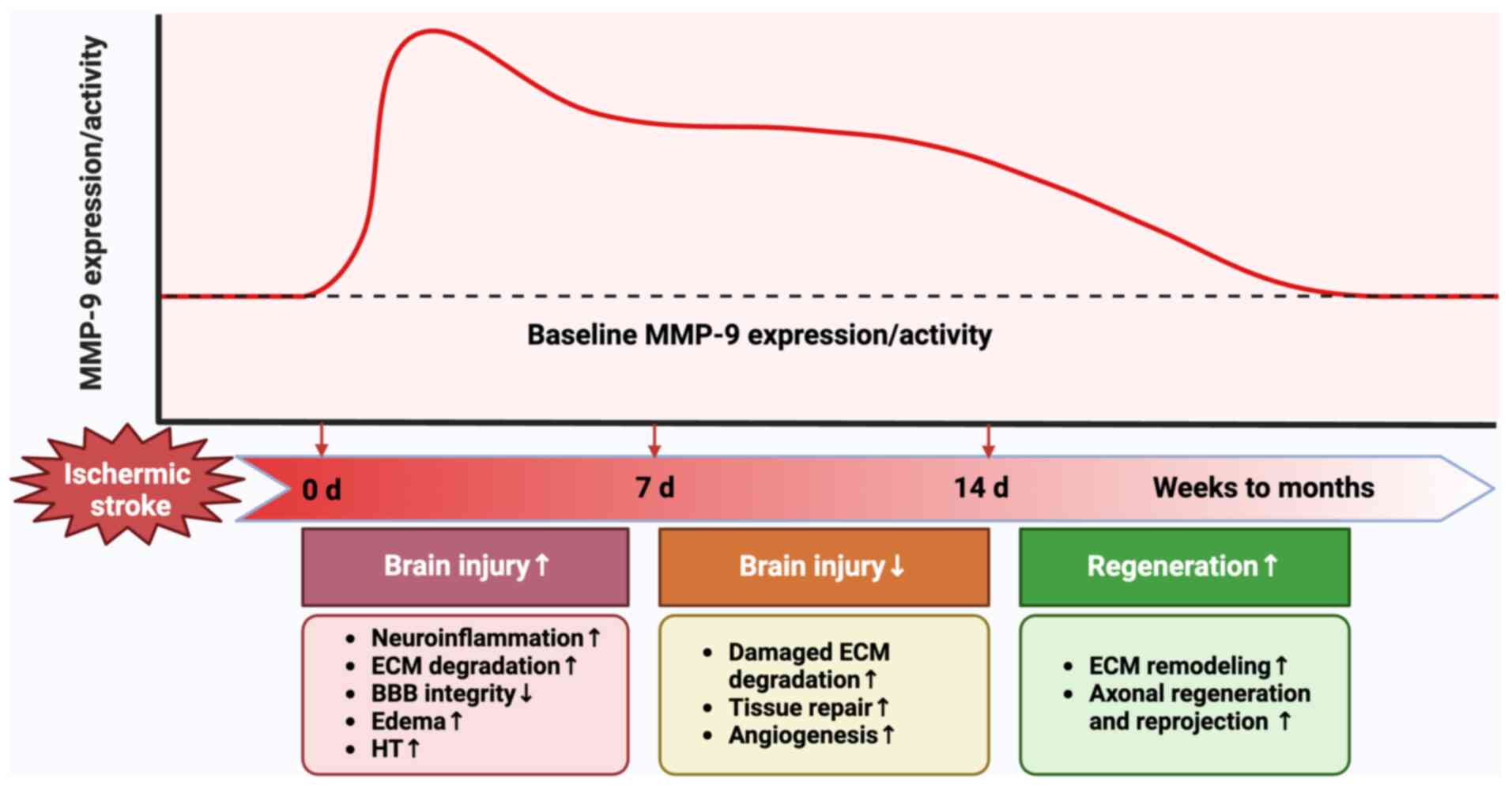
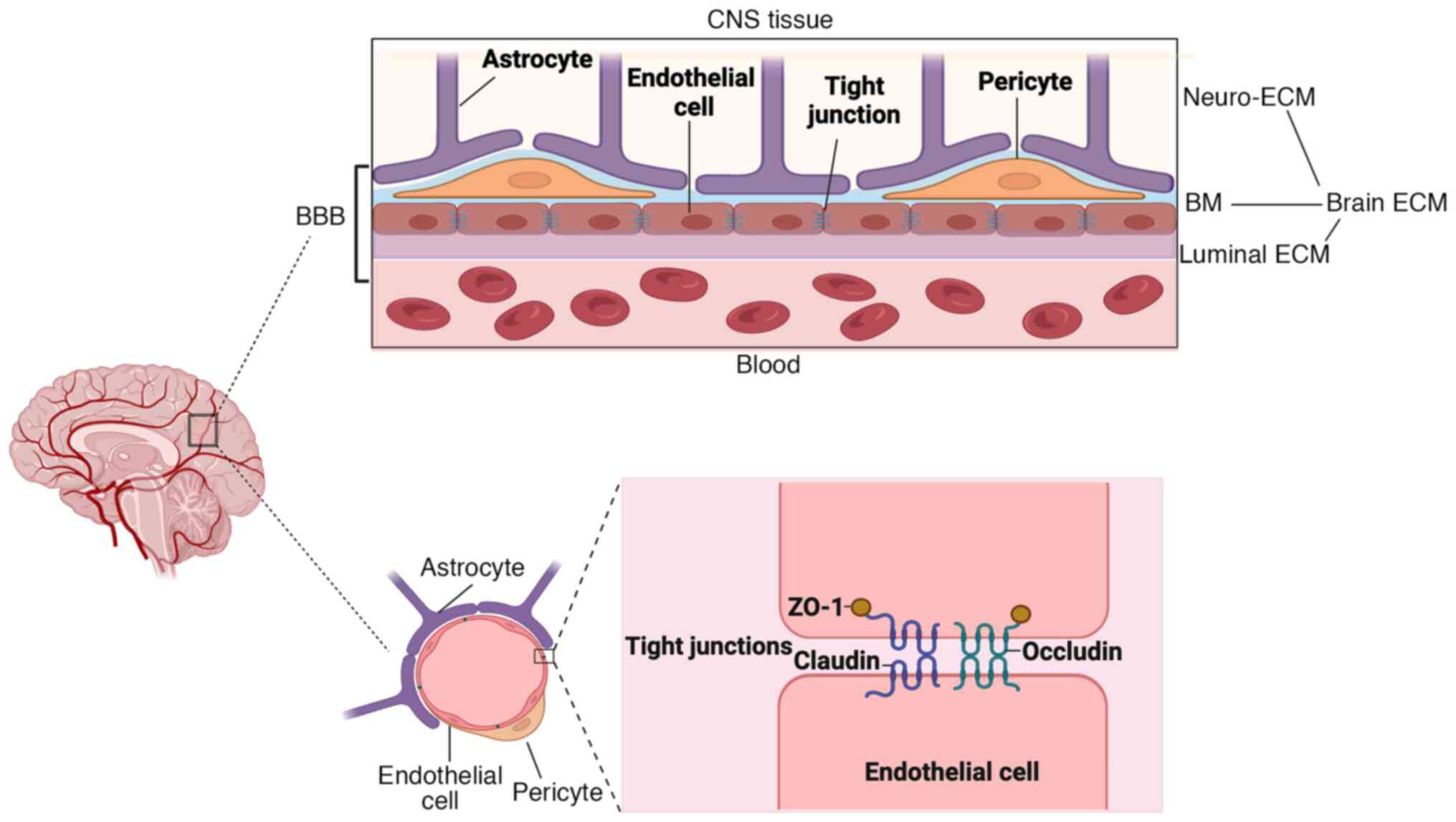
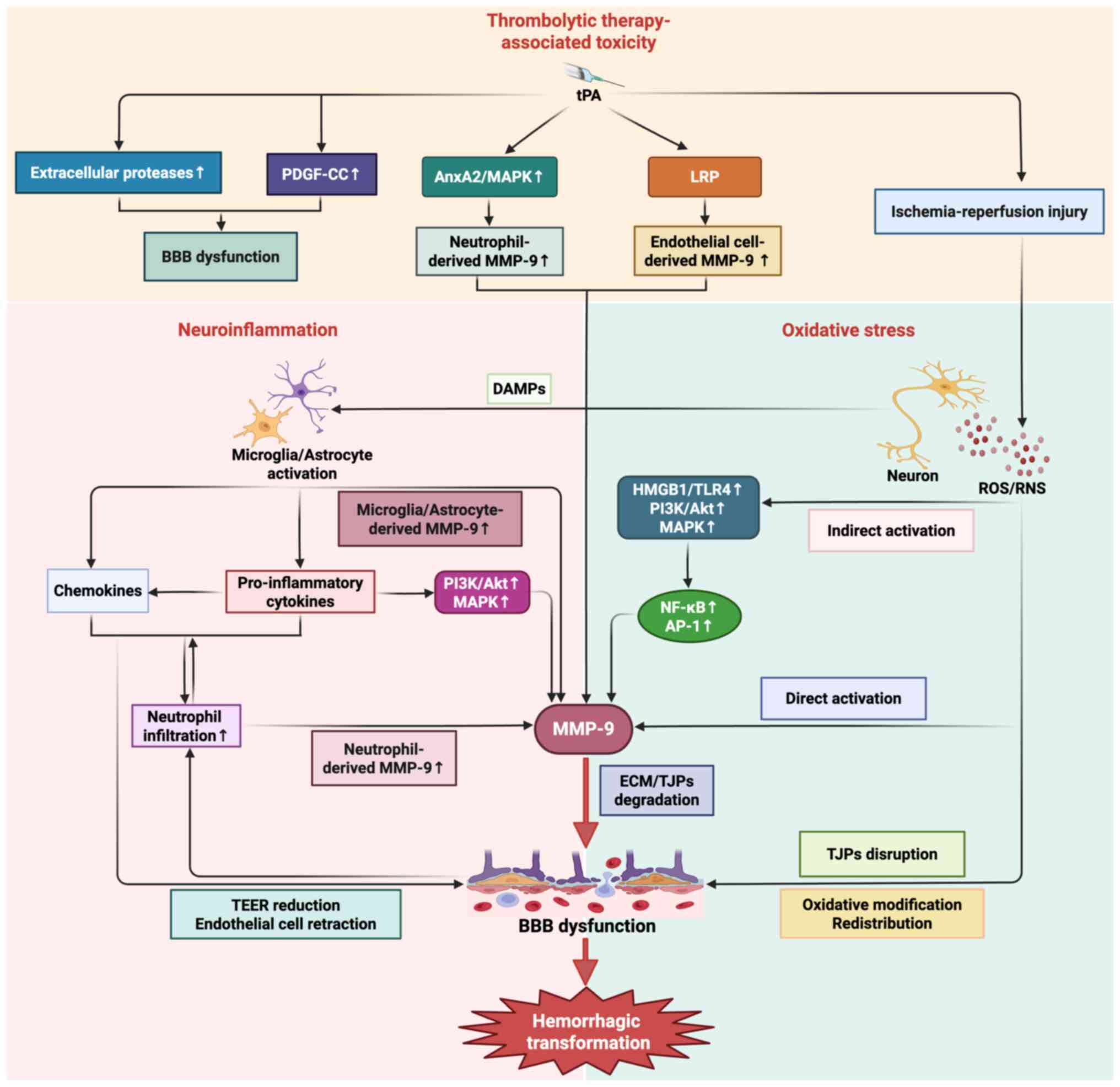
|
1
|
Feigin VL and Owolabi MO; World Stroke
Organization-Lancet Neurology Commission Stroke Collaboration
Group, : Pragmatic solutions to reduce the global burden of stroke:
A orld stroke organization-lancet neurology commission. Lancet
Neurol. 22:1160–1206. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hasan TF, Hasan H and Kelley RE: Overview
of acute ischemic stroke evaluation and management. Biomedicines.
9:14862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Otsu Y, Namekawa M, Toriyabe M, Ninomiya
I, Hatakeyama M, Uemura M, Onodera O, Shimohata T and Kanazawa M:
Strategies to prevent hemorrhagic transformation after reperfusion
therapies for acute ischemic stroke: A literature review. J Neurol
Sci. 419:1172172020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Goncalves A, Su EJ, Muthusamy A,
Zeitelhofer M, Torrente D, Nilsson I, Protzmann J, Fredriksson L,
Eriksson U, Antonetti DA and Lawrence DA: Thrombolytic tPA-induced
hemorrhagic transformation of ischemic stroke is mediated by PKCβ
phosphorylation of occludin. Blood. 140:388–400. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kovács KB, Bencs V, Hudák L, Oláh L and
Csiba L: Hemorrhagic transformation of ischemic strokes. Int J Mol
Sci. 24:140672023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lu W and Wen J: The relationship among
H2S, neuroinflammation and MMP-9 in BBB injury following ischemic
stroke. Int Immunopharmacol. 146:1139022025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Desilles JP, Rouchaud A, Labreuche J,
Meseguer E, Laissy JP, Serfaty JM, Lapergue B, Klein IF, Guidoux C,
Cabrejo L, et al: Blood-brain barrier disruption is associated with
increased mortality after endovascular therapy. Neurology.
80:844–851. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao Z, Nelson AR, Betsholtz C and
Zlokovic BV: Establishment and dysfunction of the blood-brain
barrier. Cell. 163:1064–1078. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rosell A, Cuadrado E, Ortega-Aznar A,
Hernandez-Guillamon M, Lo EH and Montaner J: MMP-9-positive
neutrophil infiltration is associated to blood-brain barrier
breakdown and basal lamina type IV collagen degradation during
hemorrhagic transformation after human ischemic stroke. Stroke.
39:1121–1126. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kapoor C, Vaidya S, Wadhwan V, Hitesh,
Kaur G and Pathak A: Seesaw of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). J
Cancer Res Ther. 12:28–35. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Misra S, Talwar P, Kumar A, Kumar P, Sagar
R, Vibha D, Pandit AK, Gulati A, Kushwaha S and Prasad K:
Association between matrix metalloproteinase family gene
polymorphisms and risk of ischemic stroke: A systematic review and
meta-analysis of 29 studies. Gene. 672:180–194. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang Y and Rosenberg GA: Matrix
metalloproteinases as therapeutic targets for stroke. Brain Res.
1623:30–38. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kimura-Ohba S and Yang Y: Oxidative DNA
damage mediated by intranuclear MMP activity is associated with
neuronal apoptosis in ischemic stroke. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016:69273282016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cui N, Hu M and Khalil RA: Biochemical and
biological attributes of matrix metalloproteinases. Prog Mol Biol
Transl Sci. 147:1–73. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Montaner J, Alvarez-Sabín J, Molina CA,
Anglés A, Abilleira S, Arenillas J and Monasterio J: Matrix
metalloproteinase expression is related to hemorrhagic
transformation after cardioembolic stroke. Stroke. 32:2762–2767.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Montaner J, Molina CA, Monasterio J,
Abilleira S, Arenillas JF, Ribó M, Quintana M and Alvarez-Sabín J:
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 pretreatment level predicts intracranial
hemorrhagic complications after thrombolysis in human stroke.
Circulation. 107:598–603. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li H, Ghorbani S, Ling CC, Yong VW and Xue
M: The extracellular matrix as modifier of neuroinflammation and
recovery in ischemic stroke and intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurobiol
Dis. 186:1062822023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang W, Li M, Chen Q and Wang J:
Hemorrhagic transformation after tissue plasminogen activator
reperfusion therapy for ischemic stroke: Mechanisms, models, and
biomarkers. Mol Neurobiol. 52:1572–1579. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang L, Wei C, Deng L, Wang Z, Song M,
Xiong Y and Liu M: The accuracy of serum matrix metalloproteinase-9
for predicting hemorrhagic transformation after acute ischemic
stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc
Dis. 27:1653–1665. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Barr TL, Latour LL, Lee KY, Schaewe TJ,
Luby M, Chang GS, El-Zammar Z, Alam S, Hallenbeck JM, Kidwell CS
and Warach S: Blood-brain barrier disruption in humans is
independently associated with increased matrix metalloproteinase-9.
Stroke. 41:e123–e128. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jha R, Battey TW, Pham L, Lorenzano S,
Furie KL, Sheth KN and Kimberly WT: Fluid-attenuated inversion
recovery hyperintensity correlates with matrix metalloproteinase-9
level and hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke.
Stroke. 45:1040–1045. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang X, Zhang Y, Su Q, Liu Y, Li Z, Yong
VW and Xue M: Ion channel dysregulation following intracerebral
hemorrhage. Neurosci Bull. 40:401–414. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mondal S, Adhikari N, Banerjee S, Amin SA
and Jha T: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and its inhibitors in
cancer: A minireview. Eur J Med Chem. 194:1122602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Das S, Amin SA and Jha T: Inhibitors of
gelatinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) for the management of hematological
malignancies. Eur J Med Chem. 223:1136232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Beroun A, Mitra S, Michaluk P, Pijet B,
Stefaniuk M and Kaczmarek L: MMPs in learning and memory and
neuropsychiatric disorders. Cell Mol Life Sci. 76:3207–3228. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cathcart J, Pulkoski-Gross A and Cao J:
Targeting matrix metalloproteinases in cancer: Bringing new life to
old ideas. Genes Dis. 2:26–34. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mizoguchi H, Nakade J, Tachibana M, Ibi D,
Someya E, Koike H, Kamei H, Nabeshima T, Itohara S, Takuma K, et
al: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 contributes to kindled seizure
development in pentylenetetrazole-treated mice by converting
pro-BDNF to mature BDNF in the hippocampus. J Neurosci.
31:12963–12971. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li YJ, Wang ZH, Zhang B, Zhe X, Wang MJ,
Shi ST, Bai J, Lin T, Guo CJ, Zhang SJ, et al: Disruption of the
blood-brain barrier after generalized tonic-clonic seizures
correlates with cerebrospinal fluid MMP-9 levels. J
Neuroinflammation. 10:802013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bronisz E and Kurkowska-Jastrzebska I:
Matrix metalloproteinase 9 in epilepsy: The role of
neuroinflammation in seizure development. Mediators Inflamm.
2016:73690202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stawarski M, Stefaniuk M and Wlodarczyk J:
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 involvement in the structural plasticity
of dendritic spines. Front Neuroanat. 8:682014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xue M, Hollenberg MD and Yong VW:
Combination of thrombin and matrix metalloproteinase-9 exacerbates
neurotoxicity in cell culture and intracerebral hemorrhage in mice.
J Neurosci. 26:10281–10291. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen H, He Y, Chen S, Qi S and Shen J:
Therapeutic targets of oxidative/nitrosative stress and
neuroinflammation in ischemic stroke: Applications for natural
product efficacy with omics and systemic biology. Pharmacol Res.
158:1048772020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Qi Z, Liang J, Pan R, Dong W, Shen J, Yang
Y, Zhao Y, Shi W, Luo Y, Ji X and Liu KJ: Zinc contributes to acute
cerebral ischemia-induced blood-brain barrier disruption. Neurobiol
Dis. 95:12–21. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li Z, Liu Y, Wei R, Yong VW and Xue M: The
important role of Zinc in neurological diseases. Biomolecules.
13:282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Foerch C, Montaner J, Furie KL, Ning MM
and Lo EH: Invited article: searching for oracles? Blood biomarkers
in acute stroke. Neurology. 73:393–399. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Romanic AM, White RF, Arleth AJ, Ohlstein
EH and Barone FC: Matrix metalloproteinase expression increases
after cerebral focal ischemia in rats: Inhibition of matrix
metalloproteinase-9 reduces infarct size. Stroke. 29:1020–1030.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rosenberg GA and Yang Y: Vasogenic edema
due to tight junction disruption by matrix metalloproteinases in
cerebral ischemia. Neurosurg Focus. 22:E42007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhao BQ, Wang S, Kim HY, Storrie H, Rosen
BR, Mooney DJ, Wang X and Lo EH: Role of matrix metalloproteinases
in delayed cortical responses after stroke. Nat Med. 12:441–445.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Candelario-Jalil E, Yang Y and Rosenberg
GA: Diverse roles of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue
inhibitors of metalloproteinases in neuroinflammation and cerebral
ischemia. Neuroscience. 158:983–994. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Iadecola C and Nedergaard M: Glial
regulation of the cerebral microvasculature. Nat Neurosci.
10:1369–1376. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cottarelli A, Corada M, Beznoussenko GV,
Mironov AA, Globisch MA, Biswas S, Huang H, Dimberg A, Magnusson
PU, Agalliu D, et al: Fgfbp1 promotes blood-brain barrier
development by regulating collagen IV deposition and maintaining
Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Development. 147:dev1851402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Heinemann U and Schuetz A: structural
features of tight-junction proteins. Int J Mol Sci. 20:60202019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Biswas S, Cottarelli A and Agalliu D:
Neuronal and glial regulation of CNS angiogenesis and
barriergenesis. Development. 147:dev1822792020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Milner R, Hung S, Wang X, Berg GI, Spatz M
and del Zoppo GJ: Responses of endothelial cell and astrocyte
matrix-integrin receptors to ischemia mimic those observed in the
neurovascular unit. Stroke. 39:191–197. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Thomsen MS, Routhe LJ and Moos T: The
vascular basement membrane in the healthy and pathological brain. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 37:3300–3317. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kadry H, Noorani B and Cucullo L: A
blood-brain barrier overview on structure, function, impairment,
and biomarkers of integrity. Fluids Barriers CNS. 17:692020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tabet A, Apra C, Stranahan AM and Anikeeva
P: Changes in brain neuroimmunology following injury and disease.
Front Integr Neurosci. 16:8945002022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jiang X, Andjelkovic AV, Zhu L, Yang T,
Bennett MVL, Chen J, Keep RF and Shi Y: Blood-brain barrier
dysfunction and recovery after ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol.
163-164:144–171. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Rashid ZA and Bardaweel SK: Novel matrix
metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) inhibitors in cancer treatment. Int J
Mol Sci. 24:121332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Luchian I, Goriuc A, Sandu D and Covasa M:
The role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-8, MMP-9, MMP-13) in
periodontal and peri-implant pathological processes. Int J Mol Sci.
23:18062022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chen X and Wang L, Wang N, Li C, Hang H,
Wu G, Ren S, Jun T and Wang L: An apolipoprotein E receptor mimetic
peptide decreases blood-brain barrier permeability following
intracerebral hemorrhage by inhibiting the CypA/MMP-9 signaling
pathway via LRP1 activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 143 (Pt
3):1130072024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hannocks MJ, Zhang X, Gerwien H,
Chashchina A, Burmeister M, Korpos E, Song J and Sorokin L: The
gelatinases, MMP-2 and MMP-9, as fine tuners of neuroinflammatory
processes. Matrix Biol. 75-76:102–113. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Könnecke H and Bechmann I: The role of
microglia and matrix metalloproteinases involvement in
neuroinflammation and gliomas. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013:9141042013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Fiorelli M, Bastianello S, von Kummer R,
del Zoppo GJ, Larrue V, Lesaffre E, Ringleb AP, Lorenzano S,
Manelfe C and Bozzao L: Hemorrhagic transformation within 36 hours
of a cerebral infarct: relationships with early clinical
deterioration and 3-month outcome in the European Cooperative Acute
Stroke Study I (ECASS I) cohort. Stroke. 30:2280–2284. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C, Toni D,
Lesaffre E, von Kummer R, Boysen G, Bluhmki E, Höxter G, Mahagne
MH, et al: Intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue
plasminogen activator for acute hemispheric stroke. The European
Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (ECASS). JAMA. 274:1017–1025. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ande SR, Grynspan J, Aviv RI and Shankar
JJS: Imaging for predicting hemorrhagic transformation of acute
ischemic stroke-a narrative review. Can Assoc Radiol J. 73:194–202.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Khatri P, Wechsler LR and Broderick JP:
Intracranial hemorrhage associated with revascularization
therapies. Stroke. 38:431–440. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ma G, Pan Z, Kong L and Du G:
Neuroinflammation in hemorrhagic transformation after tissue
plasminogen activator thrombolysis: Potential mechanisms, targets,
therapeutic drugs and biomarkers. Int Immunopharmacol.
90:1072162021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kanazawa M, Takahashi T, Nishizawa M and
Shimohata T: Therapeutic strategies to attenuate hemorrhagic
transformation after tissue plasminogen activator treatment for
acute ischemic stroke. J Atheroscler Thromb. 24:240–253. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhang Y, Khan S, Liu Y, Wu G, Yong VW and
Xue M: Oxidative stress following intracerebral hemorrhage: From
molecular mechanisms to therapeutic targets. Front Immunol.
13:8472462022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhao Y, Zhang X, Chen X and Wei Y:
Neuronal injuries in cerebral infarction and ischemic stroke: From
mechanisms to treatment (Review). Int J Mol Med. 49:152022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Abdullahi W, Tripathi D and Ronaldson PT:
Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in ischemic stroke: targeting tight
junctions and transporters for vascular protection. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 315:C343–C356. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Fraser PA: The role of free radical
generation in increasing cerebrovascular permeability. Free Radic
Biol Med. 51:967–977. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sun MS, Jin H, Sun X, Huang S, Zhang FL,
Guo ZN and Yang Y: Free radical damage in ischemia-reperfusion
injury: An obstacle in acute ischemic stroke after
revascularization therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018:38049792018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Shuvalova M, Dmitrieva A, Belousov V and
Nosov G: The role of reactive oxygen species in the regulation of
the blood-brain barrier. Tissue Barriers. May 29–2024.(Epub ahead
of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Hong S, Park KK, Magae J, Ando K, Lee TS,
Kwon TK, Kwak JY, Kim CH and Chang YC: Ascochlorin inhibits matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression by suppressing activator
protein-1-mediated gene expression through the ERK1/2 signaling
pathway: Inhibitory effects of ascochlorin on the invasion of renal
carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 280:25202–25209. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Lee GH, Jin SW, Kim SJ, Pham TH, Choi JH
and Jeong HG: Tetrabromobisphenol A induces MMP-9 expression via
NADPH Oxidase and the activation of ROS, MAPK and Akt pathways in
human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Toxicol Res. 35:93–101. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Banjara M and Ghosh C: Sterile
Neuroinflammation and strategies for therapeutic intervention. Int
J Inflam. 2017:83859612017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Gülke E, Gelderblom M and Magnus T: Danger
signals in stroke and their role on microglia activation after
ischemia. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 11:17562864187742542018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Alsbrook DL, Di Napoli M, Bhatia K, Biller
J, Andalib S, Hinduja A, Rodrigues R, Rodriguez M, Sabbagh SY,
Selim M, et al: Neuroinflammation in acute ischemic and hemorrhagic
stroke. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 23:407–431. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Yang C, Hawkins KE, Doré S and
Candelario-Jalil E: Neuroinflammatory mechanisms of blood-brain
barrier damage in ischemic stroke. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
316:C135–C153. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
McColl BW, Rothwell NJ and Allan SM:
Systemic inflammation alters the kinetics of cerebrovascular tight
junction disruption after experimental stroke in mice. J Neurosci.
28:9451–9462. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
McColl BW, Rothwell NJ and Allan SM:
Systemic inflammatory stimulus potentiates the acute phase and CXC
chemokine responses to experimental stroke and exacerbates brain
damage via interleukin-1- and neutrophil-dependent mechanisms. J
Neurosci. 27:4403–4412. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
de Vries HE, Blom-Roosemalen MC, van
Oosten M, de Boer AG, van Berkel TJ, Breimer DD and Kuiper J: The
influence of cytokines on the integrity of the blood-brain barrier
in vitro. J Neuroimmunol. 64:37–43. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Takata F, Dohgu S, Matsumoto J, Takahashi
H, Machida T, Wakigawa T, Harada E, Miyaji H, Koga M, Nishioku T,
et al: Brain pericytes among cells constituting the blood-brain
barrier are highly sensitive to tumor necrosis factor-α, releasing
matrix metalloproteinase-9 and migrating in vitro. J
Neuroinflammation. 8:1062011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Dimitrijevic OB, Stamatovic SM, Keep RF
and Andjelkovic AV: Effects of the chemokine CCL2 on blood-brain
barrier permeability during ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 26:797–810. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Kim JS: tPA Helpers in the treatment of
acute ischemic stroke: Are they ready for clinical use? J Stroke.
21:160–174. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Lees KR, Bluhmki E, von Kummer R, Brott
TG, Toni D, Grotta JC, Albers GW, Kaste M, Marler JR, Hamilton SA,
et al: Time to treatment with intravenous alteplase and outcome in
stroke: An updated pooled analysis of ECASS, ATLANTIS, NINDS, and
EPITHET trials. Lancet. 375:1695–1703. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Fan X, Jiang Y, Yu Z, Yuan J, Sun X, Xiang
S, Lo EH and Wang X: Combination approaches to attenuate
hemorrhagic transformation after tPA thrombolytic therapy in
patients with poststroke hyperglycemia/diabetes. Adv Pharmacol.
71:391–410. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Su EJ, Fredriksson L, Geyer M, Folestad E,
Cale J, Andrae J, Gao Y, Pietras K, Mann K, Yepes M, et al:
Activation of PDGF-CC by tissue plasminogen activator impairs
blood-brain barrier integrity during ischemic stroke. Nat Med.
14:731–737. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Cuadrado E, Ortega L, Hernández-Guillamon
M, Penalba A, Fernández-Cadenas I, Rosell A and Montaner J: Tissue
plasminogen activator (t-PA) promotes neutrophil degranulation and
MMP-9 release. J Leukoc Biol. 84:207–214. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Wang X, Lee SR, Arai K, Lee SR, Tsuji K,
Rebeck GW and Lo EH: Lipoprotein receptor-mediated induction of
matrix metalloproteinase by tissue plasminogen activator. Nat Med.
9:1313–1317. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Cheng T, Petraglia AL, Li Z, Thiyagarajan
M, Zhong Z, Wu Z, Liu D, Maggirwar SB, Deane R, Fernández JA, et
al: Activated protein C inhibits tissue plasminogen
activator-induced brain hemorrhage. Nat Med. 12:1278–1285. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Shi K, Zou M, Jia DM, Shi S, Yang X, Liu
Q, Dong JF, Sheth KN, Wang X and Shi FD: tPA mobilizes immune cells
that exacerbate hemorrhagic transformation in stroke. Circ Res.
128:62–75. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Mashaqi S, Mansour HM, Alameddin H, Combs
D, Patel S, Estep L and Parthasarathy S: Matrix metalloproteinase-9
as a messenger in the cross talk between obstructive sleep apnea
and comorbid systemic hypertension, cardiac remodeling, and
ischemic stroke: A literature review. J Clin Sleep Med. 17:567–591.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
di Biase L, Bonura A, Pecoraro PM, Carbone
SP and Di Lazzaro V: Unlocking the potential of stroke blood
biomarkers: Early diagnosis, ischemic vs. haemorrhagic
differentiation and haemorrhagic transformation risk: A
comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci. 24:115452023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Yuan R, Tan S, Wang D, Wu S, Cao X, Zhang
S, Wu B and Liu M: Predictive value of plasma matrix
metalloproteinase-9 concentrations for spontaneous haemorrhagic
transformation in patients with acute ischaemic stroke: A cohort
study in Chinese patients. J Clin Neurosci. 58:108–112. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Arkelius K, Wendt TS, Andersson H, Arnou
A, Gottschalk M, Gonzales RJ and Ansar S: LOX-1 and MMP-9
inhibition attenuates the detrimental effects of delayed rt-PA
therapy and improves outcomes after acute ischemic stroke. Circ
Res. 134:954–969. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Sun X, Liu Z, Zhou L, Ma R, Zhang X, Wang
T, Fu F and Wang Y: Escin avoids hemorrhagic transformation in
ischemic stroke by protecting BBB through the AMPK/Cav-1/MMP-9
pathway. Phytomedicine. 120:1550712023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Izidoro-Toledo TC, Guimaraes DA, Belo VA,
Gerlach RF and Tanus-Santos JE: Effects of statins on matrix
metalloproteinases and their endogenous inhibitors in human
endothelial cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol.
383:547–554. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Yin B, Li DD, Xu SY, Huang H, Lin J, Sheng
HS, Fang JH, Song JN and Zhang M: Simvastatin pretreatment
ameliorates t-PA-induced hemorrhage transformation and MMP-9/TIMP-1
imbalance in thromboembolic cerebral ischemic rats. Neuropsychiatr
Dis Treat. 15:1993–2002. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Li Y, Chen L, Yao S, Chen J, Hu W, Wang M,
Chen S, Chen X, Li S, Gu X, et al: Association of polymorphisms of
the matrix metalloproteinase 9 gene with ischaemic stroke in a
southern Chinese population. Cell Physiol Biochem. 49:2188–2199.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhang X, Cao X, Xu X, Li A and Xu Y:
Correlation between the −1562C/T polymorphism in the matrix
metalloproteinase-9 gene and hemorrhagic transformation of ischemic
stroke. Exp Ther Med. 9:1043–1047. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Szczudlik P and Borratyńska A: Association
between the −1562 C/T MMP-9 polymorphism and cerebrovascular
disease in a Polish population. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 44:350–357.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Fernández-Cadenas I, Del Río-Espínola A,
Carrera C, Domingues-Montanari S, Mendióroz M, Delgado P, Rosell A,
Ribó M, Giralt D, Quintana M, et al: Role of the MMP-9 gene in
hemorrhagic transformations after tissue-type plasminogen activator
treatment in stroke patients. Stroke. 43:1398–1400. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Wang B, Wang Y and Zhao L: MMP-9 gene
rs3918242 polymorphism increases risk of stroke: A meta-analysis. J
Cell Biochem. 119:9801–9808. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Yi X, Sui G, Zhou Q, Wang C, Lin J, Chai Z
and Zhou J: Variants in matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene are
associated with hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke
patients with atherothrombosis, small artery disease, and
cardioembolic stroke. Brain Behav. 9:e012942019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Kytö V, Åivo J and Ruuskanen JO: Intensity
of statin therapy after ischaemic stroke and long-term outcomes: A
nationwide cohort study. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 10:142–145. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Lapchak PA and Han MK: The
3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor
simvastatin reduces thrombolytic-induced intracerebral hemorrhage
in embolized rabbits. Brain Res. 1303:144–150. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Reuter B, Rodemer C, Grudzenski S, Meairs
S, Bugert P, Hennerici MG and Fatar M: Effect of simvastatin on
MMPs and TIMPs in human brain endothelial cells and experimental
stroke. Transl Stroke Res. 6:156–159. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Fang X, Tao D, Shen J, Wang Y, Dong X and
Ji X: Neuroprotective effects and dynamic expressions of MMP9 and
TIMP1 associated with atorvastatin pretreatment in
ischemia-reperfusion rats. Neurosci Lett. 603:60–65. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Kurzepa J, Szczepanska-Szerej A,
Stryjecka-Zimmer M, Malecka-Massalska T and Stelmasiak Z:
Simvastatin could prevent increase of the serum MMP-9/TIMP-1 ratio
in acute ischaemic stroke. Folia Biol (Praha). 52:181–183. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Turner NA, Aley PK, Hall KT, Warburton P,
Galloway S, Midgley L, O'Regan DJ, Wood IC, Ball SG and Porter KE:
Simvastatin inhibits TNFalpha-induced invasion of human cardiac
myofibroblasts via both MMP-9-dependent and -independent
mechanisms. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 43:168–176. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Skrzypiec-Spring M, Kaczorowski M,
Rak-Pasikowska A, Sapa-Wojciechowska A, Kujawa K, Żuryń A, Bil-Lula
I, Hałoń A and Szeląg A: RhoA/ROCK pathway is upregulated in
experimental autoimmune myocarditis and is inhibited by simvastatin
at the stage of myosin light chain phosphorylation. Biomedicines.
12:5962024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Liu XS, Zhang ZG, Zhang L, Morris DC,
Kapke A, Lu M and Chopp M: Atorvastatin downregulates tissue
plasminogen activator-aggravated genes mediating coagulation and
vascular permeability in single cerebral endothelial cells captured
by laser microdissection. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 26:787–796.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Gómez-Hernández A, Sánchez-Galán E, Ortego
M, Martín-Ventura JL, Blanco-Colio LM, Tarín-Vicente N,
Jiménez-Nacher JJ, López-Bescos L, Egido J and Tuñón J: Effect of
intensive atorvastatin therapy on prostaglandin E2 levels and
metalloproteinase-9 activity in the plasma of patients with
non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 102:12–18.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Zhang L, Chopp M, Jia L, Cui Y, Lu M and
Zhang ZG: Atorvastatin extends the therapeutic window for tPA to 6
h after the onset of embolic stroke in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 29:1816–1824. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Bellosta S, Via D, Canavesi M, Pfister P,
Fumagalli R, Paoletti R and Bernini F: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors
reduce MMP-9 secretion by macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 18:1671–1678. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Collins R, Reith C, Emberson J, Armitage
J, Baigent C, Blackwell L, Blumenthal R, Danesh J, Smith GD, DeMets
D, et al: Interpretation of the evidence for the efficacy and
safety of statin therapy. Lancet. 388:2532–2561. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Sun Z, Xu Q, Gao G, Zhao M and Sun C:
Clinical observation in edaravone treatment for acute cerebral
infarction. Niger J Clin Pract. 22:1324–1327. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Batino LKJ, Escabillas CG and Navarro JC:
Edaravone's safety profile in acute ischemic stroke. Brain Behav.
14:e701582024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Liu J, Jiang Y, Zhang G, Lin Z and Du S:
Protective effect of edaravone on blood-brain barrier by affecting
NRF-2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 18:2437–2442.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Barna L, Walter FR, Harazin A, Bocsik A,
Kincses A, Tubak V, Jósvay K, Zvara Á, Campos-Bedolla P and Deli
MA: Simvastatin, edaravone and dexamethasone protect against
kainate-induced brain endothelial cell damage. Fluids Barriers CNS.
17:52020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Zheng J and Chen X: Edaravone offers
neuroprotection for acute diabetic stroke patients. Ir J Med Sci.
185:819–824. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Toyoda K, Fujii K, Kamouchi M, Nakane H,
Arihiro S, Okada Y, Ibayashi S and Iida M: Free radical scavenger,
edaravone, in stroke with internal carotid artery occlusion. J
Neurol Sci. 221:11–17. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Okamura K, Tsubokawa T, Johshita H,
Miyazaki H and Shiokawa Y: Edaravone, a free radical scavenger,
attenuates cerebral infarction and hemorrhagic infarction in rats
with hyperglycemia. Neurol Res. 36:65–69. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Yagi K, Kitazato KT, Uno M, Tada Y,
Kinouchi T, Shimada K and Nagahiro S: Edaravone, a free radical
scavenger, inhibits MMP-9-related brain hemorrhage in rats treated
with tissue plasminogen activator. Stroke. 40:626–631. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Miyamoto N, Pham LD, Maki T, Liang AC and
Arai K: A radical scavenger edaravone inhibits matrix
metalloproteinase-9 upregulation and blood-brain barrier breakdown
in a mouse model of prolonged cerebral hypoperfusion. Neurosci
Lett. 573:40–45. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Harada K, Suzuki Y, Yamakawa K, Kawakami J
and Umemura K: Combination of reactive oxygen species and
tissue-type plasminogen activator enhances the induction of
gelatinase B in brain endothelial cells. Int J Neurosci. 122:53–59.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Yang CC, Hsiao LD, Tseng HC, Kuo CM and
Yang CM: Pristimerin inhibits MMP-9 expression and cell migration
through attenuating NOX/ROS-dependent NF-κB activation in rat brain
astrocytes challenged with LPS. J Inflamm Res. 13:325–341. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Zhang H and Sun SC: NF-κB in inflammation
and renal diseases. Cell Biosci. 5:632015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Ridder DA and Schwaninger M: NF-κB
signaling in cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience. 158:995–1006. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Amirshahrokhi K and Imani M: Edaravone
reduces brain injury in hepatic encephalopathy by upregulation of
Nrf2/HO-1 and inhibition of NF-κB, iNOS/NO and inflammatory
cytokines. Mol Biol Rep. 52:2222025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Mishina M, Komaba Y, Kobayashi S, Kominami
S, Fukuchi T, Mizunari T, Teramoto A and Katayama Y: Administration
of free radical scavenger edaravone associated with higher
frequency of hemorrhagic transformation in patients with
cardiogenic embolism. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 48:292–297. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Liao TV, Forehand CC, Hess DC and Fagan
SC: Minocycline repurposing in critical illness: Focus on stroke.
Curr Top Med Chem. 13:2283–2290. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Singh T, Thapliyal S, Bhatia S, Singh V,
Singh M, Singh H, Kumar A and Mishra A: Reconnoitering the
transformative journey of minocycline from an antibiotic to an
antiepileptic drug. Life Sci. 293:1203462022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Chang JJ, Kim-Tenser M, Emanuel BA, Jones
GM, Chapple K, Alikhani A, Sanossian N, Mack WJ, Tsivgoulis G,
Alexandrov AV and Pourmotabbed T: Minocycline and matrix
metalloproteinase inhibition in acute intracerebral hemorrhage: A
pilot study. Eur J Neurol. 24:1384–1391. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Fouda AY, Newsome AS, Spellicy S, Waller
JL, Zhi W, Hess DC, Ergul A, Edwards DJ, Fagan SC and Switzer JA:
Minocycline in acute cerebral hemorrhage: an early phase randomized
trial. Stroke. 48:2885–2887. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Kohler E, Prentice DA, Bates TR, Hankey
GJ, Claxton A, van Heerden J and Blacker D: Intravenous minocycline
in acute stroke: A randomized, controlled pilot study and
meta-analysis. Stroke. 44:2493–2499. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Fagan SC, Waller JL, Nichols FT, Edwards
DJ, Pettigrew LC, Clark WM, Hall CE, Switzer JA, Ergul A and Hess
DC: Minocycline to improve neurologic outcome in stroke (MINOS): A
dose-finding study. Stroke. 41:2283–2287. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Chen X, Chen S, Jiang Y, Zhu C, Wu A, Ma
X, Peng F, Ma L, Zhu D, Wang Q and Pi R: Minocycline reduces
oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced PC12 cell cytotoxicity via
matrix metalloproteinase-9, integrin β1 and phosphorylated Akt
modulation. Neurol Sci. 34:1391–1396. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Knecht T, Borlongan C and Dela Peña I:
Combination therapy for ischemic stroke: Novel approaches to
lengthen therapeutic window of tissue plasminogen activator. Brain
Circ. 4:99–108. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Murata Y, Rosell A, Scannevin RH, Rhodes
KJ, Wang X and Lo EH: Extension of the thrombolytic time window
with minocycline in experimental stroke. Stroke. 39:3372–3377.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Liu Y, Li Z, Khan S, Zhang R, Wei R, Zhang
Y, Xue M and Yong VW: Neuroprotection of minocycline by inhibition
of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer expression
following intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Neurosci Lett.
764:1362972021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Liu Y, Mu Y, Li Z, Yong VW and Xue M:
Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer in brain ischemia
and intracerebral hemorrhage. Front Immunol. 13:9864692022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Song ZP, Xiong BR, Guan XH, Cao F,
Manyande A, Zhou YQ, Zheng H and Tian YK: Minocycline attenuates
bone cancer pain in rats by inhibiting NF-κB in spinal astrocytes.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 37:753–762. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Fan Y, Meng S, Wang Y, Cao J and Wang C:
Visfatin/PBEF/Nampt induces EMMPRIN and MMP-9 production in
macrophages via the NAMPT-MAPK (p38, ERK1/2)-NF-κB signaling
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 27:607–615. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Chen Y, Won SJ, Xu Y and Swanson RA:
Targeting microglial activation in stroke therapy: Pharmacological
tools and gender effects. Curr Med Chem. 21:2146–2155. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Kase CS, Furlan AJ, Wechsler LR, Higashida
RT, Rowley HA, Hart RG, Molinari GF, Frederick LS, Roberts HC,
Gebel JM, et al: Cerebral hemorrhage after intra-arterial
thrombolysis for ischemic stroke: the PROACT II trial. Neurology.
57:1603–1610. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Arcambal A, Taïlé J, Rondeau P,
Viranaïcken W, Meilhac O and Gonthier MP: Hyperglycemia modulates
redox, inflammatory and vasoactive markers through specific
signaling pathways in cerebral endothelial cells: Insights on
insulin protective action. Free Radic Biol Med. 130:59–70. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Liu Y, Zhang H, Wang S, Guo Y, Fang X,
Zheng B, Gao W, Yu H, Chen Z, Roman RJ and Fan F: Reduced pericyte
and tight junction coverage in old diabetic rats are associated
with hyperglycemia-induced cerebrovascular pericyte dysfunction. Am
J Physiolo Heart Circ Physiol. 320:H549–H562. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Rom S, Heldt NA, Gajghate S, Seliga A,
Reichenbach NL and Persidsky Y: Hyperglycemia and advanced
glycation end products disrupt BBB and promote occludin and
claudin-5 protein secretion on extracellular microvesicles. Sci
Rep. 10:72742020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Yuan C, Chen S, Ruan Y, Liu Y, Cheng H,
Zeng Y, Chen Y, Cheng Q, Huang G, He W and He J: The stress
hyperglycemia ratio is associated with hemorrhagic transformation
in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Clin Interv Aging.
16:431–442. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Zhang FH, Lin YH, Huang HG, Sun JZ, Wen SQ
and Lou M: Rosiglitazone attenuates hyperglycemia-enhanced
hemorrhagic transformation after transient focal ischemia in rats.
Neuroscience. 250:651–657. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Li Y, Zhu ZY, Lu BW, Huang TT, Zhang YM,
Zhou NY, Xuan W, Chen ZA, Wen DX, Yu WF and Li PY: Rosiglitazone
ameliorates tissue plasminogen activator-induced brain hemorrhage
after stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. 25:1343–1352. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Marx N, Froehlich J, Siam L, Ittner J,
Wierse G, Schmidt A, Scharnagl H, Hombach V and Koenig W:
Antidiabetic PPAR gamma-activator rosiglitazone reduces MMP-9 serum
levels in type 2 diabetic patients with coronary artery disease.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:283–288. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Wu G, Wu J, Jiao Y, Wang L, Wang F and
Zhang Y: Rosiglitazone infusion therapy following minimally
invasive surgery for intracerebral hemorrhage evacuation decreases
matrix metalloproteinase-9 and blood-brain barrier disruption in
rabbits. BMC Neurol. 15:372015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Wang CX, Ding X, Noor R, Pegg C, He C and
Shuaib A: Rosiglitazone alone or in combination with tissue
plasminogen activator improves ischemic brain injury in an embolic
model in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 29:1683–1694. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Zhou M, Xu A, Lam KS, Tam PK, Che CM, Chan
L, Lee IK, Wu D and Wang Y: Rosiglitazone promotes fatty acyl CoA
accumulation and excessive glycogen storage in livers of mice
without adiponectin. J Hepatol. 53:1108–1116. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Medunjanin S, Schleithoff L, Fiegehenn C,
Weinert S, Zuschratter W and Braun-Dullaeus RC: GSK-3β controls
NF-kappaB activity via IKKγ/NEMO. Sci Rep. 6:385532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Lee CS, Kwon YW, Yang HM, Kim SH, Kim TY,
Hur J, Park KW, Cho HJ, Kang HJ, Park YB and Kim HS: New mechanism
of rosiglitazone to reduce neointimal hyperplasia: Activation of
glycogen synthase kinase-3beta followed by inhibition of MMP-9.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:472–479. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Home PD, Pocock SJ, Beck-Nielsen H, Curtis
PS, Gomis R, Hanefeld M, Jones NP, Komajda M and McMurray JJ;
RECORD Study Team, : Rosiglitazone evaluated for cardiovascular
outcomes in oral agent combination therapy for type 2 diabetes
(RECORD): A multicentre, randomised, open-label trial. Lancet.
373:2125–2135. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Nishiyama Y, Kimura K, Otsuka T, Toyoda K,
Uchiyama S, Hoshino H, Sakai N, Okada Y, Origasa H, Naritomi H, et
al: Dual antiplatelet therapy with cilostazol for secondary
prevention in lacunar stroke: Subanalysis of the CSPS.com trial.
Stroke. 54:697–705. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Uchiyama S: Results of the Cilostazol
Stroke Prevention Study II (CSPS II): A randomized controlled trial
for the comparison of cilostazol and aspirin in stroke patients.
Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 50:832–834. 2010.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Nonaka Y, Tsuruma K, Shimazawa M,
Yoshimura S, Iwama T and Hara H: Cilostazol protects against
hemorrhagic transformation in mice transient focal cerebral
ischemia-induced brain damage. Neurosci Lett. 452:156–161. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Hase Y, Okamoto Y, Fujita Y, Kitamura A,
Nakabayashi H, Ito H, Maki T, Washida K, Takahashi R and Ihara M:
Cilostazol, a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, prevents no-reflow and
hemorrhage in mice with focal cerebral ischemia. Exp Neurol.
233:523–533. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Kasahara Y, Nakagomi T, Matsuyama T, Stern
D and Taguchi A: Cilostazol reduces the risk of hemorrhagic
infarction after administration of tissue-type plasminogen
activator in a murine stroke model. Stroke. 43:499–506. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Chuang SY, Yang SH, Chen TY and Pang JH:
Cilostazol inhibits matrix invasion and modulates the gene
expressions of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in PMA-differentiated THP-1 cells.
Eur J Pharmacol. 670:419–426. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
da Motta NA and de Brito FC: Cilostazol
exerts antiplatelet and anti-inflammatory effects through AMPK
activation and NF-kB inhibition on hypercholesterolemic rats.
Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 30:327–337. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Kitashoji A, Egashira Y, Mishiro K, Suzuki
Y, Ito H, Tsuruma K, Shimazawa M and Hara H: Cilostazol ameliorates
warfarin-induced hemorrhagic transformation after cerebral ischemia
in mice. Stroke. 44:2862–2868. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|