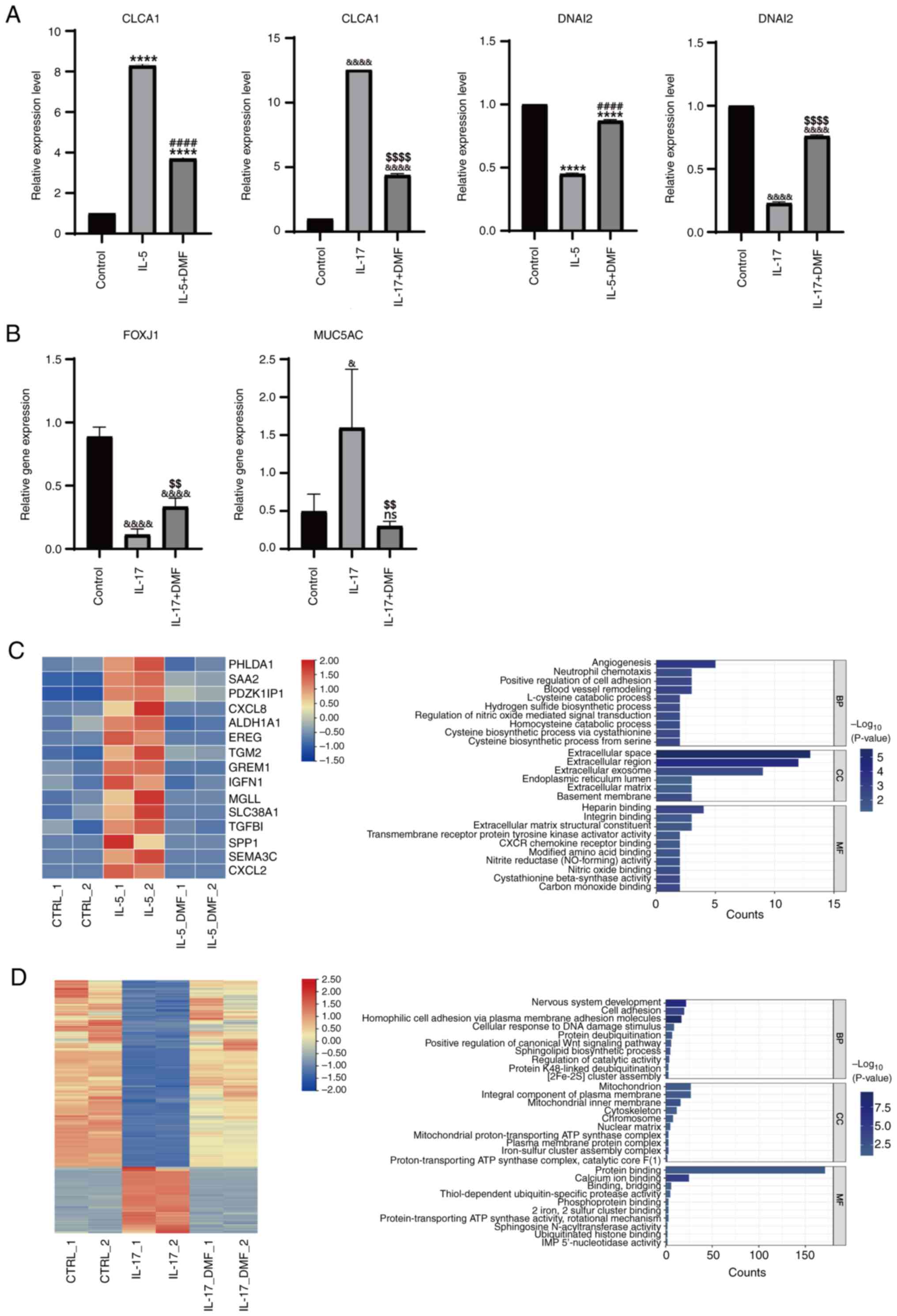
|
1
|
Stevens WW, Lee RJ, Schleimer RP and Cohen
NA: Chronic rhinosinusitis pathogenesis. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
136:1442–1453. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kato A, Schleimer RP and Bleier BS:
Mechanisms and pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 149:1491–1503. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, Hellings
PW, Kern R, Reitsma S, Toppila-Salmi S, Bernal-Sprekelsen M, Mullol
J, Alobid I, et al: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and
nasal polyps 2020. Rhinology. 58 (Suppl S29):1–464. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
DeConde AS, Mace JC, Levy JM, Rudmik L,
Alt JA and Smith TL: Prevalence of polyp recurrence after
endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal
polyposis. Laryngoscope. 127:550–555. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Riva G, Tavassoli M, Cravero E, Moresco M,
Albera A, Canale A and Pecorari G: Long-term evaluation of nasal
polyposis recurrence: A focus on multiple relapses and nasal
cytology. Am J Otolaryngol. 43:1033252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chang L, Wu H, Huang W, Li Y, Chen Y, Li
X, Yao Z, Chen X, Lai X, Zheng R, et al: IL-21 induces pyroptosis
of Treg cells via Akt-mTOR-NLRP3-caspase 1 axis in eosinophilic
chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 152:641–655.e14.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang Y, Chen H, Zhong J, Shen L and Zheng
X: Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome on different phenotypes of chronic
rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 36:607–614. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kayagaki N, Stowe IB, Lee BL, O'Rourke K,
Anderson K, Warming S, Cuellar T, Haley B, Roose-Girma M, Phung QT,
et al: Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical
inflammasome signalling. Nature. 526:666–671. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang K, Shi X, Wang Y,
Huang H, Zhuang Y, Cai T, Wang F and Shao F: Cleavage of GSDMD by
inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature.
526:660–665. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wei Y, Zhang J, Wu X, Sun W, Wei F, Liu W,
Lu T, Ji W, Li H and Wen W: Activated pyrin domain containing 3
(NLRP3) inflammasome in neutrophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with
nasal polyps (CRSwNP). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 145:1002–1005.e16.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li Y, Chang LH, Huang WQ, Bao HW, Li X,
Chen XH, Wu HT, Yao ZZ, Huang ZZ, Weinberg SE, et al: IL-17A
mediates pyroptosis via the ERK pathway and contributes to steroid
resistance in CRSwNP. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 150:337–351. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhong B, Sun S, Tan KS, Ong HH, Du J, Liu
F, Liu Y, Liu S, Ba L, Li J, et al: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α
activates the NLRP3 inflammasome to regulate epithelial
differentiation in chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
152:1444–1459.e14. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gevaert P, Han JK, Smith SG, Sousa AR,
Howarth PH, Yancey SW, Chan R and Bachert C: The roles of
eosinophils and interleukin-5 in the pathophysiology of chronic
rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol.
12:1413–1423. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nagase H, Ueki S and Fujieda S: The roles
of IL-5 and anti-IL-5 treatment in eosinophilic diseases: Asthma,
eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and eosinophilic
chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergol Int. 69:178–186. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen XH, Chang LH, Huang JC, Li X, Lai XP,
Wu XF, Huang ZZ, Wang ZY, Bao HW and Zhang GH: [Expression and
cellular provenance of interleukin 17A in non-eosinophilic chronic
rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps]. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing
Wai Ke Za Zhi. 55:604–610. 2020.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu Y, Zeng M and Liu Z: Th17 response and
its regulation in inflammatory upper airway diseases. Clin Exp
Allergy. 45:602–612. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cheng KJ, Zhou ML, Liu YC and Zhou SH:
Roles played by the PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α pathway and IL-17A in the
Chinese subtype of chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps. Mediators
Inflamm. 2022:86095902022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ye X, Li Y, Fang B, Yuan Y, Feng D, Chen
H, Li J, Meng Q, Xiong S, Ye D, et al: Type 17 mucosal-associated
invariant T cells contribute to neutrophilic inflammation in
patients with nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
152:1153–1166.e12. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Psaltis AJ, Li G, Vaezeafshar R, Cho KS
and Hwang PH: Modification of the Lund-Kennedy endoscopic scoring
system improves its reliability and correlation with
patient-reported outcome measures. Laryngoscope. 124:2216–2223.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kennedy DW: Prognostic factors, outcomes
and staging in ethmoid sinus surgery. Laryngoscope. 102 (Suppl
57):1–18. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lund VJ and Kennedy DW: Quantification for
staging sinusitis. The staging and therapy group. Ann Otol Rhinol
Laryngol Suppl. 167:17–21. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bachert C, Sousa AR, Lund VJ, Scadding GK,
Gevaert P, Nasser S, Durham SR, Cornet ME, Kariyawasam HH, Gilbert
J, et al: Reduced need for surgery in severe nasal polyposis with
mepolizumab: Randomized trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
140:1024–1031.e14. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu C, Wang K, Liu W, Zhang J, Fan Y and
Sun Y: ALOX15+ M2 macrophages contribute to epithelial
remodeling in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal
polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 154:592–608. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang Z, Gearhart MD, Lee YW, Kumar I,
Ramazanov B, Zhang Y, Hernandez C, Lu AY, Neuenkirchen N, Deng J,
et al: A non-canonical BCOR-PRC1.1 complex represses
differentiation programs in human ESCs. Cell Stem Cell.
22:235–251.e9. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pertea M, Kim D, Pertea GM, Leek JT and
Salzberg SL: Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq
experiments with HISAT, StringTie and ballgown. Nat Protoc.
11:1650–1667. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liao Y, Smyth GK and Shi W: featureCounts:
An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads
to genomic features. Bioinformatics. 30:923–930. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene
ontology consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Sato Y,
Ishiguro-Watanabe M and Tanabe M: KEGG: Integrating viruses and
cellular organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 49:D545–D551. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shin SH, Ye MK, Park J and Geum SY:
Immunopathologic role of eosinophils in eosinophilic chronic
rhinosinusitis. Int J Mol Sci. 23:133132022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ryu G, Bae JS, Kim JH, Kim EH, Lyu L,
Chung YJ and Mo JH: Role of IL-17A in chronic rhinosinusitis with
nasal polyp. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 12:507–522. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu T, Zhou YT, Wang LQ, Li LY, Bao Q,
Tian S, Chen MX, Chen HX, Cui J and Li CW: NOD-like receptor
family, pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) contributes to
inflammation, pyroptosis, and mucin production in human airway
epithelium on rhinovirus infection. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
144:777–787.e9. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Duan Y, Zhu Y, Zhang L, Wang W, Zhang M,
Tian J, Li Q, Ai J, Wang R and Xie Z: Activation of the NLRP3
inflammasome by human adenovirus type 7 L4 100-kilodalton protein.
Front Immunol. 15:12948982024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hsieh LL, Looney M, Figueroa A, Massaccesi
G, Stavrakis G, Anaya EU, D'Alessio FR, Ordonez AA, Pekosz AS,
DeFilippis VR, et al: Bystander monocytic cells drive
infection-independent NLRP3 inflammasome response to SARS-CoV-2.
mBio. 15:e00810242024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hirota JA, Hirota SA, Warner SM,
Stefanowicz D, Shaheen F, Beck PL, Macdonald JA, Hackett TL, Sin
DD, Van Eeden S and Knight DA: The airway epithelium
nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat protein 3
inflammasome is activated by urban particulate matter. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 129:1116–1125.e6. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dino P, Giuffrè MR, Buscetta M, Di
Vincenzo S, La Mensa A, Cristaldi M, Bucchieri F, Lo Iacono G,
Bertani A, Pace E and Cipollina C: Release of IL-1β and IL-18 in
human primary bronchial epithelial cells exposed to cigarette smoke
is independent of NLRP3. Eur J Immunol. 54:e24510532024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wu S, Li H, Yu L, Wang N, Li X and Chen W:
IL-1β upregulates Muc5ac expression via NF-κB-induced HIF-1α in
asthma. Immunol Lett. 192:20–26. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Khurana N, Pulsipher A, Jedrzkiewicz J,
Ashby S, Pollard CE, Ghandehari H and Alt JA: Inflammation-driven
vascular dysregulation in chronic rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy
Rhinol. 11:976–983. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vukadinović T, Vuksanović Božarić A,
Vukomanović Durđević B, Radunović M and Perić A: Angiogenesis and
eosinophilia in the nasal mucosa of patients with different
clinical phenotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis. J Infect Dev Ctries.
17:1480–1488. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Blight BJ, Gill AS, Sumsion JS, Pollard
CE, Ashby S, Oakley GM, Alt JA and Pulsipher A: Cell adhesion
molecules are upregulated and may drive inflammation in chronic
rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. J Asthma Allergy. 14:585–593.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang X, Hallen NR, Lee M, Samuchiwal S, Ye
Q, Buchheit KM, Maxfield AZ, Roditi RE, Bergmark RW, Bhattacharyya
N, et al: Type 2 inflammation drives an airway basal stem cell
program through insulin receptor substrate signaling. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 151:1536–1549. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ryser FS, Yalamanoglu A, Valaperti A,
Brühlmann C, Mauthe T, Traidl S, Soyka MB and Steiner UC:
Dupilumab-induced eosinophilia in patients with diffuse type 2
chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergy. 78:2712–2723. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kawasumi T, Takeno S, Ishikawa C, Takahara
D, Taruya T, Takemoto K, Hamamoto T, Ishino T and Ueda T: The
functional diversity of nitric oxide synthase isoforms in human
nose and paranasal sinuses: Contrasting pathophysiological aspects
in nasal allergy and chronic rhinosinusitis. Int J Mol Sci.
22:75612021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Maniscalco M, Fuschillo S, Mormile I,
Detoraki A, Sarnelli G, Paulis A, Spadaro G, Cantone E and PATH-2
TASK FORCE: Exhaled nitric oxide as biomarker of type 2 diseases.
Cells. 12:25182023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang ZQ, Liu J, Sun LY, Ong HH, Ye J, Xu
Y and Wang DY: Updated epithelial barrier dysfunction in chronic
rhinosinusitis: Targeting pathophysiology and treatment response of
tight junctions. Allergy. 79:1146–1165. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Böscke R, Vladar EK, Könnecke M, Hüsing B,
Linke R, Pries R, Reiling N, Axelrod JD, Nayak JV and Wollenberg B:
Wnt signaling in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 56:575–584. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Su H and Zhao Y: Eupatilin alleviates
inflammation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in chronic
rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps by upregulating TFF1 and
inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Histol Histopathol.
39:357–365. 2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yoon YH, Yeon SH, Choi MR, Jang YS, Kim
JA, Oh HW, Jun X, Park SK, Heo JY, Rha KS and Kim YM: Altered
mitochondrial functions and morphologies in epithelial cells are
associated with pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal
polyps. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 12:653–668. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ma Y, Tian P, Zhong H, Wu F, Zhang Q, Liu
X, Dang H, Chen Q, Zou H and Zheng Y: WDPCP modulates cilia beating
through the MAPK/ERK pathway in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal
polyps. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:6303402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Xie X, Wang P, Jin M, Wang Y, Qi L, Wu C,
Guo S, Li C, Zhang X, Yuan Y, et al: IL-1β-induced epithelial cell
and fibroblast transdifferentiation promotes neutrophil recruitment
in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Nat Commun.
15:91012024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Fox RJ, Kita M, Cohan SL, Henson LJ,
Zambrano J, Scannevin RH, O'Gorman J, Novas M, Dawson KT and
Phillips JT: BG-12 (dimethyl fumarate): A review of mechanism of
action, efficacy, and safety. Curr Med Res Opin. 30:251–262. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|