|
1
|
Li J, Cao F, Yin HL, Huang ZJ, Lin ZT, Mao
N, Sun B and Wang G: Ferroptosis: Past, present and future. Cell
Death Dis. 11:882020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhu J, Xiong Y, Zhang Y, Wen J, Cai N,
Cheng K, Liang H and Zhang W: The molecular mechanisms of
regulating oxidative stress-induced ferroptosis and therapeutic
strategy in tumors. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020:88107852020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yan HF, Zou T, Tuo QZ, Xu S, Li H, Belaidi
AA and Lei P: Ferroptosis: Mechanisms and links with diseases.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zilka O, Shah R, Li B, Friedmann Angeli
JP, Griesser M, Conrad M and Pratt DA: On the mechanism of
cytoprotection by ferrostatin-1 and liproxstatin-1 and the role of
lipid peroxidation in ferroptotic cell death. ACS Cent Sci.
3:232–243. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dringen R and Hirrlinger J: Glutathione
pathways in the brain. Biol Chem. 384:505–516. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim M, Bae JY, Yoo S, Kim HW, Lee SA, Kim
ET and Koh G: 2-Deoxy-d-ribose induces ferroptosis in renal tubular
epithelial cells via ubiquitin-proteasome system-mediated xCT
protein degradation. Free Radic Biol Med. 208:384–393. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir
H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ, Fulda S, Gascón S, Hatzios SK,
Kagan VE, et al: Ferroptosis: A regulated cell death nexus linking
metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 171:273–285. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yao MY, Liu T, Zhang L, Wang MJ, Yang Y
and Gao J: Role of ferroptosis in neurological diseases. Neurosci
Lett. 747:1356142021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, Bannuru
RR, Brown FM, Bruemmer D, Collins BS, Hilliard ME, Isaacs D,
Johnson EL, et al: 11. chronic kidney disease and risk management:
standards of care in diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care. 46 (Suppl
1):S191–S202. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Barnett AH, Bain SC, Bouter P, Karlberg B,
Madsbad S, Jervell J and Mustonen J; Diabetics Exposed to
Telmisartan and Enalapril Study Group, : Angiotensin-receptor
blockade versus converting-enzyme inhibition in type 2 diabetes and
nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 351:1952–1961. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Solomon J, Festa MC, Chatzizisis YS,
Samanta R, Suri RS and Mavrakanas TA: Sodium-glucose co-transporter
2 inhibitors in patients with chronic kidney disease. Pharmacol
Ther. 242:1083302023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang XD and Yang YY: Ferroptosis as a
novel therapeutic target for diabetes and its complications. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:8538222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang X and Li X: Abnormal iron and lipid
metabolism mediated ferroptosis in kidney diseases and its
therapeutic potential. Metabolites. 12:582022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim S, Kang SW, Joo J, Han SH, Shin H, Nam
BY, Park J, Yoo TH, Kim G, Lee P and Park JT: Characterization of
ferroptosis in kidney tubular cell death under diabetic conditions.
Cell Death Dis. 12:1602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mengstie MA, Seid MA, Gebeyehu NA, Adella
GA, Kassie GA, Bayih WA, Gesese MM, Anley DT, Feleke SF, Zemene MA,
et al: Ferroptosis in diabetic nephropathy: Mechanisms and
therapeutic implications. Metabol Open. 18:1002432023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Y, Bi R, Quan F, Cao Q, Lin Y, Yue C,
Cui X, Yang H, Gao X and Zhang D: Ferroptosis involves in renal
tubular cell death in diabetic nephropathy. Eur J Pharmacol.
888:1735742020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang WJ, Jiang X, Gao CC and Chen ZW:
Salusin-β participates in high glucose-induced HK-2 cell
ferroptosis in a Nrf-2-dependent manner. Mol Med Rep. 24:6742021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li S, Zheng L, Zhang J, Liu X and Wu Z:
Inhibition of ferroptosis by up-regulating Nrf2 delayed the
progression of diabetic nephropathy. Free Radic Biol Med.
162:435–449. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rojas-Rivera J, Ortiz A and Egido J:
Antioxidants in kidney diseases: The impact of bardoxolone methyl.
Int J Nephrol. 2012:3217142012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang YY, Yang YX, Zhe H, He ZX and Zhou
SF: Bardoxolone methyl (CDDO-Me) as a therapeutic agent: An update
on its pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties. Drug Des
Devel Ther. 8:2075–2088. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Suzuki T and Yamamoto M: Molecular basis
of the Keap1-Nrf2 system. Free Radic Biol Med. 88((Pt B)): 93–100.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu H, Guo P, Xie X, Wang Y and Chen G:
Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death, and its relationships with
tumourous diseases. J Cell Mol Med. 21:648–657. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pergola PE, Krauth M, Huff JW, Ferguson
DA, Ruiz S, Meyer CJ and Warnock DG: Effect of bardoxolone methyl
on kidney function in patients with T2D and Stage 3b-4 CKD. Am J
Nephrol. 33:469–476. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nangaku M, Takama H, Ichikawa T, Mukai K,
Kojima M, Suzuki Y, Watada H, Wada T, Ueki K, Narita I, et al:
Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study of
bardoxolone methyl in patients with diabetic kidney disease: Design
and baseline characteristics of the AYAME study. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 38:1204–1216. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pergola PE, Raskin P, Toto RD, Meyer CJ,
Huff JW, Grossman EB, Krauth M, Ruiz S, Audhya P, Christ-Schmidt H,
et al: Bardoxolone methyl and kidney function in CKD with type 2
diabetes. N Engl J Med. 365:327–336. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tadao A, Kengo Y, Tomohiro I, Kazuya M and
Masaomi N: AYAME Study: Randomized, Double-Blind,
Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Study of Bardoxolone Methyl in Diabetic
Kidney Disease (DKD) Patients FR-OR110. JASN. 34:pB12023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kanda H and Yamawaki K: Bardoxolone
methyl: Drug development for diabetic kidney disease. Clin Exp
Nephrol. 24:857–864. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans
J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL,
et al: The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of
quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem. 55:611–622.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ye L, Jin F, Kumar SK and Dai Y: The
mechanisms and therapeutic targets of ferroptosis in cancer. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 25:965–986. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dixon SJ, Patel DN, Welsch M, Skouta R,
Lee ED, Hayano M, Thomas AG, Gleason CE, Tatonetti NP, Slusher BS
and Stockwell BR: Pharmacological inhibition of cystine-glutamate
exchange induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and ferroptosis.
Elife. 3:e025232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen X, Comish PB, Tang D and Kang R:
Characteristics and biomarkers of ferroptosis. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9:6371622021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hayes JD, Dayalan Naidu S and
Dinkova-Kostova AT: Regulating Nrf2 activity: Ubiquitin ligases and
signaling molecules in redox homeostasis. Trends Biochem Sci.
50:179–205. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Taqi MO, Saeed-Zidane M, Gebremedhn S,
Salilew-Wondim D, Tholen E, Neuhoff C, Hoelker M, Schellander K and
Tesfaye D: NRF2-mediated signaling is a master regulator of
transcription factors in bovine granulosa cells under oxidative
stress condition. Cell Tissue Res. 385:769–783. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zeng XP, Li XJ, Zhang QY, Liu QW, Li L,
Xiong Y, He CX, Wang YF and Ye QF: Tert-butylhydroquinone protects
liver against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats through
Nrf2-activating anti-oxidative activity. Transplant Proc.
49:366–372. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
de Zeeuw D, Akizawa T, Audhya P, Bakris
GL, Chin M, Christ-Schmidt H, Goldsberry A, Houser M, Krauth M,
Lambers Heerspink HJ, et al: Bardoxolone methyl in type 2 diabetes
and stage 4 chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 369:2492–2503.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nangaku M, Kanda H, Takama H, Ichikawa T,
Hase H and Akizawa T: Randomized clinical trial on the effect of
bardoxolone methyl on GFR in diabetic kidney disease patients
(TSUBAKI Study). Kidney Int Rep. 5:879–890. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lu Y, Aimetti AA, Langer R and Gu Z:
Bioresponsive materials. Nat Rev Mater. 2:160752017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Alicic RZ, Neumiller JJ and Tuttle KR:
Combination therapy: An upcoming paradigm to improve kidney and
cardiovascular outcomes in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 40 (Supplement 1):i3–i17. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kaneto H, Fujii J, Myint T, Miyazawa N,
Islam KN, Kawasaki Y, Suzuki K, Nakamura M, Tatsumi H, Yamasaki Y
and Taniguchi N: Reducing sugars trigger oxidative modification and
apoptosis in pancreatic beta-cells by provoking oxidative stress
through the glycation reaction. Biochem J. 320((Pt 3)): 855–863.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tanaka Y, Tran PO, Harmon J and Robertson
RP: A role for glutathione peroxidase in protecting pancreatic beta
cells against oxidative stress in a model of glucose toxicity. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:12363–12368. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang L, Chen X and Yan C: Ferroptosis: An
emerging therapeutic opportunity for cancer. Genes Dis. 9:334–346.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|















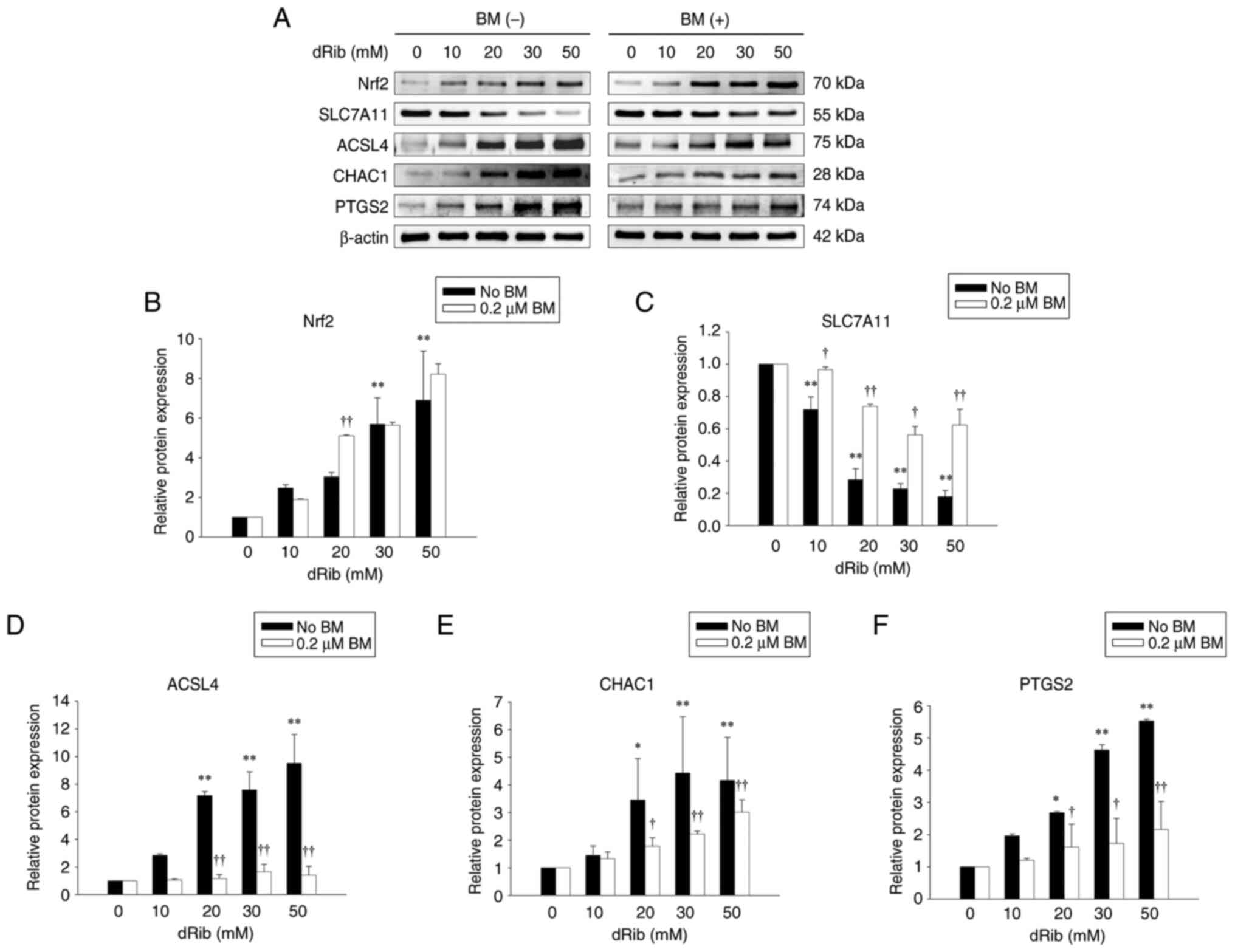
![Effects of BM treatment on the
dRib-induced decreases in (A) l-[14C]cystine uptake, (B)
intracellular GSH content and (C) cell viability. (A) NRK-52E cells
were co-stimulated with 0, 10, 30 and 50 mM dRib with or without
0.2 µM BM for 4 h in the extracellular fluid buffer containing 1.7
µM l-[14C]cystine (0.1 µCi/ml) at 37°C. The
radioactivity incorporated into the cells was determined by a
liquid scintillation counter. (B and C) The cells were
co-stimulated with 0, 10, 30 and 50 mM dRib with or without 0.2 µM
BM for 6 h in DMEM containing 10% FBS. (B) Intracellular GSH
concentration was measured using a GSH assay kit. (C) Cell
viability was measured by LDH release assay. The data are presented
as the mean ± SD. These experiments were performed thrice, in
triplicate. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs. control and
††P<0.01 vs. dRib alone, as determined by one-way
analysis of variance and Tukey's post-hoc test or Welch's ANOVA
followed by Dunnett's T3 post hoc test, depending on the result of
Levene's test. BM, bardoxolone methyl; dRib, 2-deoxy-d-ribose; GSH,
glutathione; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; DMEM, Dulbecco's Modified
Eagle Medium; FBS, fetal bovine serum; SD, standard deviation.](/article_images/mmr/32/4/mmr-32-04-13632-g00.jpg)
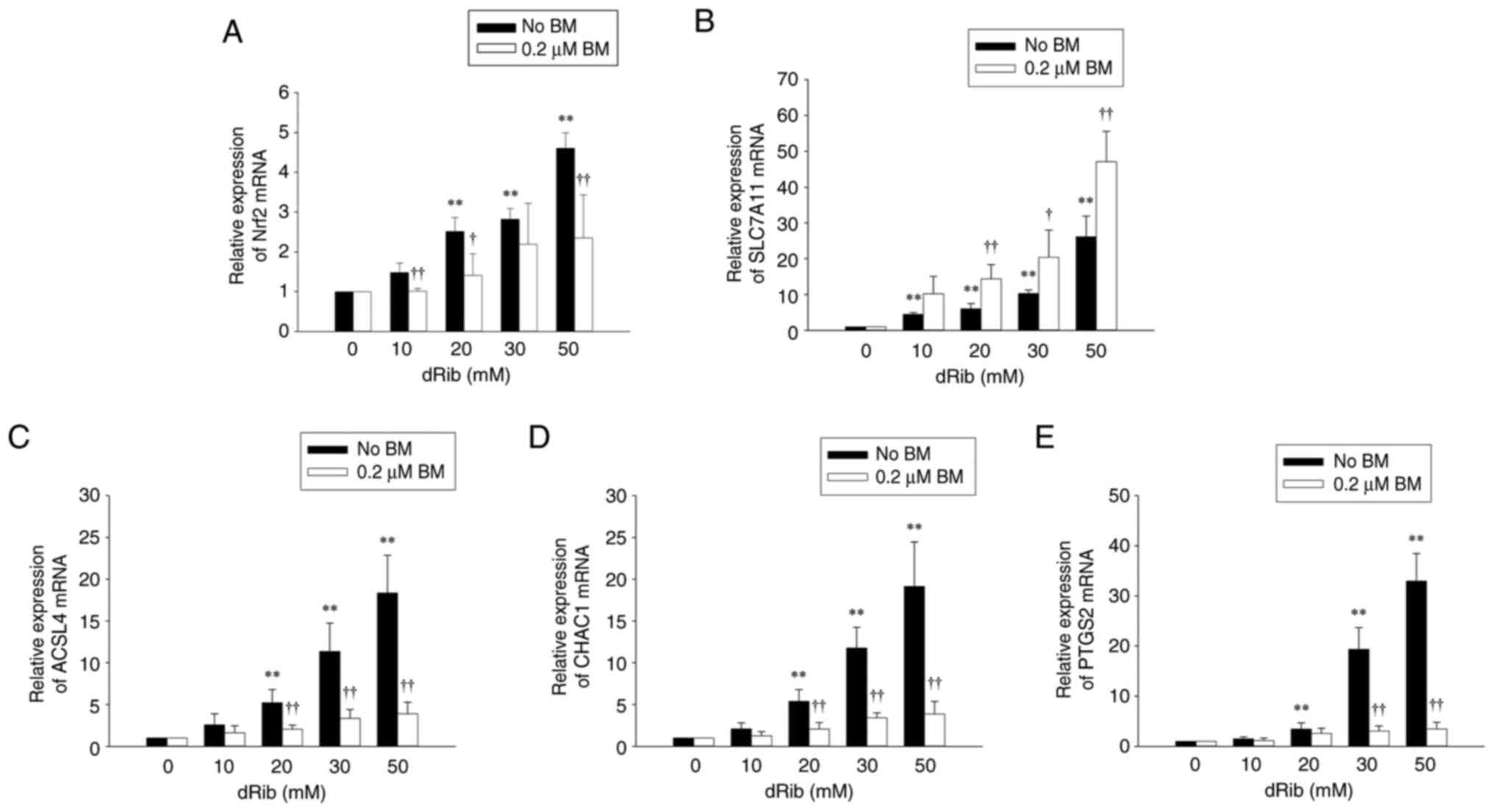
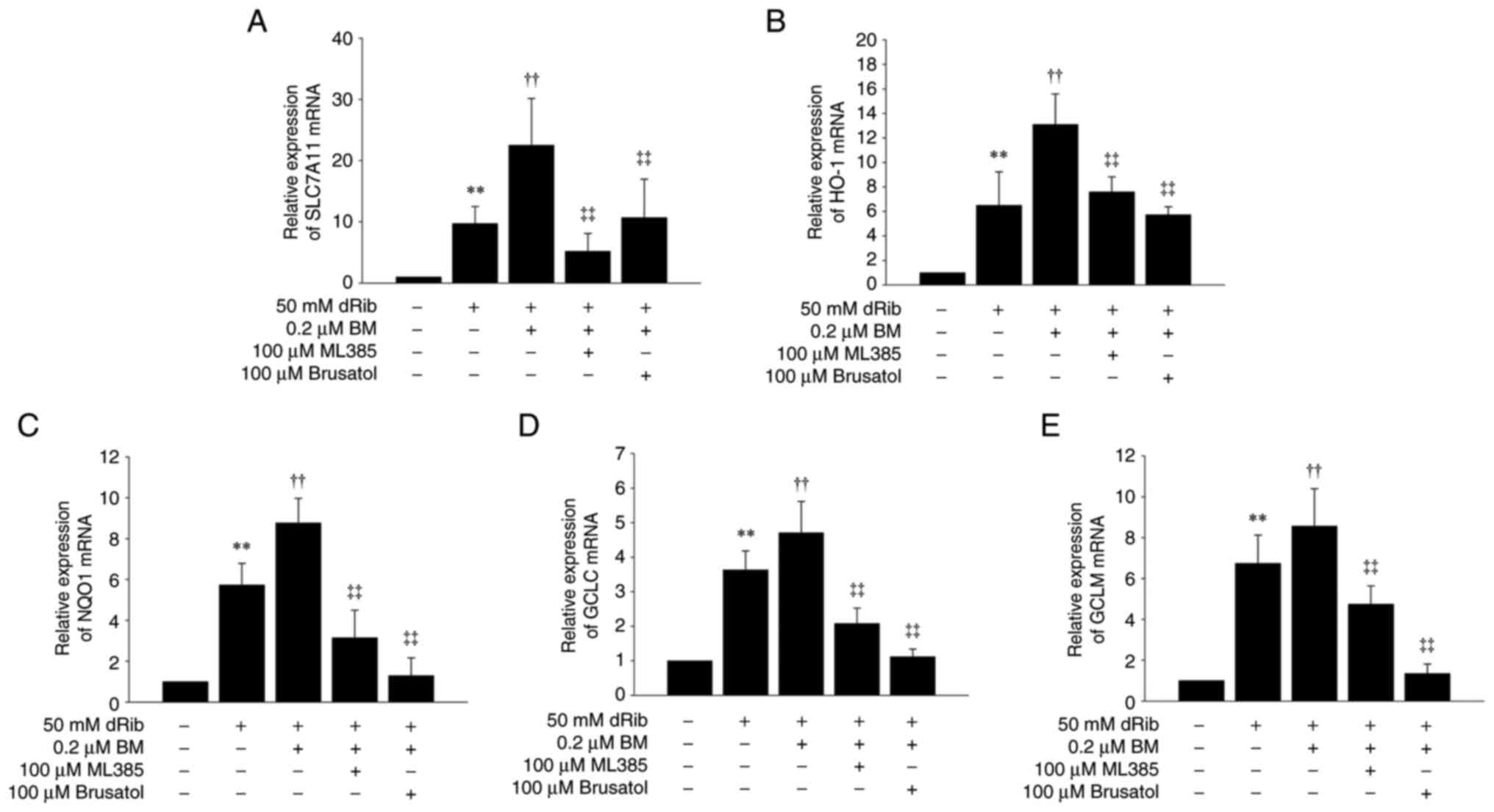
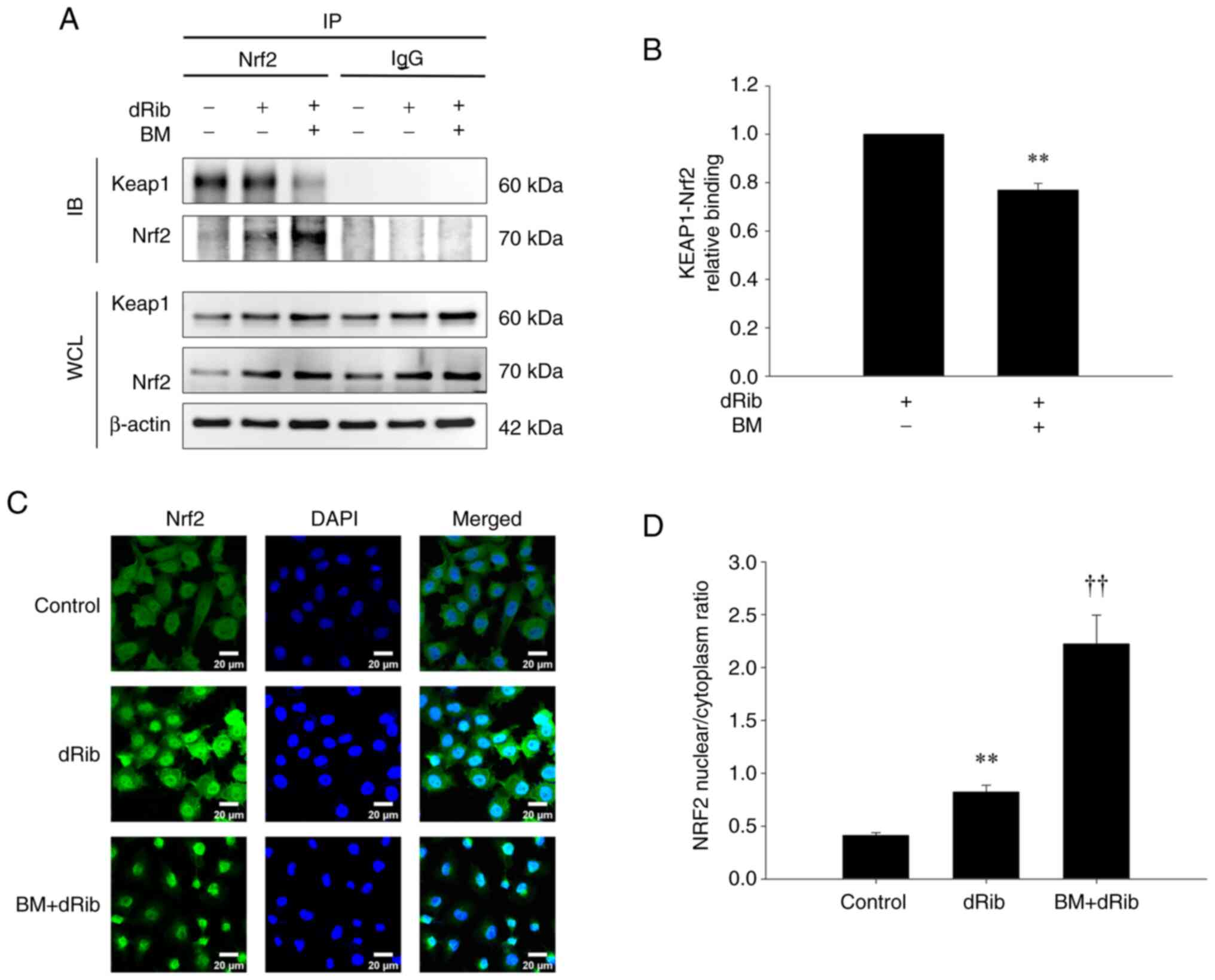
![Effects of ML385 and brusatol on the
protective effects of BM treatment on dRib-induced changes in (A)
l-[14C]cystine uptake, (B) intracellular GSH and (C)
iron contents, (D) intracellular MDA, (E) lipid ROS levels and (F)
cell viability. (A) NRK-52E cells were co-stimulated with 0.2 µM
BM, 100 µM ML385, or 100 µM brusatol and 50 mM dRib for 4 h in the
extracellular fluid buffer containing 1.7 µM
l-[14C]cystine (0.1 µCi/ml) at 37°C. The radioactivity
incorporated into the cells was determined by a liquid
scintillation counter. (B-D and F) NRK-52E cells were co-stimulated
with 0.2 µM BM, 100 µM ML385, or 100 µM brusatol and 50 mM dRib for
6 h in DMEM media containing 10% FBS. The intracellular GSH and
iron levels, intracellular MDA levels, and cell viability were
measured using a GSH assay kit, an iron assay kit, MDA assay kit,
and LDH release assay kit, respectively. These experiments were
performed thrice, in triplicate. (E) Intracellular lipid ROS level
was quantified by flow cytometry using the lipophilic fluorescent
dye C11-BODIPY. Cells were incubated with 4 µM C11-BODIPY during
the final 30 min. Fold control of the mean fluorescence intensity
of experimental groups. This experiment was performed four times.
Data are presented as the mean ± SD. **P<0.01 vs. control;
††P<0.01 vs. 50 mM dRib-alone group;
‡‡P<0.01 vs. 50 mM dRib plus 0.2 µM BM group, as
determined by one way analysis of variance and Tukey's post hoc
test. BM, bardoxolone methyl; dRib, 2-deoxy-d-ribose; GSH,
glutathione; MDA, malondialdehyde; ROS, reactive oxygen
species.](/article_images/mmr/32/4/mmr-32-04-13632-g01.jpg)