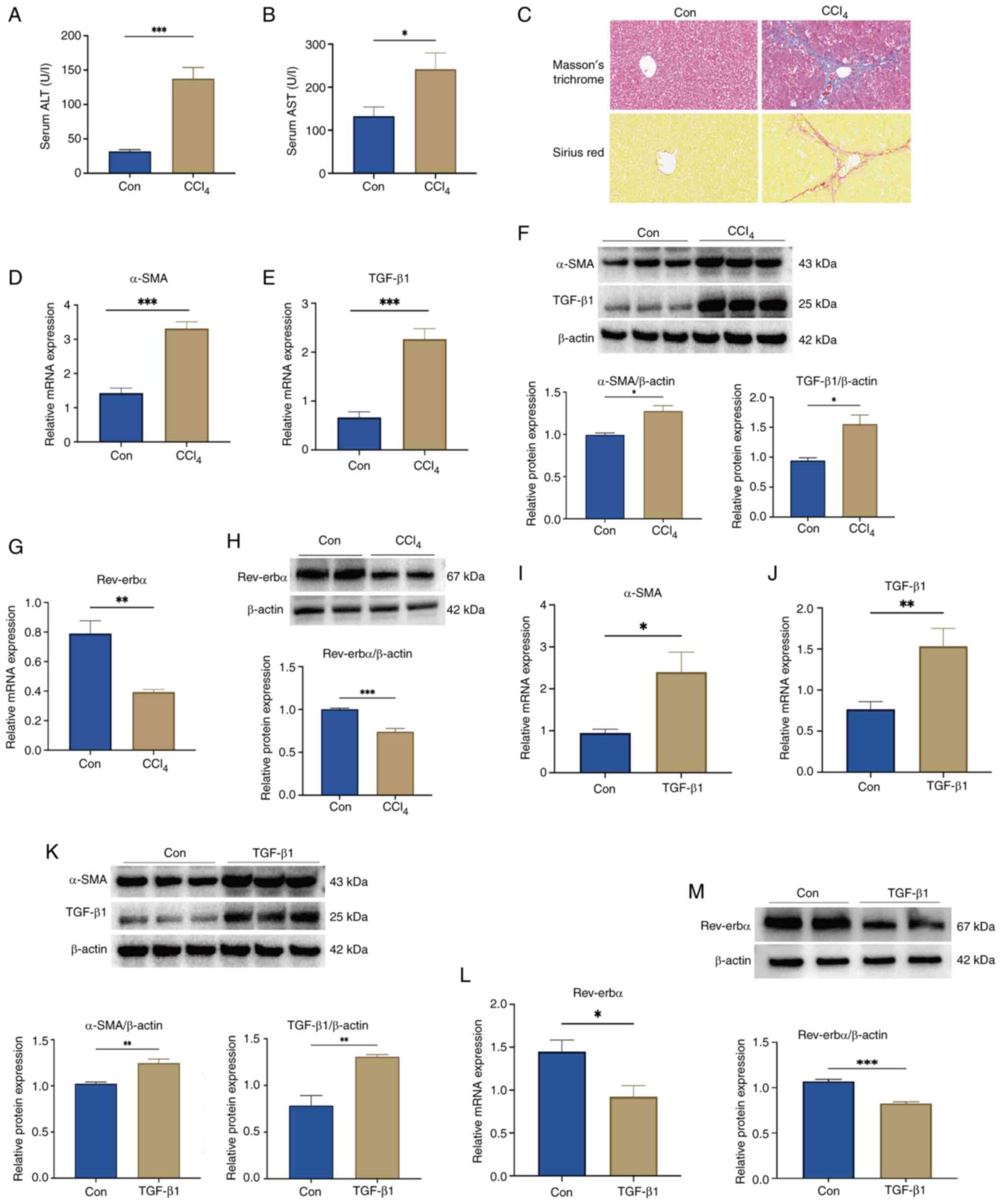
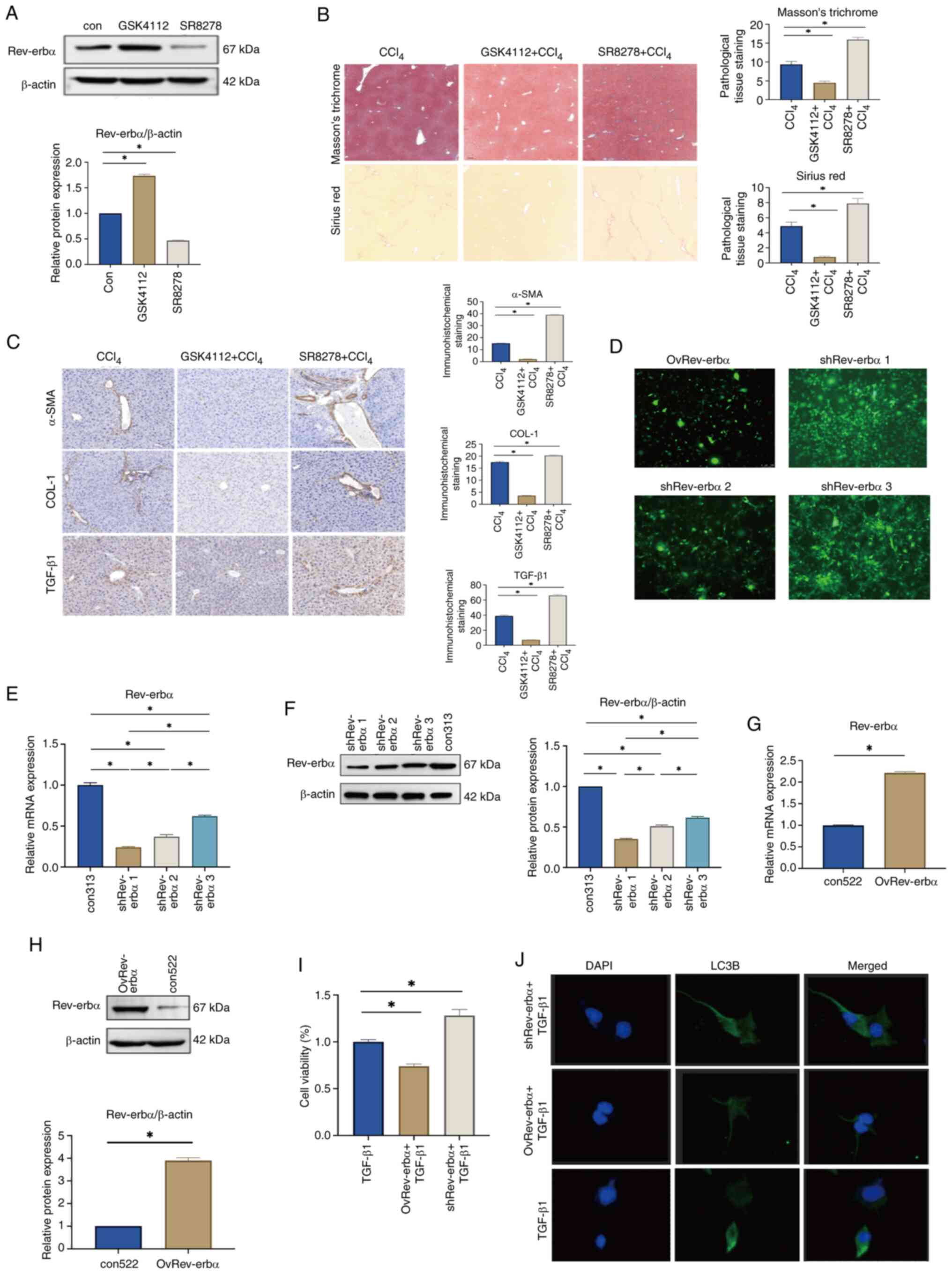
|
1
|
Hernandez-Gea V and Friedman SL:
Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:425–456. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parola M and Pinzani M: Liver fibrosis:
Pathophysiology, pathogenetic targets and clinical issues. Mol
Aspects Med. 65:37–55. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Higashi T, Friedman SL and Hoshida Y:
Hepatic stellate cells as key target in liver fibrosis. Adv Drug
Deliv Rev. 121:27–42. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tsuchida T and Friedman SL: Mechanisms of
hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
14:397–411. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Frazier K, Manzoor S, Carroll K, DeLeon O,
Miyoshi S, Miyoshi J, St George M, Tan A, Chrisler EA, Izumo M, et
al: Gut microbes and the liver circadian clock partition glucose
and lipid metabolism. J Clin Invest. 133:e1625152023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mukherji A, Bailey SM, Staels B and
Baumert TF: The circadian clock and liver function in health and
disease. J Hepatol. 71:200–211. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Piggins HD: Human clock genes. Ann Med.
34:394–400. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cox KH and Takahashi JS: Circadian clock
genes and the transcriptional architecture of the clock mechanism.
J Mol Endocrinol. 63:R93–R102. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsang AH, Sánchez-Moreno C, Bode B,
Rossner MJ, Garaulet M and Oster H: Tissue-specific interaction of
Per1/2 and Dec2 in the regulation of fibroblast circadian rhythms.
J Biol Rhythms. 27:478–489. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
González-Fernández B, Sánchez DI, Crespo
I, San-Miguel B, de Urbina JO, González-Gallego J and Tuñón MJ:
Melatonin attenuates dysregulation of the circadian clock pathway
in mice with CCl4-Induced fibrosis and human hepatic stellate
cells. Front Pharmacol. 9:5562018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen P, Kakan X, Wang S, Dong W, Jia A,
Cai C and Zhang J: Deletion of clock gene Per2 exacerbates
cholestatic liver injury and fibrosis in mice. Exp Toxicol Pathol.
65:427–432. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen P, Han Z, Yang P, Zhu L, Hua Z and
Zhang J: Loss of clock gene mPer2 promotes liver fibrosis induced
by carbon tetrachloride. Hepatol Res. 40:1117–1127. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Laitinen S, Fontaine C, Fruchart JC and
Staels B: The role of the orphan nuclear receptor Rev-Erb alpha in
adipocyte differentiation and function. Biochimie. 87:21–25. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cho H, Zhao X, Hatori M, Yu RT, Barish GD,
Lam MT, Chong LW, DiTacchio L, Atkins AR, Glass CK, et al:
Regulation of circadian behaviour and metabolism by REV-ERB-α and
REV-ERB-β. Nature. 485:123–127. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stujanna EN, Murakoshi N, Tajiri K, Xu D,
Kimura T, Qin R, Feng D, Yonebayashi S, Ogura Y, Yamagami F, et al:
Rev-erb agonist improves adverse cardiac remodeling and survival in
myocardial infarction through an anti-inflammatory mechanism. PLoS
One. 12:e01893302017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ding G, Li X, Hou X, Zhou W, Gong Y, Liu
F, He Y, Song J, Wang J, Basil P, et al: REV-ERB in GABAergic
neurons controls diurnal hepatic insulin sensitivity. Nature.
592:763–767. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
da Rocha AL, Pinto AP, Bedo BLS, Morais
GP, Oliveira LC, Carolino ROG, Pauli JR, Simabuco FM, de Moura LP,
Ropelle ER, et al: Exercise alters the circadian rhythm of
REV-ERB-α and downregulates autophagy-related genes in peripheral
and central tissues. Sci Rep. 12:200062022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Luo X, Song S, Qi L, Tien CL, Li H, Xu W,
Mathuram TL, Burris T, Zhao Y, Sun Z and Zhang L: REV-ERB is
essential in cardiac fibroblasts homeostasis. Front Pharmacol.
13:8996282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Griffin P, Dimitry JM and Musiek ES:
Rev-erbs and Glia-implications for neurodegenerative diseases. J
Exp Neurosci. 13:11790695198532332019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hu C, Zhao L, Tao J and Li L: Protective
role of melatonin in Early-stage and end-stage liver cirrhosis. J
Cell Mol Med. 23:7151–7162. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen L, Xia S, Wang F, Zhou Y, Wang S,
Yang T, Li Y, Xu M, Zhou Y, Kong D, et al: m6A methylation-induced
NR1D1 ablation disrupts the HSC circadian clock and promotes
hepatic fibrosis hepatic fibrosis. Pharmacol Res. 189:1067042023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang S, Lin Y, Yuan X, Li F, Guo L and Wu
B: REV-ERBα integrates colon clock with experimental colitis
through regulation of NF-κB/NLRP3 axis. Nat Commun. 9:42462018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tao Y, Wang N, Qiu T and Sun X: The Role
of Autophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome in liver fibrosis. Biomed Res
Int. 2020:72691502020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wree A, McGeough MD, Inzaugarat ME, Eguchi
A, Schuster S, Johnson CD, Peña CA, Geisler LJ, Papouchado BG,
Hoffman HM, et al: NLRP3 inflammasome driven liver injury and
fibrosis: Roles of IL-17 and TNF in mice. Hepatology. 67:736–749.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang K, Lin L, Zhu Y, Zhang N, Zhou M and
Li Y: Saikosaponin d alleviates liver fibrosis by negatively
regulating the ROS/NLRP3 inflammasome through activating the ERβ
pathway. Front Pharmacol. 13:8949812022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shao R, Yang Y, Fan K, Wu X, Jiang R, Tang
L, Li L, Shen Y, Liu G and Zhang L: REV-ERBα Agonist GSK4112
attenuates Fas-induced Acute Hepatic Damage in Mice. Int J Med Sci.
18:3831–3838. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim J, Park I, Jang S, Choi M, Kim D, Sun
W, Choe Y, Choi JW, Moon C, Park SH, et al: Pharmacological rescue
with SR8278, a circadian nuclear receptor REV-ERBα antagonist as a
therapy for mood disorders in Parkinson's disease.
Neurotherapeutics. 19:592–607. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kojetin D, Wang Y, Kamenecka TM and Burris
TP: Identification of SR8278, a synthetic antagonist of the nuclear
heme receptor REV-ERB. ACS Chem Biol. 6:131–134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin L, Zhou M, Que R, Chen Y, Liu X, Zhang
K, Shi Z and Li Y: Saikosaponin-d protects against liver fibrosis
by regulating the estrogen receptor-β/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway.
Biochem Cell Biol. 99:666–674. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yue J, He J, Wei Y, Shen K, Wu K, Yang X,
Liu S, Zhang C and Yang H: Decreased expression of Rev-Erbα in the
epileptic foci of temporal lobe epilepsy and activation of Rev-Erbα
have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects in the
pilocarpine model. J Neuroinflammation. 17:432020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Niu WX, Bao YY, Zhang N, Lu ZN, Ge MX, Li
YM, Li Y, Chen MH and He HW: Dehydromevalonolactone ameliorates
liver fibrosis and inflammation by repressing activation of NLRP3
inflammasome. Bioorg Chem. 127:1059712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang X, Kuang G, Wan J, Jiang R, Ma L,
Gong X and Liu X: Salidroside protects mice against CCl4-induced
acute liver injury via down-regulating CYP2E1 expression and
inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Int Immunopharmacol.
85:1066622020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kisseleva T and Brenner D: Molecular and
cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18:151–166. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pan X, Mota S and Zhang B: Circadian clock
regulation on lipid metabolism and metabolic diseases. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 1276:53–66. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bailey SM: Emerging role of circadian
clock disruption in Alcohol-induced liver disease. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 315:G364–G373. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Richards J and Gumz ML: Advances in
understanding the peripheral circadian clocks. FASEB J.
26:3602–3613. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Horii R, Honda M, Shirasaki T, Shimakami
T, Shimizu R, Yamanaka S, Murai K, Kawaguchi K, Arai K, Yamashita
T, et al: MicroRNA-10a impairs liver metabolism in Hepatitis C
Virus-related cirrhosis through deregulation of the circadian clock
gene brain and Muscle Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear
Translocator-Like 1. Hepatol Commun. 3:1687–1703. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang D, Tong X, Nelson BB, Jin E, Sit J,
Charney N, Yang M, Omary MB and Yin L: The hepatic
BMAL1/AKT/lipogenesis axis protects against alcoholic liver disease
in mice via promoting PPARα pathway. Hepatology. 68:883–896. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pan X, Queiroz J and Hussain MM:
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in CLOCK mutant mice. J Clin
Invest. 130:4282–4300. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhou B, Zhang Y, Zhang F, Xia Y, Liu J,
Huang R, Wang Y, Hu Y, Wu J, Dai C, et al: CLOCK/BMAL1 regulates
circadian change of mouse hepatic insulin sensitivity by SIRT1.
Hepatology. 59:2196–2206. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gnocchi D, Custodero C, Sabbà C and
Mazzocca A: Circadian rhythms: A possible new player in
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease pathophysiology. J Mol Med
(Berl). 97:741–759. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Forman BM, Chen J, Blumberg B, Kliewer SA,
Henshaw R, Ong ES and Evans RM: Cross-talk among ROR alpha 1 and
the Rev-erb family of orphan nuclear receptors. Mol Endocrinol.
8:1253–1261. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Le Martelot G, Claudel T, Gatfield D,
Schaad O, Kornmann B, Lo Sasso G, Moschetta A and Schibler U:
REV-ERBalpha participates in circadian SREBP signaling and bile
acid homeostasis. PLoS Biol. 7:e10001812009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhou D, Wang Y, Chen L, Jia L, Yuan J, Sun
M, Zhang W, Wang P, Zuo J, Xu Z and Luan J: Evolving roles of
circadian rhythms in liver homeostasis and pathology. Oncotarget.
7:8625–8639. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ni Y, Zhao Y, Ma L, Wang Z, Ni L, Hu L and
Fu Z: Pharmacological activation of REV-ERBα improves nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis by regulating intestinal permeability. Metabolism.
114:1544092021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lin Y, Wang S, Gao L, Zhou Z, Yang Z, Lin
J, Ren S, Xing H and Wu B: Oscillating lncRNA Platr4 regulates
NLRP3 inflammasome to ameliorate nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in
mice. Theranostics. 11:426–444. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yu F, Wang Z, Zhang T, Chen X, Xu H, Wang
F, Guo L, Chen M, Liu K and Wu B: Deficiency of intestinal Bmal1
prevents obesity induced by high-fat feeding. Nat Commun.
12:53232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lin Y, Lin L, Gao L, Wang S and Wu B:
Rev-erbα regulates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 529:916–921. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liu Q, Xu L, Wu M, Zhou Y, Yang J, Huang
C, Xu T, Li J and Zhang L: Rev-erbα exacerbates hepatic steatosis
in alcoholic liver diseases through regulating autophagy. Cell
Biosci. 11:1292021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yang Z, Smalling RV, Huang Y, Jiang Y,
Kusumanchi P, Bogaert W, Wang L, Delker DA, Skill NJ, Han S, et al:
The role of SHP/REV-ERBα/CYP4A axis in the pathogenesis of
Alcohol-associated liver disease. JCI Insight. 6:e1406872021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang J, Yin L and Lazar MA: The orphan
nuclear receptor Rev-erb alpha regulates circadian expression of
plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1. J Biol Chem.
281:33842–33848. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Crouchet E, Dachraoui M, Jühling F,
Roehlen N, Oudot MA, Durand SC, Ponsolles C, Gadenne C,
Meiss-Heydmann L, Moehlin J, et al: Targeting the liver clock
improves fibrosis by restoring TGF-β signaling. J Hepatol.
82:120–133. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Grant D, Yin L, Collins JL, Parks DJ,
Orband-Miller LA, Wisely GB, Joshi S, Lazar MA, Willson TM and
Zuercher WJ: GSK4112, a small molecule chemical probe for the cell
biology of the nuclear heme receptor Rev-erbα. ACS Chem Biol.
5:925–932. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Dong D, Sun H, Wu Z, Wu B, Xue Y and Li Z:
A validated ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass
spectrometry method to identify the pharmacokinetics of SR8278 in
normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Chromatogr B
Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 1020:142–147. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ishizuka T and Lazar MA: The N-CoR/histone
deacetylase 3 complex is required for repression by thyroid hormone
receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 23:5122–5131. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yin L and Lazar MA: The orphan nuclear
receptor Rev-erbalpha recruits the N-CoR/histone deacetylase 3
corepressor to regulate the circadian Bmal1 gene. Mol Endocrinol.
19:1452–1459. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yin L, Joshi S, Wu N, Tong X and Lazar MA:
E3 ligases Arf-bp1 and Pam mediate lithium-stimulated degradation
of the circadian heme receptor Rev-erb alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 107:11614–11619. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yin L, Wang J, Klein PS and Lazar MA:
Nuclear receptor Rev-erbalpha is a critical lithium-sensitive
component of the circadian clock. Science. 311:1002–1005. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kisseleva T and Brenner DA: Hepatic
stellate cells and the reversal of fibrosis. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 21 (Suppl 3):S84–S87. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Liu XY, Liu RX, Hou F, Cui LJ, Li CY, Chi
C, Yi E, Wen Y and Yin CH: Fibronectin expression is critical for
liver fibrogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Mol Med Rep.
14:3669–3675. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Friedman SL: Hepatic stellate cells:
Protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol
Rev. 88:125–172. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Xiang D, Zou J, Zhu X, Chen X, Luo J, Kong
L and Zhang H: Physalin D attenuates hepatic stellate cell
activation and liver fibrosis by blocking TGF-β/Smad and YAP
signaling. Phytomedicine. 78:1532942020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhang J, Jiang N, Ping J and Xu L:
TGF-β1-induced autophagy activates hepatic stellate cells via the
ERK and JNK signaling pathways. Int J Mol Med. 47:256–266. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wu Z, Liao F, Luo G, Qian Y, He X, Xu W,
Ding S and Pu J: NR1D1 Deletion induces Rupture-prone vulnerable
plaques by regulating macrophage pyroptosis via the NF-κB/NLRP3
inflammasome pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021:52175722021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ka NL, Park MK, Kim SS, Jeon Y, Hwang S,
Kim SM, Lim GY, Lee H and Lee MO: NR1D1 Stimulates antitumor immune
responses in breast cancer by activating cGAS-STING signaling.
Cancer Res. 83:3045–3058. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kou L, Chi X, Sun Y, Han C, Wan F, Hu J,
Yin S, Wu J, Li Y, Zhou Q, et al: The circadian clock protein
Rev-erbα provides neuroprotection and attenuates neuroinflammation
against Parkinson's disease via the microglial NLRP3 inflammasome.
J Neuroinflammation. 19:1332022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Huang ZN, Wang J, Wang ZY, Min LY, Ni HL,
Han YL, Tian YY, Cui YZ, Han JX and Cheng XF: SR9009 attenuates
inflammation-related NPMSC pyroptosis and IVDD through
NR1D1/NLRP3/IL-1β pathway. iScience. 27:1097332024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|