|
1
|
Nedeva C: Inflammation and cell death of
the innate and adaptive immune system during sepsis. Biomolecules.
11:10112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford
KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, Colombara DV, Ikuta KS, Kissoon N, Finfer
S, et al: Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and
mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the global burden of disease
study. Lancet. 395:200–211. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lockridge A and Hanover JA: A nexus of
lipid and O-Glcnac metabolism in physiology and disease. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:9435762022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cai H, Xiong W, Zhu H, Wang Q, Liu S and
Lu Z: Protein O-GlcNAcylation in multiple immune cells and its
therapeutic potential. Front Immunol. 14:12099702023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu D, Su S, Zha X, Wei Y, Yang G, Huang Q,
Yang Y, Xia L, Fan S and Peng X: Glutamine promotes O-GlcNAcylation
of G6PD and inhibits AGR2 S-glutathionylation to maintain the
intestinal mucus barrier in burned septic mice. Redox Biol.
59:1025812023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Srzić I, Nesek Adam V and Tunjić Pejak D:
Sepsis definition: What's new in the treatment guidelines. Acta
Clin Croat. 61 (Suppl 1):S67–S72. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
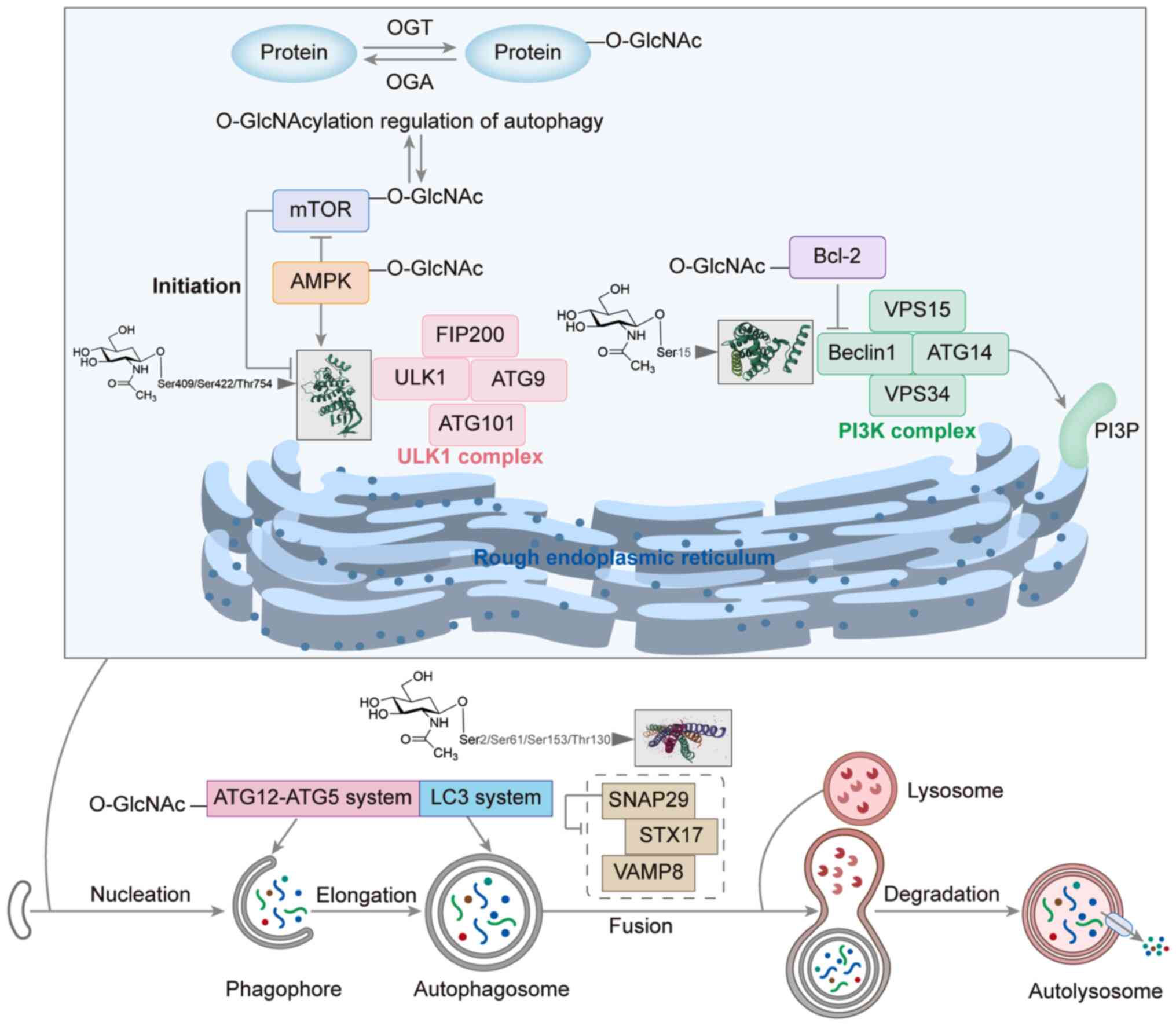
|
|
7
|
Wiersinga WJ and van der Poll T:
Immunopathophysiology of human sepsis. EBioMedicine. 86:1043632022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Torres LK, Pickkers P and van der Poll T:
Sepsis-induced immunosuppression. Annu Rev Physiol. 84:157–181.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu D, Huang SY, Sun JH, Zhang HC, Cai QL,
Gao C, Li L, Cao J, Xu F, Zhou Y, et al: Sepsis-induced
immunosuppression: Mechanisms, diagnosis and current treatment
options. Mil Med Res. 9:562022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wen X, Xie B, Yuan S and Zhang J: The
‘Self-sacrifice’ of ImmuneCells in sepsis. Front Immunol.
13:8334792022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
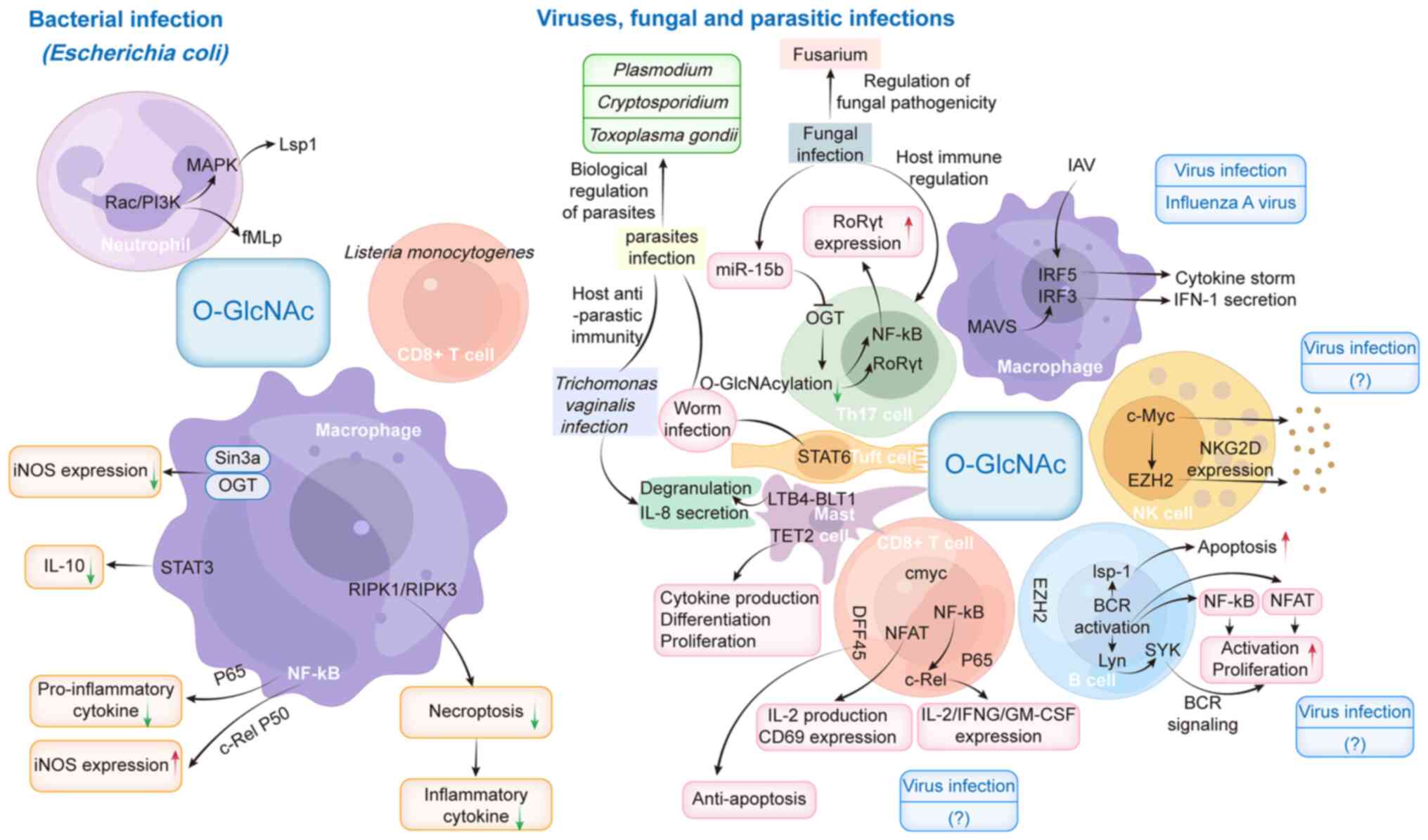
11
|
Yang L, Zhou L, Li F, Chen X, Li T, Zou Z,
Zhi Y and He Z: Diagnostic and prognostic value of
Autophagy-related key genes in sepsis and potential correlation
with immune cell signatures. Front Cell Dev Biol. 11:12183792023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Reglero-Real N, Pérez-Gutiérrez L,
Yoshimura A, Rolas L, Garrido-Mesa J, Barkaway A, Pickworth C,
Saleeb RS, Gonzalez-Nuñez M, Austin-Williams SN, et al: Autophagy
modulates endothelial junctions to restrain neutrophil diapedesis
during inflammation. Immunity. 54:1989–2004.e9. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu CL, Wang Y, Liu Q, Li HR, Yu CM, Li P,
Deng XM and Wang JF: Dysregulation of neutrophil death in sepsis.
Front Immunol. 13:9639552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qin Y, Li W, Liu J, Wang F, Zhou W, Xiao
L, Zhou P, Wu F, Chen X, Xu S, et al: Andrographolide ameliorates
sepsis-induced acute lung injury by promoting autophagy in alveolar
macrophages via the RAGE/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 139:1127192024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang H, Bai G, Chen J, Han W, Guo R and
Cui N: mTOR deletion ameliorates CD4 + T cell apoptosis during
sepsis by improving autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Apoptosis.
27:401–408. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ye L, Ding W, Xiao D, Jia Y, Zhao Z, Ao X
and Wang J: O-GlcNAcylation: Cellular physiology and therapeutic
target for human diseases. MedComm (2020). 4:e4562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gonzalez-Rellan MJ, Fondevila MF, Dieguez
C and Nogueiras R: O-GlcNAcylation: A sweet hub in the regulation
of glucose metabolism in health and disease. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 13:8735132022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chatham JC, Zhang J and Wende AR: Role of
O-Linked N-acetylglucosamine protein modification in cellular
(patho)physiology. Physiol Rev. 101:427–493. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao Q, Zhou S, Lou W, Qian H and Xu Z:
Crosstalk between O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation in
metabolism: Regulation and mechanism. Cell Death Differ.
32:1181–1199. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
El Hajjar L, Page A, Bridot C, Cantrelle
FX, Landrieu I and Smet-Nocca C: Regulation of Glycogen Synthase
Kinase-3β by Phosphorylation and O-β-Linked
N-Acetylglucosaminylation: Implications on tau protein
phosphorylation. Biochemistry. 63:1513–1533. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cardozo CF, Vera A, Quintana-Peña V,
Arango-Davila CA and Rengifo J: Regulation of Tau protein
phosphorylation by glucosamine-induced O-GlcNAcylation as a
neuroprotective mechanism in a brain ischemia-reperfusion model.
Int J Neurosci. 133:194–200. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
da Costa Rodrigues B, Dos Santos Lucena
MC, Costa A, de Araújo Oliveira I, Thaumaturgo M, Paes-Colli Y,
Beckman D, Ferreira ST, de Mello FG, de Melo Reis RA, et al:
O-GlcNAcylation regulates tyrosine hydroxylase serine 40
phosphorylation and l-DOPA levels. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
328:C825–C835. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen YF, Zhu JJ, Li J and Ye XS:
O-GlcNAcylation increases PYGL activity by promoting
phosphorylation. Glycobiology. 32:101–109. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu F, Zhang Z, Leng Y and Chen AF:
O-GlcNAc modification of GSDMD attenuates LPS-induced endothelial
cells pyroptosis. Inflamm Res. 73:5–17. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Correction for Zhang et al. HIPK2
phosphorylates HDAC3 for NF-κB acetylation to ameliorate
colitis-associated colorectal carcinoma and sepsis. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 122:e25060471222025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li C, Yu L, Mai C, Mu T and Zeng Y: KLF4
down-regulation resulting from TLR4 promotion of ERK1/2
phosphorylation underpins inflammatory response in sepsis. J Cell
Mol Med. 25:2013–2024. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dong R, Xue Z, Fan G, Zhang N, Wang C, Li
G and Da Y: Pin1 Promotes NLRP3 inflammasome activation by
phosphorylation of p38 MAPK Pathway in Septic Shock. Front Immunol.
12:6202382021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jin L, Yuan F, Dai G, Yao Q, Xiang H, Wang
L, Xue B, Shan Y and Liu X: Blockage of O-linked GlcNAcylation
induces AMPK-dependent autophagy in bladder cancer cells. Cell Mol
Biol Lett. 25:172020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sheng X, Xia Z, Yang H and Hu R: The
ubiquitin codes in cellular stress responses. Protein Cell.
15:157–190. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li MD, Ruan HB, Hughes ME, Lee JS, Singh
JP, Jones SP, Nitabach MN and Yang X: O-GlcNAc signaling entrains
the circadian clock by inhibiting BMAL1/CLOCK ubiquitination. Cell
Metab. 17:303–310. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu B, Zhang C, Jiang A, Zhang X, Liang F,
Wang X, Li D, Liu C, Liu X, Xia J, et al: Histone methyltransferase
Dot1L recruits O-GlcNAc transferase to target chromatin sites to
regulate histone O-GlcNAcylation. J Biol Chem. 298:1021152022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang Q, Wei D, Li C, Yang X, Su K, Wang T,
Zou R, Wang L, Cun D, Tang B, et al: O-GlcNAcylation with
ubiquitination stabilizes METTL3 to promoting HMGB1 degradation to
inhibit ferroptosis and enhance gemcitabine resistance in
pancreatic cancer. Mol Med. 31:2282025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Koo SY, Park EJ, Noh HJ, Jo SM, Ko BK,
Shin HJ and Lee CW: Ubiquitination links DNA damage and repair
signaling to cancer metabolism. Int J Mol Sci. 24:84412023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dikic I and Schulman BA: An expanded
lexicon for the ubiquitin code. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 24:273–287.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen L, Li Y, Zeng S, Duan S, Huang Z and
Liang Y: The interaction of O-GlcNAc-modified NLRX1 and IKK-α
modulates IL-1β expression in M1 macrophages. In Vitro Cell Dev
Biol Anim. 58:408–418. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ning M, Liu Y, Wang D, Wei J, Hu G and
Xing P: Knockdown of TRIM27 alleviated sepsis-induced inflammation,
apoptosis, and oxidative stress via suppressing ubiquitination of
PPARγ and reducing NOX4 expression. Inflamm Res. 71:1315–1325.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang J, He Y and Zhou D: The role of
ubiquitination in microbial infection induced endothelial
dysfunction: Potential therapeutic targets for sepsis. Expert Opin
Ther Targets. 27:827–839. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yu Y, Fu Q and Li J, Zen X and Li J: E3
ubiquitin ligase COP1-mediated CEBPB ubiquitination regulates the
inflammatory response of macrophages in sepsis-induced myocardial
injury. Mamm Genome. 35:56–67. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li ZQ, Chen X and Wang Y: Small molecules
targeting ubiquitination to control inflammatory diseases. Drug
Discov Today. 26:2414–2422. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
O-GlcNAc transferase is a key regulator of
DNA methylation and transposon silencing. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
32:1137–1138. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shin H, Leung A, Costello KR, Senapati P,
Kato H, Moore RE, Lee M, Lin D, Tang X, Pirrotte P, et al:
Inhibition of DNMT1 methyltransferase activity via
glucose-regulated O-GlcNAcylation alters the epigenome. Elife.
12:e855952023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lin AP, Qiu Z, Ethiraj P, Sasi B, Jaafar
C, Rakheja D and Aguiar R: MYC, mitochondrial metabolism and
O-GlcNAcylation converge to modulate the activity and subcellular
localization of DNA and RNA demethylases. Leukemia. 36:1150–1159.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lorente-Sorolla C, Garcia-Gomez A,
Català-Moll F, Toledano V, Ciudad L, Avendaño-Ortiz J, Maroun-Eid
C, Martín-Quirós A, Martínez-Gallo M, Ruiz-Sanmartín A, et al:
Inflammatory cytokines and organ dysfunction associate with the
aberrant DNA methylome of monocytes in sepsis. Genome Med.
11:662019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
El Gazzar M, Yoza BK, Chen X, Hu J,
Hawkins GA and McCall CE: G9a and HP1 couple histone and DNA
methylation to TNFalpha transcription silencing during endotoxin
tolerance. J Biol Chem. 283:32198–32208. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhu Z, Ren W, Li S, Gao L and Zhi K:
Functional significance of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine protein
modification in regulating autophagy. Pharmacol Res.
202:1071202024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li S, Ren W, Zheng J, Li S, Zhi K and Gao
L: Role of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine protein modification in
oxidative stress-induced autophagy: A novel target for bone
remodeling. Cell Commun Signal. 22:3582024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Jeon M, Park J, Yang E, Baek HJ and Kim H:
Regulation of autophagy by protein methylation and acetylation in
cancer. J Cell Physiol. 237:13–28. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang Q, Na Q and Song W: Moderate
mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition induces autophagy in
HTR8/SVneo cells via O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine signaling. J
Obstet Gynaecol Res. 43:1585–1596. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Qiu Z, Cui J, Huang Q, Qi B and Xia Z:
Roles of O-GlcNAcylation in mitochondrial homeostasis and
cardiovascular diseases. Antioxidants (Basel). 13:5712024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Marsh SA, Powell PC, Dell'italia LJ and
Chatham JC: Cardiac O-GlcNAcylation blunts autophagic signaling in
the diabetic heart. Life Sci. 92:648–656. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Rahman MA, Cho Y, Hwang H and Rhim H:
Pharmacological Inhibition of O-GlcNAc transferase promotes
mTOR-Dependent autophagy in rat cortical neurons. Brain Sci.
10:9582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Pyo KE, Kim CR, Lee M, Kim JS, Kim KI and
Baek SH: ULK1 O-GlcNAcylation is crucial for activating VPS34 via
ATG14L during Autophagy initiation. Cell Rep. 25:2878–2890.e4.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Shi Y, Yan S, Shao GC, Wang J, Jian YP,
Liu B, Yuan Y, Qin K, Nai S, Huang X, et al: O-GlcNAcylation
stabilizes the autophagy-initiating kinase ULK1 by inhibiting
chaperone-mediated autophagy upon HPV infection. J Biol Chem.
298:1023412022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang J, Li C, Shuai W, Chen T, Gong Y, Hu
H, Wei Y, Kong B and Huang H: Maresin2 fine-tunes ULK1
O-GlcNAcylation to improve post myocardial infarction remodeling.
Eur J Pharmacol. 962:1762232024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Alghusen IM, Carman MS, Wilkins HM, Strope
TA, Gimore C, Fedosyuk H, Shawa J, Ephrame SJ, Denson AR, Wang X,
et al: O-GlcNAc impacts mitophagy via the PINK1-dependent pathway.
Front Aging Neurosci. 16:13879312024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Guo B, Liang Q, Li L, Hu Z, Wu F, Zhang P,
Ma Y, Zhao B, Kovács AL, Zhang Z, et al: O-GlcNAc-modification of
SNAP-29 regulates autophagosome maturation. Nat Cell Biol.
16:1215–1226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Dodson M, Liu P, Jiang T, Ambrose AJ, Luo
G, Rojo de la Vega M, Cholanians AB, Wong PK, Chapman E and Zhang
DD: Increased O-GlcNAcylation of SNAP29 drives Arsenic-induced
autophagic dysfunction. Mol Cell Biol. 38:e00595–e00517. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Pellegrini FR, De Martino S, Fianco G,
Ventura I, Valente D, Fiore M, Trisciuoglio D and Degrassi F:
Blockage of autophagosome-lysosome fusion through SNAP29
O-GlcNAcylation promotes apoptosis via ROS production. Autophagy.
19:2078–2093. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Huang L, Yuan P, Yu P, Kong Q, Xu Z, Yan
X, Shen Y, Yang J, Wan R, Hong K, et al: O-GlcNAc-modified SNAP29
inhibits autophagy-mediated degradation via the disturbed
SNAP29-STX17-VAMP8 complex and exacerbates myocardial injury in
type I diabetic rats. Int J Mol Med. 42:3278–3290. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhou F, Yang X, Zhao H, Liu Y, Feng Y, An
R, Lv X, Li J and Chen B: Down-regulation of OGT promotes cisplatin
resistance by inducing autophagy in ovarian cancer. Theranostics.
8:5200–5212. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Patel A and Faesen AC: Metamorphosis by
ATG13 and ATG101 in human autophagy initiation. Autophagy.
20:968–969. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang X and Jia J: Magnolol improves
Alzheimer's disease-like pathologies and cognitive decline by
promoting autophagy through activation of the AMPK/mTOR/ULK1
pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 161:1144732023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ge Y, Zhou M, Chen C, Wu X and Wang X:
Role of AMPK mediated pathways in autophagy and aging. Biochimie.
195:100–113. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Pizzimenti C, Fiorentino V, Ruggeri C,
Franchina M, Ercoli A, Tuccari G and Ieni A: Autophagy involvement
in Non-neoplastic and neoplastic endometrial pathology: The state
of the art with a focus on carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 25:121182024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wang TF, Feng ZQ, Sun YW, Zhao SJ, Zou HY,
Hao HS, Du WH, Zhao XM, Zhu HB and Pang YW: Disruption of
O-GlcNAcylation homeostasis induced ovarian granulosa cell injury
in bovine. Int J Mol Sci. 23:78152022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Xu J, Gu J, Pei W, Zhang Y, Wang L and Gao
J: The role of lysosomal membrane proteins in autophagy and related
diseases. FEBS J. 291:3762–3785. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wang P and Hanover JA: Nutrient-driven
O-GlcNAc cycling influences autophagic flux and neurodegenerative
proteotoxicity. Autophagy. 9:604–606. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Park S, Lee Y, Pak JW, Kim H, Choi H, Kim
JW, Roth J and Cho JW: O-GlcNAc modification is essential for the
regulation of autophagy in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 72:3173–3183. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zheng D, Tong M, Zhang S, Pan Y, Zhao Y,
Zhong Q and Liu X: Human YKT6 forms priming complex with STX17 and
SNAP29 to facilitate autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Cell Rep.
43:1137602024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ben Ahmed A, Lemaire Q, Scache J, Mariller
C, Lefebvre T and Vercoutter-Edouart AS: O-GlcNAc dynamics: The
sweet side of protein trafficking regulation in mammalian cells.
Cells. 12:13962023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Du P, Zhang X, Lian X, Hölscher C and Xue
G: O-GlcNAcylation and its roles in neurodegenerative diseases. J
Alzheimers Dis. 97:1051–1068. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
He XF, Hu X, Wen GJ, Wang Z and Lin WJ:
O-GlcNAcylation in cancer development and immunotherapy. Cancer
Lett. 566:2162582023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Liu C, Dong W, Li J, Kong Y and Ren X:
O-GlcNAc modification and its role in diabetic retinopathy.
Metabolites. 12:7252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Bruserud Ø, Mosevoll KA, Bruserud Ø,
Reikvam H and Wendelbo Ø: The regulation of neutrophil migration in
patients with sepsis: The complexity of the molecular mechanisms
and their modulation in sepsis and the heterogeneity of sepsis
patients. Cells. 12:10032023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhou YY and Sun BW: Recent advances in
neutrophil chemotaxis abnormalities during sepsis. Chin J
Traumatol. 25:317–324. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Kneass ZT and Marchase RB: Neutrophils
exhibit rapid Agonist-induced increases in protein-associated
O-GlcNAc. J Biol Chem. 279:45759–45765. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Cong R, Sun L, Yang J, Cui H, Ji X, Zhu J,
Gu JH and He B: Protein O-GlcNAcylation alleviates small intestinal
injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion and oxygen-glucose
deprivation. Biomed Pharmacother. 138:1114772021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Hossain M, Qadri SM, Xu N, Su Y, Cayabyab
FS, Heit B and Liu L: Endothelial LSP1 modulates extravascular
neutrophil chemotaxis by regulating nonhematopoietic vascular
PECAM-1 Expression. J Immunol. 195:2408–2416. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Machin PA, Johnsson AE, Massey EJ,
Pantarelli C, Chetwynd SA, Chu JY, Okkenhaug H, Segonds-Pichon A,
Walker S, Malliri A, et al: Dock2 generates characteristic
spatiotemporal patterns of Rac activity to regulate neutrophil
polarisation, migration and phagocytosis. Front Immunol.
14:11808862023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Kneass ZT and Marchase RB: Protein
O-GlcNAc modulates motility-associated signaling intermediates in
neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 280:14579–14585. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Wu KK, Xu X, Wu M, Li X, Hoque M, Li G,
Lian Q, Long K, Zhou T, Piao H, et al: MDM2 induces
pro-inflammatory and glycolytic responses in M1 macrophages by
integrating iNOS-nitric oxide and HIF-1α pathways in mice. Nat
Commun. 15:86242024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Hwang SY, Hwang JS, Kim SY and Han IO:
O-GlcNAc transferase inhibits LPS-mediated expression of inducible
nitric oxide synthase through an increased interaction with mSin3A
in RAW264.7 cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 305:C601–C608. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Hwang SY, Hwang JS, Kim SY and Han IO:
O-GlcNAcylation and p50/p105 binding of c-Rel are dynamically
regulated by LPS and glucosamine in BV2 microglia cells. Br J
Pharmacol. 169:1551–1560. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
He Y, Ma X, Li D and Hao J: Thiamet G
mediates neuroprotection in experimental stroke by modulating
microglia/macrophage polarization and inhibiting NF-κB p65
signaling. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 37:2938–2951. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Seo J, Kim Y, Ji S, Kim HB, Jung H, Yi EC,
Lee YH, Shin I, Yang WH and Cho JW: O-GlcNAcylation of RIPK1
rescues red blood cells from necroptosis. Front Immunol.
14:11604902023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Janas ML, Groves P, Kienzle N and Kelso A:
IL-2 regulates perforin and granzyme gene expression in CD8+ T
cells independently of its effects on survival and proliferation. J
Immunol. 175:8003–8010. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Reina-Campos M, Scharping NE and Goldrath
AW: CD8+ T cell metabolism in infection and cancer. Nat Rev
Immunol. 21:718–738. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Lopez Aguilar A, Gao Y, Hou X, Lauvau G,
Yates JR and Wu P: Profiling of protein O-GlcNAcylation in murine
CD8+ effector- and Memory-like T cells. ACS Chem Biol.
12:3031–3038. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Chen H, Shi Y, Ying J, Dong Z, Wang Y,
Zheng Y and Ruan P: O-linked N-acetylglucosamine modification
induced by lipopolysaccharide is involved in inflammatory signaling
pathway in endothelial cells. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi
Xue. 35:164–169. 2023.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Zeng Z, Liao X and Zhao X: O-GlcNAc
transferase mediates O-GlcNAcylation of NLRP3 regulates pyroptosis
in spinal cord injury. Brain Res Bull. 222:1112332025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
He C, Wu Q, Zeng Z, Yang Y, He H, Hu M and
Liu S: OGT-induced O-GlcNAcylation of NEK7 protein aggravates
osteoarthritis progression by enhancing NEK7/NLRP3 axis.
Autoimmunity. 57:23192022024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Yaqin Z, Kehan W, Yi Z, Naijian W, Wei Q
and Fei M: Resveratrol alleviates inflammatory bowel disease by
inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 pathway activity via the reduction of
O-GlcNAcylation of STAT3 in intestinal epithelial cells. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 484:1168822024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhang CC, Li Y, Jiang CY, Le QM, Liu X, Ma
L and Wang FF: O-GlcNAcylation mediates H2O2-induced apoptosis
through regulation of STAT3 and FOXO1. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
45:714–727. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Li Y, Peng J, Xia Y, Pan C, Li Y, Gu W,
Wang J, Wang C, Wang Y, Song J, et al: Sufu limits sepsis-induced
lung inflammation via regulating phase separation of TRAF6.
Theranostics. 13:3761–3780. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Matsui S, Ri C, Bolanos LC, Choi K,
Shibamiya A, Ishii A, Takaishi K, Oshima-Hasegawa N, Tsukamoto S,
Takeda Y, et al: Metabolic reprogramming regulated by TRAF6
contributes to the leukemia progression. Leukemia. 38:1032–1045.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Qiang A, Slawson C and Fields PE: The Role
of O-GlcNAcylation in immune cell activation. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 12:5966172021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Liu R, Ma X, Chen L, Yang Y, Zeng Y, Gao
J, Jiang W, Zhang F, Li D, Han B, et al: MicroRNA-15b Suppresses
Th17 differentiation and is associated with pathogenesis of
multiple sclerosis by targeting O-GlcNAc transferase. J Immunol.
198:2626–2639. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Machacek M, Saunders H, Zhang Z, Tan EP,
Li J, Li T, Villar MT, Artigues A, Lydic T, Cork G, et al: Elevated
O-GlcNAcylation enhances pro-inflammatory Th17 function by altering
the intracellular lipid microenvironment. J Biol Chem.
294:8973–8990. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Thomaidis T, Maderer A, Formentini A,
Bauer S, Trautmann M, Schwarz M, Neumann W, Kittner JM, Schad A,
Link KH, et al: Proteins of the VEGFR and EGFR pathway as
predictive markers for adjuvant treatment in patients with stage
II/III colorectal cancer: Results of the FOGT-4 trial. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 33:832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Gao YZ, Wang YT, He S, Li H, Wang Y and Wu
Z: FpOGT is required for fungal growth, stress response, and
virulence of Fusarium proliferatum by affecting the expression of
glucokinase and other glucose metabolism-related genes. Phytopathol
Res. 6:22024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Naseem S and Konopka JB:
N-acetylglucosamine regulates virulence properties in microbial
pathogens. PLoS Pathog. 11:e10049472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Ansari S, Kumar V, Bhatt DN, Irfan M and
Datta A: N-acetylglucosamine sensing and metabolic engineering for
attenuating human and plant pathogens. Bioengineering (Basel).
9:642022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Seo J, Park YS, Kweon TH, Kang J, Son S,
Kim HB, Seo YR, Kang MJ, Yi EC, Lee YH, et al: O-Linked
N-acetylglucosamine modification of mitochondrial antiviral
signaling protein regulates antiviral signaling by modulating its
activity. Front Immunol. 11:5892592020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Song N, Qi Q, Cao R, Qin B, Wang B, Wang
Y, Zhao L, Li W, Du X, Liu F, et al: MAVS O-GlcNAcylation is
essential for host antiviral immunity against lethal RNA viruses.
Cell Rep. 28:2386–2396.e5. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Wang Q, Fang P, He R, Li M, Yu H, Zhou L,
Yi Y, Wang F, Rong Y, Zhang Y, et al: O-GlcNAc transferase promotes
influenza A virus-induced cytokine storm by targeting interferon
regulatory factor-5. Sci Adv. 6:eaaz70862020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Yao AY, Tang HY, Wang Y, Feng MF and Zhou
RL: Inhibition of the activating signals in NK92 cells by
recombinant GST-sHLA-G1a chain. Cell Res. 14:155–160. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Mariuzza RA, Singh P, Karade SS, Shahid S
and Sharma VK: Recognition of self and viral ligands by NK cell
receptors. Immunol Rev. 329:e134352025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Yu M, Su Z, Huang X, Zhou Y, Zhang X, Wang
B, Wang Z, Liu Y, Xing N, Xia M, et al: Histone methyltransferase
Ezh2 negatively regulates NK cell terminal maturation and function.
J Leukoc Biol. 110:1033–1045. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Lo PW, Shie JJ, Chen CH, Wu CY, Hsu TL and
Wong CH: O-GlcNAcylation regulates the stability and enzymatic
activity of the histone methyltransferase EZH2. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 115:7302–7307. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Feinberg D, Ramakrishnan P, Wong DP,
Asthana A and Parameswaran R: Inhibition of O-GlcNAcylation
decreases the cytotoxic function of natural killer cells. Front
Immunol. 13:8412992022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Loftus RM, Assmann N, Kedia-Mehta N,
O'Brien KL, Garcia A, Gillespie C, Hukelmann JL, Oefner PJ, Lamond
AI, Gardiner CM, et al: Amino acid-dependent cMyc expression is
essential for NK cell metabolic and functional responses in mice.
Nat Commun. 9:23412018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Ramakrishnan P: O-GlcNAcylation and immune
cell signaling: A review of known and a preview of unknown. J Biol
Chem. 300:1073492024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Chang YH, Weng CL and Lin KI:
O-GlcNAcylation and its role in the immune system. J Biomed Sci.
27:572020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Wu JL, Wu HY, Tsai DY, Chiang MF, Chen YJ,
Gao S, Lin CC, Lin CH, Khoo KH, Chen YJ and Lin KI: Temporal
regulation of Lsp1 O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation during
apoptosis of activated B cells. Nat Commun. 7:125262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Guo M, Price MJ, Patterson DG, Barwick BG,
Haines RR, Kania AK, Bradley JE, Randall TD, Boss JM and Scharer
CD: EZH2 represses the B cell transcriptional program and regulates
Antibody-secreting cell metabolism and antibody production. J
Immunol. 200:1039–1052. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Ramakrishnan P, Clark PM, Mason DE, Peters
EC, Hsieh-Wilson LC and Baltimore D: Activation of the
transcriptional function of the NF-κB protein c-Rel by O-GlcNAc
glycosylation. Sci Signal. 6:ra752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Swamy M, Pathak S, Grzes KM, Damerow S,
Sinclair LV, van Aalten DM and Cantrell DA: Glucose and glutamine
fuel protein O-GlcNAcylation to control T cell self-renewal and
malignancy. Nat Immunol. 17:712–720. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Liu AR and Ramakrishnan P: Regulation of
nuclear Factor-kappaB Function by O-GlcNAcylation in inflammation
and cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:7517612021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Saha A and Fernández-Tejada A: Chemical
biology tools to interrogate the roles of O-GlcNAc in immunity.
Front Immunol. 13:10898242022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Zhao M, Ren K, Xiong X, Xin Y, Zou Y,
Maynard JC, Kim A, Battist AP, Koneripalli N, Wang Y, et al:
Epithelial STAT6 O-GlcNAcylation drives a concerted anti-helminth
alarmin response dependent on tuft cell hyperplasia and Gasdermin
C. Immunity. 55:13272022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Xiong X, Huang R, Li Z, Yang C, Wang Q,
Ruan HB and Xu L: Intestinal epithelial STAT6 activation rescues
the defective Anti-helminth responses caused by ogt deletion. Int J
Mol Sci. 23:111372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Min A, Lee YA, Kim KA and Shin MH:
BLT1-mediated O-GlcNAcylation is required for NOX2-dependent
migration, exocytotic degranulation and IL-8 release of human mast
cell induced by Trichomonas vaginalis-secreted LTB4.
Microbes Infect. 20:376–384. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Montagner S, Leoni C, Emming S, Della
Chiara G, Balestrieri C, Barozzi I, Piccolo V, Togher S, Ko M, Rao
A, et al: TET2 regulates mast cell differentiation and
proliferation through catalytic and Non-catalytic activities. Cell
Rep. 15:1566–1579. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Alberione MP, Avalos-Padilla Y, Rangel GW,
Ramírez M, Romero-Uruñuela T, Fenollar A, Crispim M, Smith TK,
Llinás M and Izquierdo L: Hexosamine biosynthesis disruption
impairs GPI production and arrests Plasmodium falciparum
growth at schizont stages. PLoS Pathog. 21:e10128322025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Wang D, Wang C and Zhu G: Genomic
reconstruction and features of glycosylation pathways in the
apicomplexan Cryptosporidium parasites. Front Mol Biosci.
9:10510722022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Gowda DC and Miller LH: Glycosylation in
malaria parasites: What do we know. Trends Parasitol. 40:131–146.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Zhang N, Jiang N and Chen Q: Key
regulators of parasite biology viewed through a Post-translational
modification repertoire. Proteomics. December 17–2024.(Epub ahead
of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Hwang JS, Kim KH, Park J, Kim SM, Cho H,
Lee Y and Han IO: Glucosamine improves survival in a mouse model of
sepsis and attenuates sepsis-induced lung injury and inflammation.
J Biol Chem. 294:608–622. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Li X, Gong W, Wang H, Li T, Attri KS,
Lewis RE, Kalil AC, Bhinderwala F, Powers R, Yin G, et al: O-GlcNAc
transferase suppresses inflammation and necroptosis by targeting
Receptor-Interacting Serine/Threonine-protein kinase 3. Immunity.
50:576–590.e6. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Lang Y, Li J and Zhang L: O-GlcNAcylation
dictates pyroptosis. Front Immunol. 15:15135422024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Ferron M, Cadiet J, Persello A, Prat V,
Denis M, Erraud A, Aillerie V, Mevel M, Bigot E, Chatham JC, et al:
O-GlcNAc stimulation: A new metabolic approach to treat septic
shock. Sci Rep. 9:187512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Denis M, Dupas T, Persello A, Dontaine J,
Bultot L, Betus C, Pelé T, Dhot J, Erraud A, Maillard A, et al: An
O-GlcNAcylomic approach reveals ACLY as a potential target in
sepsis in the young rat. Int J Mol Sci. 22:92362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Dupas T, Persello A, Blangy-Letheule A,
Denis M, Erraud A, Aillerie V, Leroux AA, Rivière M, Lebreton J,
Tessier A, et al: Beneficial effects of O-GlcNAc stimulation in a
young rat model of sepsis: Beyond modulation of gene expression.
Int J Mol Sci. 23:64302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Trapannone R, Rafie K and van Aalten DM:
O-GlcNAc transferase inhibitors: Current tools and future
challenges. Biochem Soc Trans. 44:88–93. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Elbatrawy AA, Kim EJ and Nam G:
O-GlcNAcase: Emerging mechanism, substrate recognition and
Small-Molecule inhibitors. ChemMedChem. 15:1244–1257. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Ortiz-Meoz RF, Jiang J, Lazarus MB, Orman
M, Janetzko J, Fan C, Duveau DY, Tan ZW, Thomas CJ and Walker S: A
small molecule that inhibits OGT activity in cells. ACS Chem Biol.
10:1392–1397. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Fehl C and Hanover JA: Tools, tactics and
objectives to interrogate cellular roles of O-GlcNAc in disease.
Nat Chem Biol. 18:8–17. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Cheng SS, Mody AC and Woo CM:
Opportunities for therapeutic modulation of O-GlcNAc. Chem Rev.
124:12918–13019. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|