Introduction
Interleukin 8 (IL8) is produced by macrophages,
neutrophils, endothelial cells and cancer cells. It is a
proinflammatory chemokine associated with the promotion of
neutrophil chemotaxis and degranulation (1). This chemokine activates intracellular
signaling pathways using G protein-coupled receptors (1). A number of chemokines, such as IL8,
promote and regulate neoplastic progression, including angiogenesis
and metastasis (2). IL8 is a potent
angiogenic factor and controls the expression of vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in endothelial cells (3). Overexpression of VEGF is closely
associated with the progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma
(CCRCC) (4).
Hypomethylation of genomic DNA has been associated
with increased rates of genomic instability (5). Hypomethylation of CpG dinucleotides in
genomic DNA is known as one of the somatic epigenetic alterations
identified in human cancers (5).
DNA hypomethylation is postulated to affect carcinogenesis due to
its involvement in cancer initiation and progression (6). In this study, we analyzed the
hypomethylation status of candidate genes, including IL8, in CCRCC
using a large-scale, high-throughput DNA methylation profiling
technique. The correlation between the hypomethylation status of
the candidate gene (IL8) and clinicopathological parameters was
examined.
Material and methods
Tissue specimens consisted of 46 cancer tissues and
46 matched adjacent normal tissues from CCRCC patients who had
undergone nephrectomy at Kyung Hee University Hospital between 1999
and 2005. The study was approved by the institutional review board
at Kyung Hee University Medical Center. Preparation of DNA samples
and DNA extraction were implemented as previously described
(7). Bisulfite conversion of all
DNA samples was performed with EZ-96 DNA Methylation kit (Zymo
Research, Orange, CA, USA). The methylcytosine content was
quantified using a GoldenGate Methylation Cancer Panel I microarray
(Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) (8).
Following the bisulfite conversion and methylation chip assay,
technical replicates were prepared for each sample using the same
converted DNA. Beta values for matching normal and cancer clinical
samples were compared; differential methylation was readily
detected (8). The methylation
status of CpG sites was examined by bisulfite sequencing according
to the protocol employed by Herman et al(9). The methylation status of the 1505 CpG
sites was measured using a data matrix of beta values. An
additional filter based on a Student’s t-test was applied. This
required a maximal difference in beta value between the two groups
(10). The hypomethylation status
and clinicopathological characteristics of CCRCC patients were
analyzed.
Results
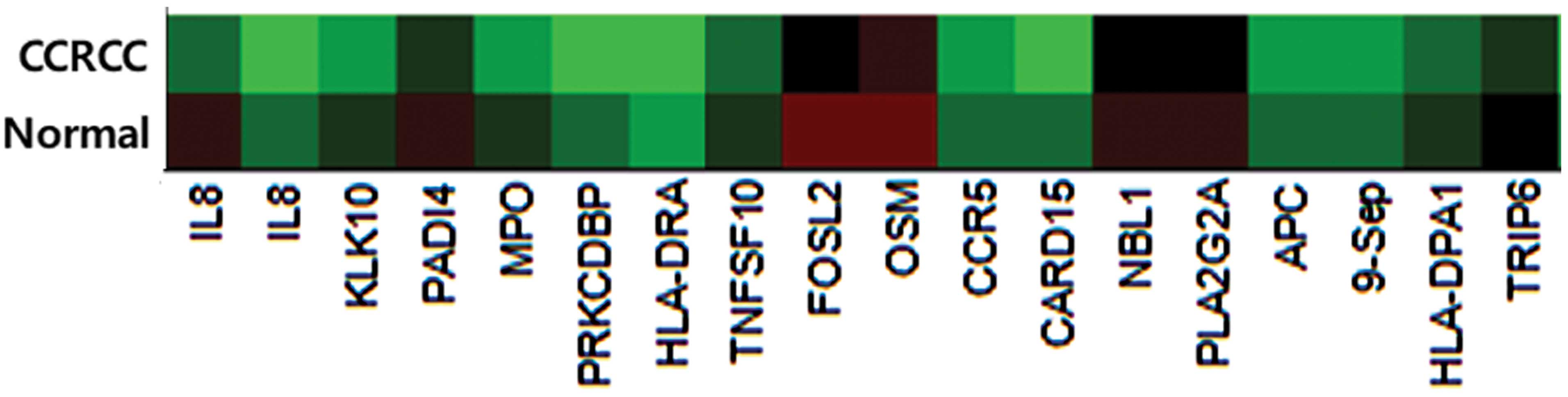
We identified one marker (IL8) out of 807
cancer-related candidate genes (Fig.
1). Results revealed that the mean beta value difference of IL8
was 0.406 (cancer tissue mean beta value, 0.346; normal tissue mean
beta value, 0.752). Of the 46 CCRCC patients, two groups were
defined according to their beta value difference; weak
hypomethylation (a difference smaller than the mean value) and
strong hypomethylation (a difference greater than the mean value).
Table I indicates that the
hypomethylation status of IL8 had no significant correlation with
either Fuhrman’s nuclear grade or tumor node metastasis (TNM) stage
(P>0.05).
 | Table IBaseline characteristic of clear cell
renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) patients. |
Table I
Baseline characteristic of clear cell
renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) patients.
| Weak hypomethylation
(n=23) | Strong
hypomethylation (n=23) | P-value |
|---|
| Age | 61.30±11.166 | 62.74±10.618 | 0.502 |
| Gender | | | 0.738 |
| Male | 18 | 16 | |
| Female | 5 | 7 | |
| Fuhrman’s nuclear
grade | | | |
| I | 2 | 2 | |
| II | 11 | 7 | |
| III | 7 | 9 | |
| IV | 3 | 5 | 0.316 |
| TNM stage | | | |
| T1 | 16 | 15 | |
| T2 | 4 | 4 | |
| T3 | 3 | 4 | |
| T4 | 0 | 0 | 0.695 |
| N0 | 22 | 22 | |
| N1 | 1 | 1 | 1.000 |
| M0 | 21 | 19 | |
| M1 | 2 | 4 | 0.386 |
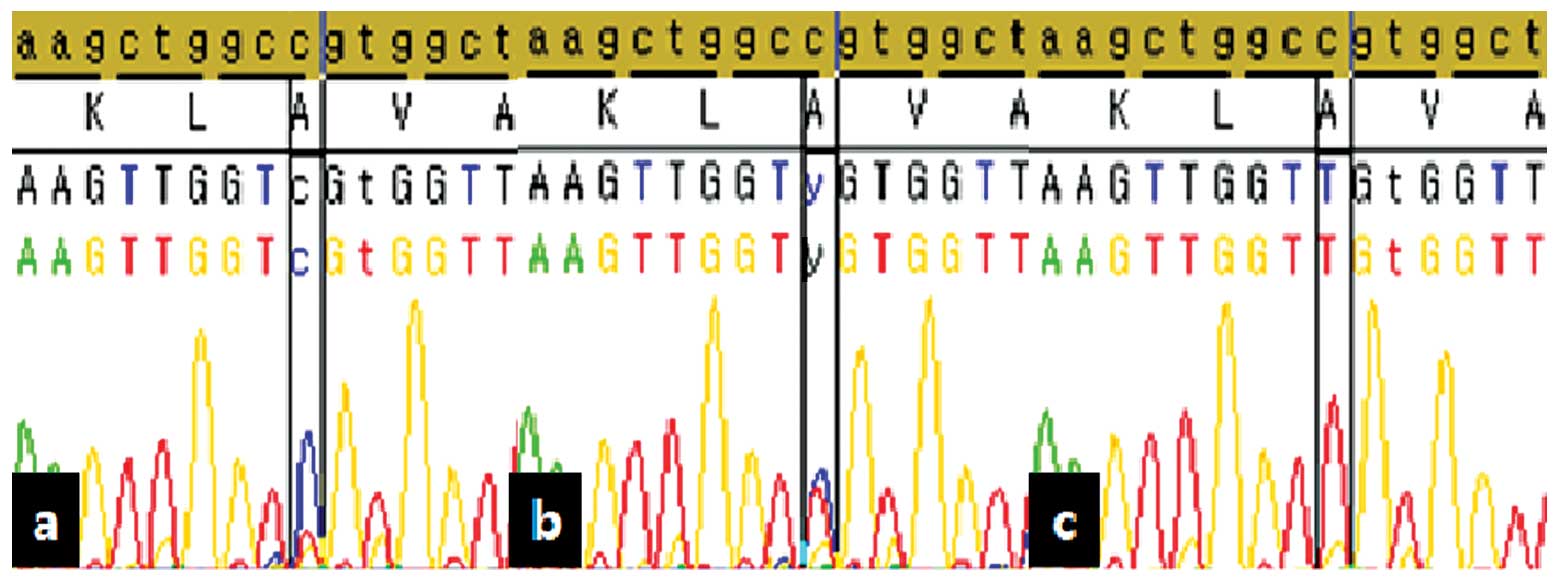
We examined the methylation status of the CpG site
by bisulfite sequencing. Fig. 2
reveals the hypomethylation results of IL8 using bisulfite
sequencing. Validation results using sequencing analysis
demonstrated that the methylation rate was 2.4% in cancer tissue
and 14.7% in normal tissue, whilst the non-nmethylation rate was
82.9% in cancer tissue and 52.9% in normal tissue. The overall
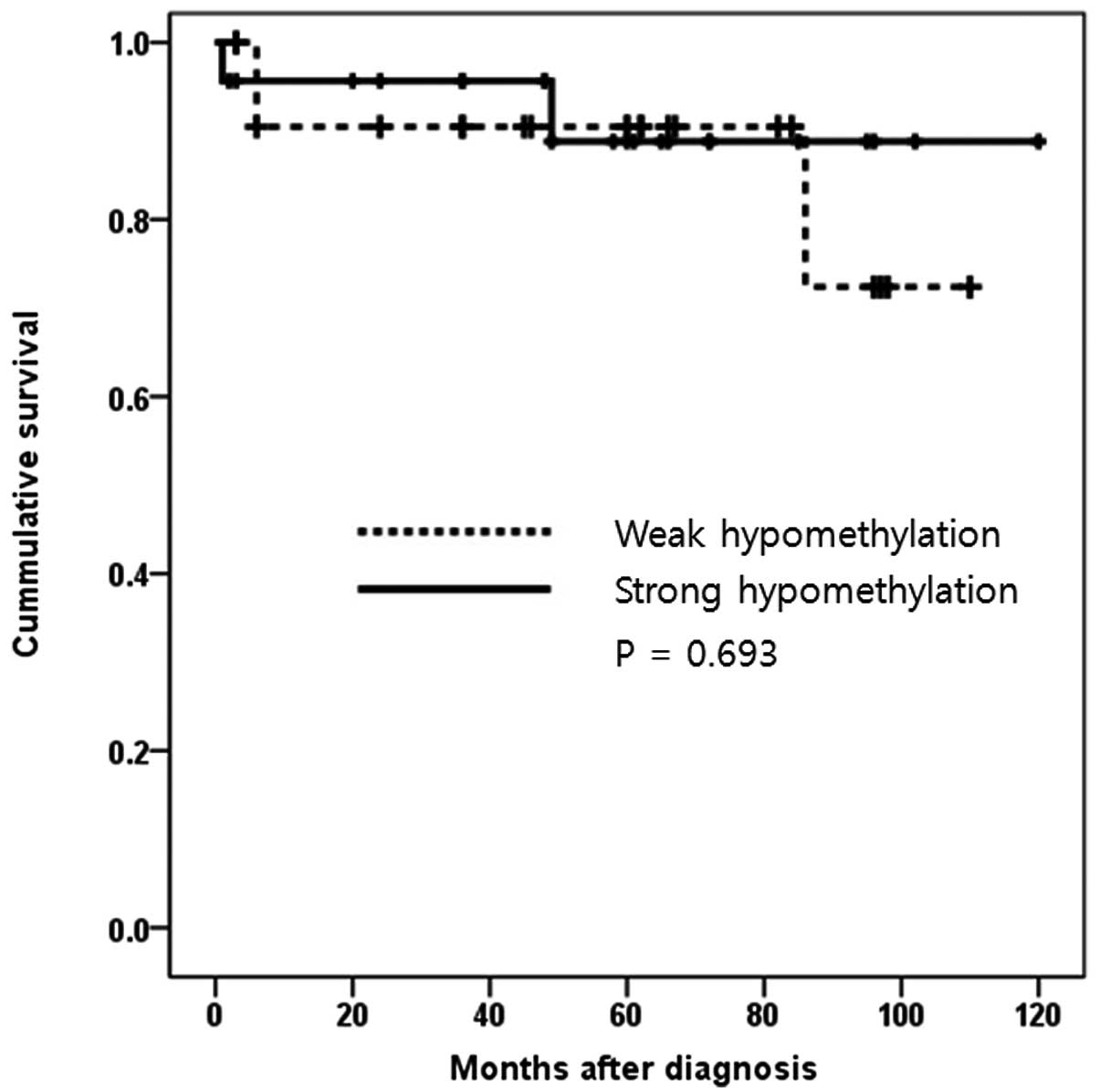
survival time of CCRCC patients was analyzed according to either a
weak or strong hypomethylation status of IL8 (Fig. 3). There was no statistical influence
of IL8 hypomethylation status on survival, as demonstrated by the
Kaplan-Meier survival curve (P=0.693).
Discussion
In this study, beta value differences of cancer and
normal tissue were not associated with clinicopathological status.
However, DNA hypomethylation of IL8 was widely detected in cancer
compared to normal kidney tissue. Alteration of genomic DNA
methylation, such as hyper- and hypomethylation, affects human
tumorigenesis (5). Hypermethylation
of promoter CpG islands is capable of inactivating important
tumor-suppressor genes (11).
Hypomethylation of genomic DNA has been associated with increased
rates of genomic instability (6,12).
Suzuki et al demonstrated that genomic DNA
hyper- and hypomethylation alterations in gastrointestinal cancer
were distributed gradually and increased with cancer patient age
(13). It was concluded that
age-dependent accumulation of DNA demethylation precedes diploidy
loss in gastrointestinal cancer. Cadieux et al demonstrated
that hypomethylation of Sat2 sequences is associated with copy
number alterations of the adjacent euchromatin in human
glioblastomas (14). This
implicated hypomethylation to be a predisposing factor for specific
genetic alterations in glioblastoma. The analysis between DNA
hypomethylation and prostate cancer was reported by
Yegnasubramanian et al, who performed a tiered gene
expression microarray and bisulfite genomic sequencing-based
approach to identify the methylation status of prostate cancer
(5). The authors demonstrated that
a class of cancer testis antigen genes undergoes CpG island
hypomethylation and overexpression in primary and metastatic
prostate cancer. DNA hypomethylation patterns were heterogenous
across different metastatic sites within the same patients.
IL8 is a proinflammatory cytokine for leukocytes and
is involved in tumor growth, metastasis and survival of solid organ
cancer (15,16). Certain studies have analyzed IL8
methylation status in human cancer (17,18).
Dimberg et al revealed the protein expression of IL8 in
plasma, tumor and paired normal tissue, and the methylation status
of the IL8 gene in colorectal cancer (17). The authors demonstrated that a
significantly higher level of IL8 was present in cancer tissue
compared to normal tissue. IL8 hypomethylation was detected in 64%
of the cancer tissue, whereas no hypomethylation was found in the
paired normal tissue. De Larco et al analyzed the
correlation between the metastatic potential of breast carcinoma
cell lines and the ectopic expression of IL8 (18). The authors revealed that an aberrant
methylation pattern may be responsible for the differences in IL8
between high and low metastatic cell lines. Two CpG sites of IL8
were fully methylated in the high metastatic cell lines. However,
these cell lines produced large quantities of IL8. The authors
suggested that there may be additional epigenetic control
mechanisms that have not yet been fully appreciated or
explored.
In summary, this study demonstrated that the IL8
gene was maximally hypomethylated in CCRCC cancer tissue compared
to normal tissue. However, levels of DNA hypomethylation were not
correlated with the clinicopathological status of the patient.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant
from the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF), funded
by the Korean government (MOST) (No. R13-2002-020-02001-0,
2007).
References
|
1
|
Waugh DJ and Wilson C: The interleukin-8
pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6735–6741. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vandercappellen J, Van Damme J and Struyf
S: The role of CXC chemokines and their receptors in cancer. Cancer
Lett. 267:226–244. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Martin D, Galisteo R and Gutkind JS:
CXCL8/IL8 stimulates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
expression and the autocrine activation of VEGFR2 in endothelial
cells by activating NFkappaB through the CBM (Carma3/Bcl10/Malt1)
complex. J Biol Chem. 284:6038–6042. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Djordjevic G, Mozetic V, Mozetic DV, et
al: Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factor
expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract.
203:99–106. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yegnasubramanian S, Haffner MC, Zhang Y,
et al: DNA hypomethylation arises later in prostate cancer
progression than CpG island hypermethylation and contributes to
metastatic tumor heterogeneity. Cancer Res. 68:8954–8967. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Karpf AR and Matsui S: Genetic disruption
of cytosine DNA methyltransferase enzymes induces chromosomal
instability in human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 65:8635–8639. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim GY, Park JH, Kim YW, Jung WW, Unni KK
and Park YK: Absence of amplification of HER-2/neu (c-erbB-2) gene
in Ewing’s sarcoma: a real-time polymerase chain reaction method.
Pathol Res Pract. 200:663–667. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bibikova M, Lin Z, Zhou L, et al:
High-throughput DNA methylation profiling using universal bead
arrays. Genome Res. 16:383–393. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Herman JG, Graff JR, Myöhänen S, Nelkin BD
and Baylin SB: Methylation-specific PCR: a novel PCR assay for
methylation status of CpG islands. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
93:9821–9826. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yoo KH, Park YK, Kim HS, Jung WW and Chang
SG: Epigenetic inactivation of HOXA5 and MSH2 gene in clear cell
renal cell carcinoma. Pathol Int. 60:661–666. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jones PA and Laird PW: Cancer epigenetics
comes of age. Nat Genet. 21:163–167. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Eden A, Gaudet F, Waghmare A and Jaenisch
R: Chromosomal instability and tumors promoted by DNA
hypomethylation. Science. 300:4552003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Suzuki K, Suzuki I, Leodolter A, et al:
Global DNA demethylation in gastrointestinal cancer is age
dependent and precedes genomic damage. Cancer Cell. 9:199–207.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cadieux B, Ching TT, VandenBerg SR and
Costello JF: Genome-wide hypomethylation in human glioblastomas
associated with specific copy number alteration,
methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase allele status, and increased
proliferation. Cancer Res. 66:8469–8476. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Xie K: Interleukin-8 and human cancer
biology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 12:375–391. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Strieter RM, Belperio JA, Phillips RJ and
Keane MP: CXC chemokines in angiogenesis of cancer. Semin Cancer
Biol. 14:195–200. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dimberg J, Ström K, Löfgren S, Zar N,
Lindh M and Matussek A: DNA promoter methylation status and protein
expression of interleukin-8 in human colorectal adenocarcinomas.
Int J Colorectal Dis. 27:709–714. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
De Larco JE, Wuertz BR, Yee D, Rickert BL
and Furcht LT: Atypical methylation of the interleukin-8 gene
correlates strongly with the metastatic potential of breast
carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:13988–13993.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|