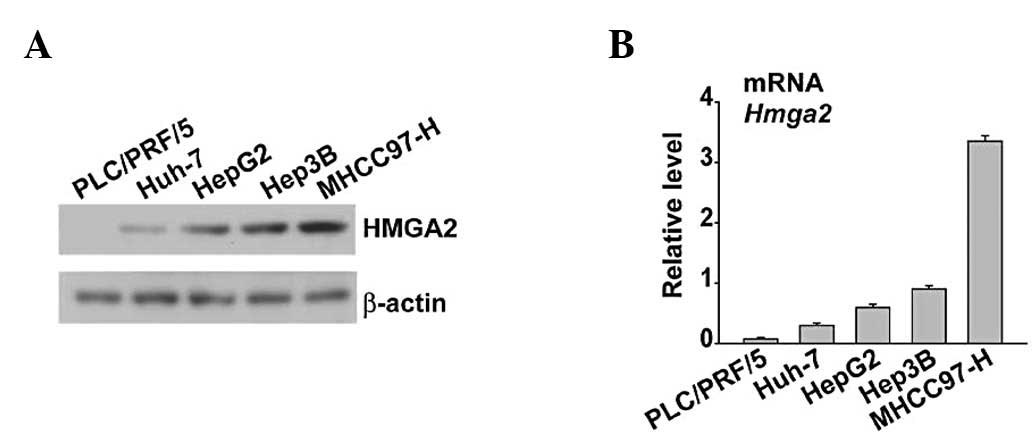
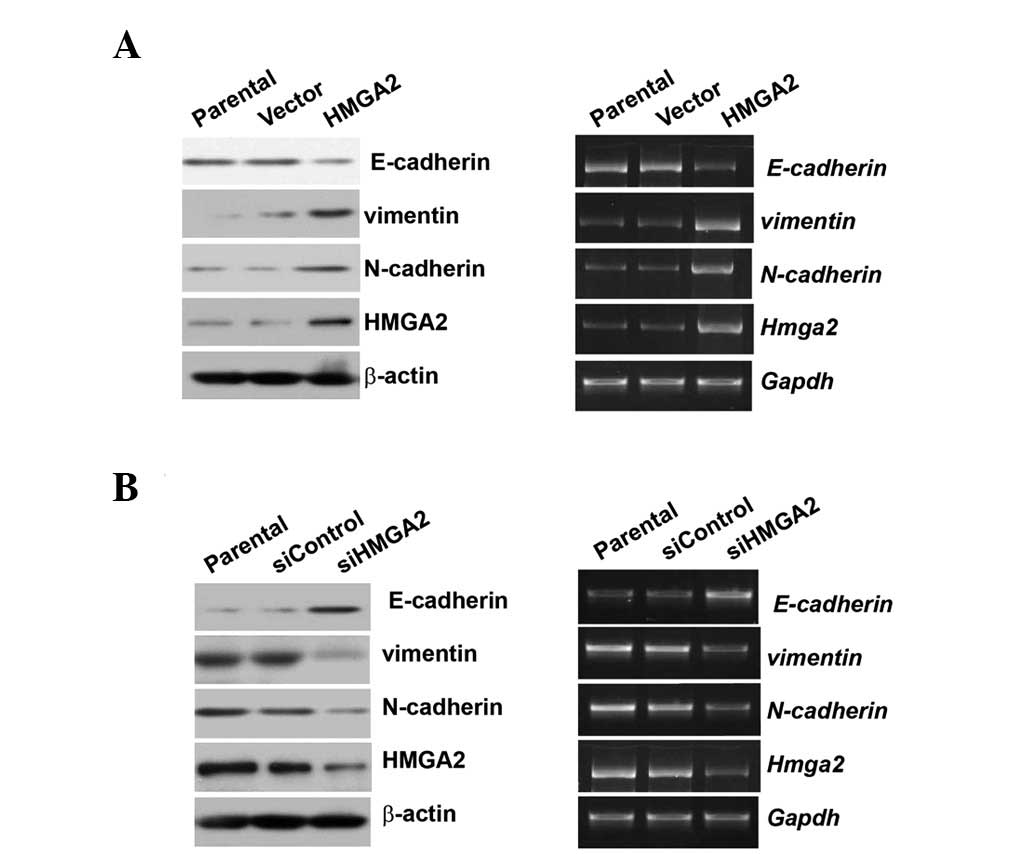
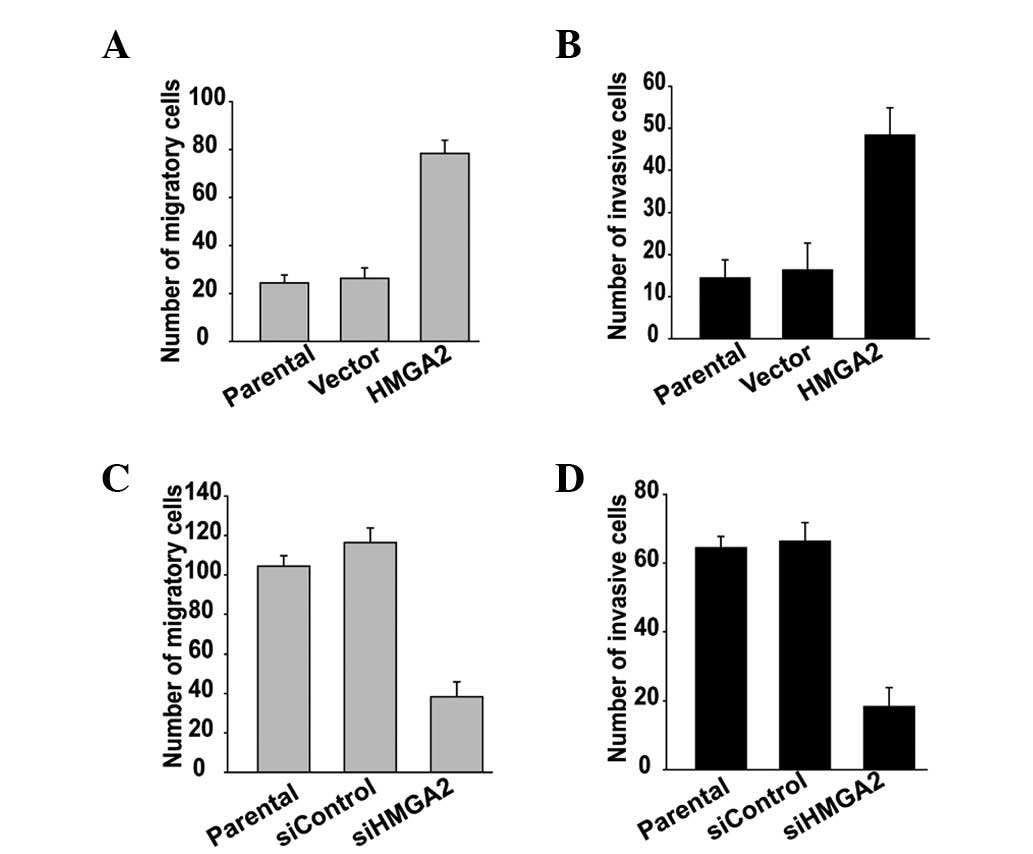
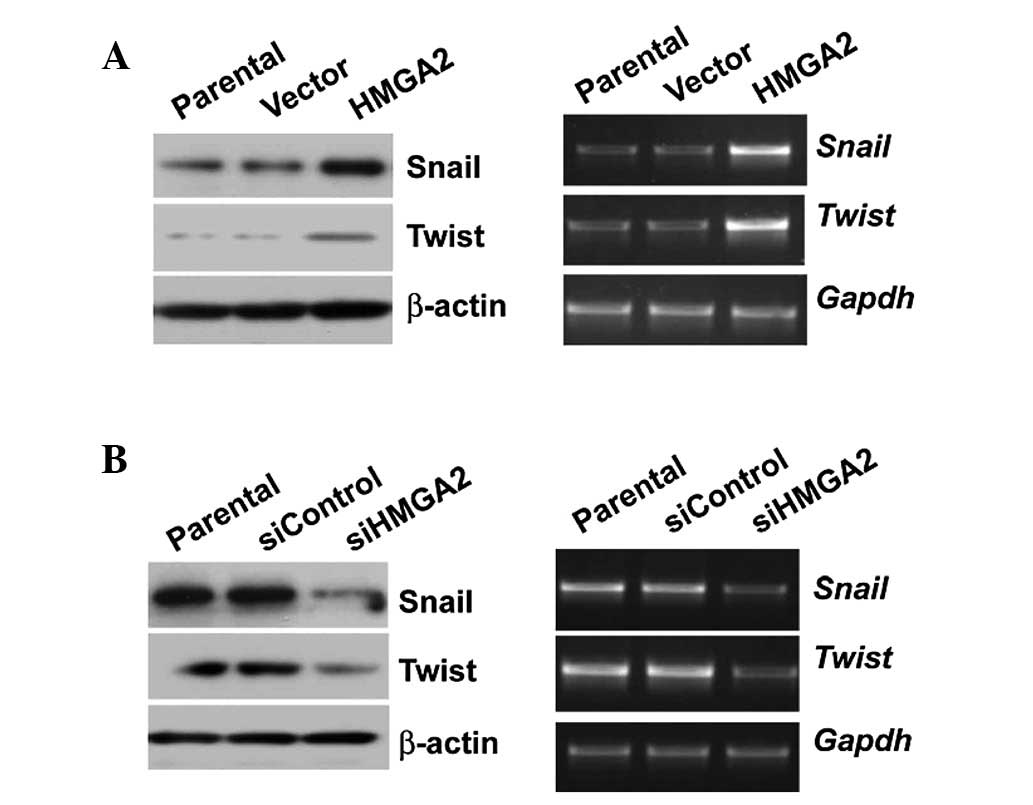
|
1
|
Chaffer CL and Weinberg RA: A perspective
on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 331:1559–1564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Qin Q, Xu Y, He T, Qin C and Xu J: Normal
and disease-related biological functions of Twist1 and underlying
molecular mechanisms. Cell Res. 22:90–106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fusco A and Fedele M: Roles of HMGA
proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:899–910. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sgarra R, Zammitti S, Lo Sardo A, et al:
HMGA molecular network: from transcriptional regulation to
chromatin remodeling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1799:37–47. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sarhadi VK, Wikman H, Salmenkivi K, et al:
Increased expression of high mobility group A proteins in lung
cancer. J Pathol. 209:206–212. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shell S, Park SM, Radjabi AR, et al: Let-7
expression defines two differentiation stages of cancer. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 104:11400–11405. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Langelotz C, Schmid P, Jakob C, et al:
Expression of high-mobility-group-protein HMGI-C mRNA in the
peripheral blood is an independent poor prognostic indicator for
survival in metastatic breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 88:1406–1410.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Miyazawa J, Mitoro A, Kawashiri S, Chada
KK and Imai K: Expression of mesenchyme-specific gene HMGA2 in
squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity. Cancer Res.
64:2024–2029. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dangi-Garimella S, Krantz SB, Barron MR,
et al: Three-dimensional collagen I promotes gemcitabine resistance
in pancreatic cancer through MT1-MMP-mediated expression of HMGA2.
Cancer Res. 71:1019–1028. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang X, Liu X, Li AY, et al:
Overexpression of HMGA2 promotes metastasis and impacts survival of
colorectal cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 17:2570–2580. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li AY, Lin HH, Kuo CY, et al:
High-mobility group A2 protein modulates hTERT transcription to
promote tumorigenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 31:2605–17. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Palmieri D, D’Angelo D, Valentino T, et
al: Downregulation of HMGA-targeting microRNAs has a critical role
in human pituitary tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 31:3857–3865. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tan EJ, Thuault S, Caja L, Carletti T,
Heldin CH and Moustakas A: Regulation of transcription factor Twist
expression by the DNA architectural protein high mobility group A2
during epithelialto-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem.
287:7134–7145. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Thuault S, Tan EJ, Peinado H, Cano A,
Heldin CH and Moustakas A: HMGA2 and Smads co-regulate SNAIL1
expression during induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. J Biol Chem. 283:33437–33446. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li Y, Tang ZY, Ye SL, et al: Establishment
of cell clones with different metastatic potential from the
metastatic hepatocellular carcin oma cell line MHCC97. World J
Gastroenterol. 7:630–636. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Monzen K, Ito Y, Naito AT, et al: A
crucial role of a high mobility group protein HMGA2 in
cardiogenesis. Nat Cell Biol. 10:567–574. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nishino J, Kim I, Chada K and Morrison SJ:
Hmga2 promotes neural stem cell self-renewal in young but not old
mice by reducing p16Ink4a and p19Arf expression. Cell. 135:227–239.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fabjani G, Tong D, Wolf A, et al: HMGA2 is
associated with invasiveness but not a suitable marker for the
detection of circulating tumor cells in breast cancer. Oncol Rep.
14:737–741. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|