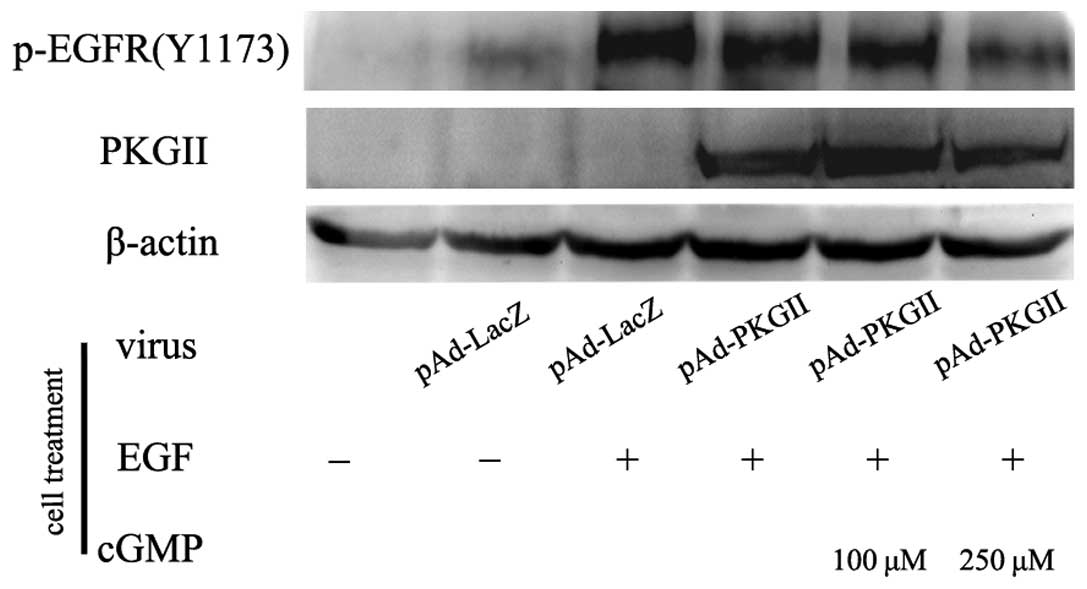
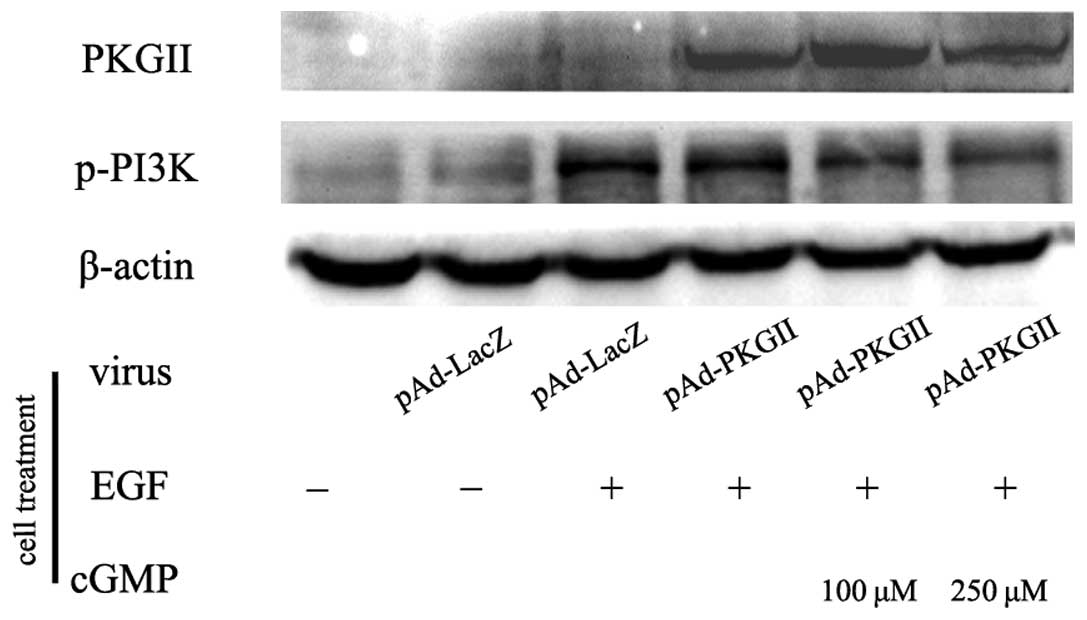
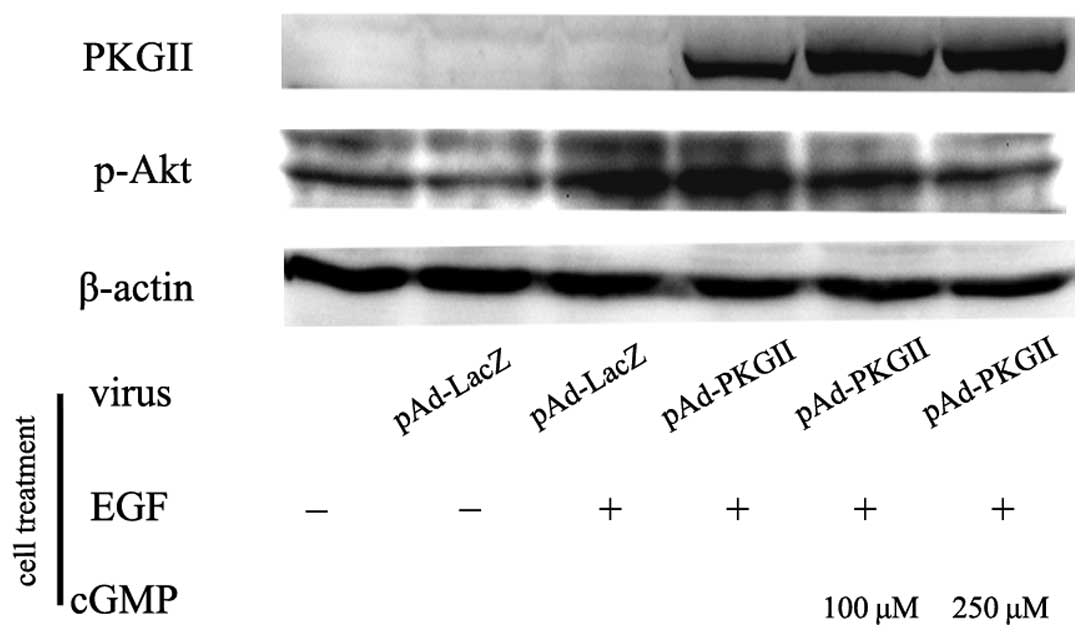
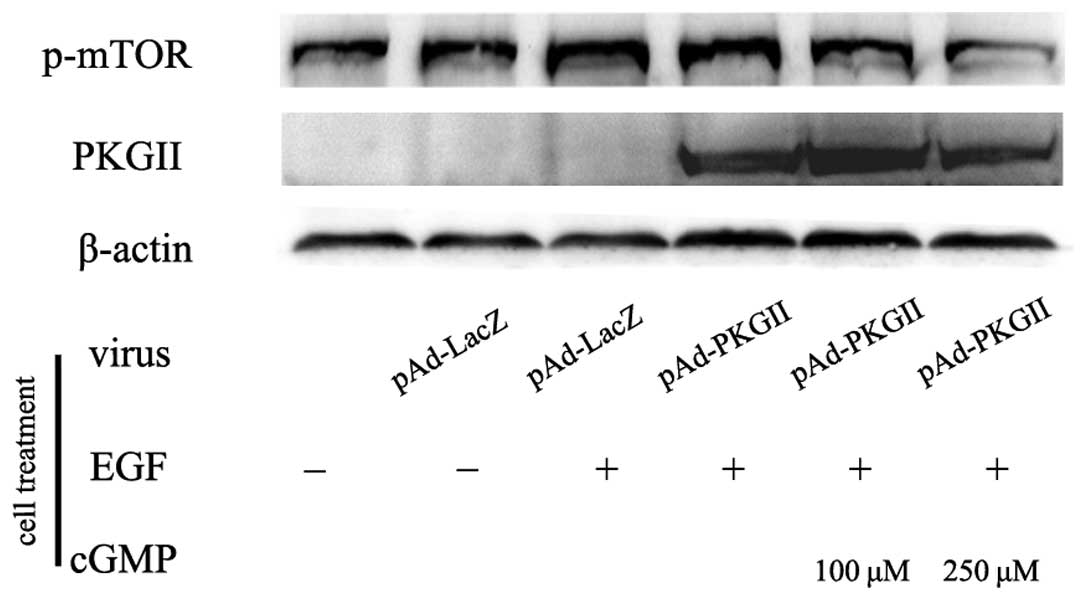
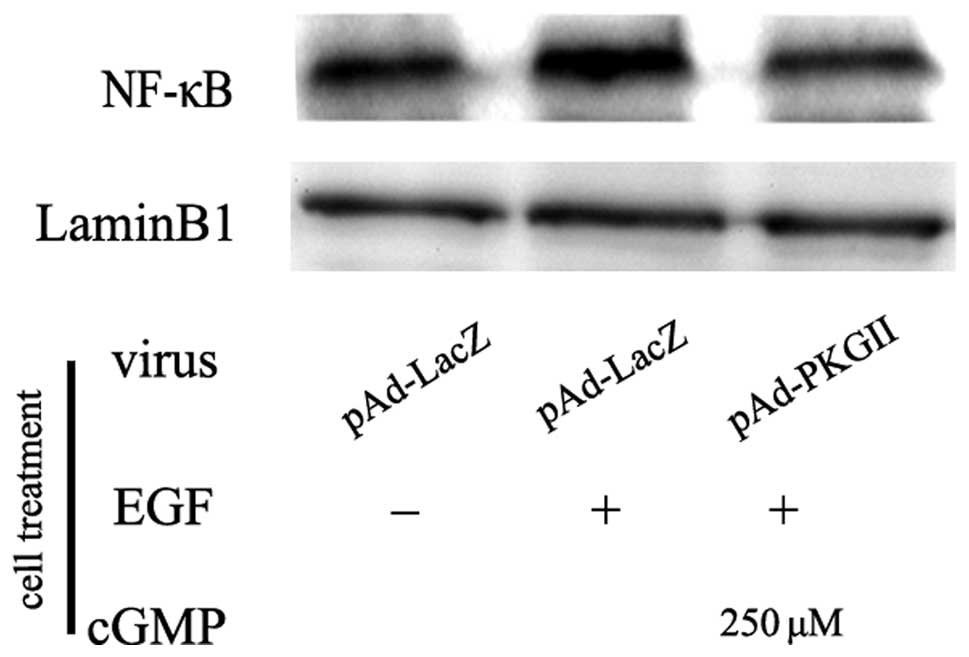
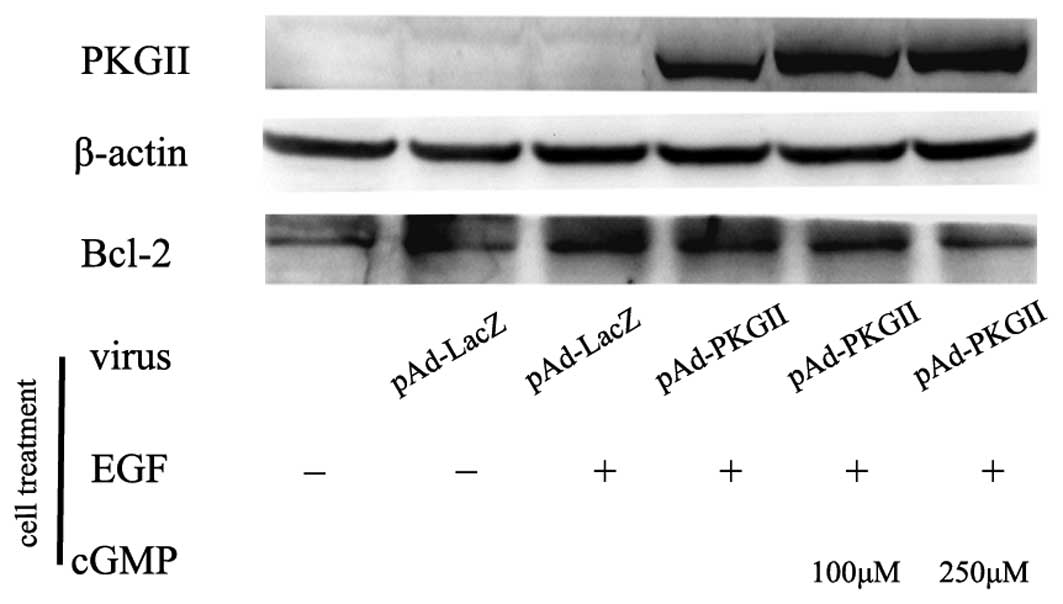
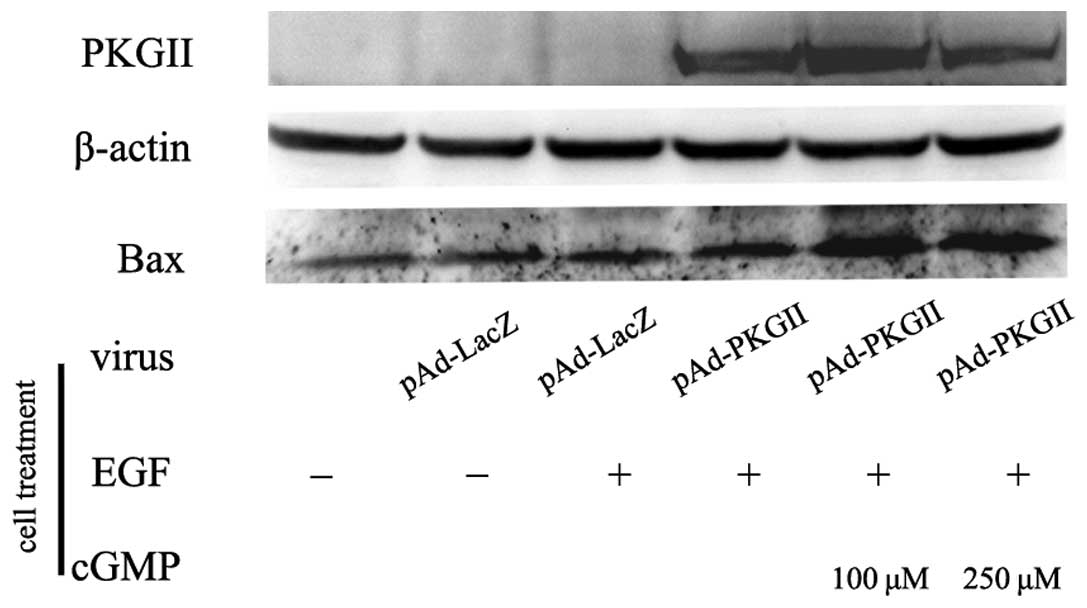
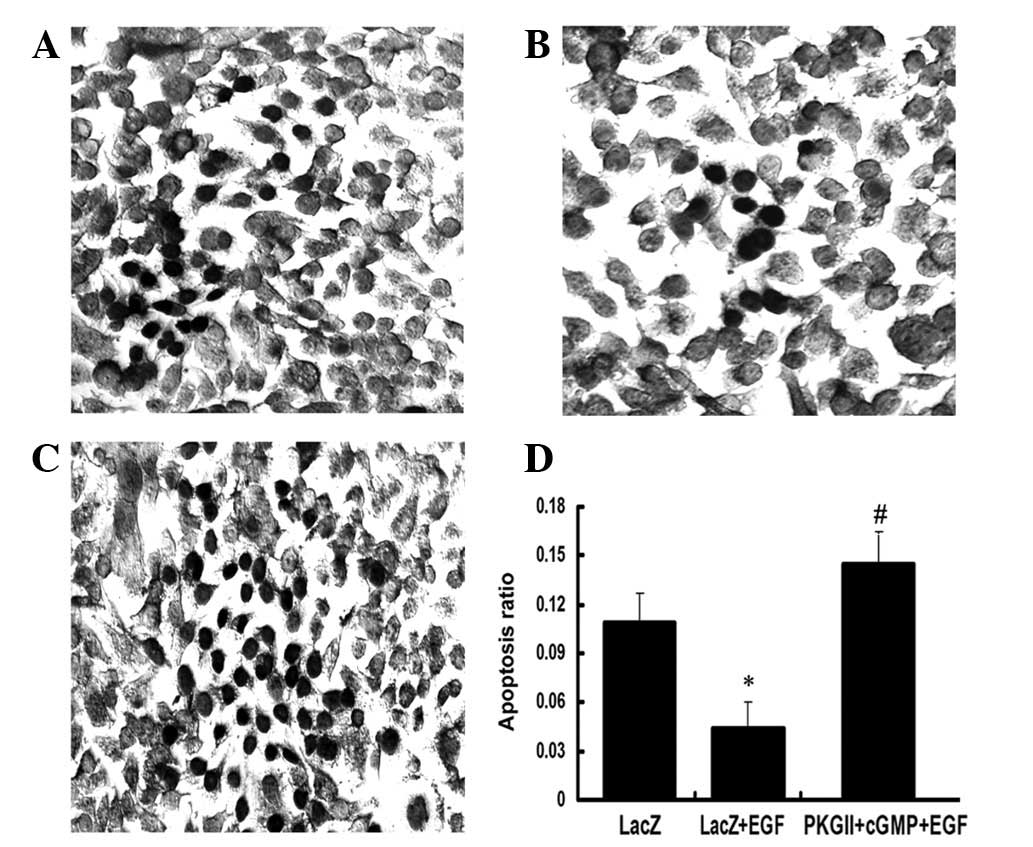
|
1
|
Marone R, Cmiljanovic V, Giese B and
Wymann MP: Targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinase: moving towards
therapy. Biochem Biophys Acta. 1784:159–185. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Song G, Ouyang G and Bao S: The activation
of Akt/PKB signaling pathway and cell survival. J Cell Mol Med.
9:59–71. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Edward LA, Thiesen B, Dragowska WH, et al:
Inhibiton of ILK in PTEN-mutant human glioblastomas inhibits
PKB/Akt activation, induces apoptosis and delays tumor growth.
Oncogene. 24:3596–3605. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Berg M and Soreide K: EGFR and downstream
genetic alterations in KRAS/BRAF and PI3K/AKT pathways in
colorectal cancer: implications for targeted therapy. Discov Med.
14:207–214. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Osaki M, Oshimura M and Ito H: PI3K-Akt
pathway: its functions and alteration in human cancer. Apoptosis.
9:667–676. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Orstavik S, Natarajan V, Taskén K, et al:
Characterization of the human gene encoding the type I alpha and
type I beta cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PRKG1). Genomics.
42:311–318. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Orstavik S, Solberg R, Taskén K, et al:
Molecular cloning, cDNA structure and chromosomal localization of
the human type II cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 220:759–765. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Browing DD: Protein kinase G as a
therapeutic target for the treatment of metastatic colorectal
cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 12:367–376. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang SQ, Chen YC, Wang Y, et al:
Expression of cGMP dependent protein kinase II in cancer cell lines
was obviously decreased. J Jiangsu Univ (Medicine Edition). 18:1–5.
2008.
|
|
10
|
Chen YC, Ren F, Sang JR, et al: Type II
cGMP-dependent protein kinase inhibits proliferation of the gastric
cancer cell line BGC-823. Mol Med Rep. 3:361–366. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu Y, Chen Y, Qu R, et al: Type II
cGMP-dependent protein kinase inhibits EGF-triggered signal
transduction of the MAPK/ERK-mediated pathway in gastric cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 27:553–558. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lan T, Chen Y, Sang J, et al: Type II
cGMP-dependent protein kinase inhibits EGF-induced MAPK/JNK signal
transduction in breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 27:2039–2044.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dong P, Xu Z, Jia N, et al: Elevated
expression of p53 gain-of-function mutation R175H in endometrial
cancer cells can increase the invasive phenotypes by activation of
the EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol Cancer. 8:1032009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Quesnelle KM, Boehm AL and Grandis JR:
STAT-mediated EGFR signaling in cancer. J Cell Biochem.
102:311–319. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hofmann F: The biology of cyclic
GMP-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 280:1–4. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nie HG, Chen L, Han DY, et al: Regulation
of epithelial sodium channels by cGMP/PKGII. J Physiol.
587:2663–2676. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rangaswami H, Marathe N, Zhuang S, et al:
Type II cGMP-dependent protein kinase mediates osteoblast
mechanotransduction. J Biol Chem. 284:14796–14808. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rangaswami H, Schwappacher R, Marathe N,
et al: Cyclic GMP and protein kinase G control a Src-containing
mechanosome in osteoblasts. Sci Signal. 3:ra912010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cook AL and Haynes JM: Protein kinase G
II-mediated proliferative effects in human cultured prostatic
stromal cells. Cell Signal. 16:253–261. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Swartling FJ, Ferletta M, Kastemar M, et
al: Cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase II inhibits cell
proliferation, Sox9 expression and Akt phosphorylation in human
glioma cell lines. Oncogene. 28:3121–3131. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fallahian F, Karami-Tehrani F, Salami S
and Aghaei M: Cyclic GMP induced apoptosis via protein kinase G in
oestrogen receptor-positive and -negative breast cancer cell lines.
FEBS J. 278:3360–3369. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xie Z, Peng J, Pennypacker SD and Chen Y:
Critical role for the catalytic activity of phospholipase C-γ1 in
epidermal growth factor-induced cell migration. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 399:425–428. 2010.
|
|
23
|
Yap TA, Garrett MD, Walton MI, et al:
Targeting the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway: progress, pitfalls, and
promises. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 8:393–412. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Normanno N, Bianco C, De Luca A, et al:
Target-based agents against ErbB receptors and their ligands: a
novel approach to cancer treatment. Endocr Relat Cancer. 10:1–21.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J and Haber
DA: Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat
Rev Cancer. 7:169–181. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hynes NE and MacDonald G: ErbB receptors
and signaling pathways in cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 21:177–184.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Quatrale AE, Porcelli L, Silvestris N, et
al: EGFR tyrosine kinases inhibitors in cancer treatment: in vitro
and in vivo evidence. Front Biosci. 16:1962–1972. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|