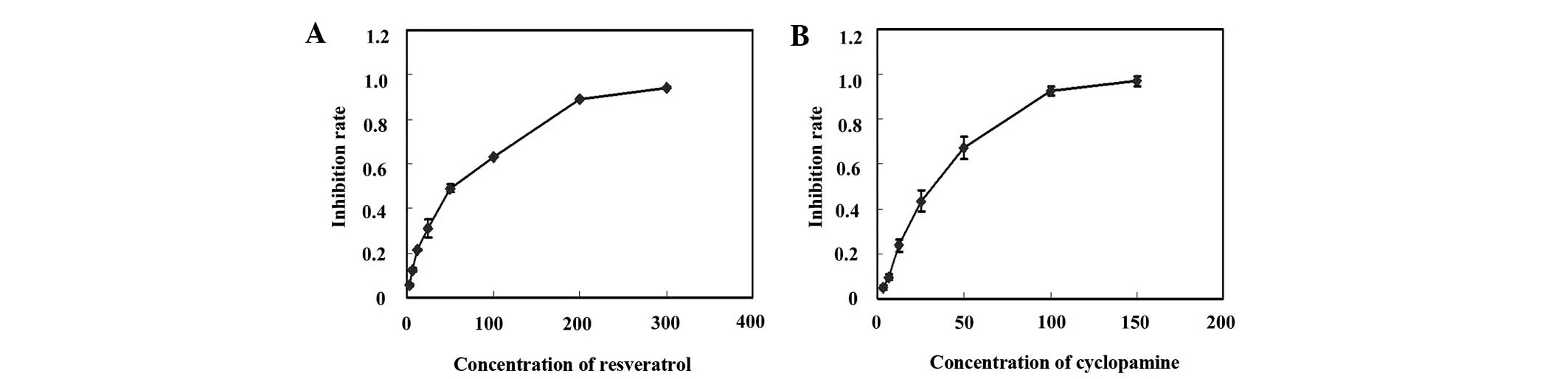
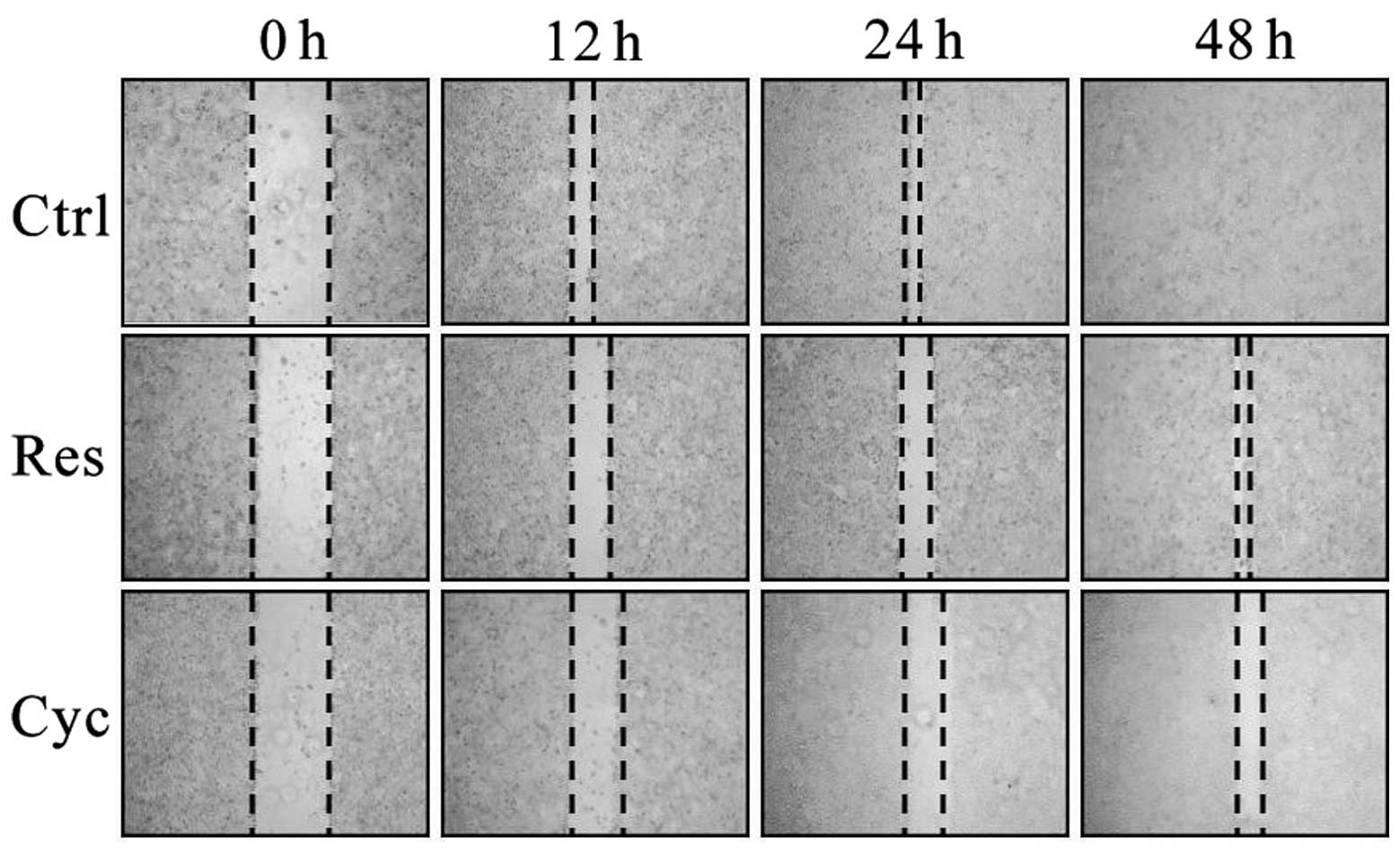
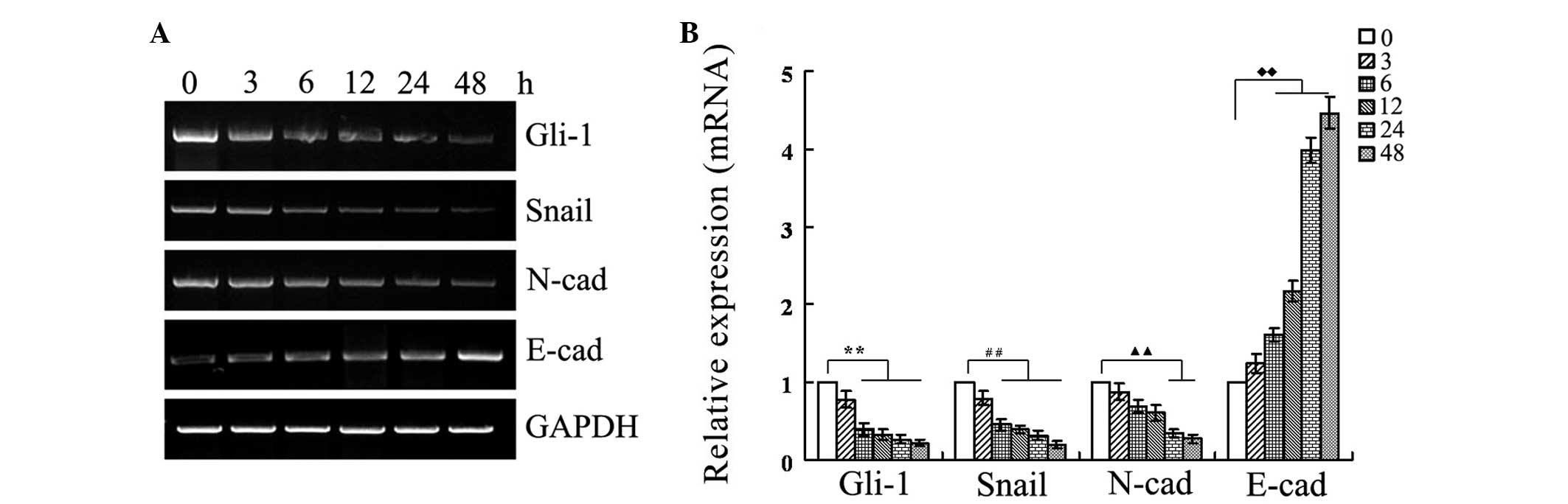
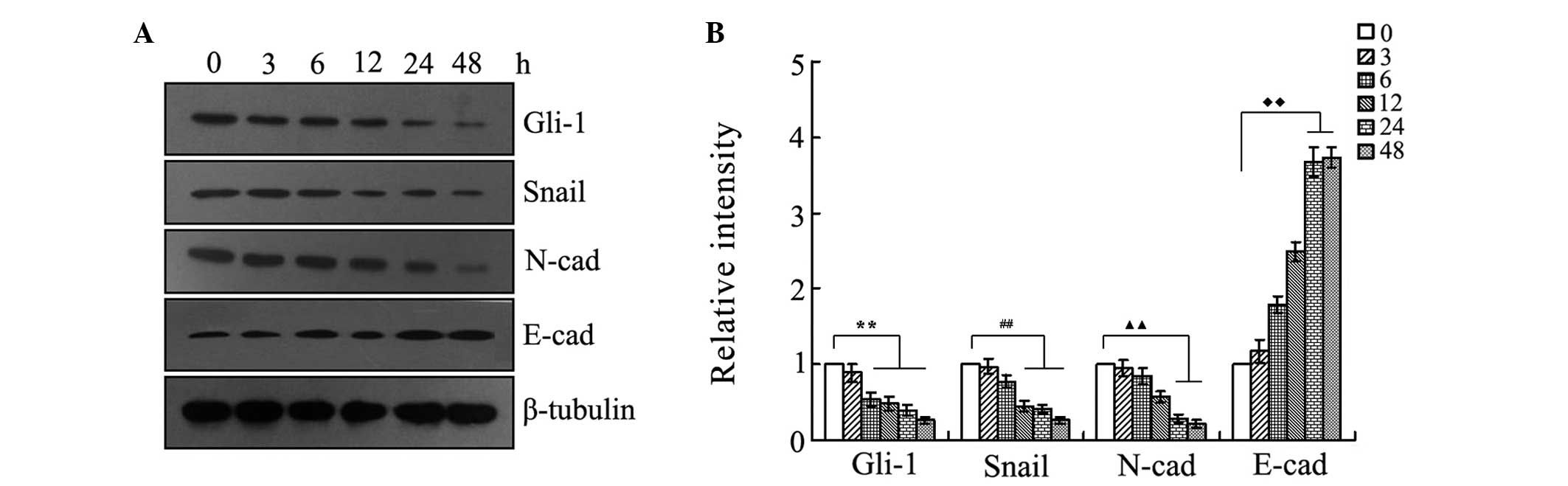
|
1
|
Parkin DM: Global cancer statistics in the
year 2000. Lancet Oncol. 2:533–543. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Khosravi Shahi P, Díaz Muñozde la Espada
VM, García Alfonso P, et al: Management of gastric adenocarcinoma.
Clin Transl Oncol. 9:438–442. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Radisky DC: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. J Cell Sci. 118:4325–4326. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chang CJ, Chao CH, Xia W, et al: p53
regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem cell
properties through modulating miRNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 13:317–323.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Voulgari A and Pintzas A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis: mechanisms
markers and strategies to overcome drug resistance in the clinic.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1796:75–90. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kundu JK and Surh YJ: Cancer
chemopreventive and therapeutic potential of resveratrol:
mechanistic perspectives. Cancer Lett. 269:243–261. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xie D, Gore C, Liu J, et al: Role of
DAB2IP in modulating epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and
prostate cancer metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:2485–2490.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gjerdrum C, Tiron C, Høiby T, et al: Axl
is an essential epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-induced
regulator of breast cancer metastasis and patient survival. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:1124–1129. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Moreno-Bueno G, Peinado H, Molina P, et
al: The morphological and molecular features of the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Nat Protoc. 4:1591–1613.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li X, Deng W, Nail CD, Bailey SK, Kraus
MH, Ruppert JM and Lobo-Ruppert SM: Snail induction is an early
response to Gli1 that determines the efficiency of epithelial
transformation. Oncogene. 25:609–621. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Louro ID, Bailey EC, Li X, et al:
Comparative gene expression profile analysis of GLI and c-MYC in an
epithelial model of malignant transformation. Cancer Res.
62:5867–5873. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
McMahon AP, Ingham PW and Tabin CJ:
Developmental roles and clinical significance of hedgehog
signaling. Curr Top Dev Biol. 53:1–114. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee J, Platt KA, Censullo P and Ruiz i
Altaba A: Gli1 is a target of Sonic hedgehog that induces ventral
neural tube development. Development. 124:2537–2552.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ohta M, Tateishi K, Kanai F, et al:
p53-independent negative regulation of p21/cyclin-dependent
kinase-interacting protein 1 by the sonic
hedgehog-glioma-associated oncogene 1 pathway in gastric carcinoma
cells. Cancer Res. 65:10822–10829. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Watkins DN, Berman DM, Burkholder SG, Wang
B, Beachy PA and Baylin SB: Hedgehog signalling within airway
epithelial progenitors and in small-cell lung cancer. Nature.
422:313–317. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kubo M, Nakamura M, Tasaki A, et al:
Hedgehog signaling pathway is a new therapeutic target for patients
with breast cancer. Cancer Res. 64:6071–6074. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mimeault M, Moore E, Moniaux N, et al:
Cytotoxic effects induced by a combination of cyclopamine and
gefitinib, the selective hedgehog and epidermal growth factor
receptor signaling inhibitors, in prostate cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 118:1022–1031. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Qualtrough D, Buda A, Gaffield W, Williams
AC and Paraskeva C: Hedgehog signalling in colorectal tumour cells:
induction of apoptosis with cyclopamine treatment. Int J Cancer.
110:831–837. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Thayer SP, di Magliano MP, Heiser PW, et
al: Hedgehog is an early and late mediator of pancreatic cancer
tumorigenesis. Nature. 425:851–856. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yoo YA, Kang MH, Lee HJ, et al: Sonic
hedgehog pathway promotes metastasis and lymphangiogenesis via
activation of Akt, EMT and MMP-9 pathway in gastric cancer. Cancer
Res. 71:7061–7070. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yanai K, Nagai S, Wada J, et al: Hedgehog
signaling pathway is a possible therapeutic target for gastric
cancer. J Surg Oncol. 95:55–62. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang Y, Catana F, Yang Y, Roderick R and
van Breemen RB: An LC-MS method for analyzing total resveratrol in
grape juice, cranberry juice and in wine. J Agric Food Chem.
50:431–435. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Burns J, Yokota T, Ashihara H, Lean ME and
Crozier A: Plant foods and herbal sources of resveratrol. J Agric
Food Chem. 50:3337–3340. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Qadri SM, Föller M and Lang F: Inhibition
of suicidal erythrocyte death by resveratrol. Life Sci. 85:33–38.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Baur JA and Sinclair DA: Therapeutic
potential of resveratrol: the in vivo evidence. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 5:493–506. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kundu JK and Surh YJ: Cancer
chemopreventive and therapeutic potential of resveratrol:
mechanistic perspectives. Cancer Lett. 269:243–261. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang H, Zhang H, Tang L, et al:
Resveratrol inhibits TGF-β1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition and suppresses lung cancer invasion and metastasis.
Toxicology. 303:139–146. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li W, Ma J, Ma Q, et al: Resveratrol
inhibits the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer
cells via suppression of the PI-3 K/Akt/NF-κB pathway. Curr Med
Chem. 20:4185–4194. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vergara D, Valente CM, Tinelli A, et al:
Resveratrol inhibits the epidermal growth factor-induced epithelial
mesenchymal transition in MCF-7 cells. Cancer Lett. 310:1–8. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Slusarz A, Shenouda NS, Sakla MS, et al:
Common botanical compounds inhibit the hedgehog signaling pathway
in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 70:3382–3390. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sarkar FH, Li Y, Wang Z and Kong D: The
role of nutraceuticals in the regulation of Wnt and Hedgehog
signaling in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 29:383–394. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shakibaei M, Harikumar KB and Aggarwal BB:
Resveratrol addiction: to die or not to die. Mol Nutr Food Res.
53:115–128. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bisht K, Wagner KH and Bulmer AC:
Curcumin, resveratrol and flavonoids as anti-inflammatory, cyto-
and DNA-protective dietary compounds. Toxicology. 278:88–100. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Michels G, Wätjen W, Weber N, et al:
Resveratrol induces apoptotic cell death in rat H4IIE hepatoma
cells but necrosis in C6 glioma cells. Toxicology. 225:173–182.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Busquets S, Ametller E, Fuster G, et al:
Resveratrol a natural diphenol, reduces metastatic growth in an
experimental cancer model. Cancer Lett. 245:144–148. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Olas B, Wachowicz B, Tomczak A, et al:
Comparative anti-platelet and antioxidant properties of
polyphenol-rich extracts from: berries of Aronia melanocarpa, seeds
of grape and bark of Yucca schidigera in vitro. Platelets.
19:70–77. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Knobloch J, Hag H, Jungck D, Urban K and
Koch A: Resveratrol impairs the release of steroid-resistant
cytokines from bacterial endotoxin-exposed alveolar macrophages in
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Basic Clin Pharmacol
Toxicol. 109:138–143. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee SY, Lee HJ, Sikder MA, et al:
Resveratrol inhibits mucin gene expression production and secretion
from airway epithelial cells. Phytother Res. 26:1082–1087. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nüsslein-Volhard C and Wieschaus E:
Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila.
Nature. 287:795–801. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chang DT, López A, von Kessler DP, et al:
Products, genetic linkage and limb patterning activity of a murine
hedgehog gene. Development. 120:3339–3353. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Echelard Y, Epstein DJ, St-Jacques B, et
al: Sonic hedgehog, a member of a family of putative signaling
molecules, is implicated in the regulation of CNS polarity. Cell.
75:1417–1430. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Krauss S, Concordet JP and Ingham PW: A
functionally conserved homolog of the Drosophila segment polarity
gene hh is expressed in tissues with polarizing activity in
zebrafish embryos. Cell. 75:1431–1444. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Riddle RD, Johnson RL, Laufer E and Tabin
C: Sonic hedgehog mediates the polarizing activity of the ZPA.
Cell. 75:1401–1416. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lum L and Beachy PA: The hedgehog response
network: sensors, switches and routers. Science. 304:1755–1759.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Eaton S: Multiple roles for lipids in the
Hedgehog signalling pathway. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:437–445.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Pasca di Magliano M and Hebrok M: Hedgehog
signalling in cancer formation and maintenance. Nat Rev Cancer.
3:903–911. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ingham PW and McMahon AP: Hedgehog
signaling in animal development: paradigms and principles. Genes
Dev. 15:3059–3087. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Louro ID, Bailey EC, Li X, et al:
Comparative gene expression profile analysis of Gli1 and c-Myc in
an epithelial model of malignant transformation. Cancer Res.
62:5867–5873. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Shankar S, Nall D, Tang SN, Meeker D,
Passarini J, Sharma J and Srivastava RK: Resveratrol inhibits
pancreatic cancer stem cell characteristics in human and KrasG12D
transgenic mice by inhibiting pluripotency maintaining factors and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One. 6:e165302011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Incardona JP, Gaffield W, Kapur RP and
Roelink H: The teratogenic Veratrum alkaloid cyclopamine inhibits
Sonic hedgehog signal transduction. Development. 125:3553–3562.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang Y, Zhou Z, Walsh CT and McMahon AP:
Selective translocation of intracellular Smoothened to the primary
cilium in response to Hedgehog pathway modulation. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 106:2623–2628. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chen JK, Taipale J, Cooper MK and Beachy
PA: Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling by direct binding of
cyclopamine to Smoothened. Genes Dev. 16:2743–2748. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Scales SJ and de Sauvage FJ: Mechanisms of
Hedgehog pathway activation in cancer and implications for therapy.
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 30:303–312. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|