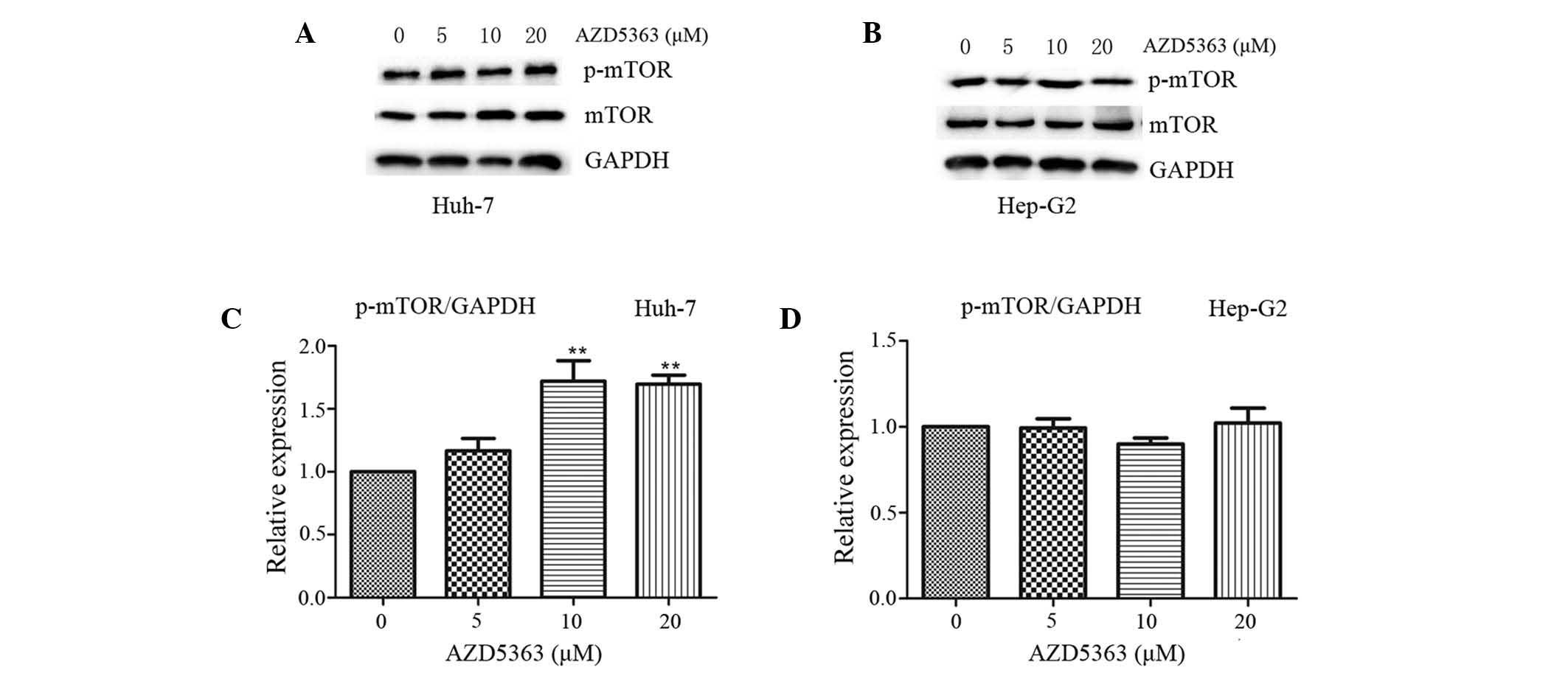
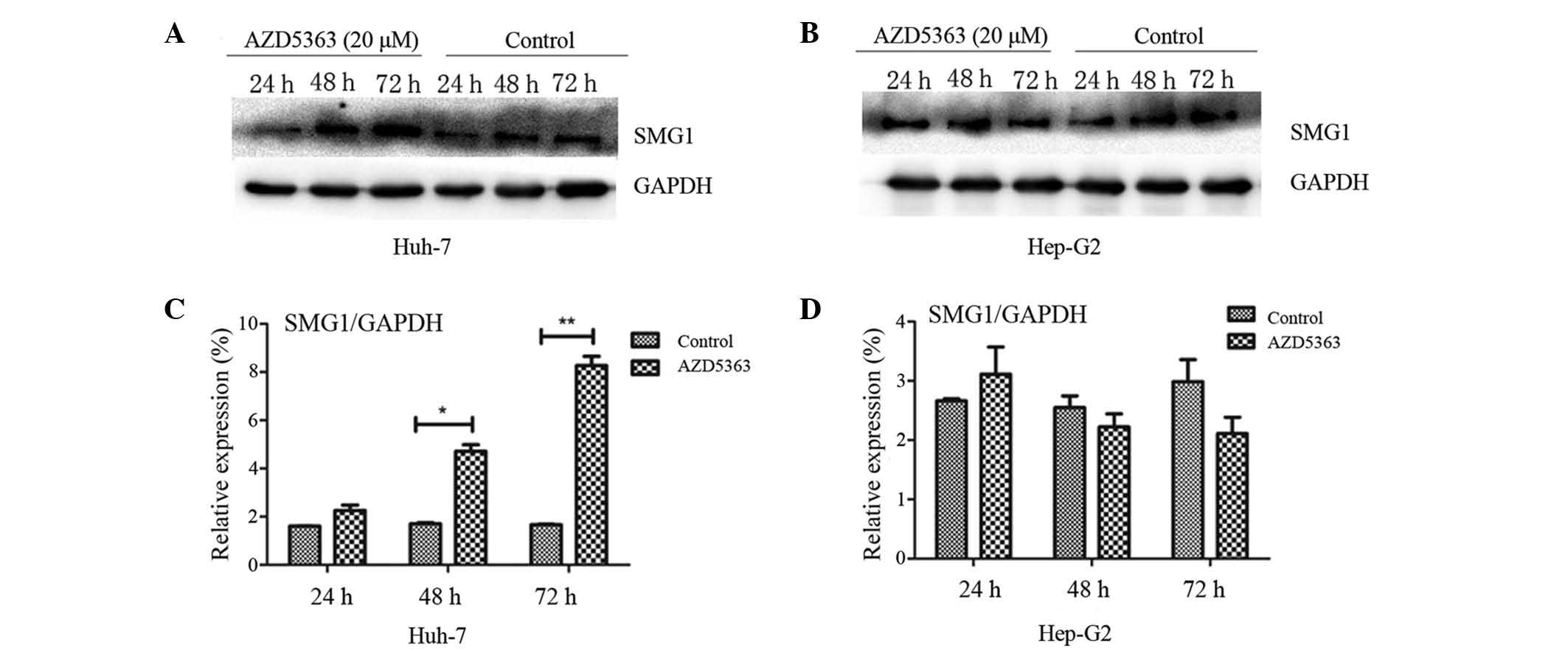
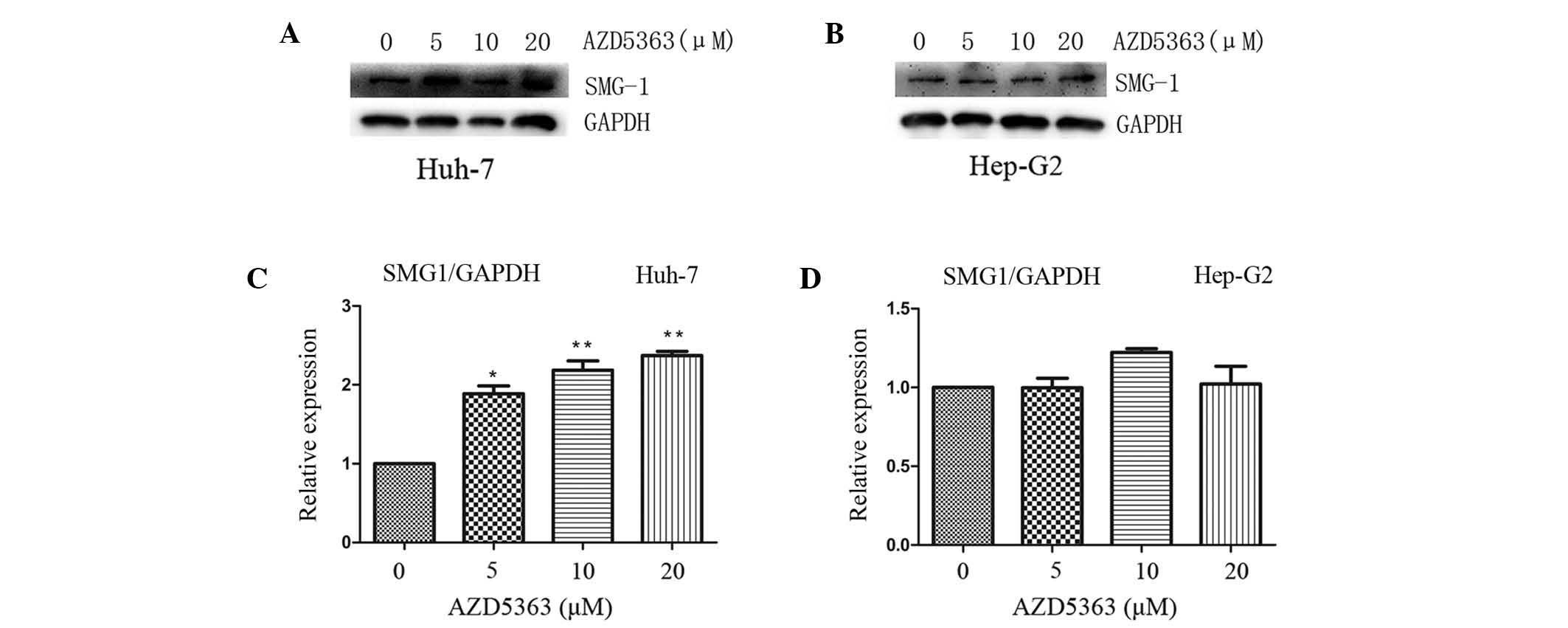
|
1
|
Bruix J and Sherman M: American
Association for the Study of Liver Diseases: Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology. 53:1020–1022.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
El-Serag HB: Hepatocellular carcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 365:1118–1127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bruix J and Sherman M: American
Association for the Study of Liver Diseases: Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology. 53:1020–1022.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Abou-Alfa GK, Schwartz L, Ricci S, Amadori
D, Santoro A, Figer A, De Greve J, Douillard JY, Lathia C, Schwartz
B, et al: Phase II study of sorafenib in patients with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 24:4293–4300. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mitsui H, Takuwa N, Maruyama T, Maekawa H,
Hirayama M, Sawatari T, Hashimoto N, Takuwa Y and Kimura S: The
MEK1-ERK map kinase pathway and the PI 3-kinase-Akt pathway
independently mediate anti-apoptotic signals in HepG2 liver cancer
cells. Int J Cancer. 92:55–62. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bhaskar PT and Hay N: The two TORCs and
Akt. Dev Cell. 12:487–502. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Engelman JA: Targeting PI3K signalling in
cancer: Opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:550–562. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Villanueva A, Chiang DY, Newell P, Peix J,
Thung S, Alsinet C, Tovar V, Roayaie S, Minguez B, Sole M, et al:
Pivotal role of mTOR signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 135:1972–1983, 1983.e1-1983.e11. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Calvisi DF, Wang C, Ho C, et al: Increased
lipogenesis, induced by AKT-mTORC1-RPS6 signaling, promotes
development of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
140:1071–1083. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Stiles B, Wang Y, Stahl A, et al:
Liver-specific deletion of negative regulator Pten results in fatty
liver and insulin hypersensitivity [corrected]. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 101:2082–2087. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
O'Reilly KE, Rojo F, She QB, Solit D,
Mills GB, Smith D, Lane H, Hofmann F, Hicklin DJ, Ludwig DL, et al:
mTOR inhibition induces upstream receptor tyrosine kinase signaling
and activates Akt. Cancer Res. 66:1500–1508. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
González-Estévez C, Felix DA, Smith MD,
Paps J, Morley SJ, James V, Sharp TV and Aboobaker AA: SMG-1 and
mTORC1 act antagonistically to regulate response to injury and
growth in planarians. PLoS Genet. 8:e10026192012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Han EK, Leverson JD, McGonigal T, Shah OJ,
Woods KW, Hunter T, Giranda VL and Luo Y: Akt inhibitor A-443654
induces rapid Akt Ser-473 phosphorylation independent of mTORC1
inhibition. Oncogene. 26:5655–5661. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Levy DS, Kahana JA and Kumar R: AKT
inhibitor, GSK690693, induces growth inhibition and apoptosis in
acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines. Blood. 113:1723–1729.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin J, Sampath D, Nannini MA, Lee BB,
Degtyarev M, Oeh J, Savage H, Guan Z, Hong R, Kassees R, et al:
Targeting activated Akt with GDC-0068, a novel selective Akt
inhibitor that is efficacious in multiple tumor models. Clin Cancer
Res. 19:1760–1772. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li Z, Oh DY, Nakamura K and Thiele CJ:
Perifosine-induced inhibition of Akt attenuates brain-derived
neurotrophic factor/TrkB-induced chemoresistance in neuroblastoma
in vivo. Cancer. 117:5412–5422. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu R, Liu D, Trink E, Bojdani E, Ning G
and Xing M: The Akt-specific inhibitor MK2206 selectively inhibits
thyroid cancer cells harboring mutations that can activate the
PI3K/Akt pathway. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 96:E577–E585. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Davies BR, Greenwood H, Dudley P, Crafter
C, Yu DH, Zhang J, Li J, Gao B, Ji Q, Maynard J, et al: Preclinical
pharmacology of AZD5363, an inhibitor of AKT: Pharmacodynamics,
antitumor activity, and correlation of monotherapy activity with
genetic background. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:873–887. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chong ZZ, Shang YC, Zhang L, Wang S and
Maiese K: Mammalian target of rapamycin: Hitting the bull's-eye for
neurological disorders. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 3:374–391. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chong ZZ and Maiese K: Mammalian target of
rapamycin signaling in diabetic cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc
Diabetol. 11:452012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yamashita A, Ohnishi T, Kashima I, Taya Y
and Ohno S: Human SMG-1, a novel phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase-related protein kinase, associates with components of the
mRNA surveillance complex and is involved in the regulation of
nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Genes Dev. 15:2215–2228. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Grimson A, O'Connor S, Newman CL and
Anderson P: SMG-1 is a phosphatidylinositol kinase-related protein
kinase required for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in
Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Cell Biol. 24:7483–7490. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hwang J and Maquat LE: Nonsense-mediated
mRNA decay (NMD) in animal embryogenesis: To die or not to die,
that is the question. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 21:422–430. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yamashita A: Role of SMG-1-mediated Upf1
phosphorylation in mammalian nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Genes
Cells. 18:161–175. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Engelman JA, Chen L, Tan X, Crosby K,
Guimaraes AR, Upadhyay R, Maira M, McNamara K, Perera SA, Song Y,
et al: Effective use of PI3K and MEK inhibitors to treat mutant
Kras G12D and PIK3CA H1047R murine lung cancers. Nat Med.
14:1351–1356. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chandarlapaty S, Sawai A, Scaltriti M,
Rodrik-Outmezguine V, Grbovic-Huezo O, Serra V, Majumder PK,
Baselga J and Rosen N: AKT inhibition relieves feedback suppression
of receptor tyrosine kinase expression and activity. Cancer Cell.
19:58–71. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Karbowniczek M, Robertson GP and Henske
EP: Rheb inhibits C-raf activity and B-raf/C-raf
heterodimerization. J Biol Chem. 281:25447–25456. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Barrett D, Brown VI, Grupp SA and Teachey
DT: Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling axis in children with
hematologic malignancies. Paediatr Drugs. 14:299–316. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Serra V, Markman B, Scaltriti M, Eichhorn
PJ, Valero V, Guzman M, Botero ML, Llonch E, Atzori F, Di Cosimo S,
et al: NVP-BEZ235, a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, prevents PI3K
signaling and inhibits the growth of cancer cells with activating
PI3K mutations. Cancer Res. 68:8022–8030. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yu K, Shi C, Toral-Barza L, Lucas J, Shor
B, Kim JE, Zhang WG, Mahoney R, Gaydos C, Tardio L, et al: Beyond
rapalog therapy: Preclinical pharmacology and antitumor activity of
WYE-125132, an ATP-competitive and specific inhibitor of mTORC1 and
mTORC2. Cancer Res. 70:621–631. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lloyd JP and Davies B: SMG1 is an ancient
nonsense-mediated mRNA decay effector. Plant J. 76:800–810. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Oliveira V, Romanow WJ, Geisen C,
Otterness DM, Mercurio F, Wang HG, Dalton WS and Abraham RT: A
protective role for the human SMG-1 kinase against tumor necrosis
factor-alpha-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 283:13174–13184. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nicholson P, Yepiskoposyan H, Metze S,
Orozco Zamudio R, Kleinschmidt N and Mühlemann O: Nonsense-mediated
mRNA decay in human cells: Mechanistic insights, functions beyond
quality control and the double-life of NMD factors. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 67:677–700. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Masse I, Molin L, Mouchiroud L, Vanhems P,
Palladino F, Billaud M and Solari F: A novel role for the SMG-1
kinase in lifespan and oxidative stress resistance in
Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS One. 3:e33542008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
McIlwain DR, Pan Q, Reilly PT, Elia AJ,
McCracken S, Wakeham AC, Itie-Youten A, Blencowe BJ and Mak TW:
Smg1 is required for embryogenesis and regulates diverse genes via
alternative splicing coupled to nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:12186–12191. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gewandter JS, Bambara RA and O'Reilly MA:
The RNA surveillance protein SMG1 activates p53 in response to DNA
double-strand breaks but not exogenously oxidized mRNA. Cell Cycle.
10:2561–2567. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gubanova E, Brown B, Ivanov SV, Helleday
T, Mills GB, Yarbrough WG and Issaeva N: Downregulation of SMG-1 in
HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma due to promoter
hypermethylation correlates with improved survival. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:1257–1267. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Roberts TL, Ho U, Luff J, Lee CS, Apte SH,
MacDonald KP, Raggat LJ, Pettit AR, Morrow CA, Waters MJ, et al:
Smg1 haploinsufficiency predisposes to tumor formation and
inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:E285–E294. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Altman JK, Sassano A and Platanias LC:
Targeting mTOR for the treatment of AML. New agents and new
directions. Oncotarget. 2:510–517. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Oviedo NJ, Pearson BJ, Levin M and Sánchez
Alvarado A: Planarian PTEN homologs regulate stem cells and
regeneration through TOR signaling. Dis Model Mech. 1:131–143.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pearson BJ and Sánchez Alvarado A: A
planarian p53 homolog regulates proliferation and self-renewal in
adult stem cell lineages. Development. 137:213–221. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|