|
1
|
Shiraha H, Yamamoto K and Namba M: Human
hepatocyte carcinogenesis (review). Int J Oncol. 42:1133–1138.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bruix J, Gores GJ and Mazzaferro V:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Clinical frontiers and perspectives. Gut.
63:844–855. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang JD and Roberts LR: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: A global view. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:448–458.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
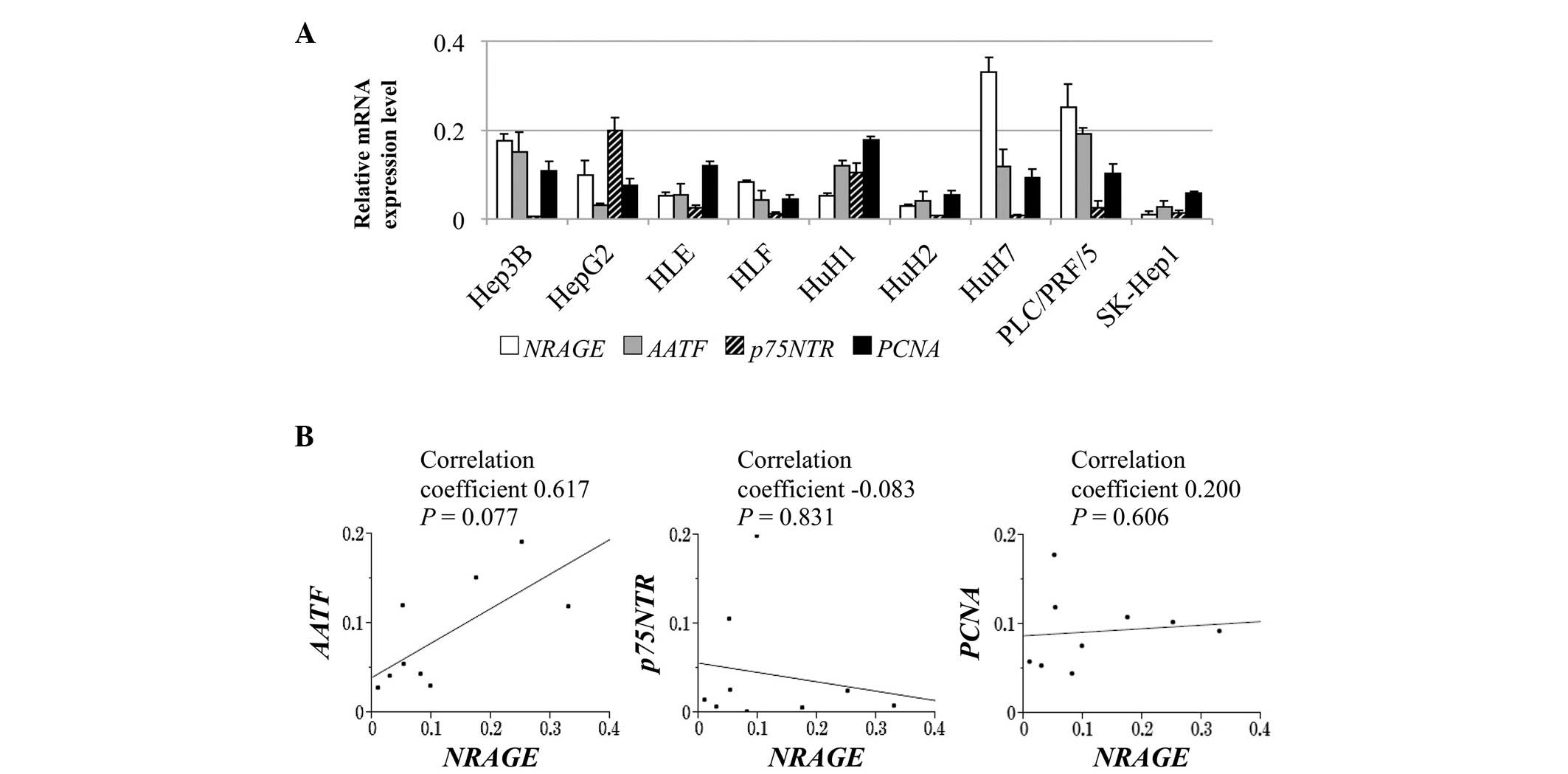
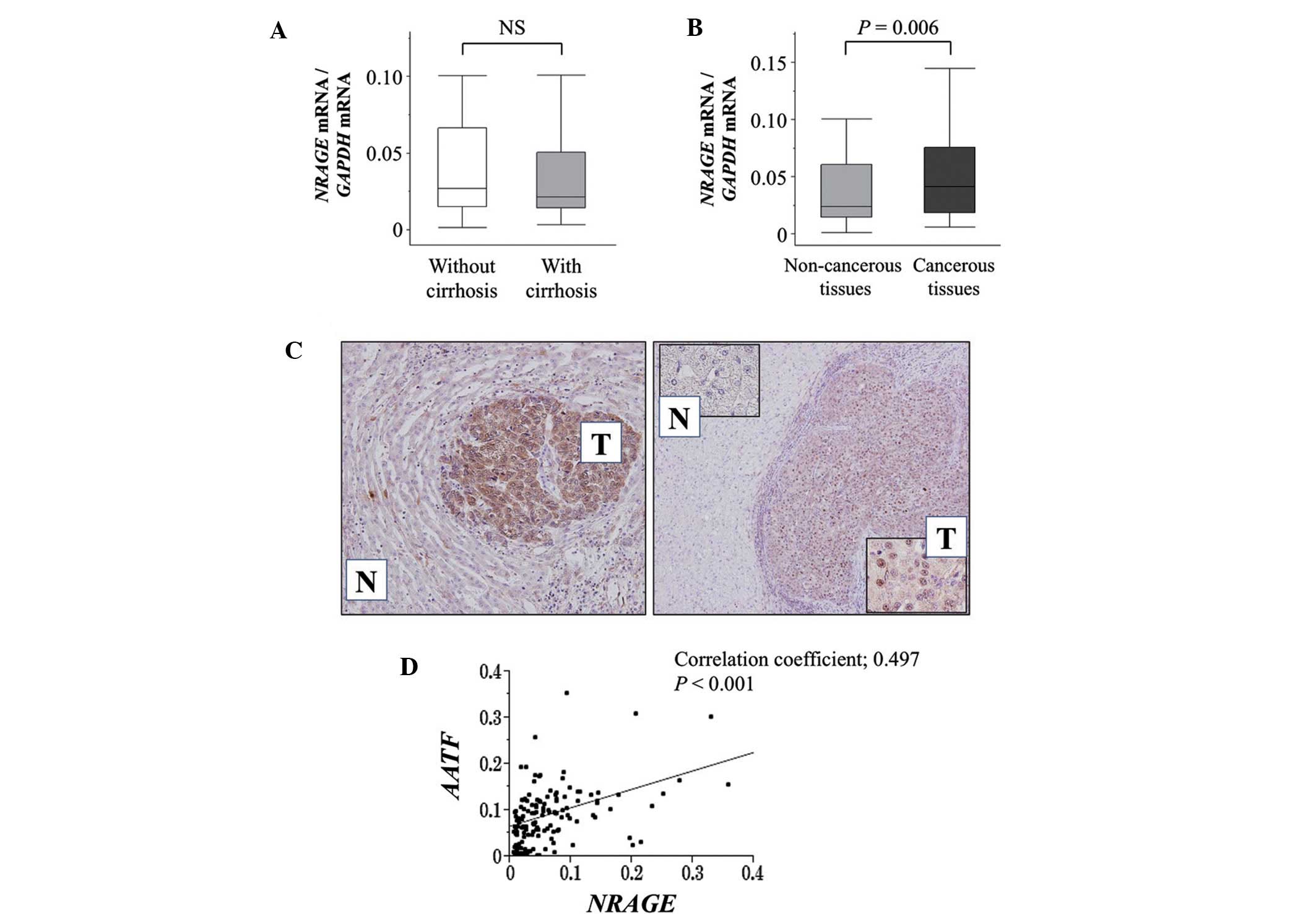
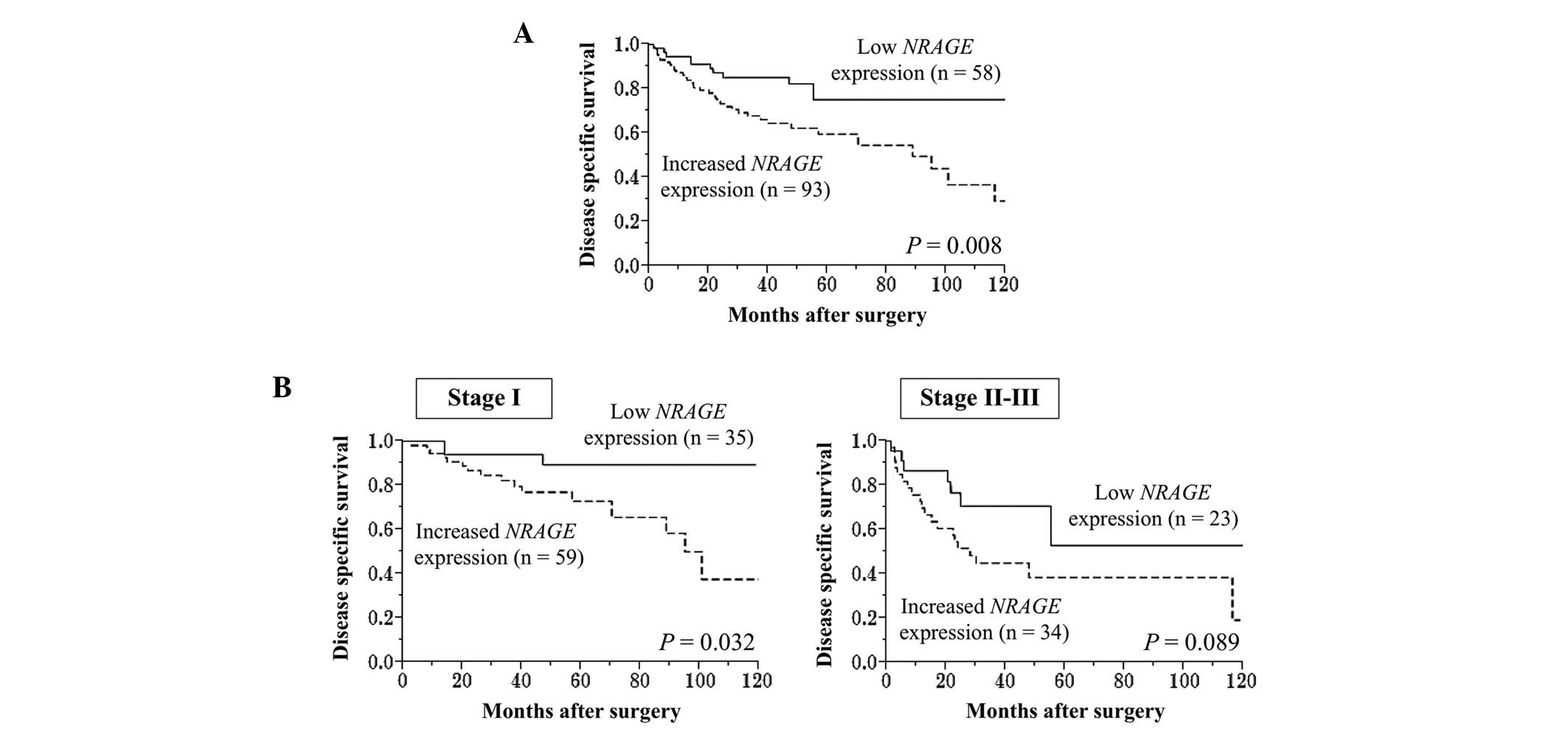
4
|
GLOBOCAN Estimated Cancer Incidence,
Mortality and Prevalence Worldwide in 2012. Stomach Cancer.
2012.
|
|
5
|
Zhao YJ, Ju Q and Li GC: Tumor markers for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Clin Oncol. 1:593–598.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kanda M, Sugimoto H, Nomoto S, Oya H,
Hibino S, Shimizu D, Takami H, Hashimoto R, Okamura Y, Yamada S, et
al: B-cell translocation gene 1 serves as a novel prognostic
indicator of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 46:641–648.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Flores A and Marrero JA: Emerging trends
in hepatocellular carcinoma: Focus on diagnosis and therapeutics.
Clin Med Insights Oncol. 8:71–76. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Giannelli G, Rani B, Dituri F, Cao Y and
Palasciano G: Moving towards personalised therapy in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma: The role of the microenvironment. Gut.
63:1668–1676. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kanda M, Nomoto S, Okamura Y, et al:
Detection of metallothionein 1G as a methylated tumor suppressor
gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma using a novel method of
double combination array analysis. Int J Oncol. 35:477–483.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Miki D, Ochi H, Hayes CN, Aikata H and
Chayama K: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Towards personalized medicine.
Cancer Sci. 103:846–850. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Khare S, Zhang Q and Ibdah JA: Epigenetics
of hepatocellular carcinoma: Role of microRNA. World J
Gastroenterol. 19:5439–5445. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kanda M, Nomoto S, Oya H, Takami H, Hibino
S, Hishida M, Suenaga M, Yamada S, Inokawa Y, Nishikawa Y, et al:
Downregulation of DENND2D by promoter hypermethylation is
associated with early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Oncol. 44:44–52. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chomez P, De Backer O, Bertrand M, De
Plaen E, Boon T and Lucas S: An overview of the MAGE gene family
with the identification of all human members of the family. Cancer
Res. 61:5544–5551. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tseng HY, Chen LH, Ye Y, Tay KH, Jiang CC,
Guo ST, Jin L, Hersey P and Zhang XD: The melanoma-associated
antigen MAGE-D2 suppresses TRAIL receptor 2 and protects against
TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human melanoma cells. Carcinogenesis.
33:1871–1881. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Takami H, Kanda M, Oya H, Hibino S,
Sugimoto H, Suenaga M, Yamada S, Nishikawa Y, Asai M, Fujii T, et
al: Evaluation of MAGE-D4 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma in
Japanese patients. J Surg Oncol. 108:557–562. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sang M, Wang L, Ding C, Zhou X, Wang B,
Wang L, Lian Y and Shan B: Melanoma-associated antigen genes - an
update. Cancer Lett. 302:85–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Oya H, Kanda M, Takami H, Hibino S,
Shimizu D, Niwa Y, Koike M, Nomoto S, Yamada S, Nishikawa Y, et al:
Overexpression of melanoma-associated antigen D4 is an independent
prognostic factor in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Dis
Esophagus. 28:188–195. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chang CC, Campoli M, Luo W, Zhao W,
Zaenker KS and Ferrone S: Immunotherapy of melanoma targeting human
high molecular weight melanoma-associated antigen: Potential role
of nonimmunological mechanisms. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1028:340–350.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hussein TD: Serological tumor markers of
hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Int J Biol Markers.
30:e32–e42. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jordan BW, Dinev D, LeMellay V, Troppmair
J, Gotz R, Wixler L, Sendtner M, Ludwig S and Rapp UR: Neurotrophin
receptor-interacting mage homologue is an inducible inhibitor of
apoptosis protein-interacting protein that augments cell death. J
Biol Chem. 276:39985–39989. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang X, Gao X and Xu Y: MAGED1: Molecular
insights and clinical implications. Ann Med. 43:347–355. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang Q, Ou C, Liu M, Xiao W, Wen C and Sun
F: NRAGE promotes cell proliferation by stabilizing PCNA in a
ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in esophageal carcinomas.
Carcinogenesis. 35:1643–1651. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Barker PA and Salehi A: The MAGE proteins:
Emerging roles in cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and
neurogenetic disease. J Neurosci Res. 67:705–712. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Du Q, Zhang Y, Tian XX, Li Y and Fang WG:
MAGE-D1 inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of human
breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 22:659–665. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Salehi AH, Roux PP, Kubu CJ, Zeindler C,
Bhakar A, Tannis LL, Verdi JM and Barker PA: NRAGE, a novel MAGE
protein, interacts with the p75 neurotrophin receptor and
facilitates nerve growth factor-dependent apoptosis. Neuron.
27:279–288. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Di Certo MG, Corbi N, Bruno T, Iezzi S, De
Nicola F, Desantis A, Ciotti MT, Mattei E, Floridi A, Fanciulli M
and Passananti C: NRAGE associates with the anti-apoptotic factor
Che-1 and regulates its degradation to induce cell death. J Cell
Sci. 120:1852–1858. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Passananti C and Fanciulli M: The
anti-apoptotic factor Che-1/AATF links transcriptional regulation,
cell cycle control, and DNA damage response. Cell Div. 2:212007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Krämer BF, Schoor O, Krüger T, Reichle C,
Müller M, Weinschenk T, Hennenlotter J, Stenzl A, Rammensee HG and
Stevanovic S: MAGED4-expression in renal cell carcinoma and
identification of an HLA-A*25-restricted MHC class I ligand from
solid tumor tissue. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:943–948. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zeng ZL, Wu WJ, Yang J, Tang ZJ, Chen DL,
Qiu MZ, Luo HY, Wang ZQ, Jin Y, Wang DS and Xu RH: Prognostic
relevance of melanoma antigen D1 expression in colorectal
carcinoma. J Transl Med. 10:1812012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee D, Lee GK, Yoon KA and Lee JS:
Pathway-based analysis using genome-wide association data from a
Korean non-small cell lung cancer study. PLoS One. 8:e653962013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: International Union Against Cancer. TNM Classification of
Malignant Tumors (7th). (New York). Wiley-Blackwell. 2009.
|
|
32
|
Kanda M, Shimizu D, Nomoto S, Hibino S,
Oya H, Takami H, Kobayashi D, Yamada S, Inokawa Y, Tanaka C, et al:
Clinical significance of expression and epigenetic profiling of
TUSC1 in gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 110:136–144. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kanda M, Nomoto S, Oya H, Shimizu D,
Takami H, Hibino S, Hashimoto R, Kobayashi D, Tanaka C, Yamada S,
et al: Dihydropyrimidinase-like 3 facilitates malignant behavior of
gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:662014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kanda M, Shimizu D, Nomoto S, Takami H,
Hibino S, Oya H, Hashimoto R, Suenaga M, Inokawa Y, Kobayashi D, et
al: Prognostic impact of expression and methylation status of
DENN/MADD domain-containing protein 2D in gastric cancer. Gastric
Cancer. 18:288–296. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kubista M, Andrade JM, Bengtsson M,
Forootan A, Jonák J, Lind K, Sindelka R, Sjöback R, Sjögreen B,
Strömbom L, et al: The real-time polymerase chain reaction. Mol
Aspects Med. 27:95–125. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kanda M, Nomoto S, Oya H, Hashimoto R,
Takami H, Shimizu D, Sonohara F, Kobayashi D, Tanaka C, Yamada S,
et al: Decreased expression of prenyl diphosphate synthase subunit
2 correlates with reduced survival of patients with gastric cancer.
J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:882014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kanda M, Nomoto S, Okamura Y, Hayashi M,
Hishida M, Fujii T, Nishikawa Y, Sugimoto H, Takeda S and Nakao A:
Promoter hypermethylation of fibulin 1 gene is associated with
tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Carcinog.
50:571–579. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xue XY, Liu ZH, Jing FM, Li YG, Liu HZ and
Gao XS: Relationship between NRAGE and the radioresistance of
esophageal carcinoma cell line TE13R120. Chin J Cancer. 29:900–906.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|