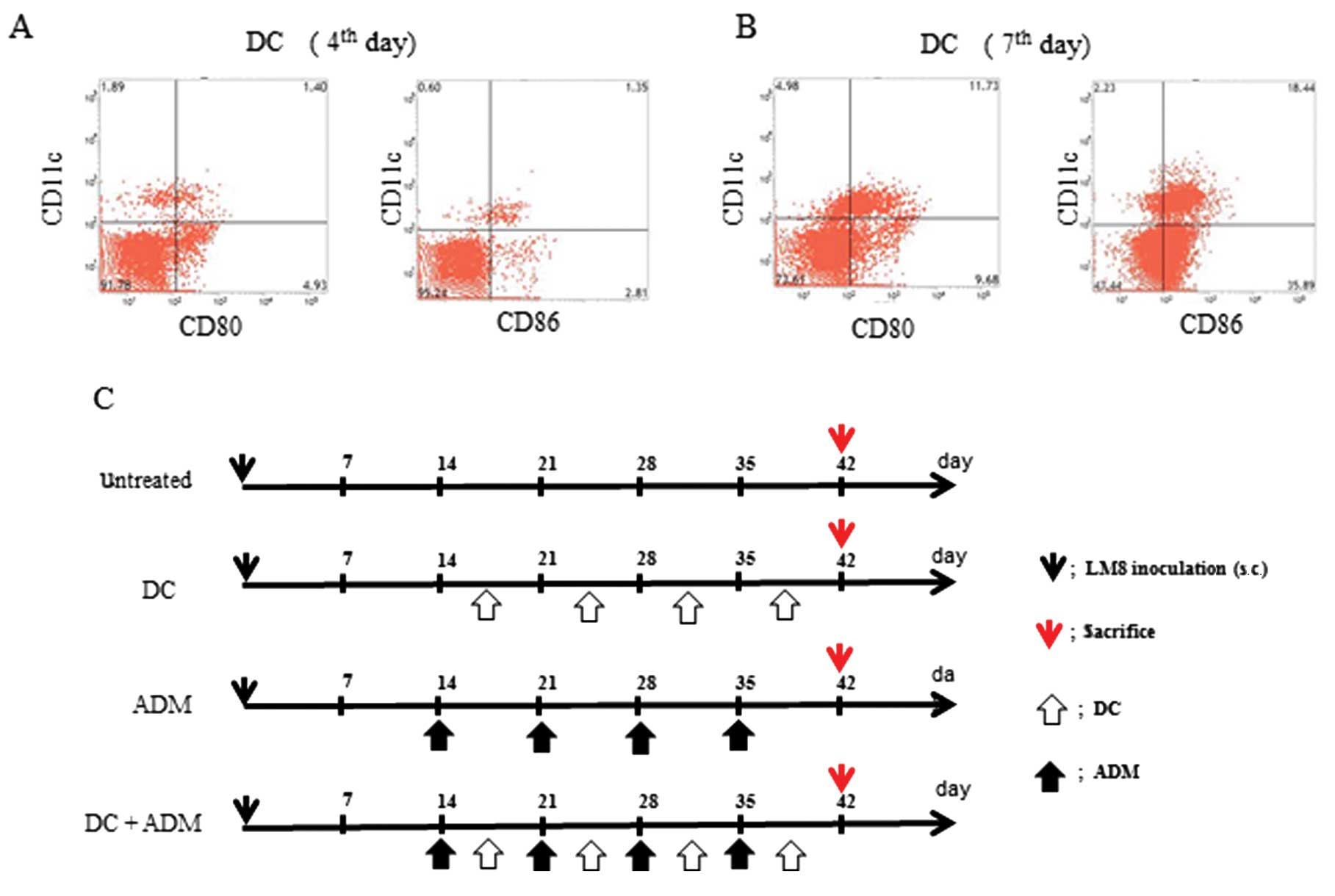
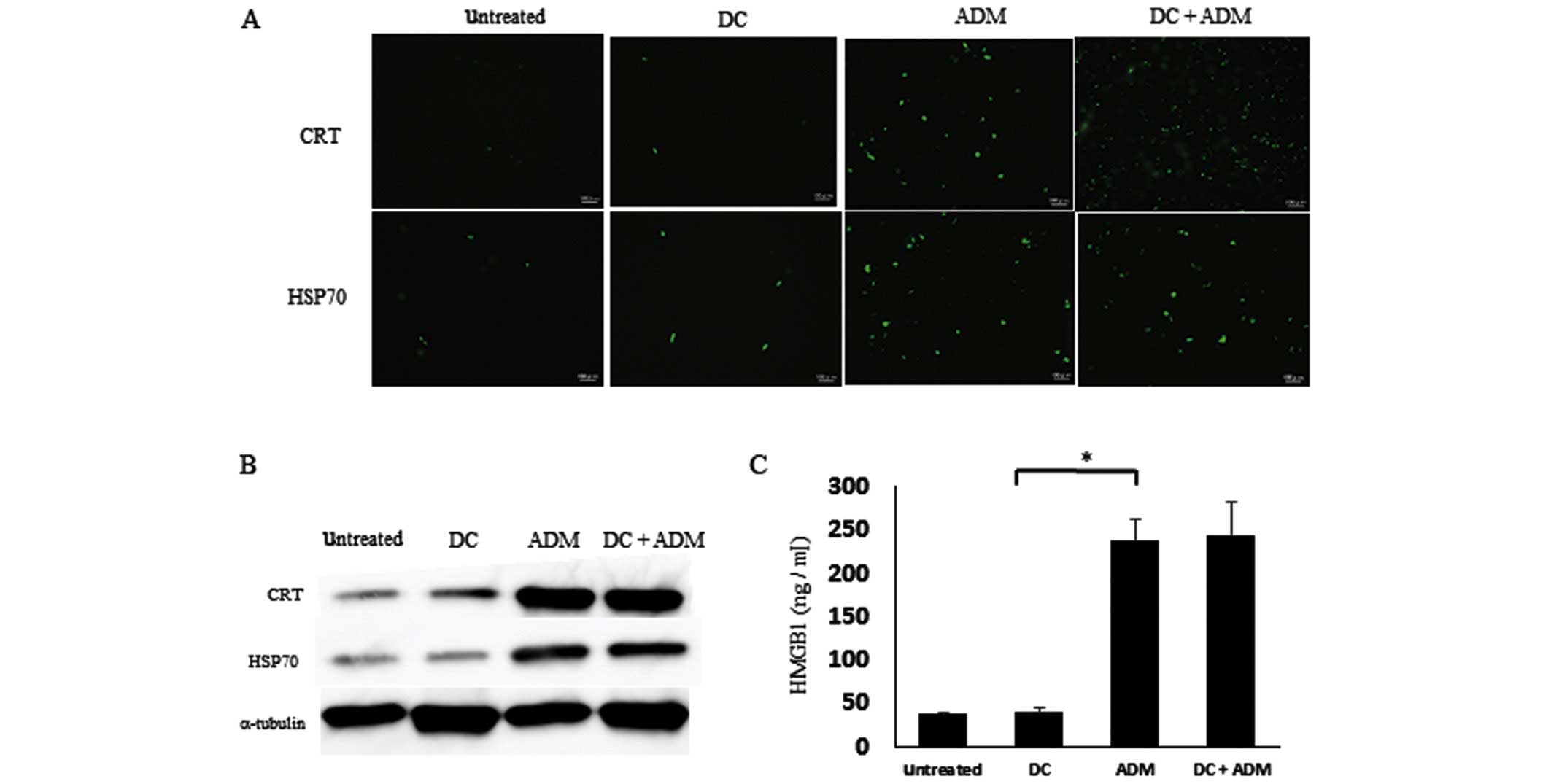
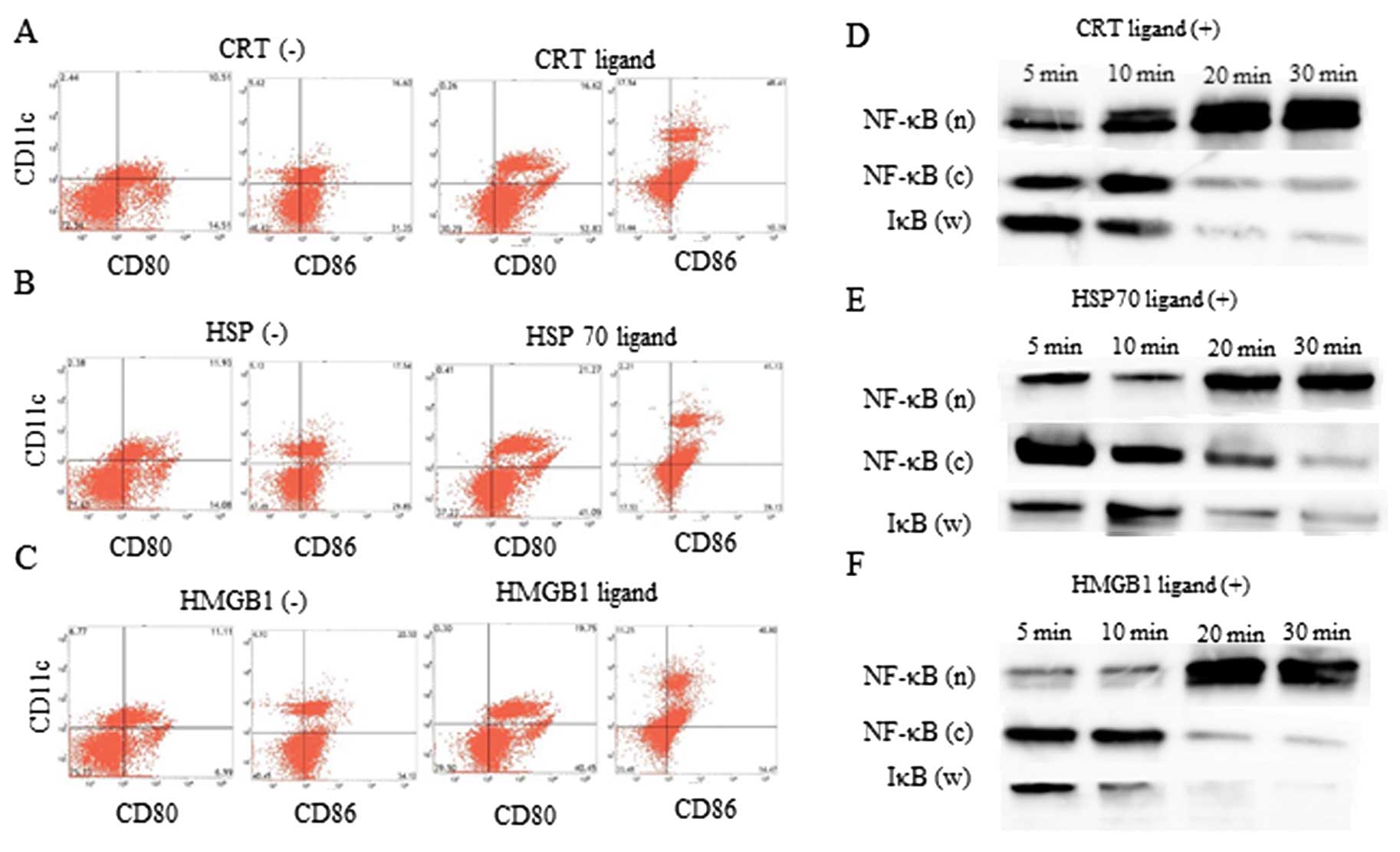
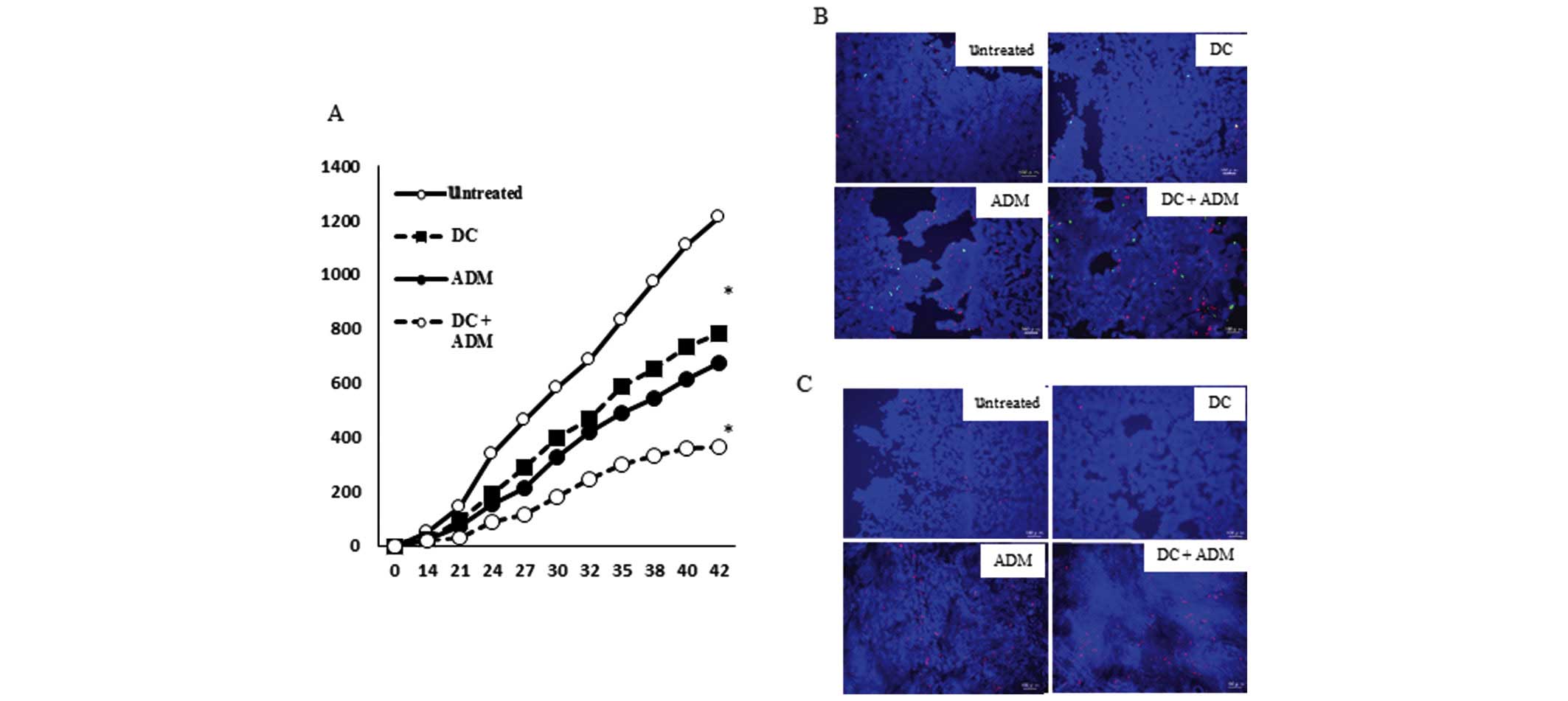
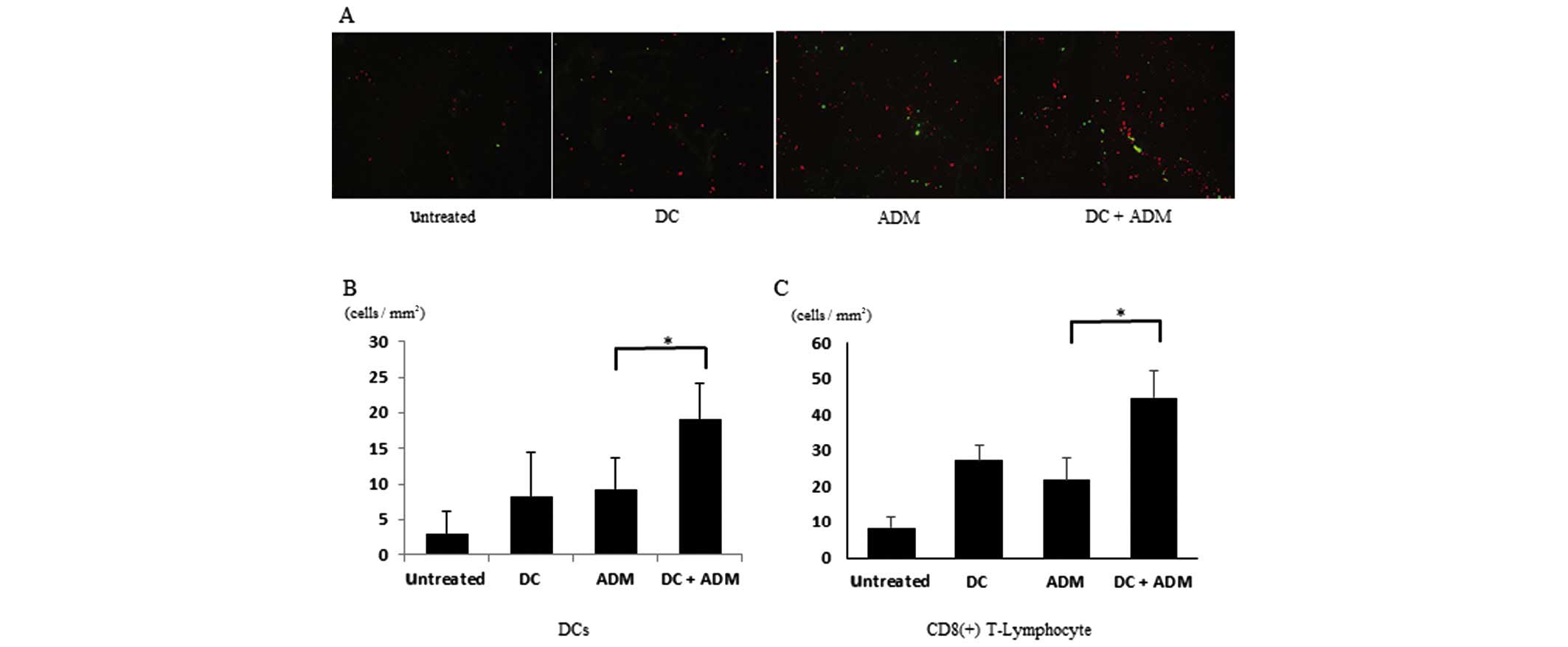
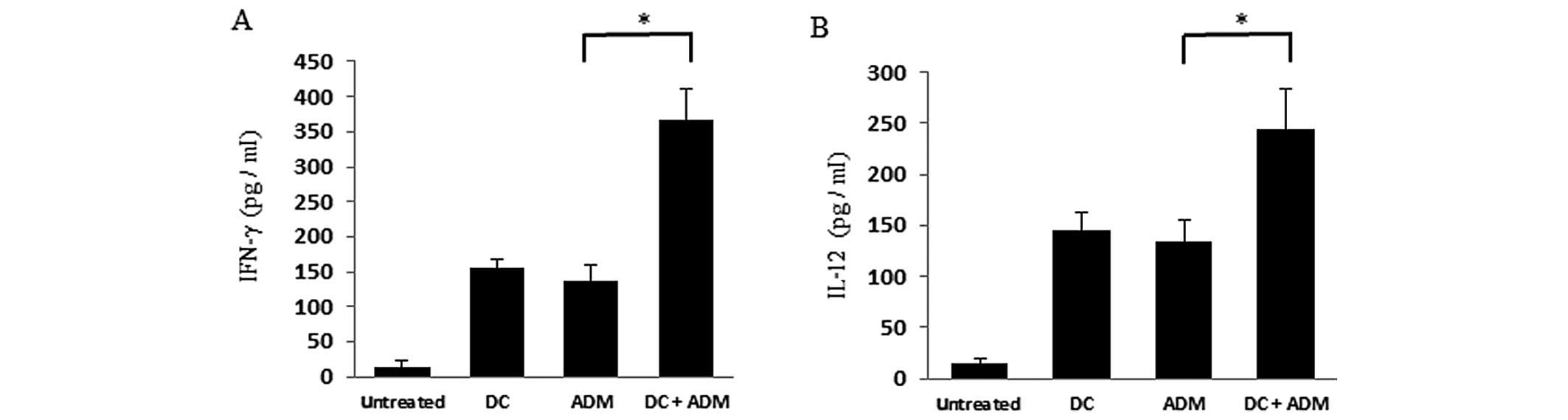
|
1
|
Stiller CA, Bielack SS, Jundt G and
Steliarova-Foucher E: Bone tumours in European children and
adolescents, 1978–1997. Report from the Automated Childhood Cancer
Information System project. Eur J Cancer. 42:2124–2135. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bielack SS, Kempf-Bielack B, Delling G,
Exner GU, Flege S, Helmke K, Kotz R, Salzer-Kuntschik M, Werner M,
Winkelmann W, et al: Prognostic factors in high-grade osteosarcoma
of the extremities or trunk: An analysis of 1,702 patients treated
on neoadjuvant cooperative osteosarcoma study group protocols. J
Clin Oncol. 20:776–790. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Milosević DB: The different level of
immunological recovery after chemotherapy in leukemia and lymphoma
patients. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 20:517–522. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tesniere A, Panaretakis T, Kepp O, Apetoh
L, Ghiringhelli F, Zitvogel L and Kroemer G: Molecular
characteristics of immunogenic cancer cell death. Cell Death
Differ. 15:3–12. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Apetoh L, Mignot G, Panaretakis T, Kroemer
G and Zitvogel L: Immunogenicity of anthracyclines: Moving towards
more personalized medicine. Trends Mol Med. 14:141–151. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Tesniere A,
Obeid M, Ortiz C, Criollo A, Mignot G, Maiuri MC, Ullrich E,
Saulnier P, et al: Toll-like receptor 4-dependent contribution of
the immune system to anticancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Nature. 13:1050–1059. 2007.
|
|
7
|
Fucikova J, Kralikova P, Fialova A,
Brtnicky T, Rob L, Bartunkova J and Spísek R: Human tumor cells
killed by anthracyclines induce a tumor-specific immune response.
Cancer Res. 71:4821–4833. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sancho D, Joffre OP, Keller AM, Rogers NC,
Martínez D, Hernanz-Falcón P, Rosewell I and Sousa Reise C:
Identification of a dendritic cell receptor that couples sensing of
necrosis to immunity. Nature. 458:899–903. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lutz MB and Rössner S: Factors influencing
the generation of murine dendritic cells from bone marrow: The
special role of fetal calf serum. Immunobiology. 212:855–862. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kawano M, Nishida H, Nakamoto Y, Tsumura H
and Tsuchiya H: Cryoimmunologic antitumor effects enhanced by
dendritic cells in osteosarcoma. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
468:1373–1383. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kawano M, Itonaga I, Iwasaki T, Tsuchiya H
and Tsumura H: Anti-TGF-β antibody combined with dendritic cells
produce antitumor effects in osteosarcoma. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
470:2288–2294. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kawano M, Itonaga I, Iwasaki T and Tsumura
H: Enhancement of antitumor immunity by combining anti-cytotoxic T
lymphocyte antigen-4 antibodies and cryotreated tumor lysate-pulsed
dendritic cells in murine osteosarcoma. Oncol Rep. 29:1001–1006.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zitvogel L, Kepp O and Kroemer G: Immune
parameters affecting the efficacy of chemotherapeutic regimens. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 8:151–160. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Locher C, Conforti R, Aymeric L, Ma Y,
Yamazaki T, Rusakiewicz S, Tesnière A, Ghiringhelli F, Apetoh L,
Morel Y, et al: Desirable cell death during anticancer
chemotherapy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1209:99–108. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zitvogel L, Kepp O, Senovilla L, Menger L,
Chaput N and Kroemer G: Immunogenic tumor cell death for optimal
anticancer therapy: The calreticulin exposure pathway. Clin Cancer
Res. 16:3100–3104. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Obeid M, Tesniere A, Ghiringhelli F, Fimia
GM, Apetoh L, Perfettini JL, Castedo M, Mignot G, Panaretakis T,
Casares N, et al: Calreticulin exposure dictates the immunogenicity
of cancer cell death. Nat Med. 13:54–61. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Michaud M, Sukkurwala AQ, Di Sano F,
Zitvogel L, Kepp O and Kroemer G: Synthetic induction of
immunogenic cell death by genetic stimulation of endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Oncoimmunology. 3:e282762014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hoshino K and Kaisho T: Nucleic acid
sensing toll-like receptors in dendritic cells. Curr Opin Immunol.
20:408–413. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang H, Vishnubhakat JM, Bloom O, Zhang M,
Ombrellino M, Sama A and Tracey KJ: Proinflammatory cytokines
(tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1) stimulate release of high
mobility group protein-1 by pituicytes. Surgery. 126:389–392. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Scaffidi P, Misteli T and Bianchi ME:
Release of chromatin protein HMGB1 by necrotic cells triggers
inflammation. Nature. 418:191–195. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park JS, Svetkauskaite D, He Q, Kim JY,
Strassheim D, Ishizaka A and Abraham E: Involvement of toll-like
receptors 2 and 4 in cellular activation by high mobility group box
1 protein. J Biol Chem. 279:7370–7377. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Tesniere A,
Criollo A, Ortiz C, Lidereau R, Mariette C, Chaput N, Mira JP,
Delaloge S, et al: The interaction between HMGB1 and TLR4 dictates
the outcome of anticancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Immunol
Rev. 220:47–59. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rosenberg SA, Restifo NP, Yang JC, Morgan
RA and Dudley ME: Adoptive cell transfer: A clinical path to
effective cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:299–308. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nowak AK, Lake RA and Robinson BW:
Combined chemoimmunotherapy of solid tumours: Improving vaccines?
Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 58:975–990. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|